Lab 6: The Cerebrum
1/63
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Anat & Phy 338
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
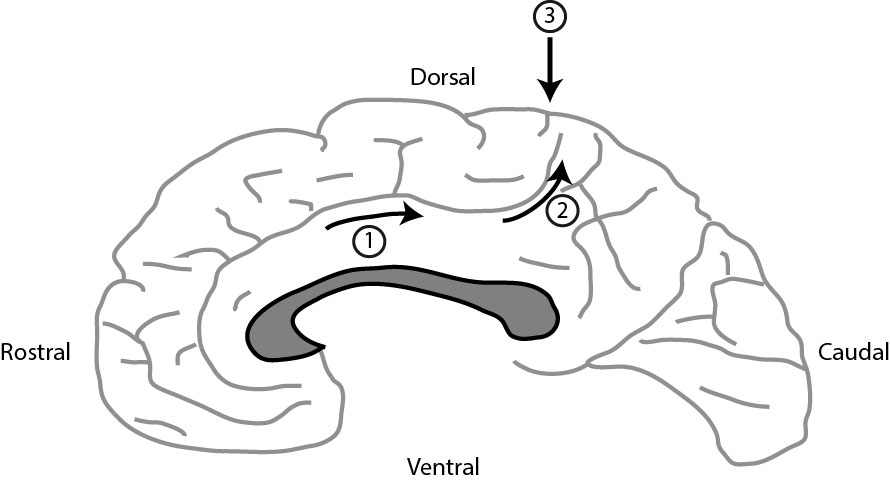
rostral
refers to structures closer to the nose
caudal
refers to structures toward the back of the head (tail)
ventral
inferior; anterior
dorsal
superior; posterior
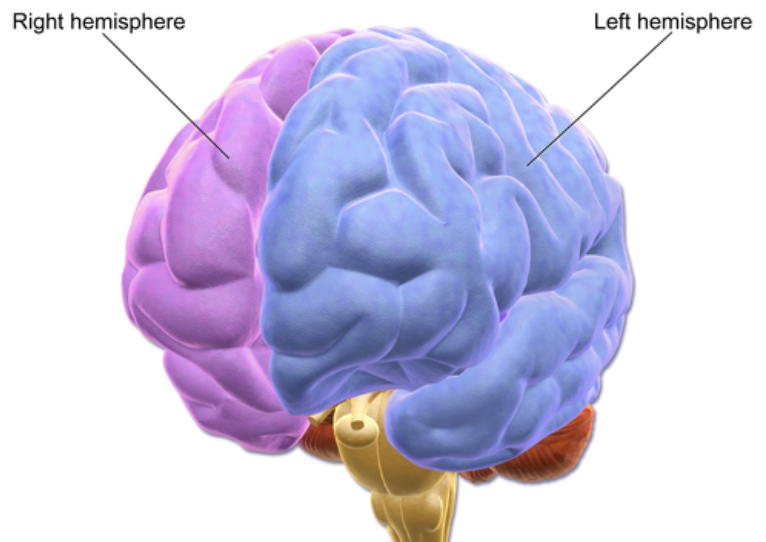
cerebrum
cerebral hemispheres
sulci
are the folds dividing inward
gyri
are ridges of the cortex that are visible on the surface of the brain
cerebral cortex
the surface of the cerebral hemispheres is made up of the ___, which is a layer of gray matter
median longitudinal fissure

corpus callosum
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/1856/K0N85HhHdfNuTbpyntCTuA_Corpus_callosum_1.png)
central sulcus
3
:watermark(/images/watermark_only_413.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url_sm.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/central-sulcus-5/EA5s78sWDnpf1o2YSAMEg_Central_sulcus.png)
precentral gyrus
:watermark(/images/watermark_only_413.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url_sm.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/precentral-gyrus-5/sAXgG89JgqYlbKYa84QCw_Precentral_gyrus.png)
frontal lobe

A
parietal lobe

B
postcentral gyrus
:watermark(/images/watermark_only_413.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url_sm.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/postcentral-gyrus-6/mV4RNLg1o4SYFdA7AGBg6A_Postcentral_gyrus.png)
temporal lobe

C
superior temporal gyrus
:watermark(/images/watermark_only_413.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url_sm.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/gyrus-temporalis-superior/Vht8DYrjrmsobFQ1dtA8A_Gyrus_temporalis_superior_01.png)
middle temporal gyrus

inferior temporal gyrus
:watermark(/images/watermark_only_413.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url_sm.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/gyrus-temporalis-inferior/rb56ctliarthYm7CBjaXVQ_Gyrus_temporalis_inferior_01.png)
amygdala
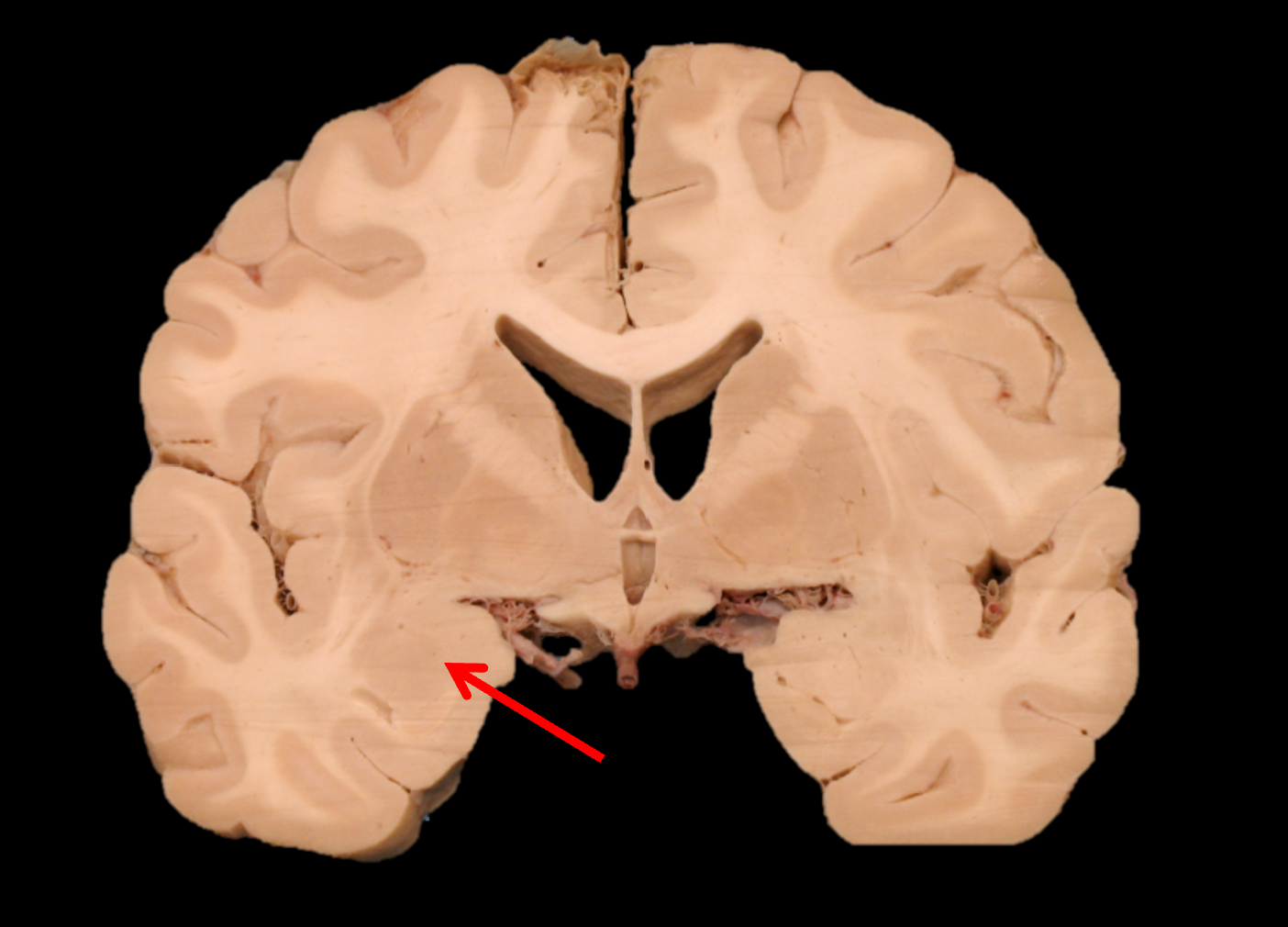
putamen
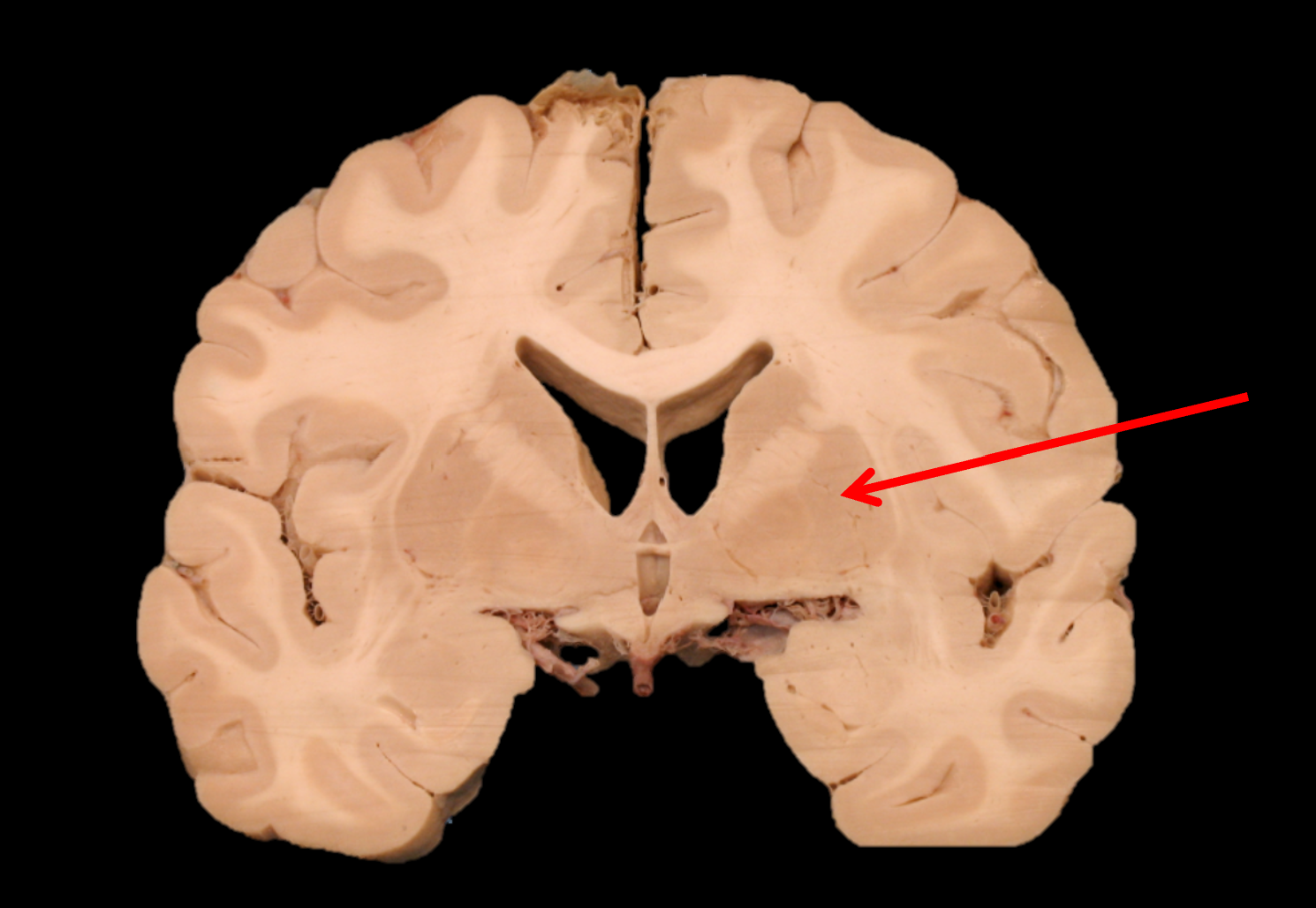
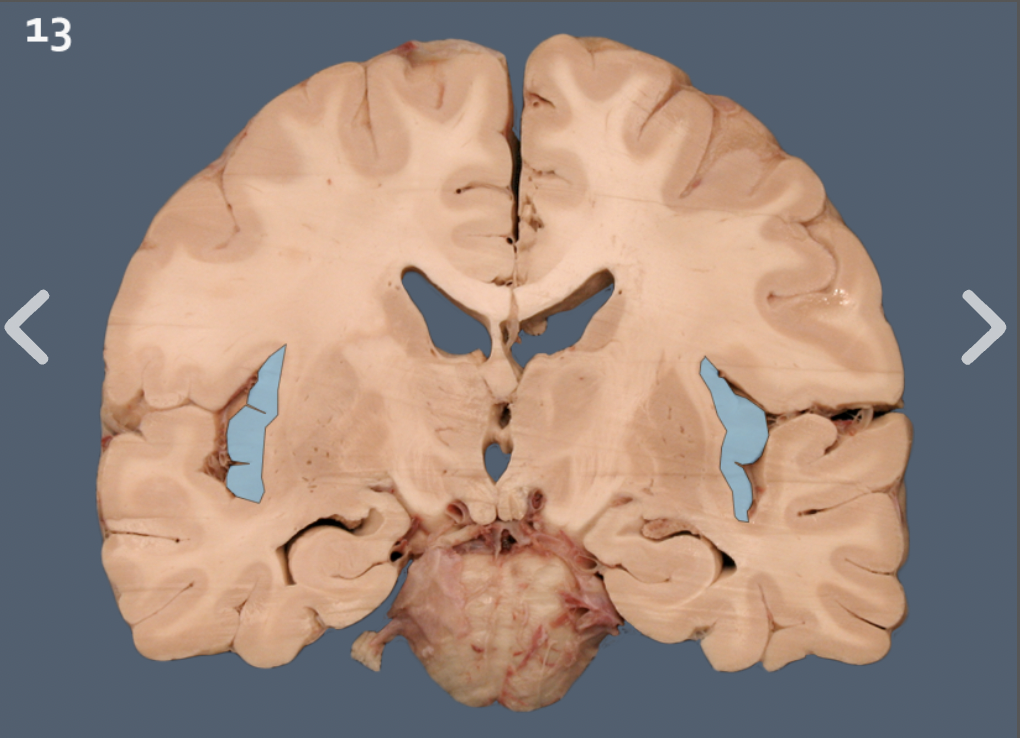
inferior horn of lateral ventricle
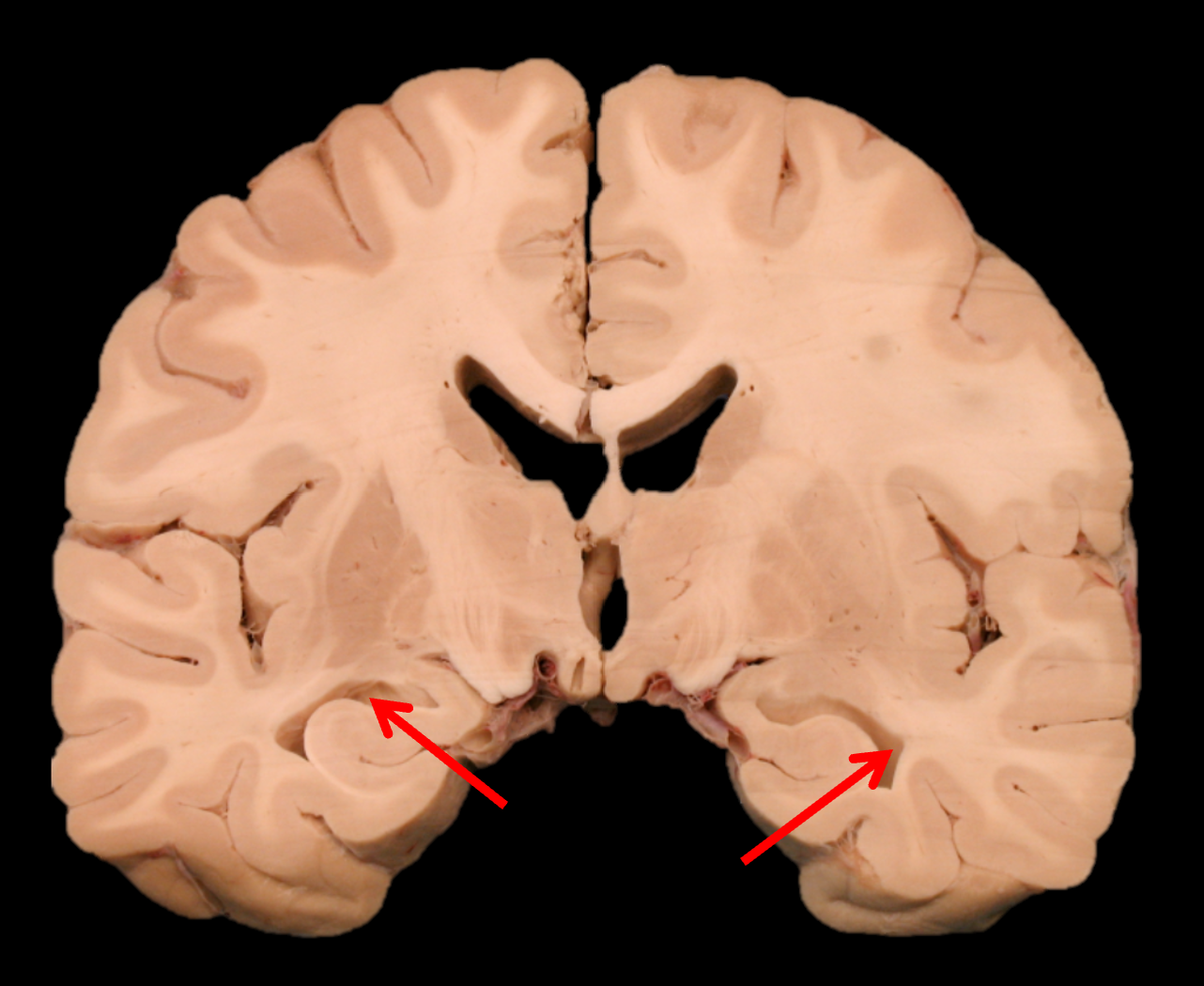
hippocampus
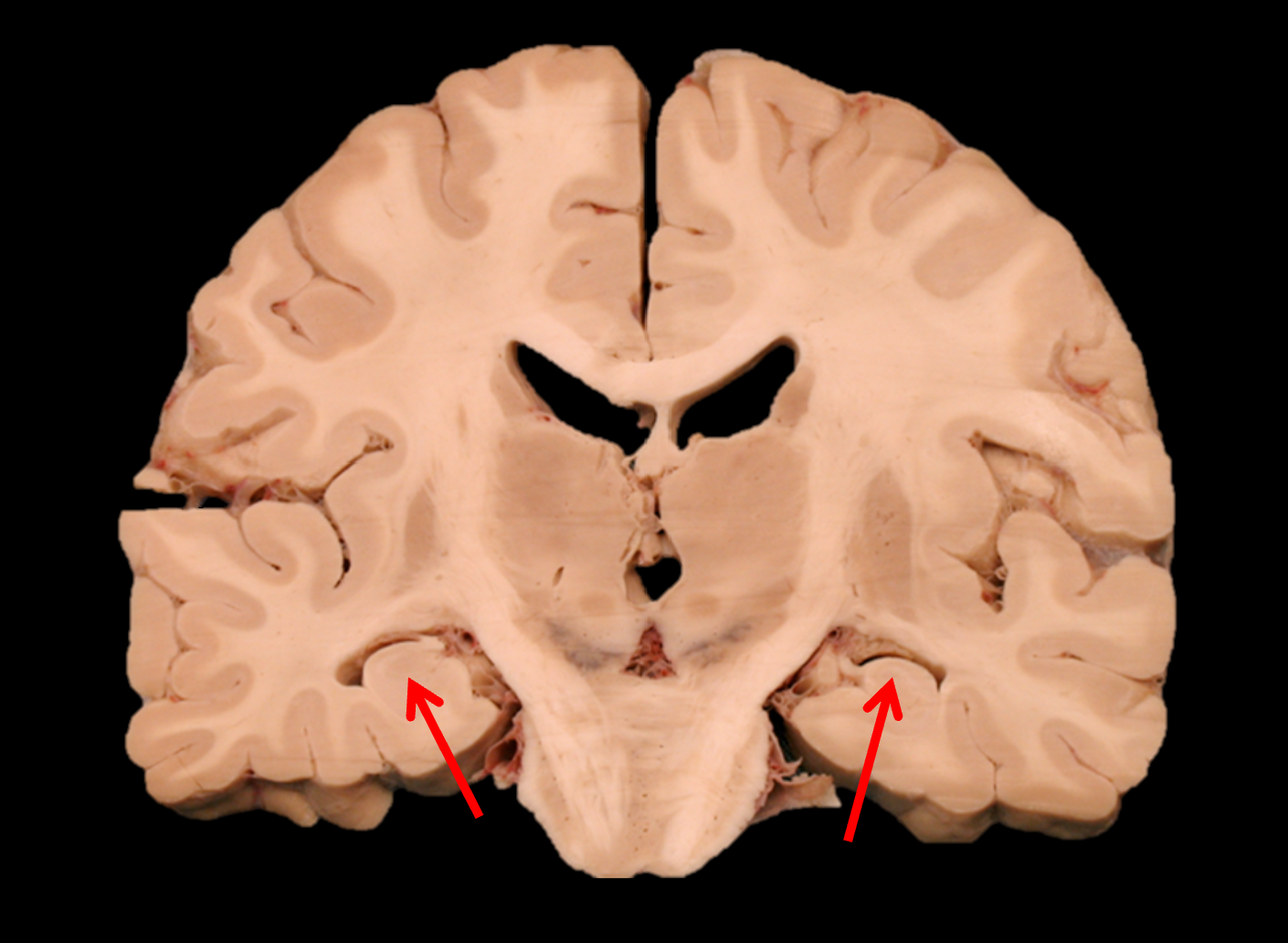
thalamus
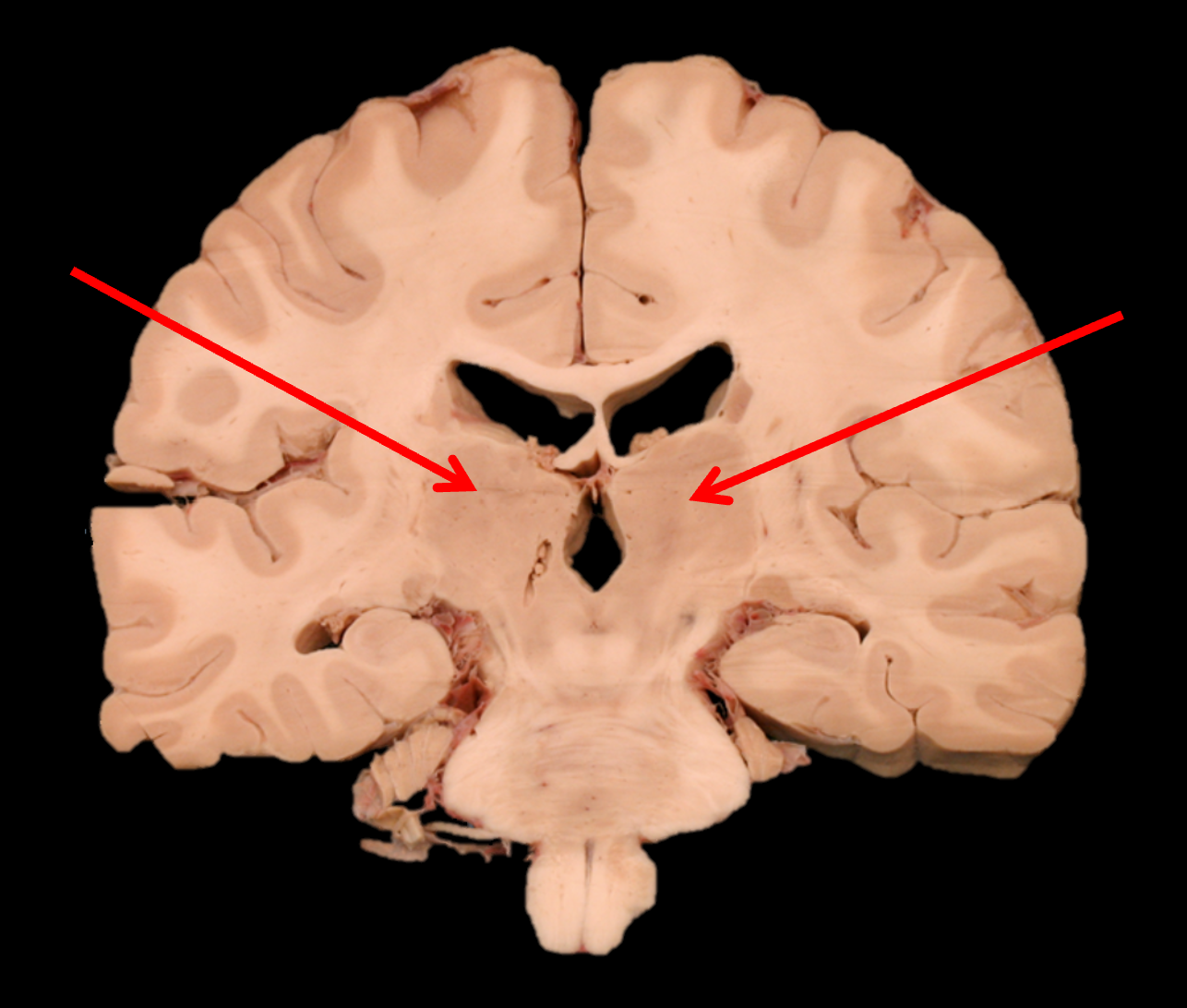
posterior horn of lateral ventricle
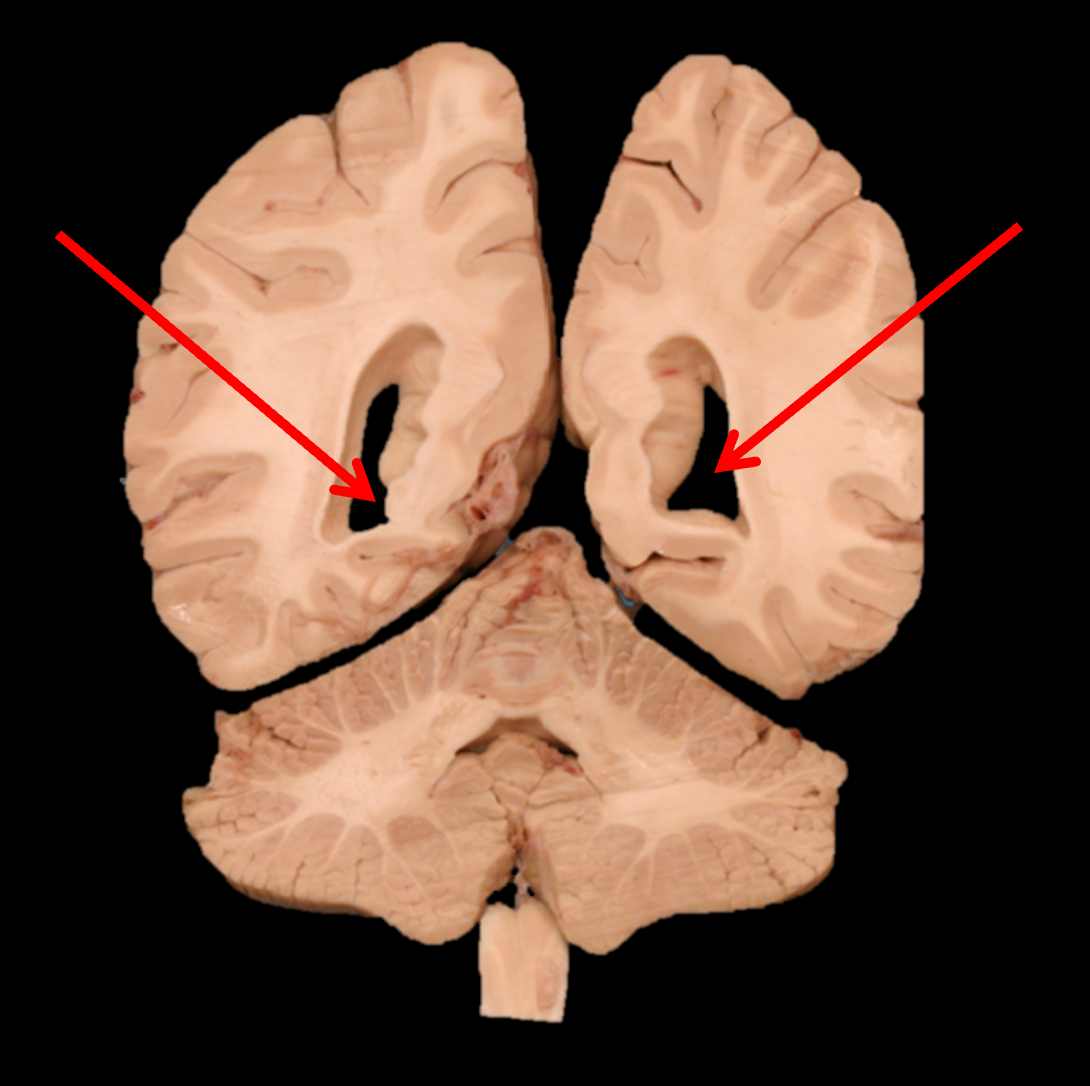
occipital lobe

D
calcarine sulcus
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/article/calcarine-sulcus/zwcWUEWSjrw5He2fIf0LgQ_zA051IYkRMjGtnhd2Qj8lw_image1_medial.png)
lateral (sylvian) fissure
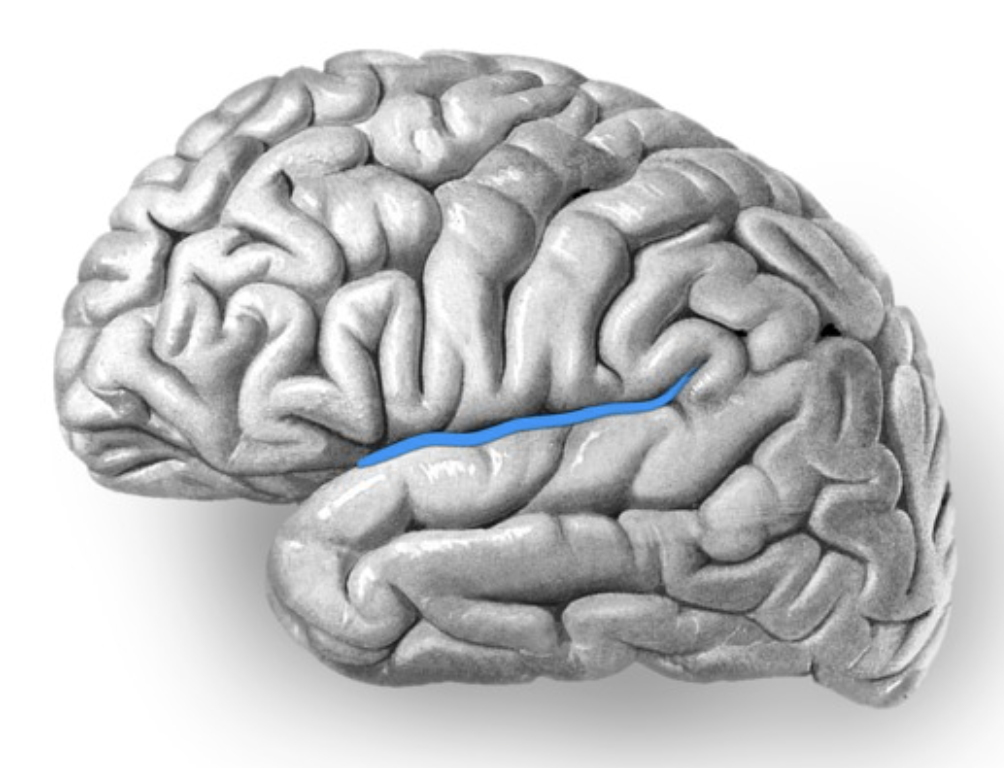
parieto-occipital sulcus

F
insula
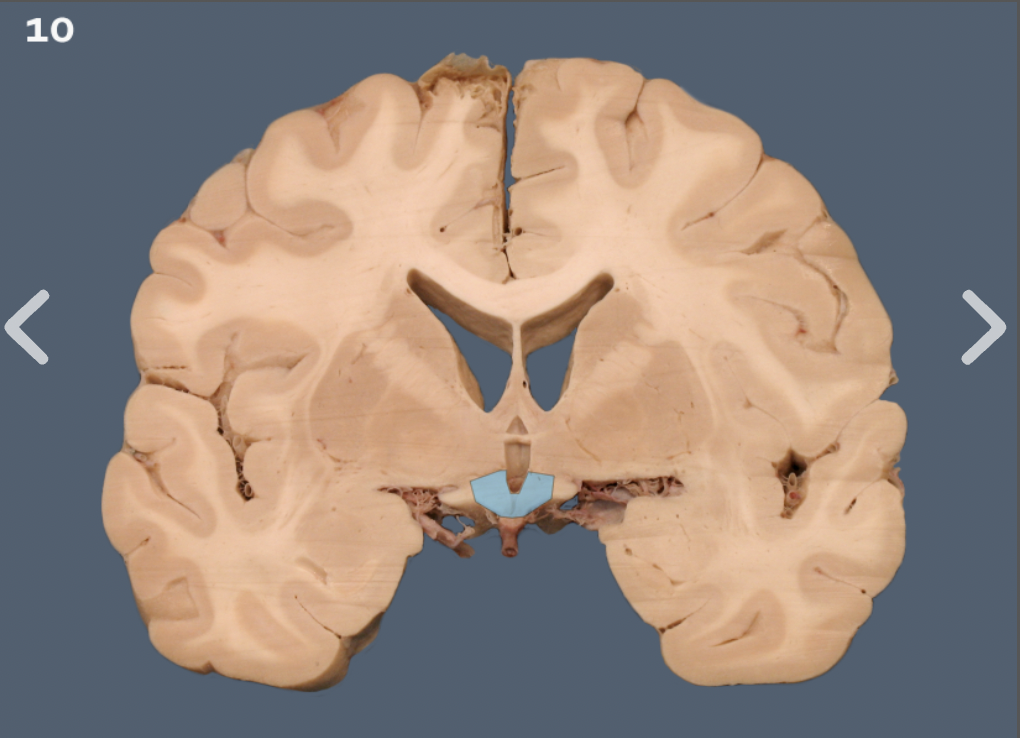
hypothalamus
caudate nucleus
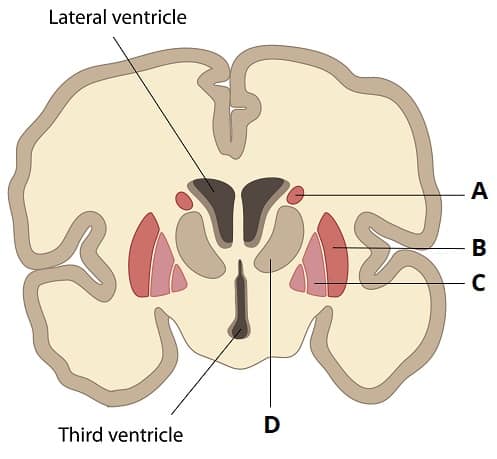
A
globus pallidus

C
tentorium cerebelli

internal capsule
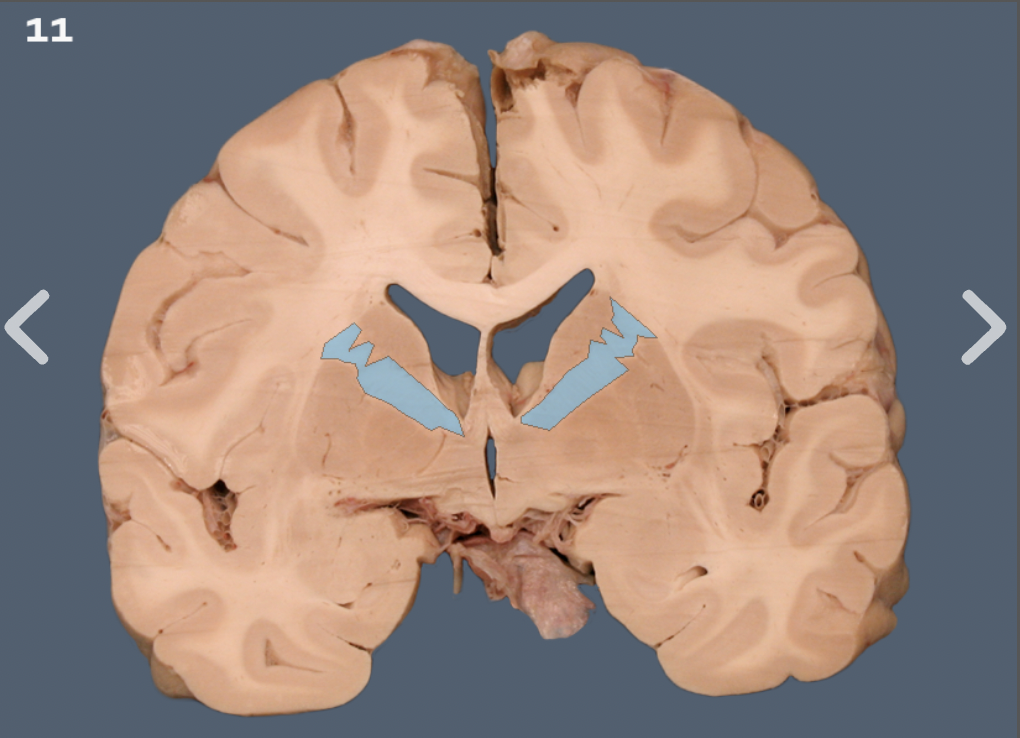
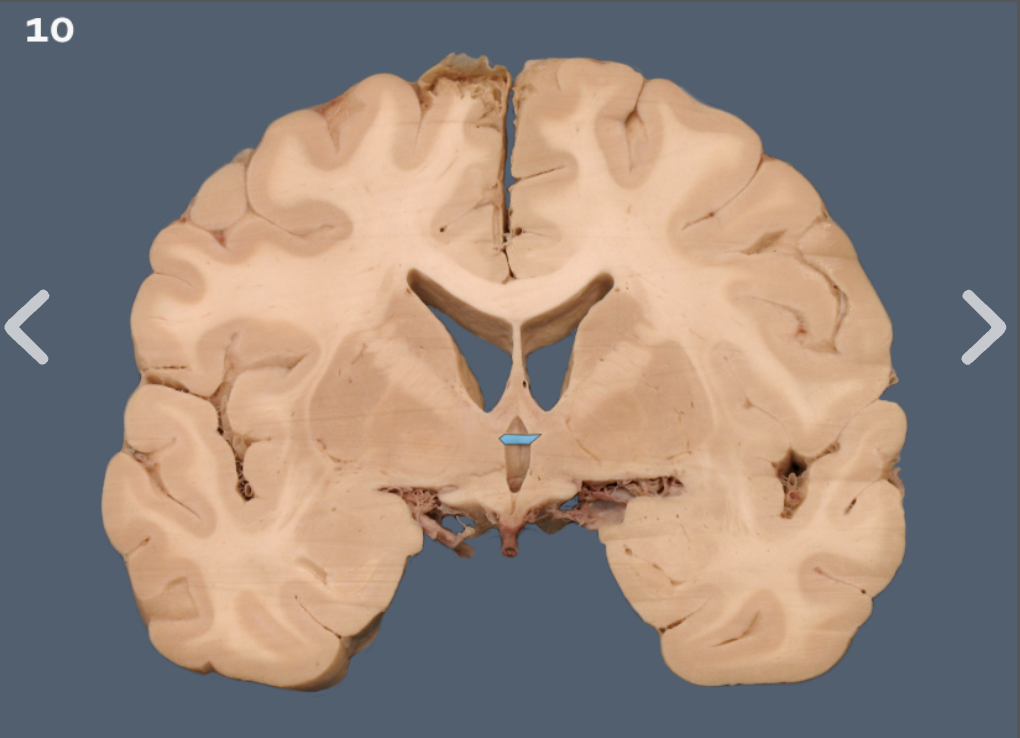
anterior commissure
basal ganglia
are brain structures that help control muscle movements
dura mater
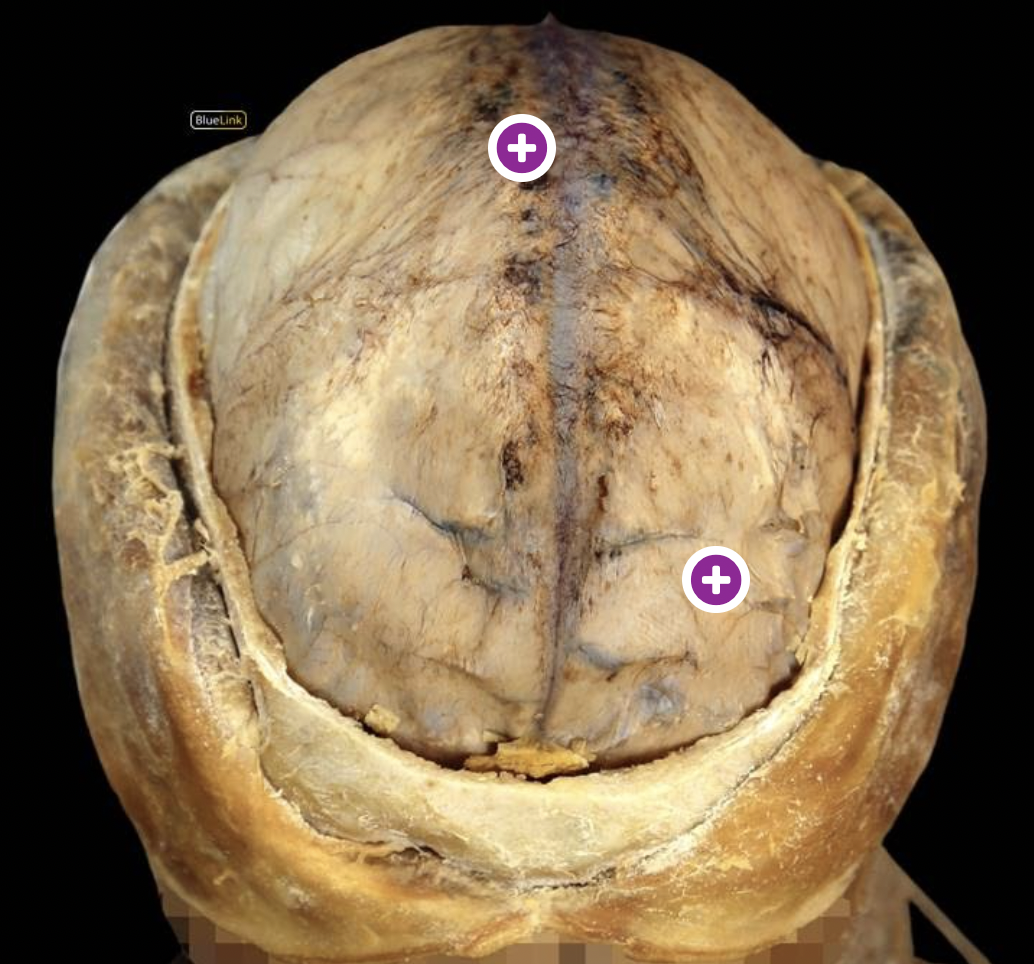
falx cerebri
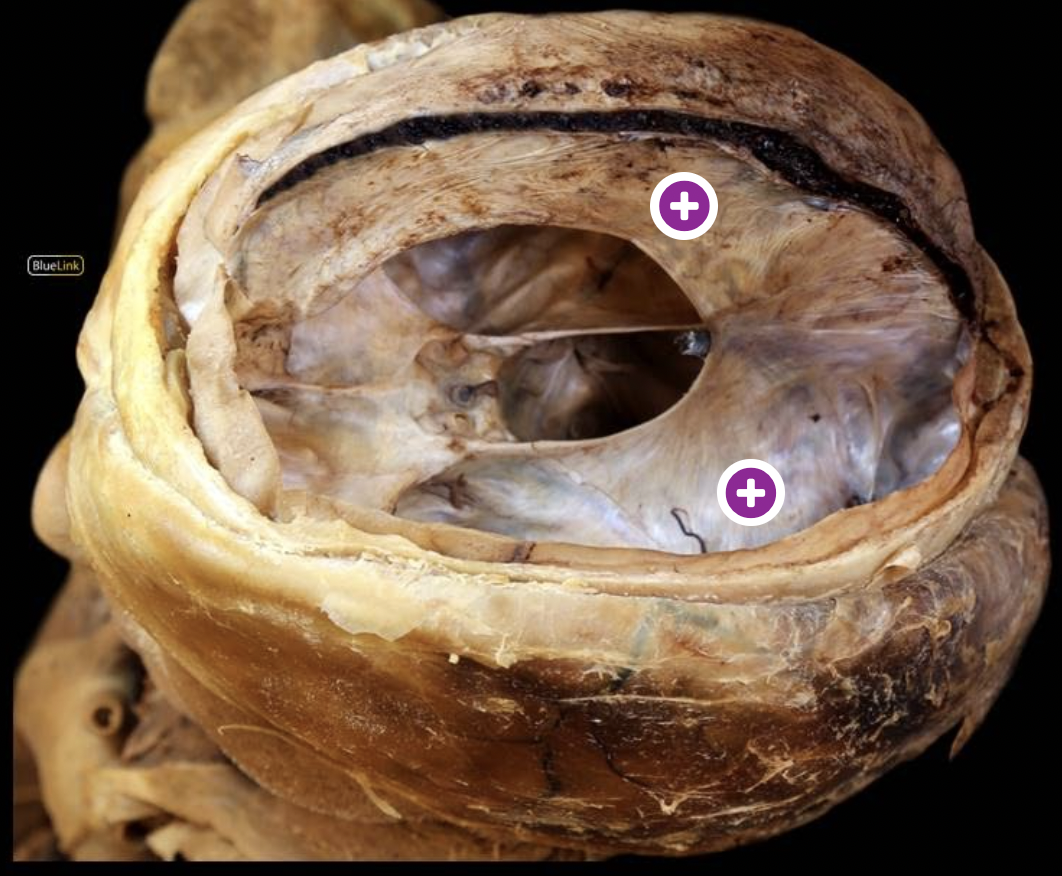
arachnoid mater
right
pia mater

left
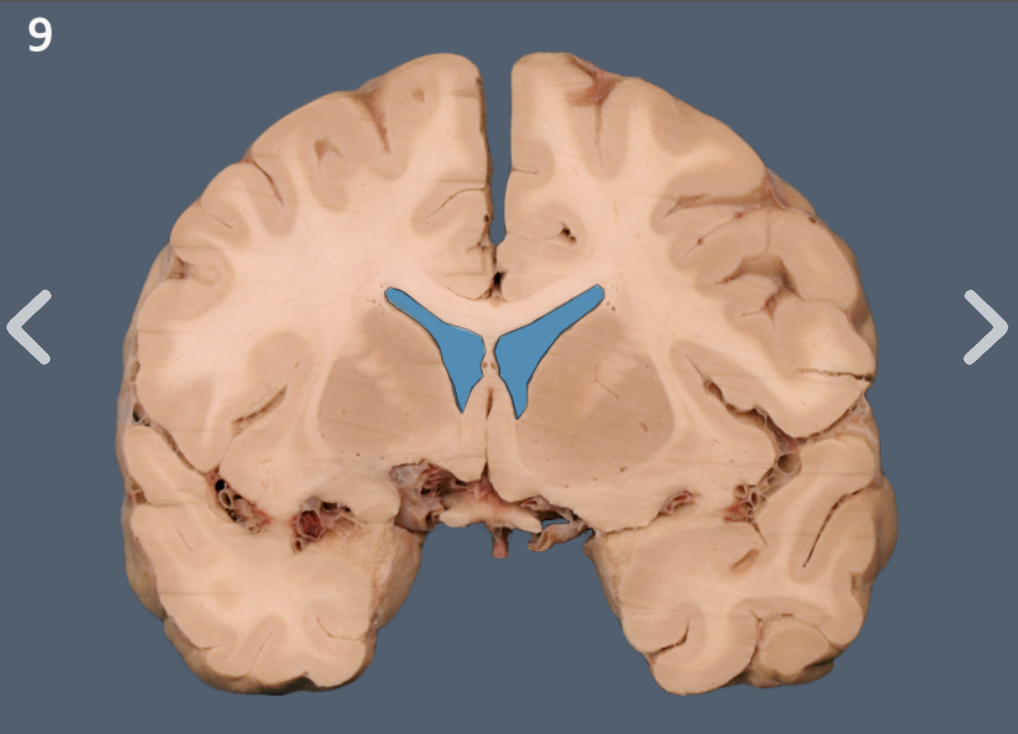
lateral ventricle
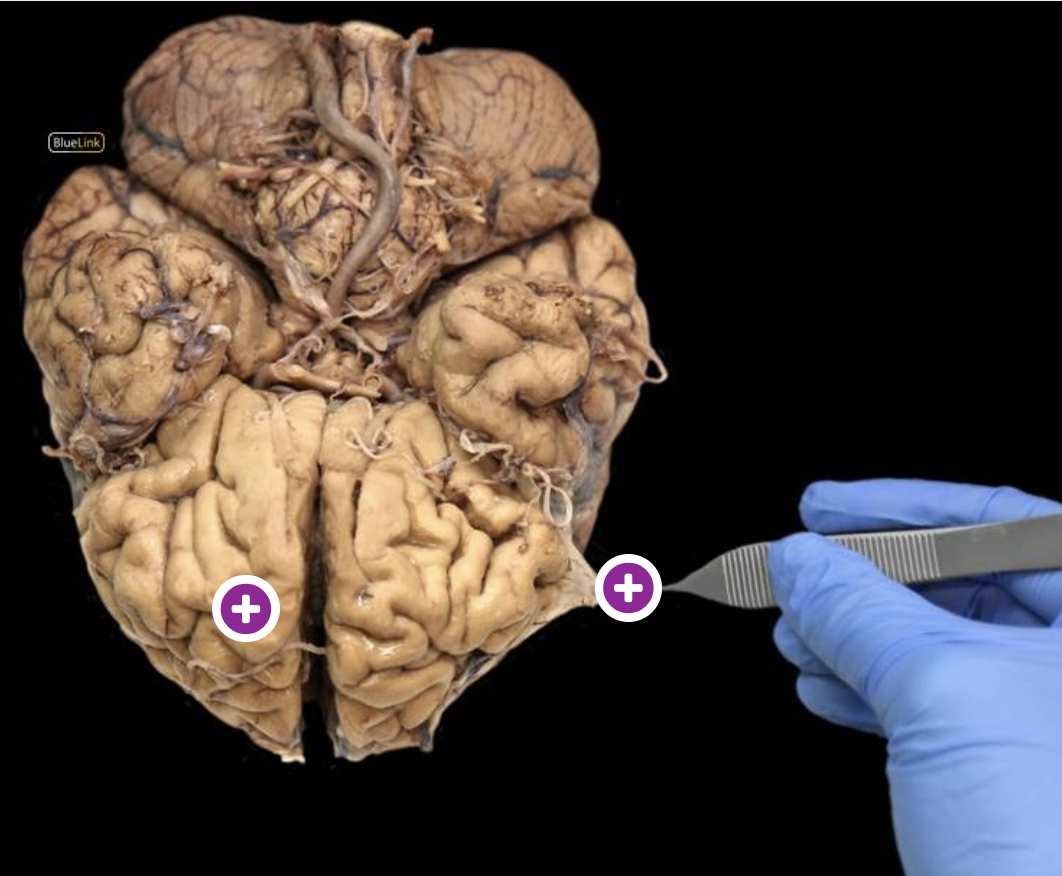
top
third ventricle
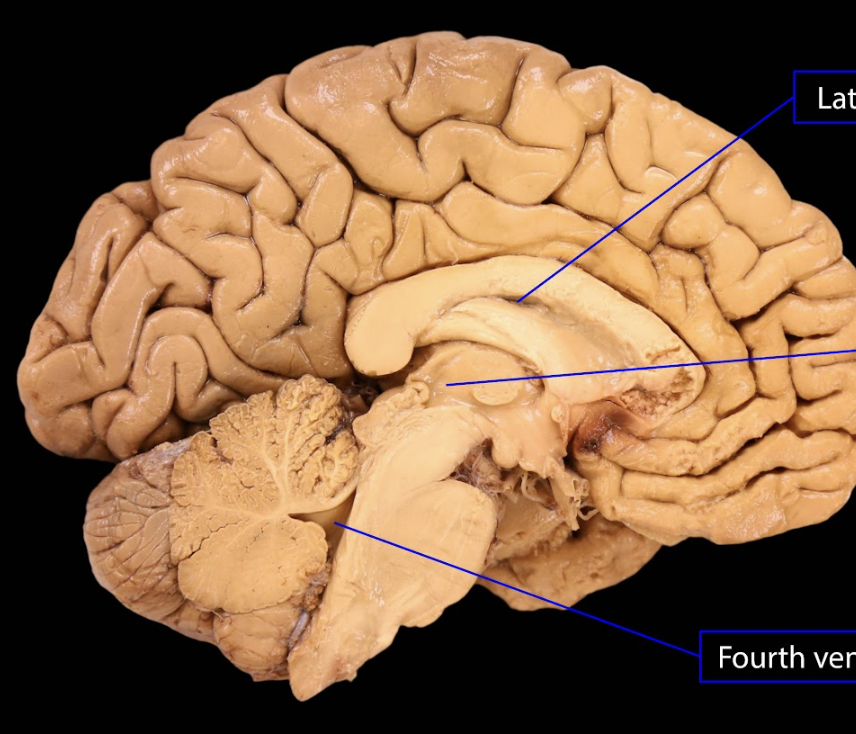
middle
fourth ventricle
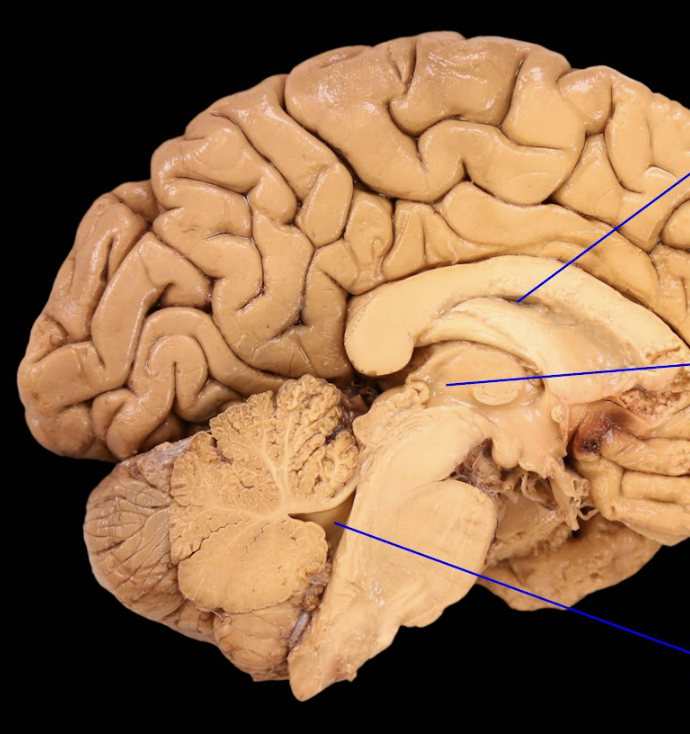
bottom
anterior horn of lateral ventricle

body of lateral ventricle
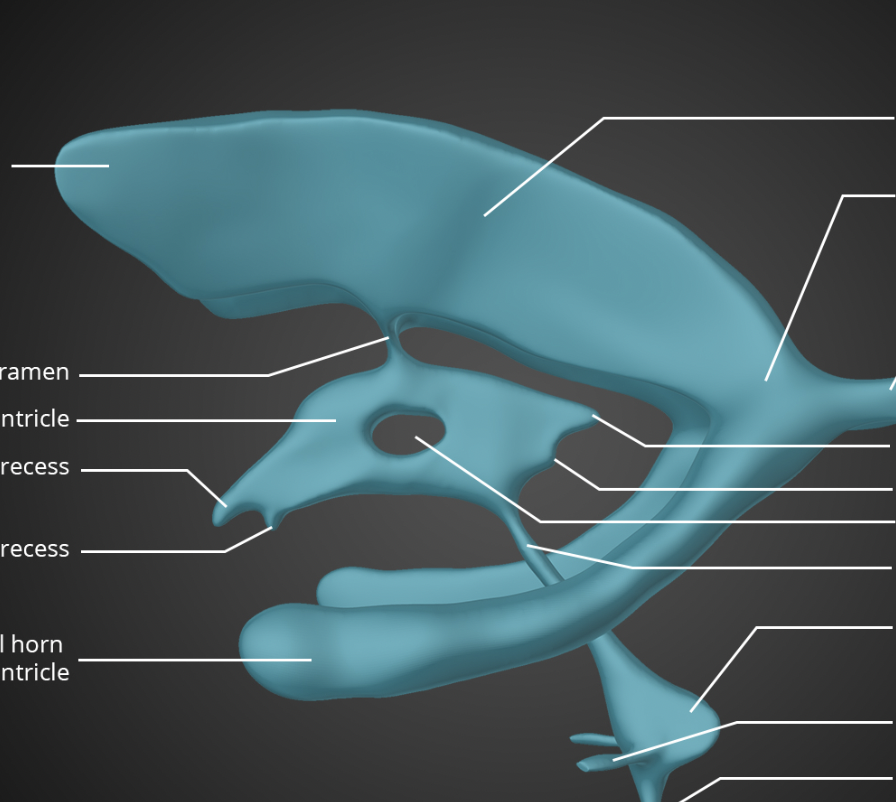
top
interventricular foramen of monro

C
cerebral aqueduct

E
interthalamic adhesion
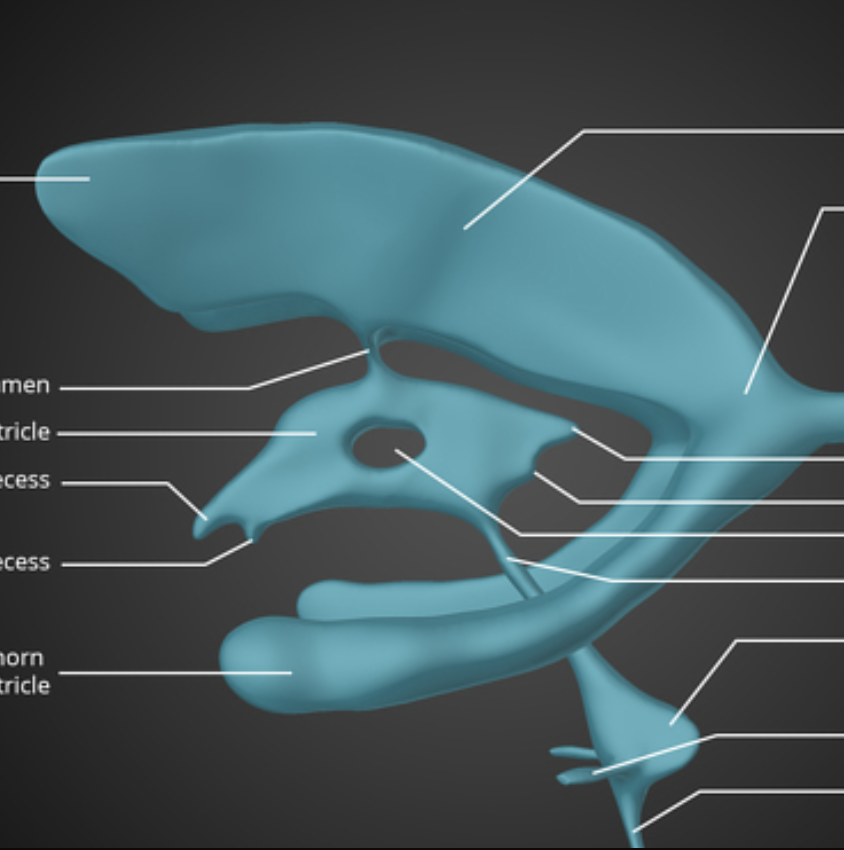
hole in the center of the third ventricle
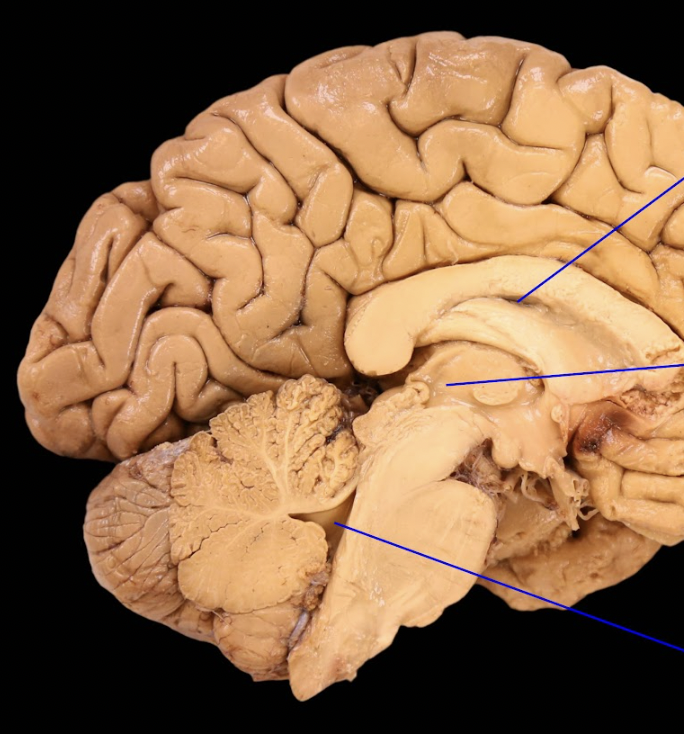
cerebellum

red
brainstem

blue
midbrain
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/article/midbrain-pons-gross-anatomy/FZGi6OOL1A2Ph2BJPp5Q_Midbrain_01.png)
pons
:watermark(/images/watermark_only_413.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url_sm.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/pons/OvrpA8gKgEdBcHG1jbtBsA_image1_medial.png)
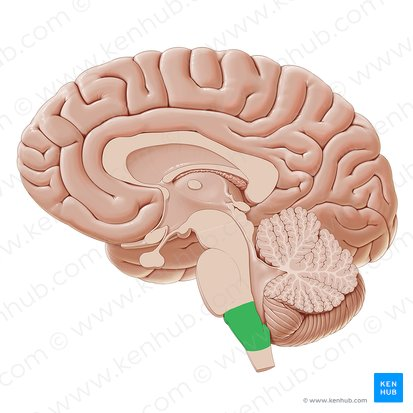
medulla oblongata
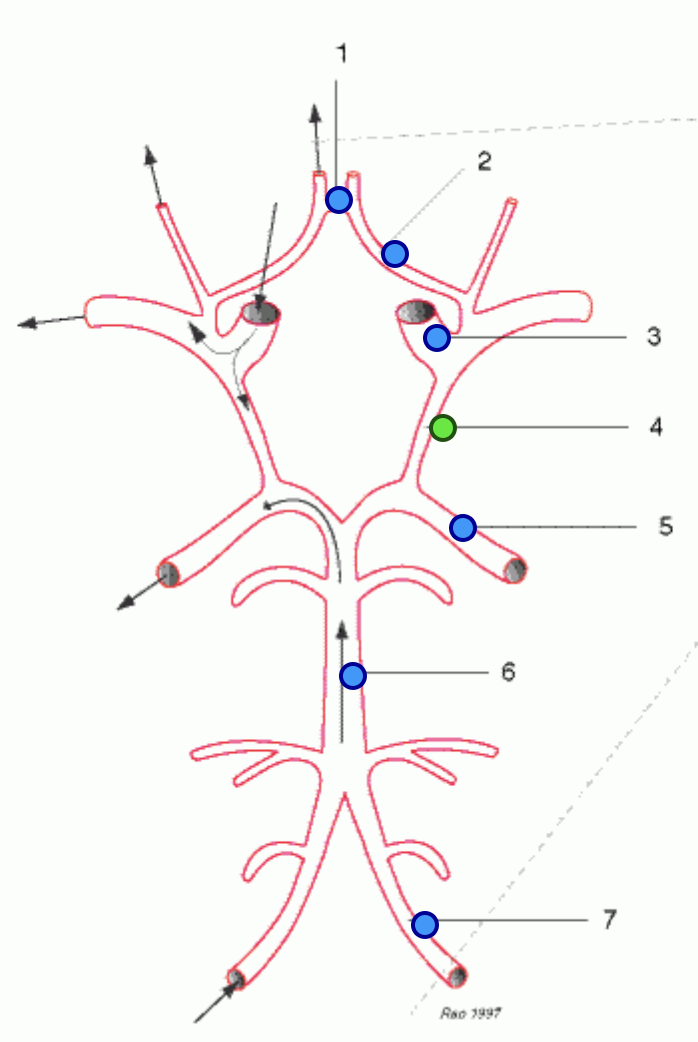
basilar artery
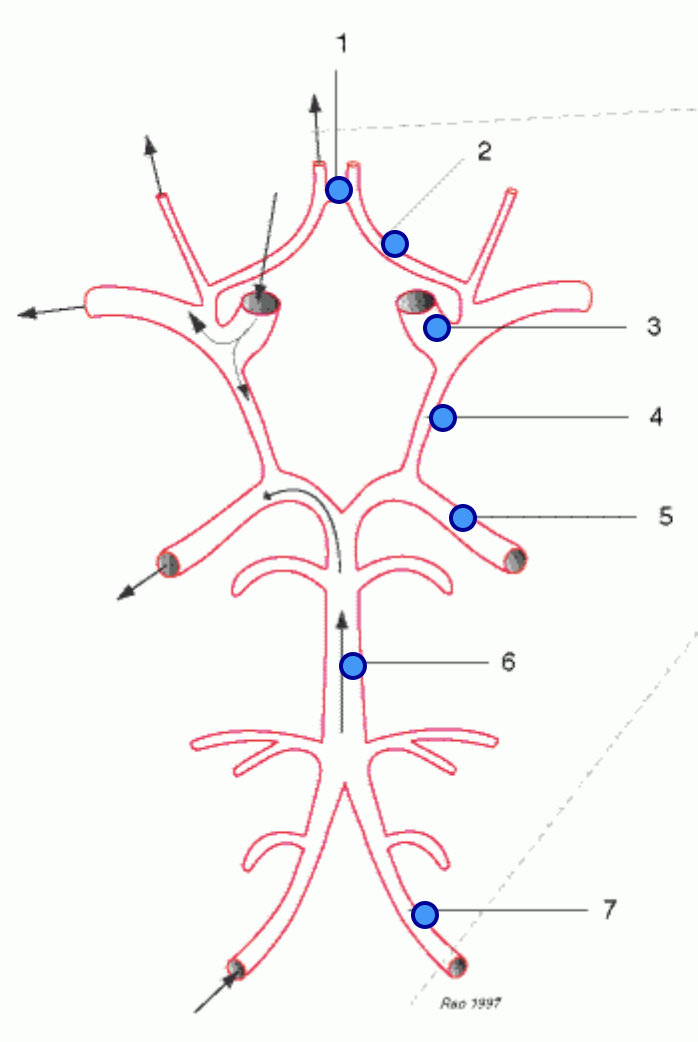
6
internal carotid arteries
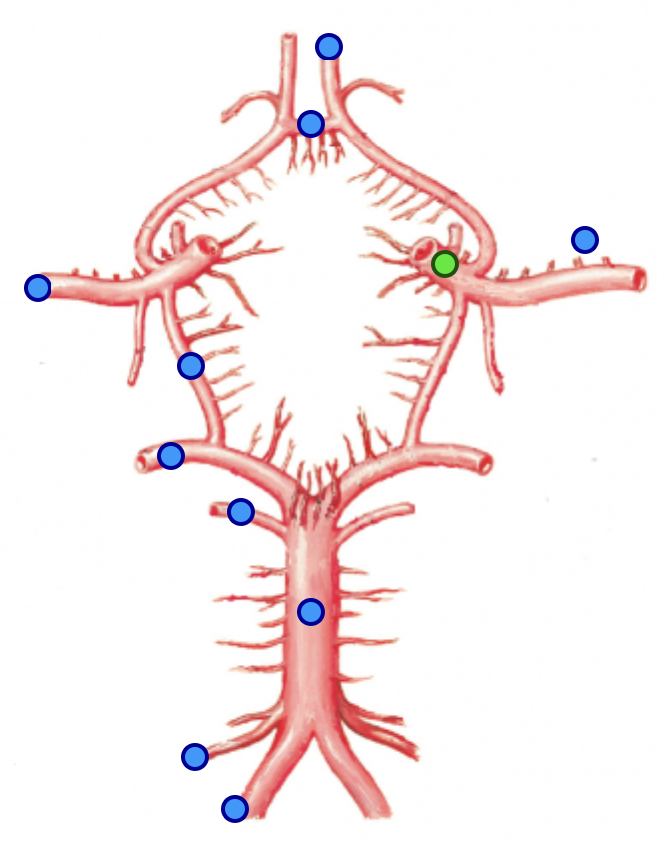
posterior cerebral arteries
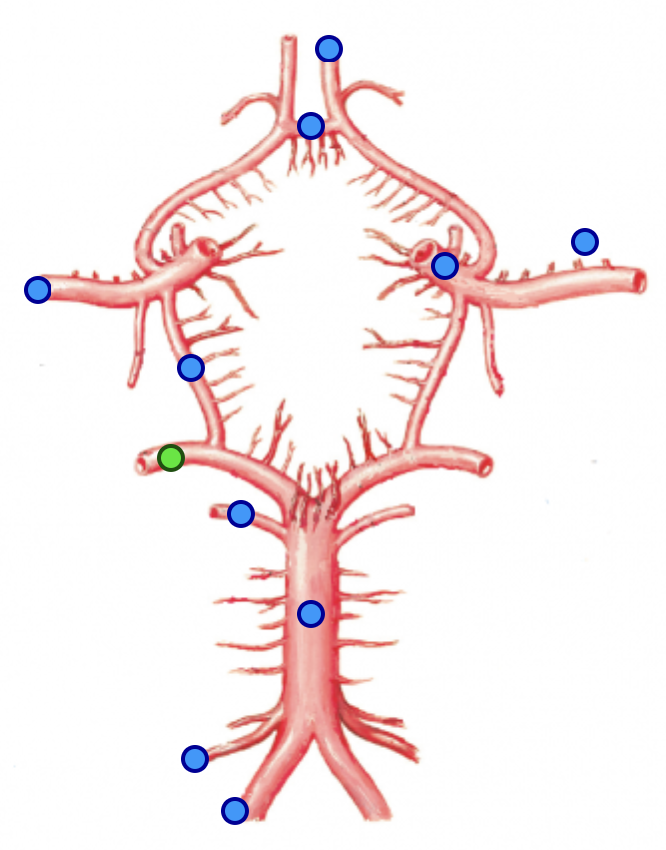
anterior cerebral arteries

anterior communicating artery
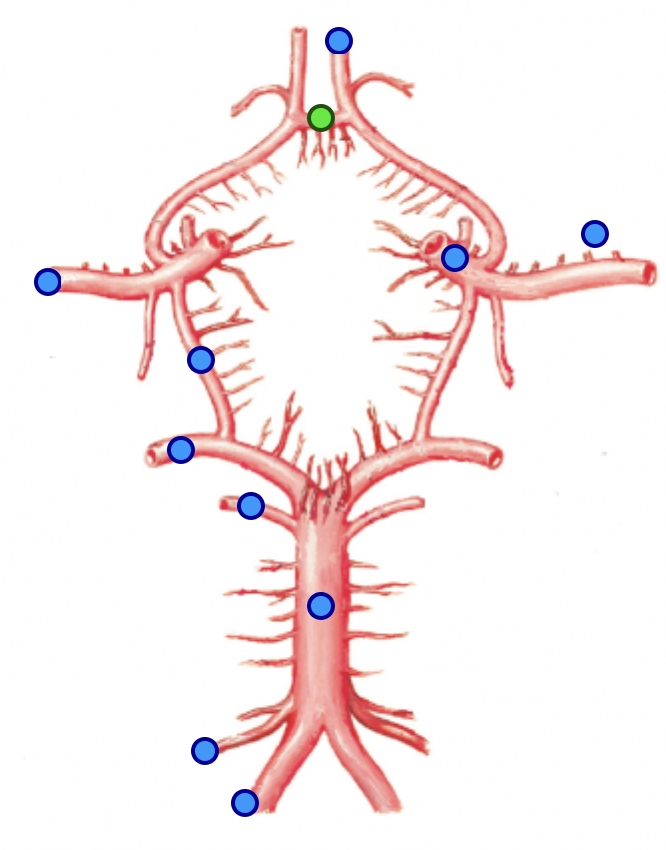
vertebral arteries
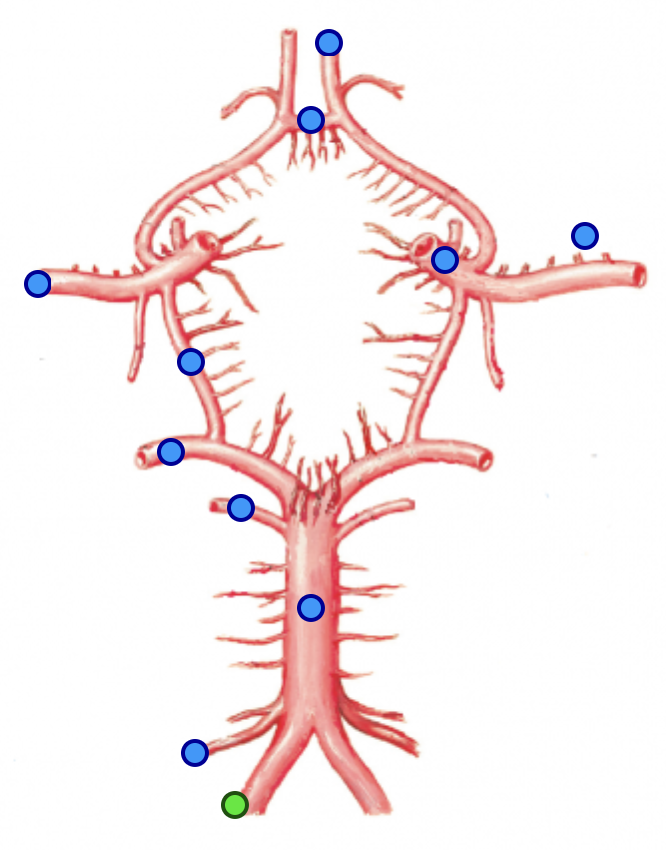
middle cerebral arteries
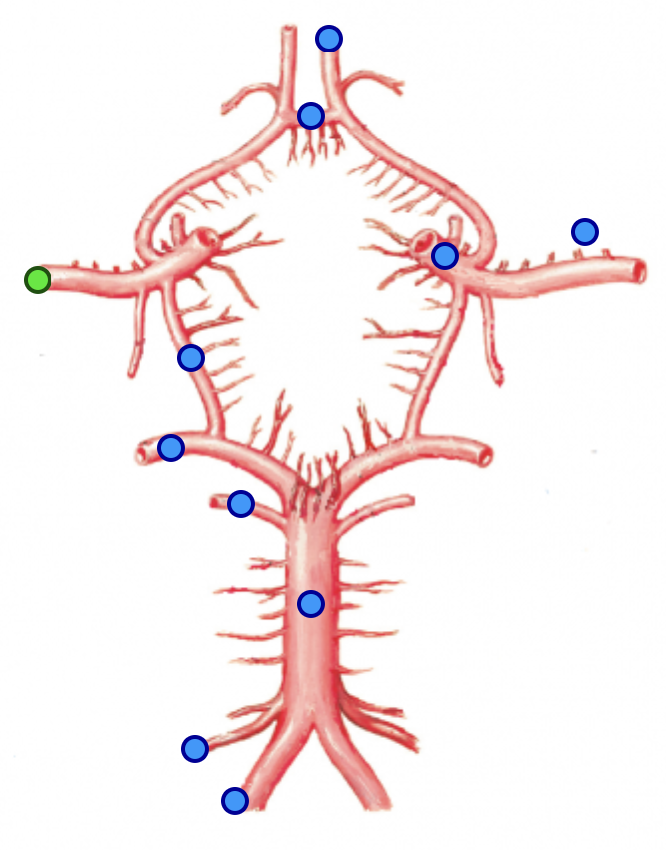
posterior communicating artery
lateral ventricle —> interventricular foramen of monro —> third ventricle —> cerebral aqueduct —> fourth ventricle —> lateral apertures/median aperture/central canal
flow of cerebrospinal fluid (6)