protein turnover
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
what is protein turnover
Replacement of older cells as theyre broken down within the cell
•Is equal to protein degradation.
•Many cellular proteins are constantly degraded and resynthesized.
ØThe total amount of proteins in the body remains constant (Rate of protein synthesis is constant).
•Many rapidly degraded proteins function as regulatory molecules, such as transcription factors.
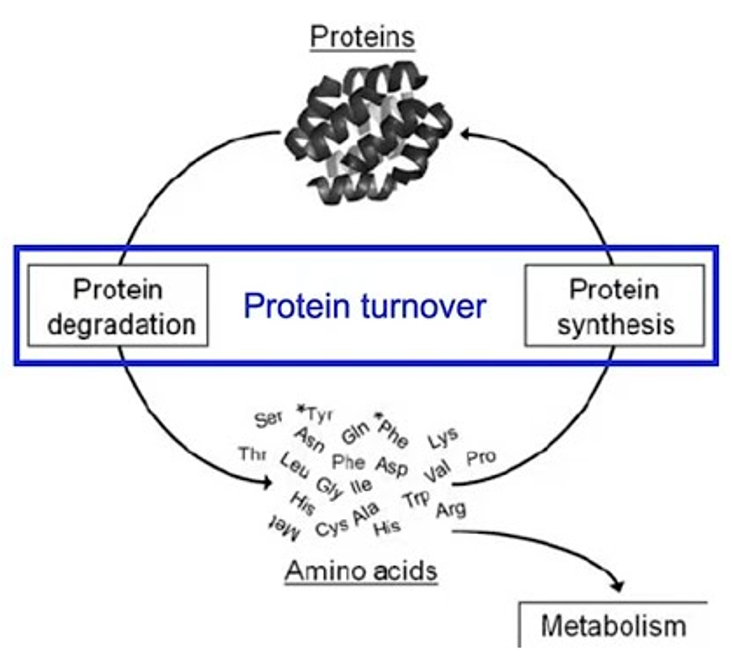
The rate of protein degradation is related to
the half-life of the protein.
what affects protein turnover
food intake
How can a cell distinguish proteins that are meant for degradation?
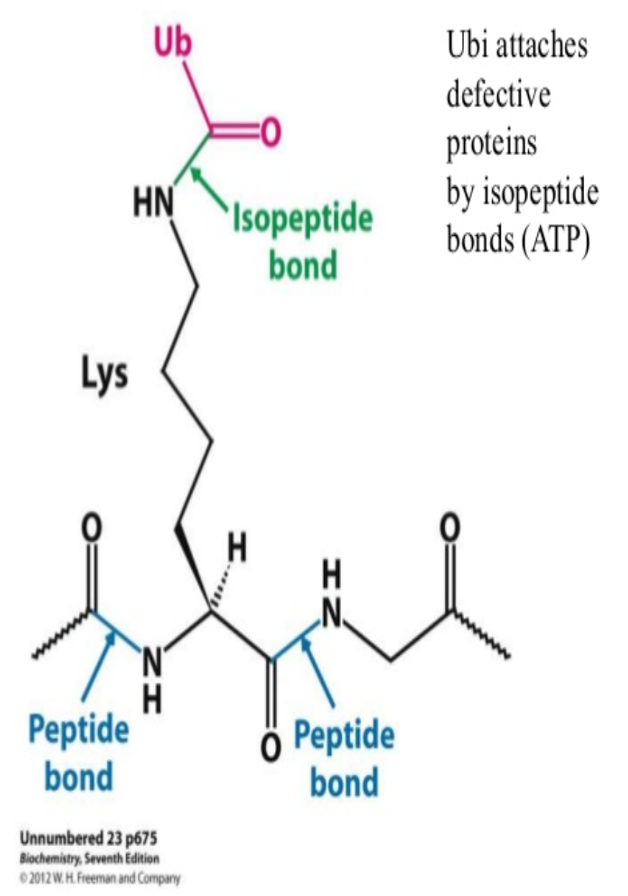
•Damaged or unneeded proteins are marked for destruction by the covalent attachment of chains of a small protein, ubiquitin.
•
•Polyubiquitinated proteins are subsequently degraded by a large, ATP-dependent complex called the proteasome.
ubiquitination def
PTM
ubiquitin protein attaches to substrate protein to be degraded
76 AA
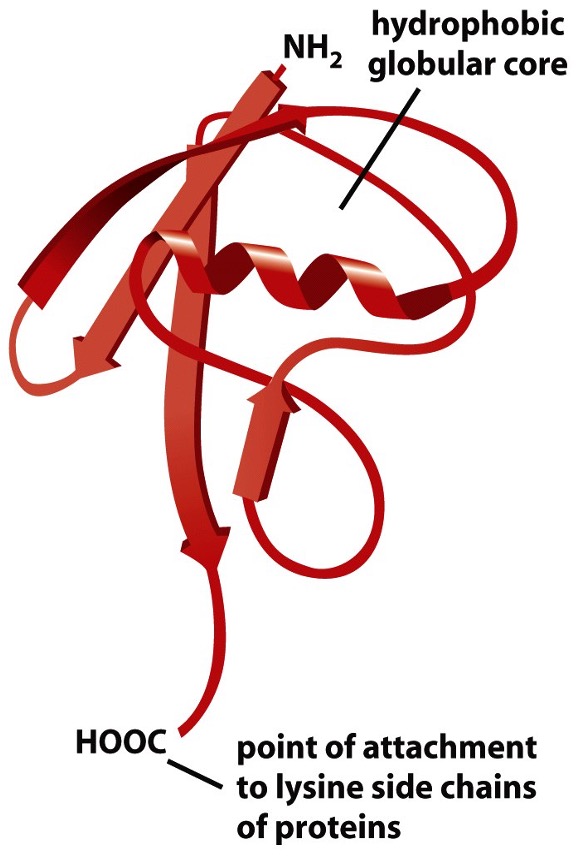

Ubiquitin structure
has 2 end - N and C terminal
its C-terminal glycine residue binds to the epsilon-amino group of a lysine residue on the target protein, forming an isopeptide bond;
energy for bond formation comes froom hydrolysis of ATP
Examples of cellular functions regulated by ubiquitination
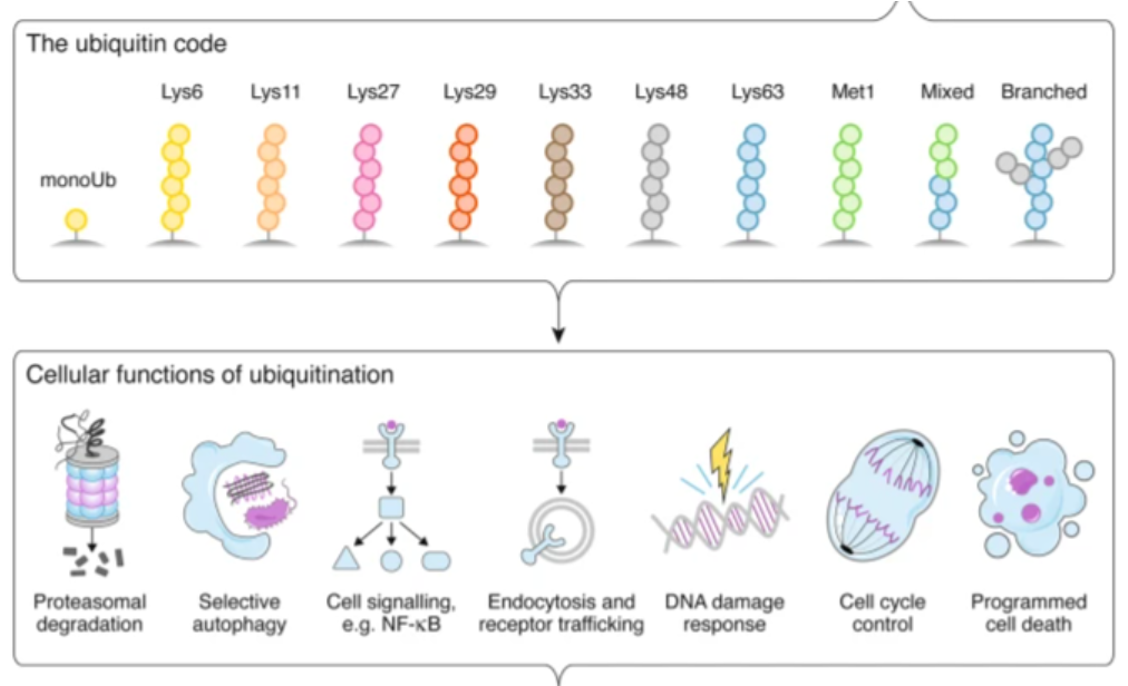
•How cells interpret ubiquitination signal depend on: 2
Number of ubiquitin molecules added (mono, multi-mono or poly-ubiquitinated)
How ubiquitin molecules linked together (linkage through Lys48 or Lys63)
Poly-ubiquitinated proteins are targeted for degradation via
the proteosome
•Protein destruction machine
•Abundant-ATP dependent protease
•Found in cytosol and nucleus
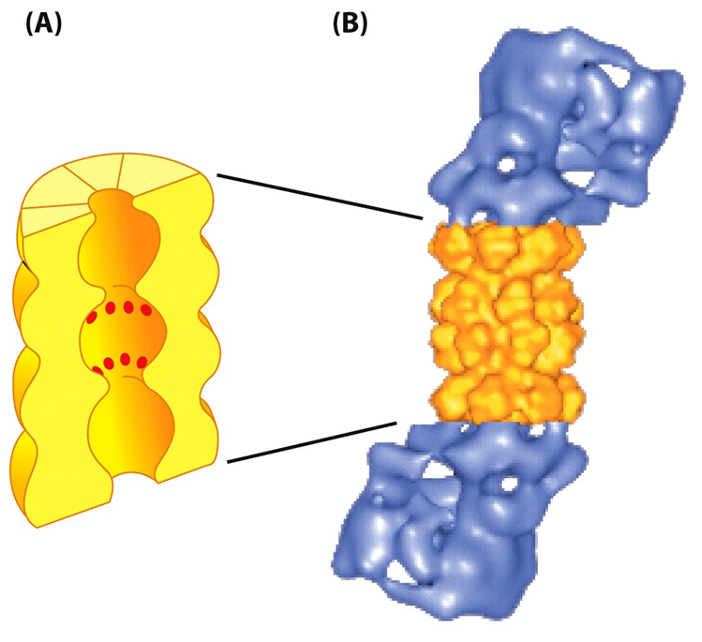
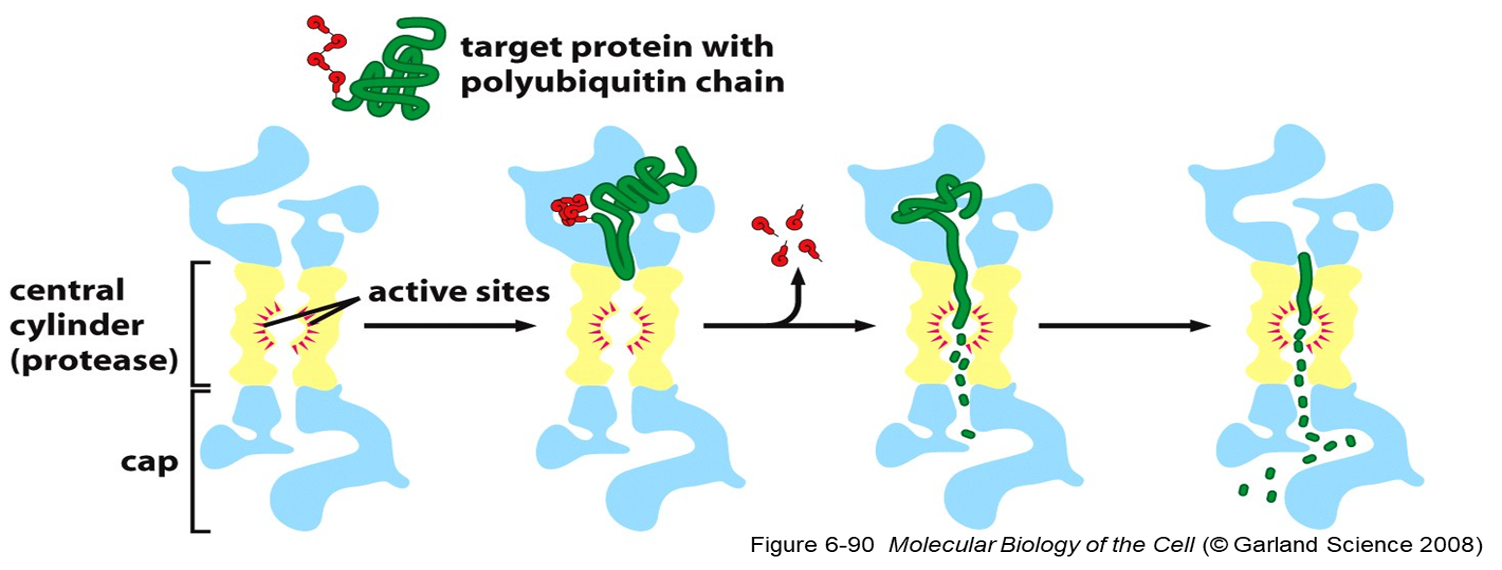
Proteasome recognizes substrate protein via
•poly-ubiquitin chain.
•Translocate target proteins into core-degraded.
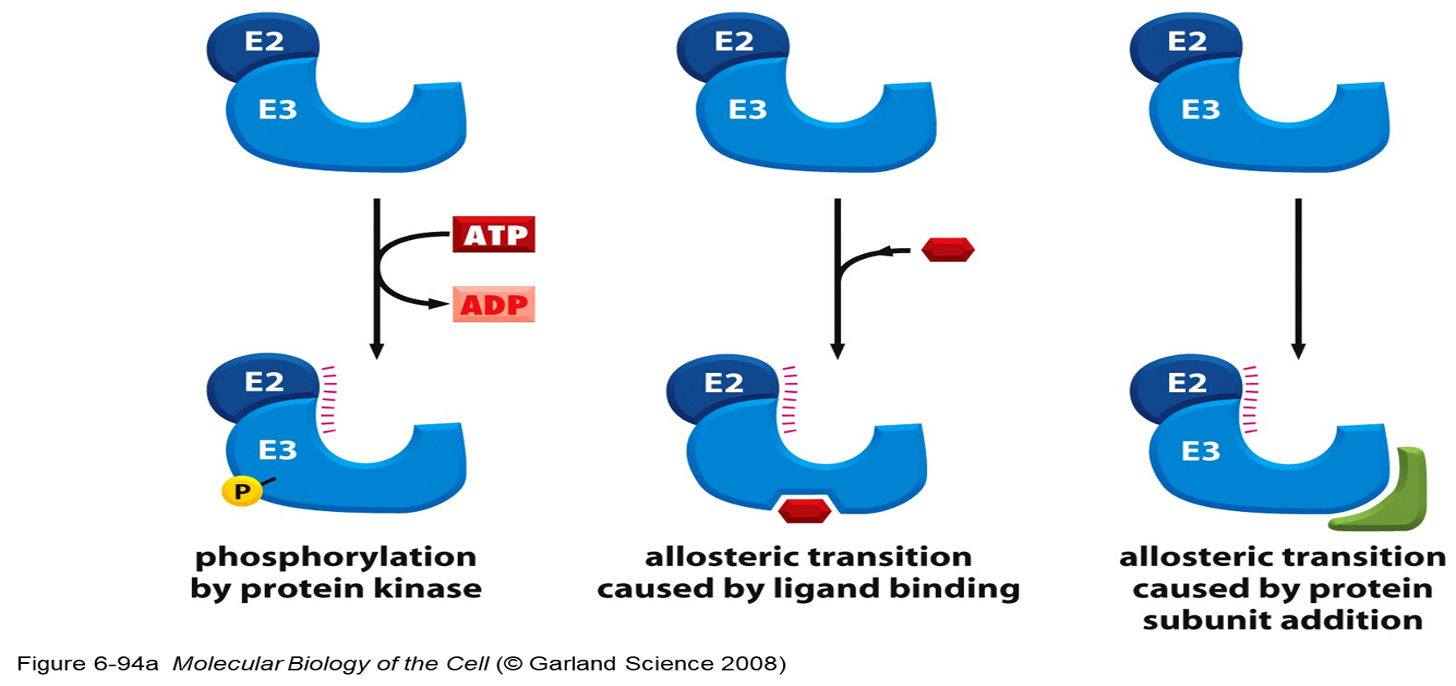
Two general ways of inducing degradation of a specific protein:
1.Activation of a ubiquitin ligase (E3)
-Different protein ligases (E3) for different target proteins.
-
2. Expose degradation signal on the target protein.
- Allows binding to ubiquitin ligase
1.Activation of a ubiquitin ligase (E3)
-Different protein ligases (E3) for different target proteins.
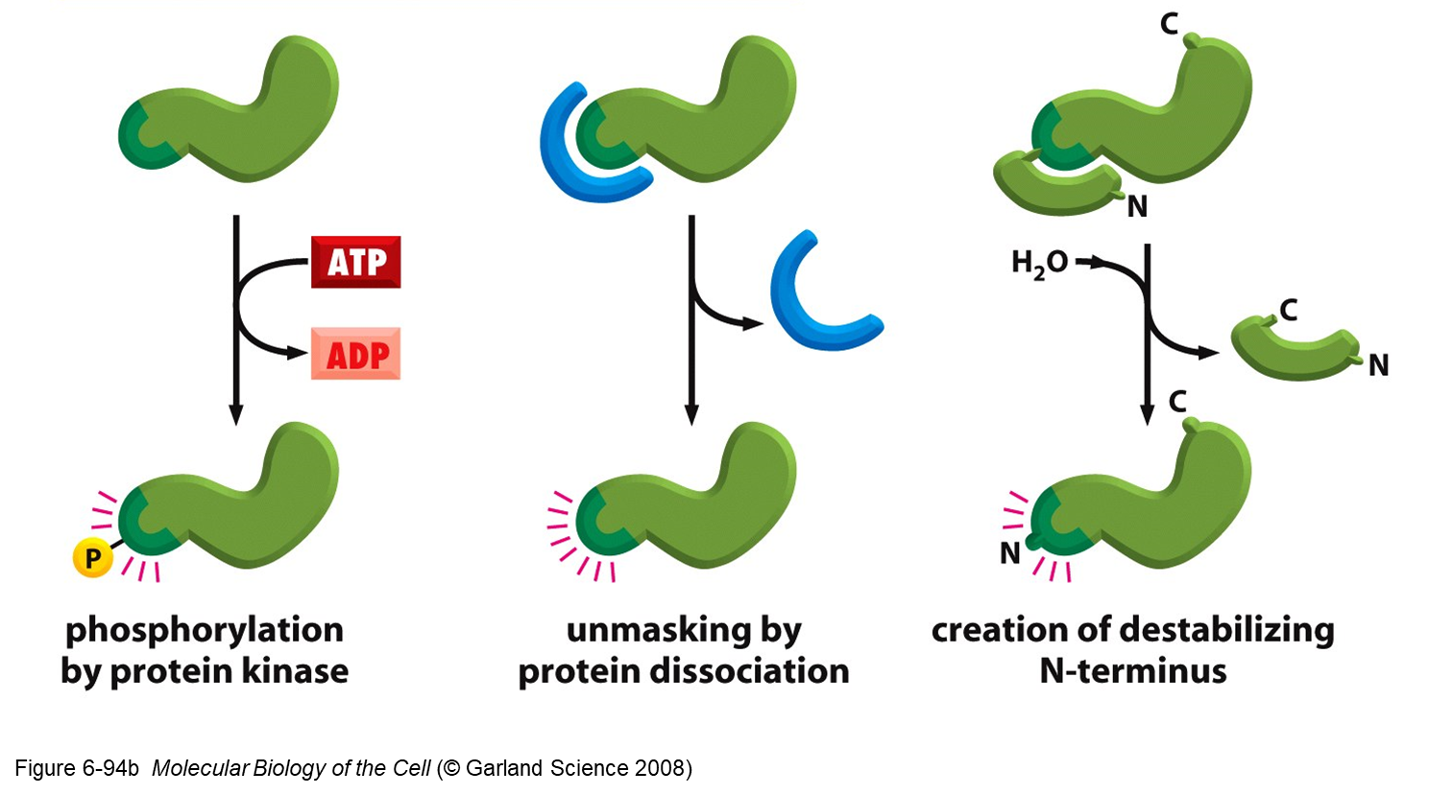
2. Expose degradation signal on target proteins
Von Hippel-Lindau Syndrome
•Autosomal dominant disorder (1 in 36,000 individuals).
•Formation of tumours (noncancerous or cancerous) and cysts in many different parts of the body.
•Most frequently appeared during young adulthood.
•
•It affects: eye, back of the brain, spinal cord, kidneys, adrenal glands or pancreas.
•Common tumours:
-Angiomas- enlarged blood vessels in the retina.
-Hemangioblastomas- vascular tumours along the spine.
-Renal and pancreatic tumours.
-Pheochromocytomas- commonly occur in adrenal glands
what gene is mutated and role
•Caused by mutations in VHL gene.
•VHL gene encodes the Von Hippel-Lindau tumour suppressor (pVHL).
pVHL controls
-Angiogenesis
-Extracellular matrix formation
-Cell metabolism
-Mitogenesis
role of pVHL
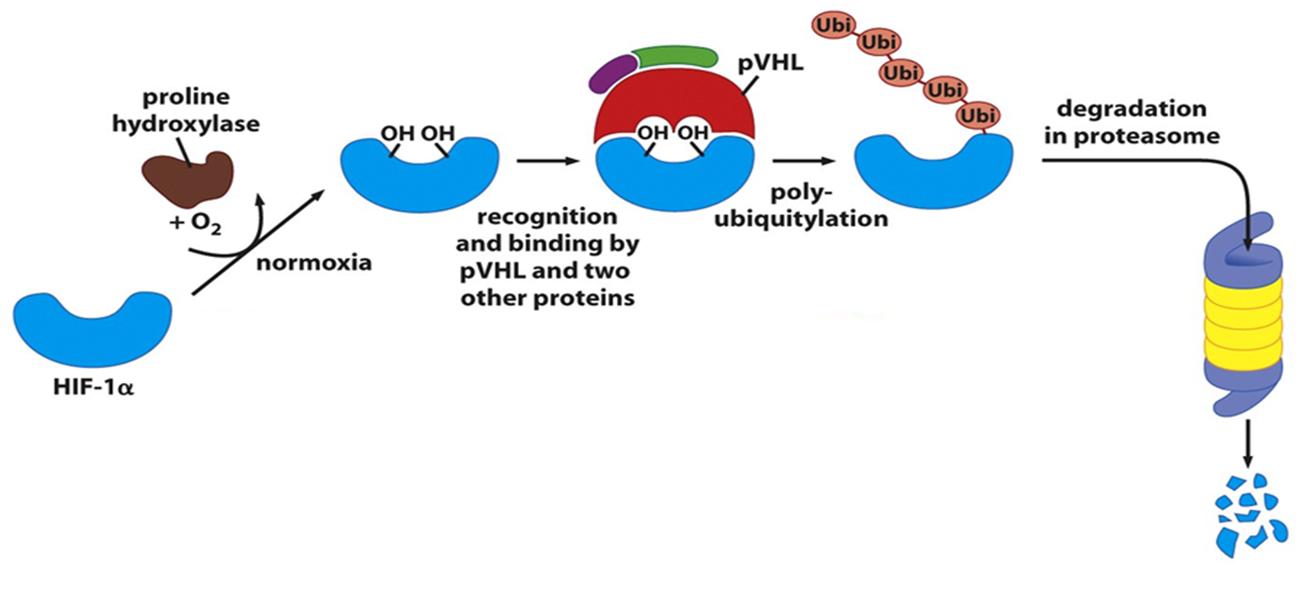
•Role: part of multi subunit E3 ubiquitin protein ligase (VHL complex).
•It is the substrate recognition unit of E3 ligase that targets transcription factor HIF-1α (hypoxia induced factor).
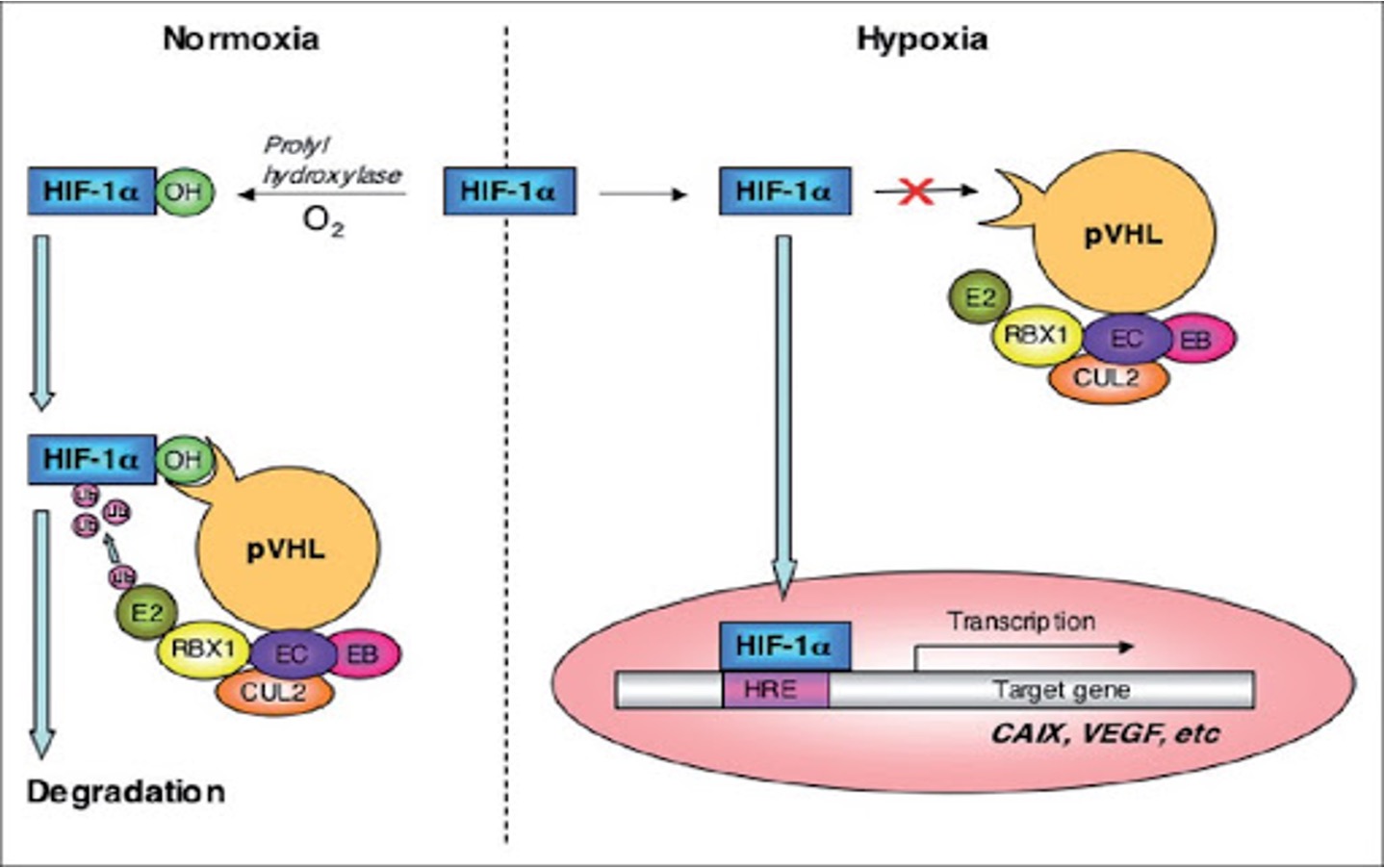
•It binds and ubiquitylates HIF-1α for degradation in conditions of normoxia.
IF NORMAL LEVELS OF O2 FACTORS NOT NEEDED
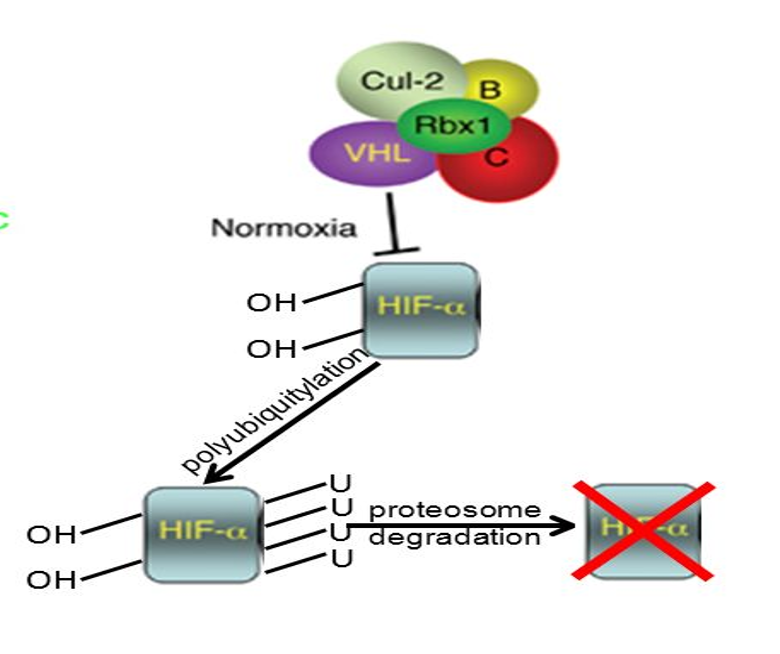
•pVHL complex regulates levels of activator TF HIF-1α
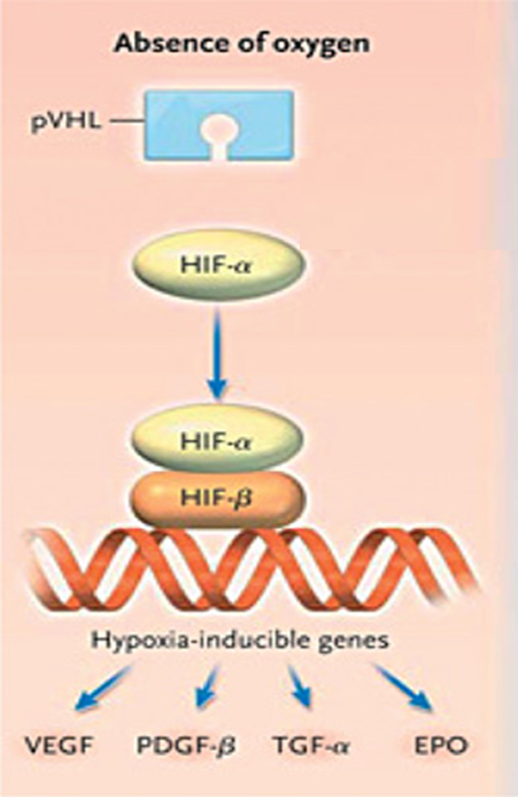
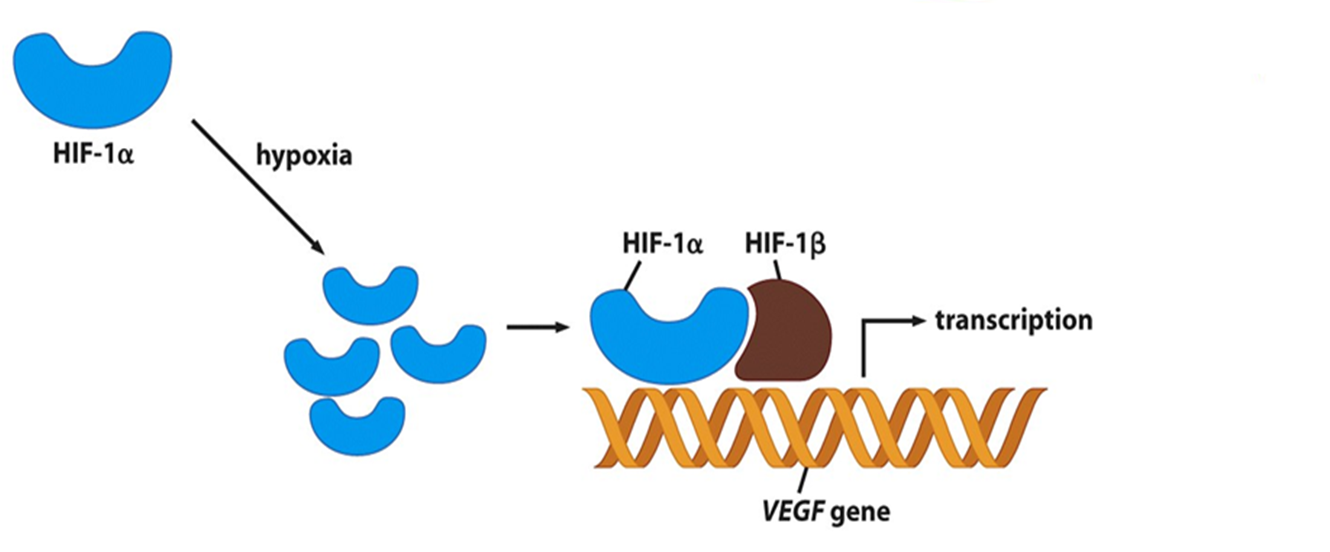
•HIF-1 α regulates cellular response to hypoxia (low oxygen).
•Switches on genes that promote cell survival and angiogenesis.
E.G. vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF
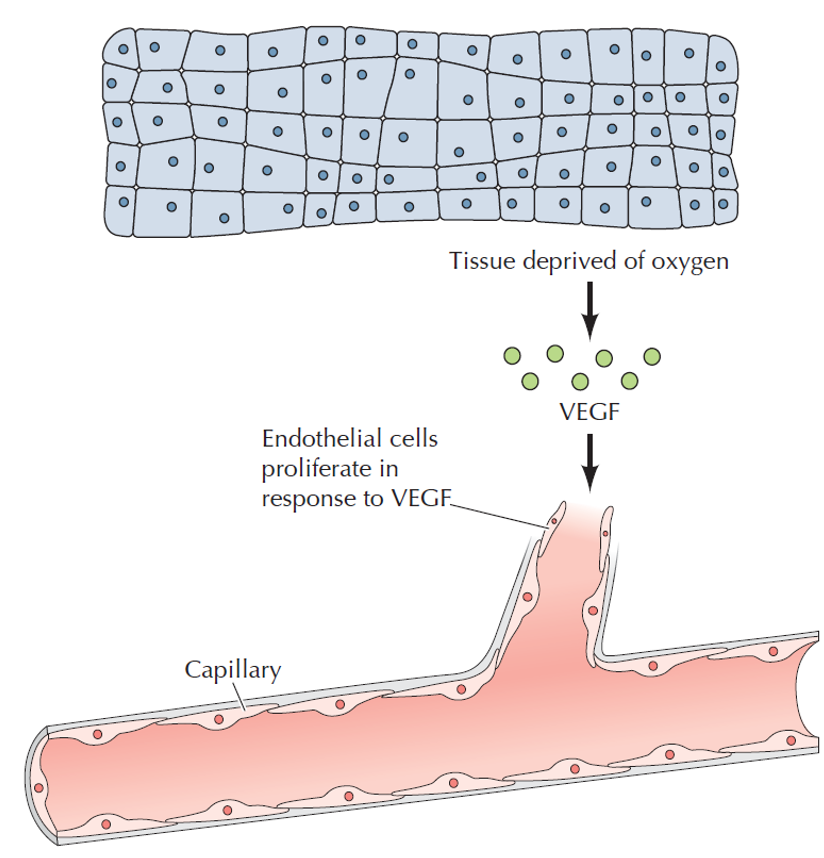
release of VEGF
•Stimulate cell proliferation and outgrowth of new capillaries
•pVHL complex targets HIF-1α for degradation under normoxic conditions.
pVHL complex is inactivated in hypoxic conditions, which lead to
increase levels of HIF-1α.
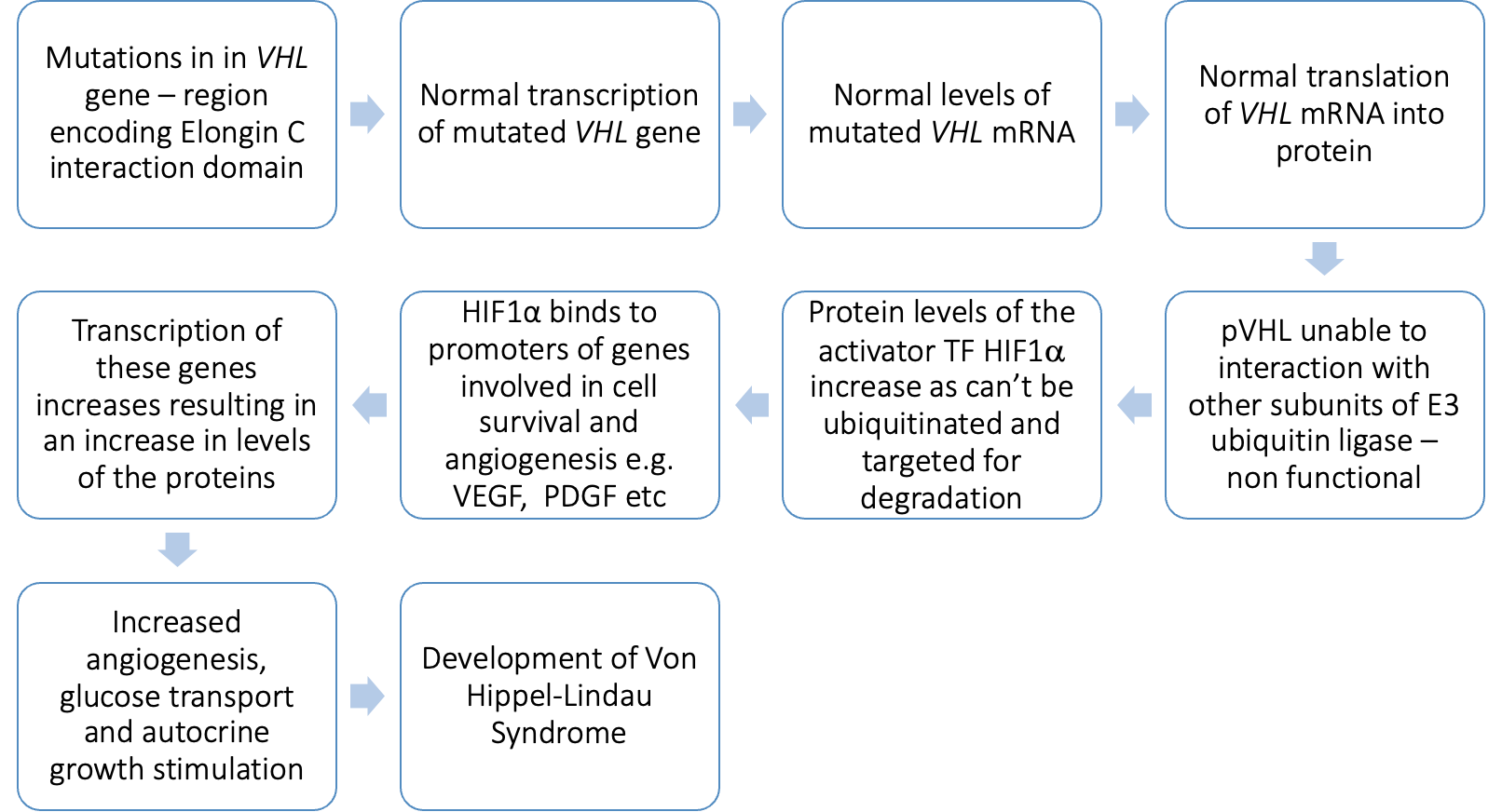
Mutations in VHL gene lead to
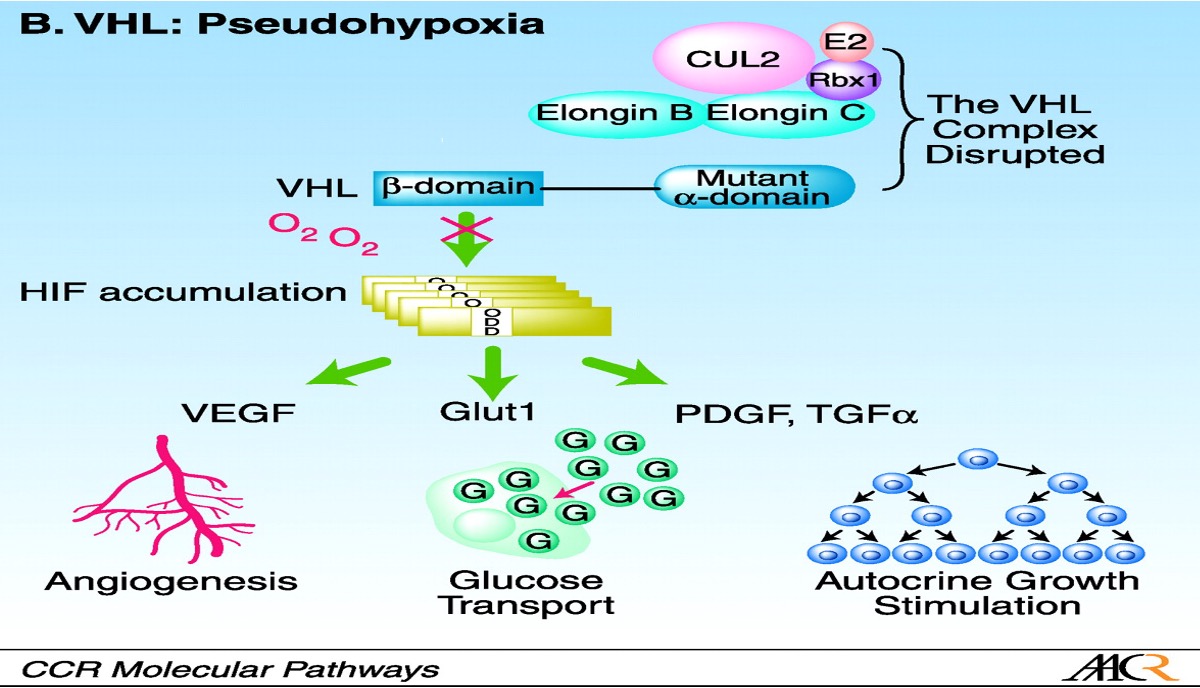
•a lack of regulation of cell growth and survival, allowing cells to grow and divide uncontrollably.
•Normoxia – but HIF-α is not targeted for degradation.
•> 370 inherited mutations in VHL gene.
Ø80% cases are missense mutations.
20% large germline deletions.
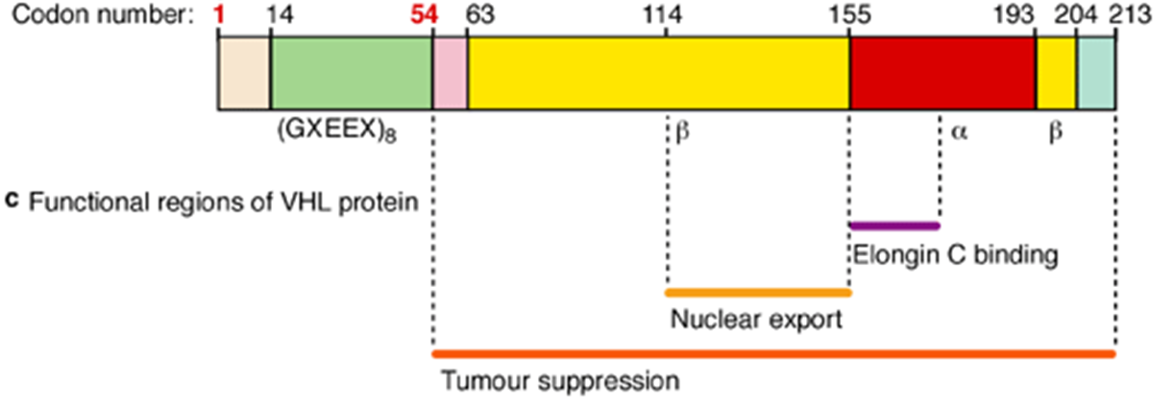
•Some missense mutations are clustered in the Elongin C binding site, which supports its role in VHL protein function.
Missense mutations-
POSTIONS..
•Arg167Gln - Substitutes Arginine (R) with Glutamine (Q) at position 167
Arg167Trp - Substitutes Arginine (R) with Tryptophan (W) at position 167.
•is a hotspot mutation in many populations.
•It was associated with renal cell carcinoma RCC, renal cysts and pheochromocytoma.
what do the missense mutations cause - functionally
•Mutation disrupts hydrogen bonding in VHL complex
•Elongin C binding region destabilised
•Loss of interaction between pVHL and elonginC
•No functional VHL complex (E3 ligase)
•No degradation of HIF1a à increases protein levels
summary of Von Hippel-Lindau Syndrome