Cardiac Physiology and Electrophysiology
1/103
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
104 Terms
the right atrium receives blood from…
vena cava
the right ventricle receives blood from…
right atrium
the left atrium receives blood from…
pulmonary veins
the left ventricle receives blood from…
left atrium
the vena cava receives blood from…
systemic veins
the pulmonary trunk (artery) receives blood from…
right ventricle
the pulmonary vein receives blood from…
veins of the lungs
the aorta receives blood from…
left ventricle
the right atrium sends blood to…
right ventricle
the right ventricle sends blood to…
lungs
the left atrium sends blood to…
left ventricle
the left ventricle sends blood to…
body except for lungs
the vena cava sends blood to…
right atrium
the pulmonary trunk (artery) sends blood to…
lungs
the pulmonary vein sends blood to…
left atrium
the pulmonary vein sends blood to…
left atrium
the aorta sends blood to…
systemic arteries
where do ascending arteries go to?
head and brain
arms
where does the abdominal aorta go to?
trunk
where does the hepatic artery go to?
liver
where do the descending arteries go to?
digestive tract
kidneys
pelvis
legs
convection
substances move along in the blood because they are dissolved or contained within it
bulk flow requires a ______ gradient
pressure
flow rate equation and units
Q = deltaP / R
Q = flow rate
deltaP = pressure difference
R = resistance
flow depends on the pressure ______ not on the _______ pressure
gradient, absolute
resistance to blood flow by Poiseuille’s Law (and units)
R = 8ln / pir^4
r = radius of tube
l = length of tube
n = viscosity of liquid
Poiseuille Equation (blood flow)
Q = deltaP * ( pir^4 / 8ln )
role of the right heart
provides the energy necessary to move blood through the pulmonary vessels
allows for oxygenation and removal of carbon dioxide
role of the left heart
provides the energy necessary to move blood through the systemic organs
tricuspid valve
between right atrium and right ventricle
pulmonic valve
between right ventricle and pulmonary artery
mitral valve
between left atrium and left ventricle
aortic valve
between left ventricle and aorta
systole
phase of cardiac cycle where cardiac muscle cells are contracting (can be either atrial or ventricular)
diastole
phase of cardiac cycle where cardiac muscle cells are at rest (can be atrial or ventricular)
where does the interstitial fluid come from?
plasma that leaks from capillaries
pulmonary and system circulation run in _______
parallel
blood that leaves the left side of the heart is _____
oxygenated
blood that enters the right side of the heart is _______
deoxygenated
the left and right heart handle the _____ volume of blood at the ____ rate
same
each organ system can control blood flow ______ of others
independently
blood conditioning organs
modifies the blood as it moves through the tissue
receive increased blood flow compared to their metabolic needs
meaning of cardiac output
amount of blood pumped per minute from each ventricle
cardiac output formula
CO = SV x HR
what is stroke volume SV?
volume of blood ejected per beat
preload
represents the filling of the ventricle that occurs during diastole
reflects Starling’s law, where the more ventricular stretch the more tension that can be generated
afterload
pressure that the heart is working against
reflects values within the aorta that the heart must overcome to efficiently eject blood forward
what is a measure of the heart’s efficiency as a pump?
cardiac output
at rest, the _______ branch of the ANS dominates control of the heart
parasympathetic
as preload increases, so does the strength of the heart’s _______
contraction
the stretch of the ventricle’s cardiac muscle is indicated by ventricular ________
end-diastolic volume
the force of a ventricle’s cardiac muscle is indicated by _______
stroke volume
positive inotropy is a result of stimuli that increase _______ availability within cardiac muscle cells
calcium
what effect does hypertension have in terms of afterload?
this creates extra stress on the heart to provide a stronger contraction to overcome the the aortic pressure
5 requirements for an effective heart as a pump
synchronized and regular contractions of individual cardiac cells
valves fully open
non-leaky valves
muscle contractions are forcefail
ventricle exhibit compliance
function of arteries
elastic and act as a pressure reservoir
function of arterioles
high resistance and direct blood flow to individual tissues
function of capillaries
leaky vessels that allow for exchange of materials between plasma,ISF, and ICF
function of veins
capacitance vessels that act as a volume reservoir from which the blood can be sent to the arterial side of circulation
total peripheral resistance TPR
the contraction or relaxation of vascular smooth muscle that modifies overall resistance in the circuit
mean arterial blood pressure MAP formula
MAP = CO x TPR
what are the two phases of the cardiac cycle?
diastole (filling)
systole (contraction and eventual blood ejection)
left heart cardiac cycle: diastolic phase
valves that separate the atria from ventricles (mitral valve) must passively open in response to ventricular pressure falling blow atrial pressure
the filling of the ventricle occurs if there is…
an appropriate cardiac return
ability of AV valves to open fully
ability of the ventricular wall to expand passively with little resistance (high compliance)
atrial depolarization (leading to contraction) is captured as what on an EKG recording?
p wave
during normal resting conditions, ________ is not essential for ventricular filling
atrial contraction
what causes the left cardiac cycle: systolic phase?
the movement of an action potential from atrial to ventricular leading to muscle contraction
ventricular cardiac muscle cells develop tension that result in the following chronological events:
mitral valve closes and intraventricular pressure increases in a closed system (isovolumetric contraction)
early and rapid ejection period once intraventricular pressure exceeds that in the aorta
peak systolic pressure
after peak systolic pressure, strength of the contraction diminishes and intraventricular pressure falls which leads to…
closure of aortic valve (dicrotic notch)
isovolumetric relaxation phase where pressure falls again below atrial values
what do the axes of the left heart cardiac pressure volume loop represent?
x axis: intraventricular volume
y axis: intraventricular pressure
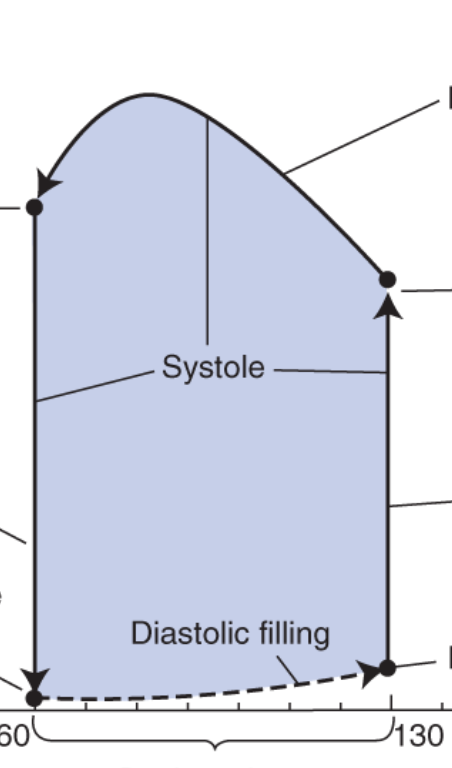
what does the bottom left point represent?
mitral valve opens
ventricle is at lowest volume
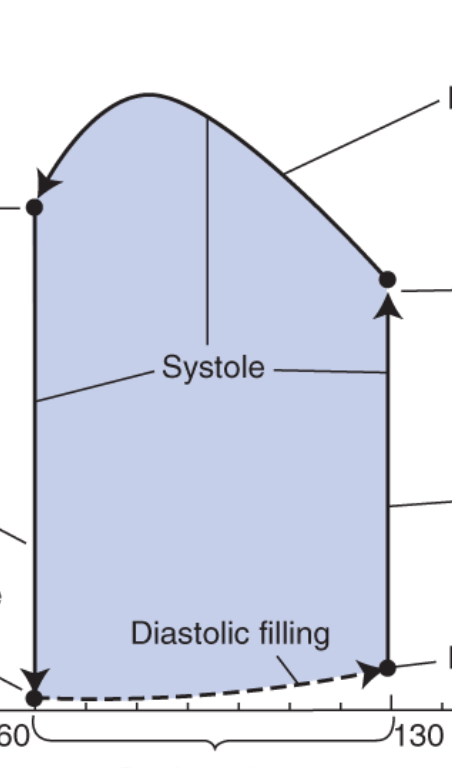
what does the bottom dotted line represent?
ventricular filling, with constant pressure due to stretching (compliance)
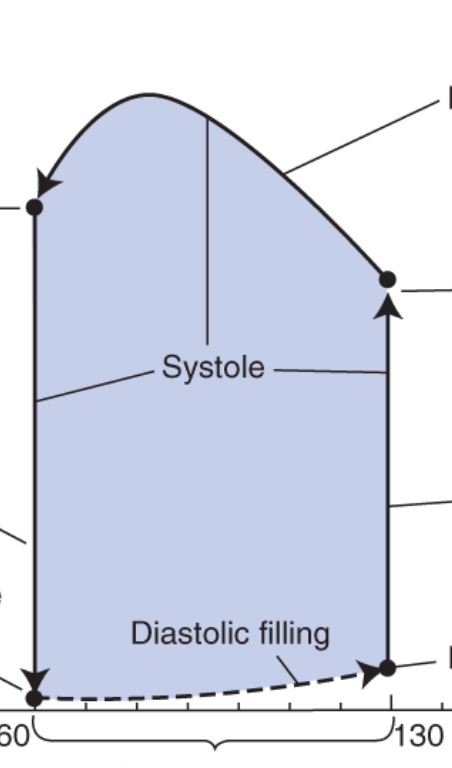
what does the bottom right point represent?
end-diastolic volume
equivalent to preload
mitral valve closes
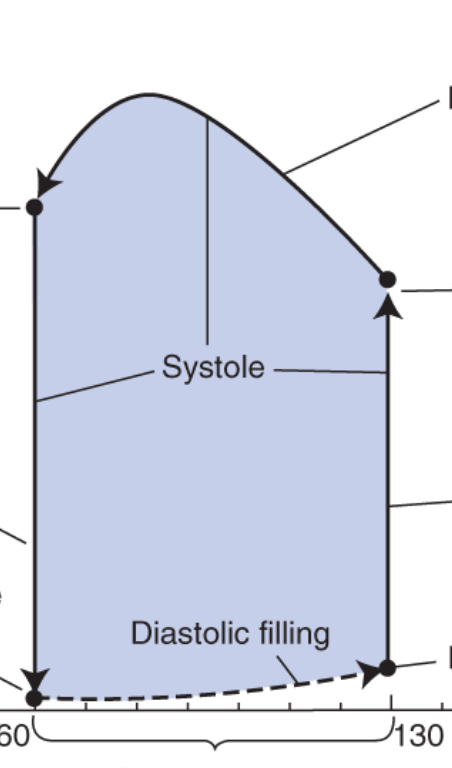
what does the right vertical line represent?
isovolumetric contraction
closed system
the ventricle depolarizes and creates a contraction to produce increasing pressure
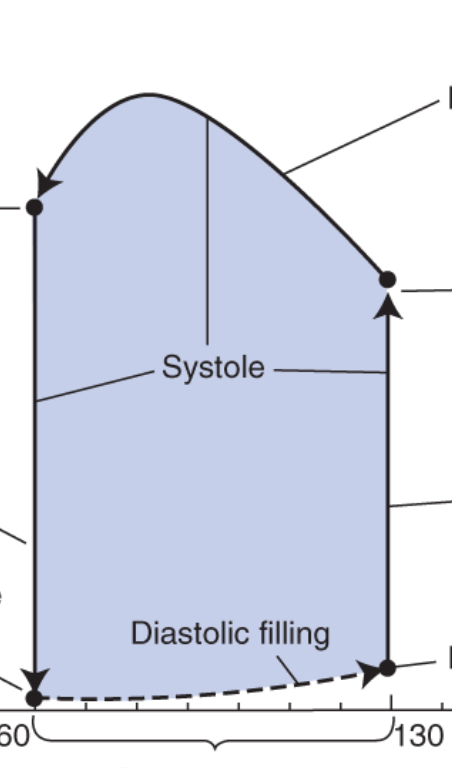
what does the upper right point represent?
aortic valve opens
ventricular pressure exceeds aorta
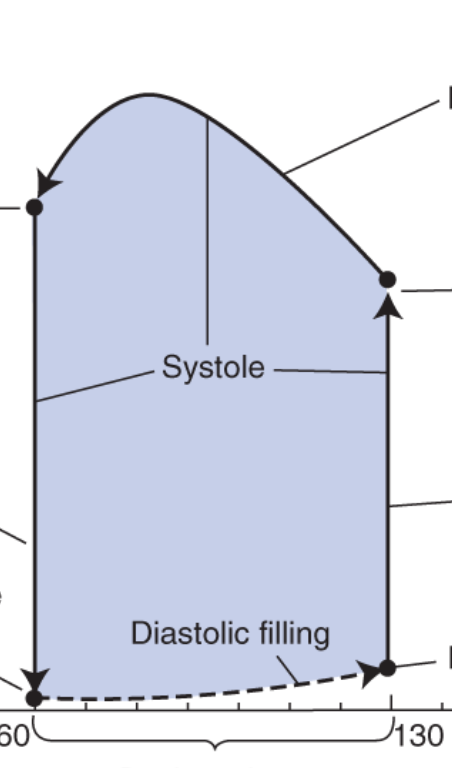
what does the top arrow represent?
blood is ejected into aorta
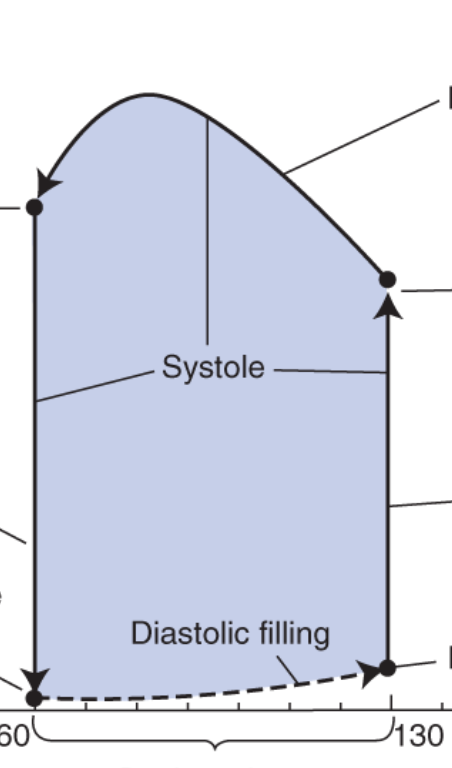
what does the top left point represent?
end-systolic volume
contraction is over
aortic valve closes
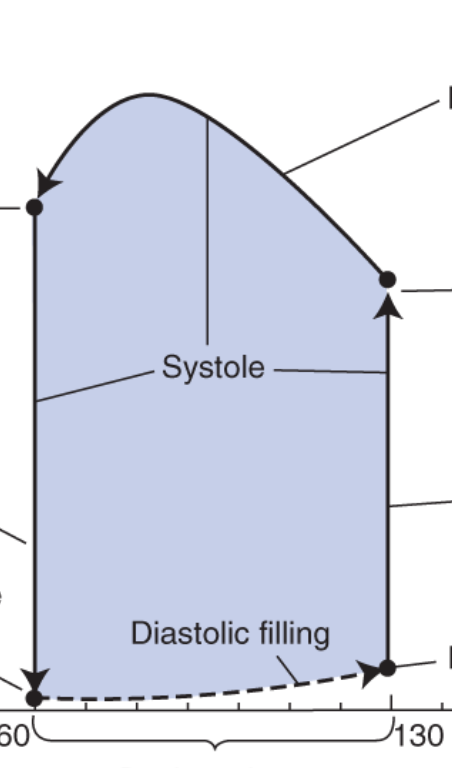
what does the left line represent?
isovolumetric relaxation
closed system
ventricular pressure is decreasing as it expands

what does the width of this graph represent?
stroke volume
formula for stroke volume SV
SV = EDV - ESV
what does the ejection fraction indicate?
how much of the filled volume in the left ventricle will be ejected into the aorta
ejection fraction formula EF
EF = SV / EDV
a ventricle that lacks contractile strength to force blood into the aorta will cause an increase in ________
end-systolic volume
what influences stroke volume ( and ejection fraction)?
starling’s law of the heart
changes in ventricular afterload
changes to cardiac muscle contractility
cardiac electrophysiology flow chart
SA node
internodal pathways
AV node
AV bundle
bundle branches
purkinje fibers
the SA node demonstrates _______ over heart rate
dominance
what neurotransmitter causes positive inotropy (or increased contractility of the heart)?
norepinephrine
what neurotransmitter causes negative inotropy (or decreased contractility of the heart)?
acetylcholine
sympathetic nerves release norepinephrine onto ______ of the _____
B1 receptors, SA node
vagal terminals release acetylcholine onto ______ of the ______
M2 receptors, SA node
location of SA node
upper right atrium
location of AV node
bottom right atrium
internodal pathways
allows signal from SA node to travel to the AV node, leading to excitation and depolarization of the atrial tissue during travel
bundle branches
allows signal from AV node down into the ventricle
purkinje cells
carries signal to apex of heart and around walls of the ventricles, allowing for depolarization of contraction of the ventricle
as a result in patients with mutations to gap junction proteins, _____ may result
arrhythmias
the ECG represents the _________ activity of all cells recorded from the surface of the body
summed electrical
p wave
atrial depolarization
PR segment
conduction through AV node and AV bundle
QRS complex
ventricular depolarization