Mendelian Genetics and the Central Dogma of Biology
1/122
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
123 Terms
DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid, genetic material in organisms.
RNA
Ribonucleic acid, involved in protein synthesis.
mRNA
Messenger RNA, carries genetic information from DNA.
tRNA
Transfer RNA, brings amino acids to ribosomes.
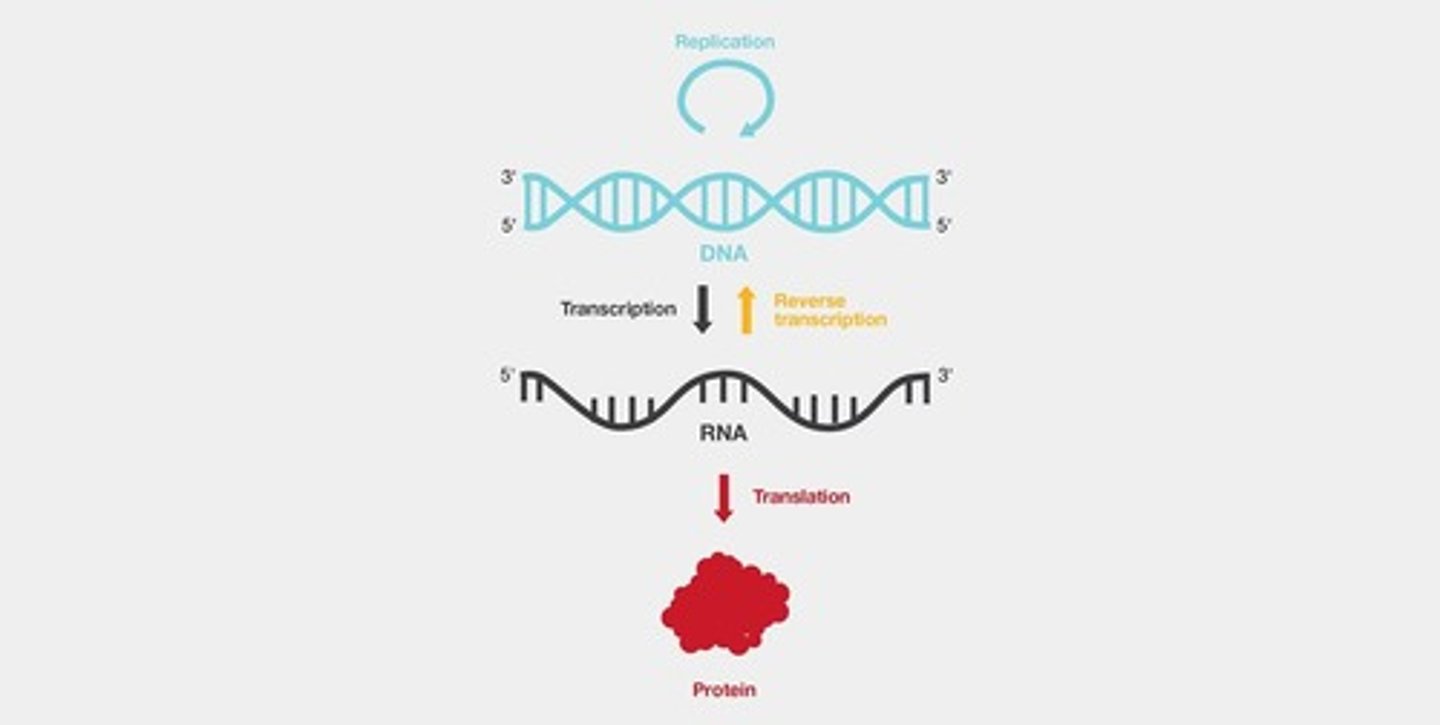
Central Dogma
Process: DNA → RNA → Protein synthesis.
Nucleotide
Building block of DNA and RNA.
Gene
Segment of DNA coding for a protein.
Chromosome
Structure containing DNA, organized into genes.
Allele
Variant form of a gene at a locus.
Phenotype
Observable traits resulting from genotype expression.
Genotype
Genetic makeup of an organism.
Mutation
Change in DNA sequence affecting genetic information.
Karyotype
Visual representation of an organism's chromosomes.
Homozygous
Having two identical alleles for a trait.
Heterozygous
Having two different alleles for a trait.
Telomere
End region of a chromosome, protects DNA.
Locus
Specific location of a gene on a chromosome.
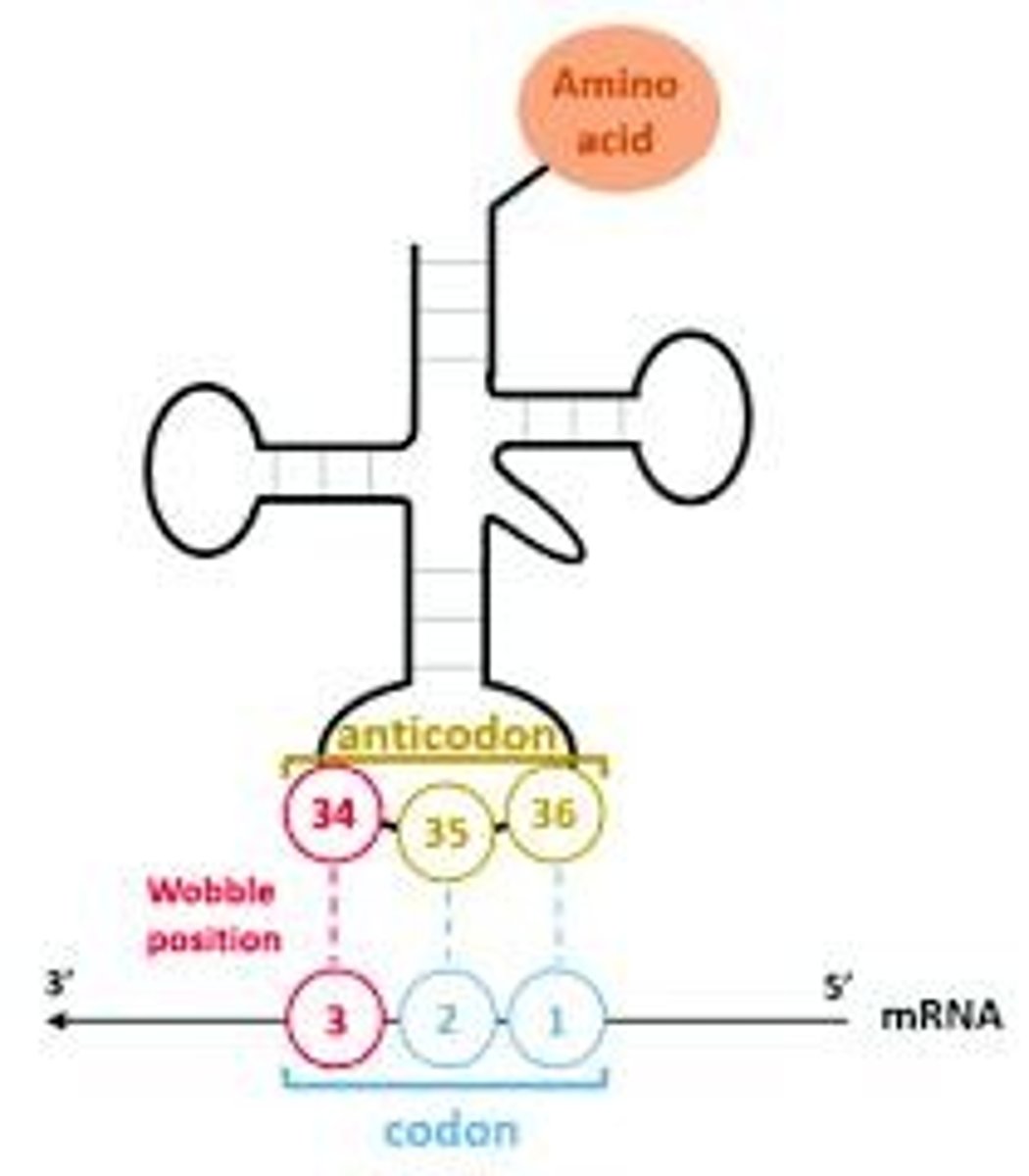
Codon
Three-nucleotide sequence coding for an amino acid.
Centromere
Region joining two sister chromatids in a chromosome.
Central Dogma
Flow of genetic information: DNA → RNA → Protein.
Reverse Transcription
RNA to DNA conversion by reverse transcriptase.
Reverse Transcriptase
Enzyme in retroviruses for reverse transcription.
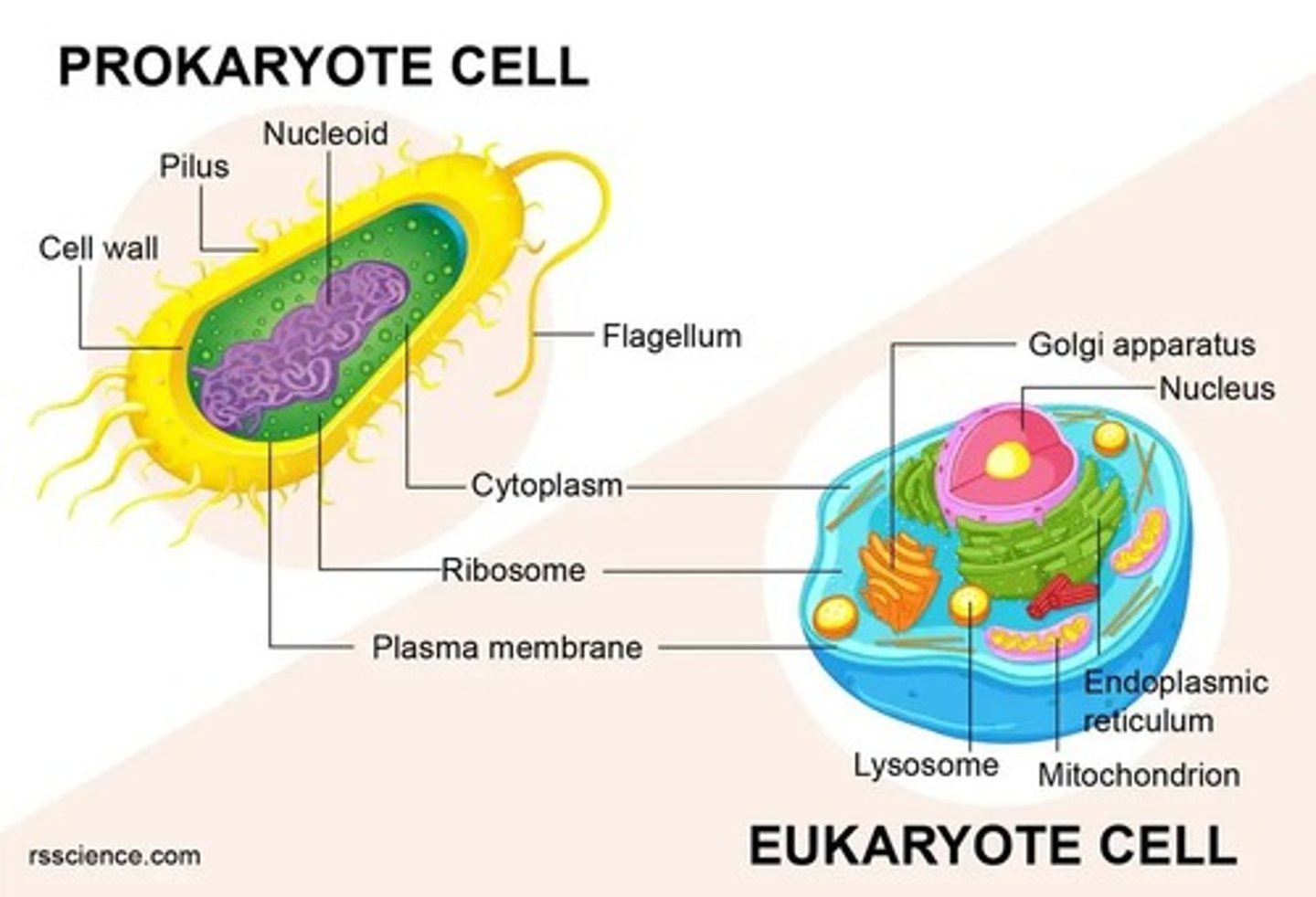
Prokaryotic Cells
Cells without a nucleus, transcription and translation simultaneous.
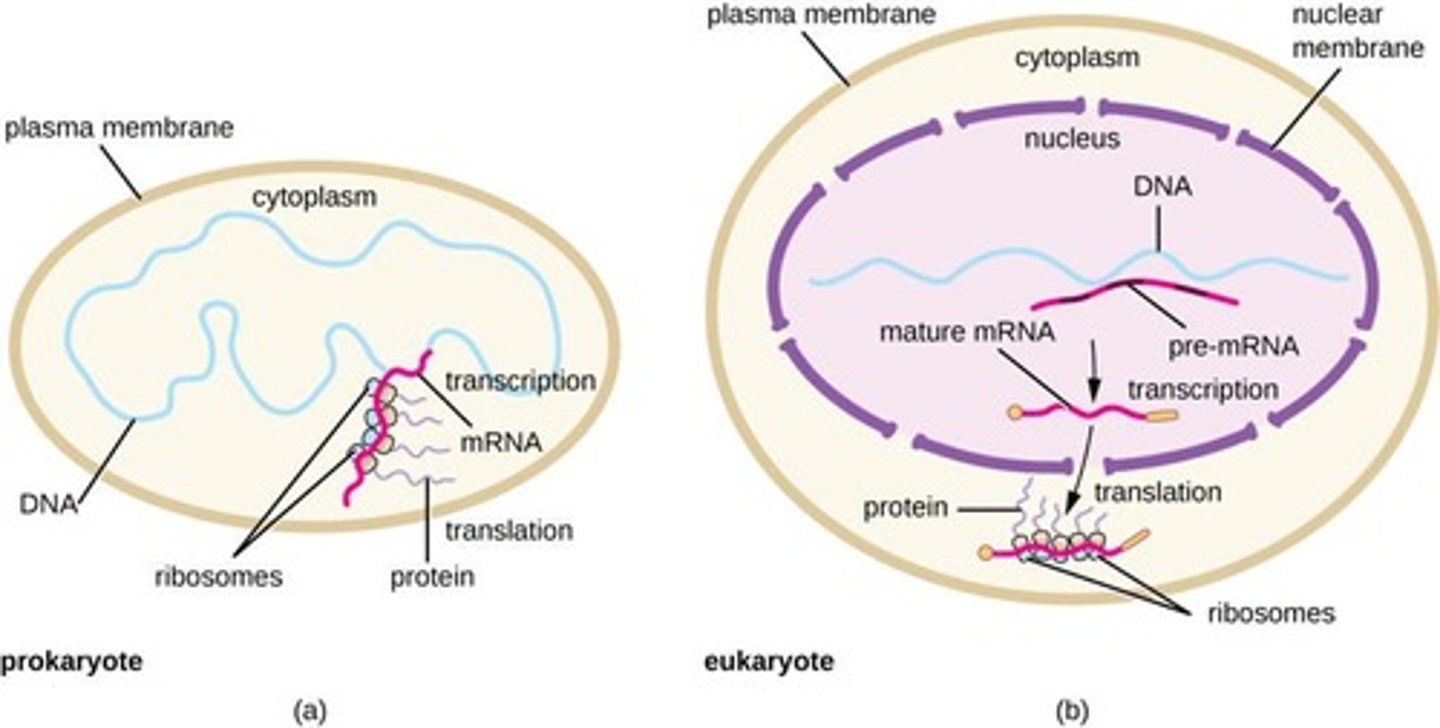
Eukaryotic Cells
Cells with a nucleus, separate transcription and translation.
Transcription
Process of synthesizing RNA from DNA template.
Translation
Process of synthesizing proteins from mRNA.
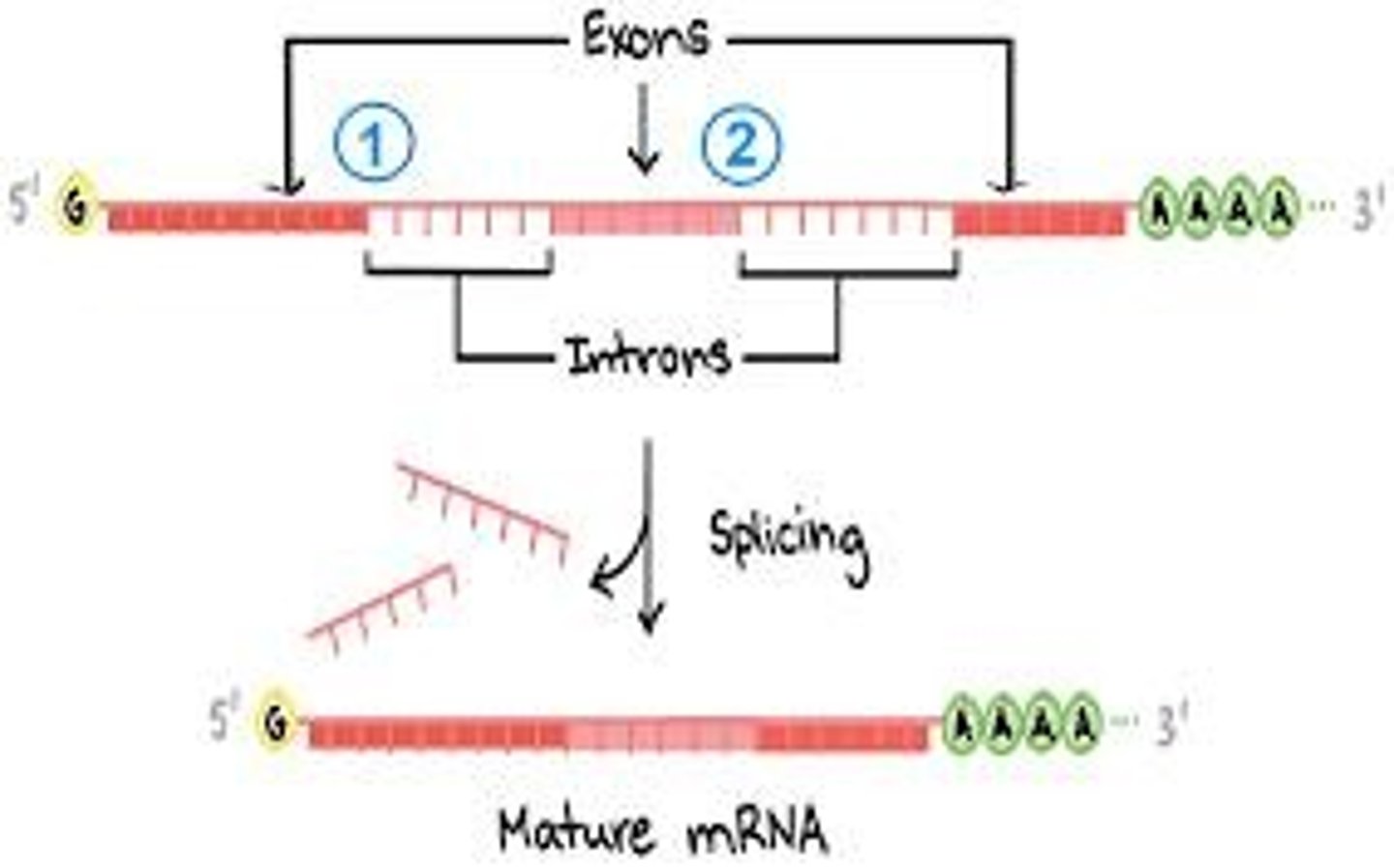
mRNA Splicing
Removal of introns and joining of exons.
Introns
Non-coding regions removed during mRNA processing.
Exons
Coding regions that exit the nucleus for translation.
DNA Polymerase
Enzyme that synthesizes new DNA strands.
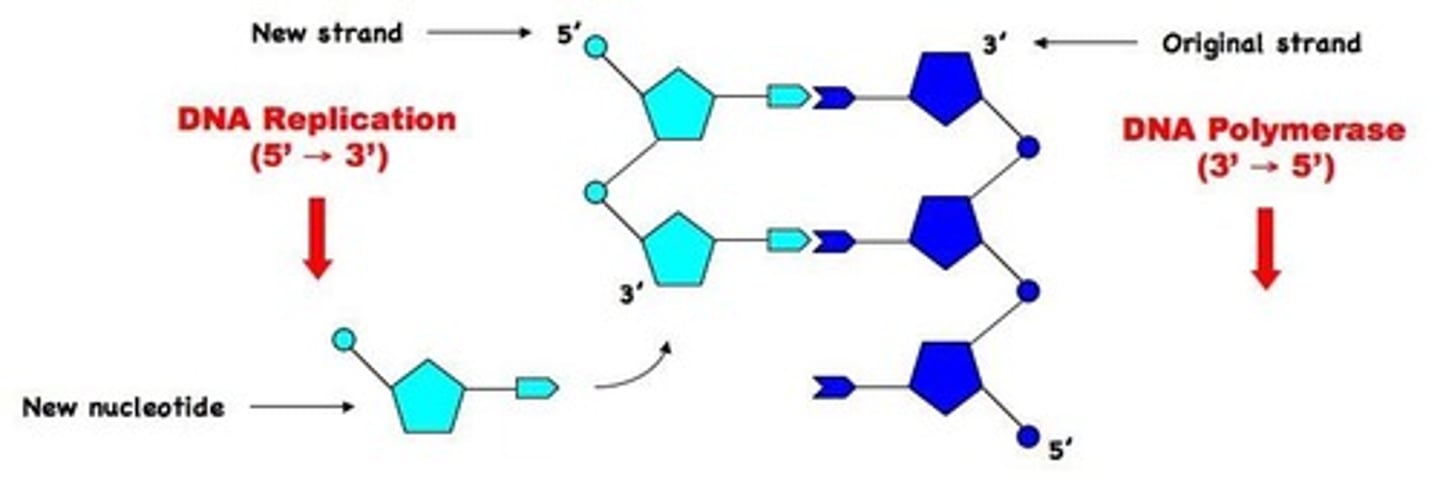
Replication Fork
Y-shaped region where DNA is replicated.
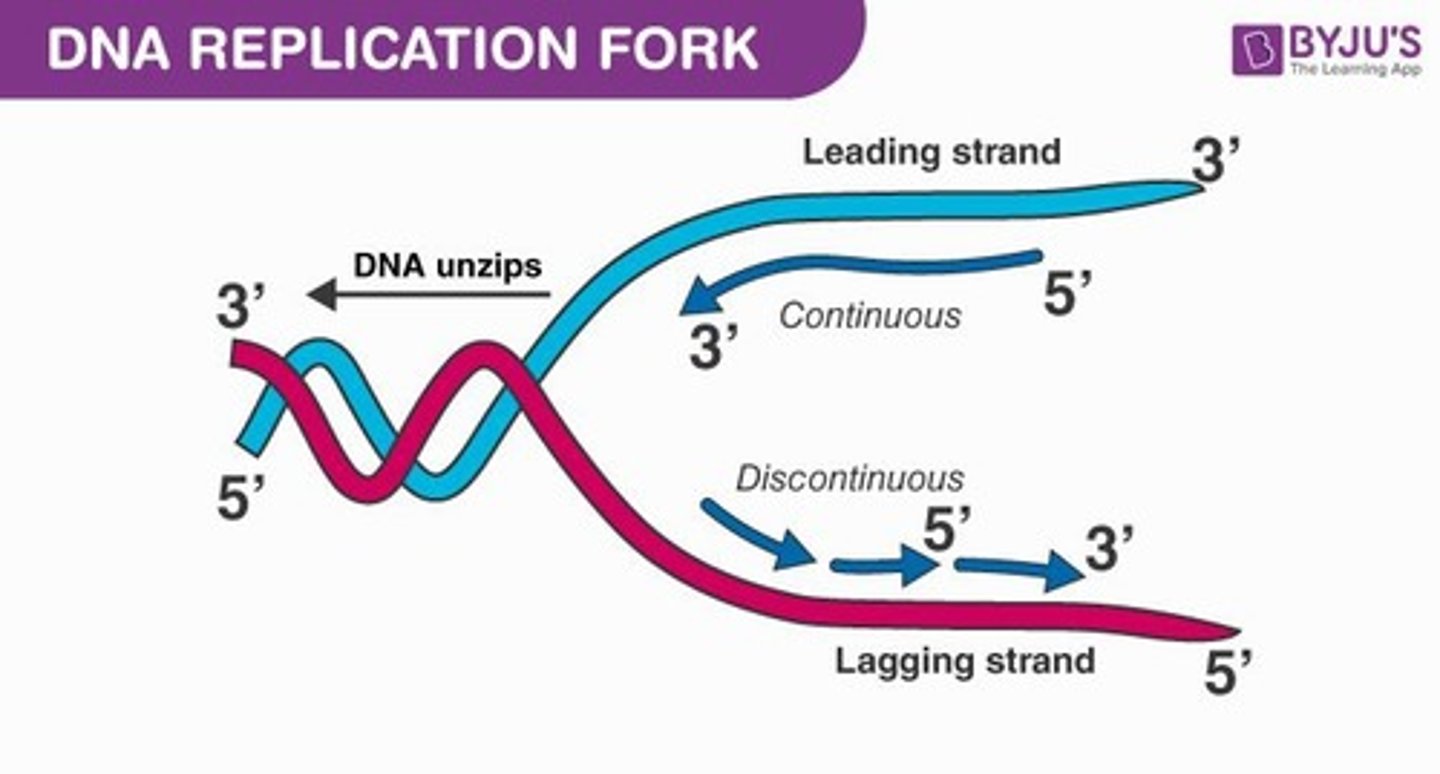
Leading Strand
Continuously synthesized DNA strand during replication.
Lagging Strand
Discontinuously synthesized DNA strand with Okazaki fragments.
Okazaki Fragments
Short DNA segments on the lagging strand.
Telomeres
Repeated DNA sequences at chromosome ends.
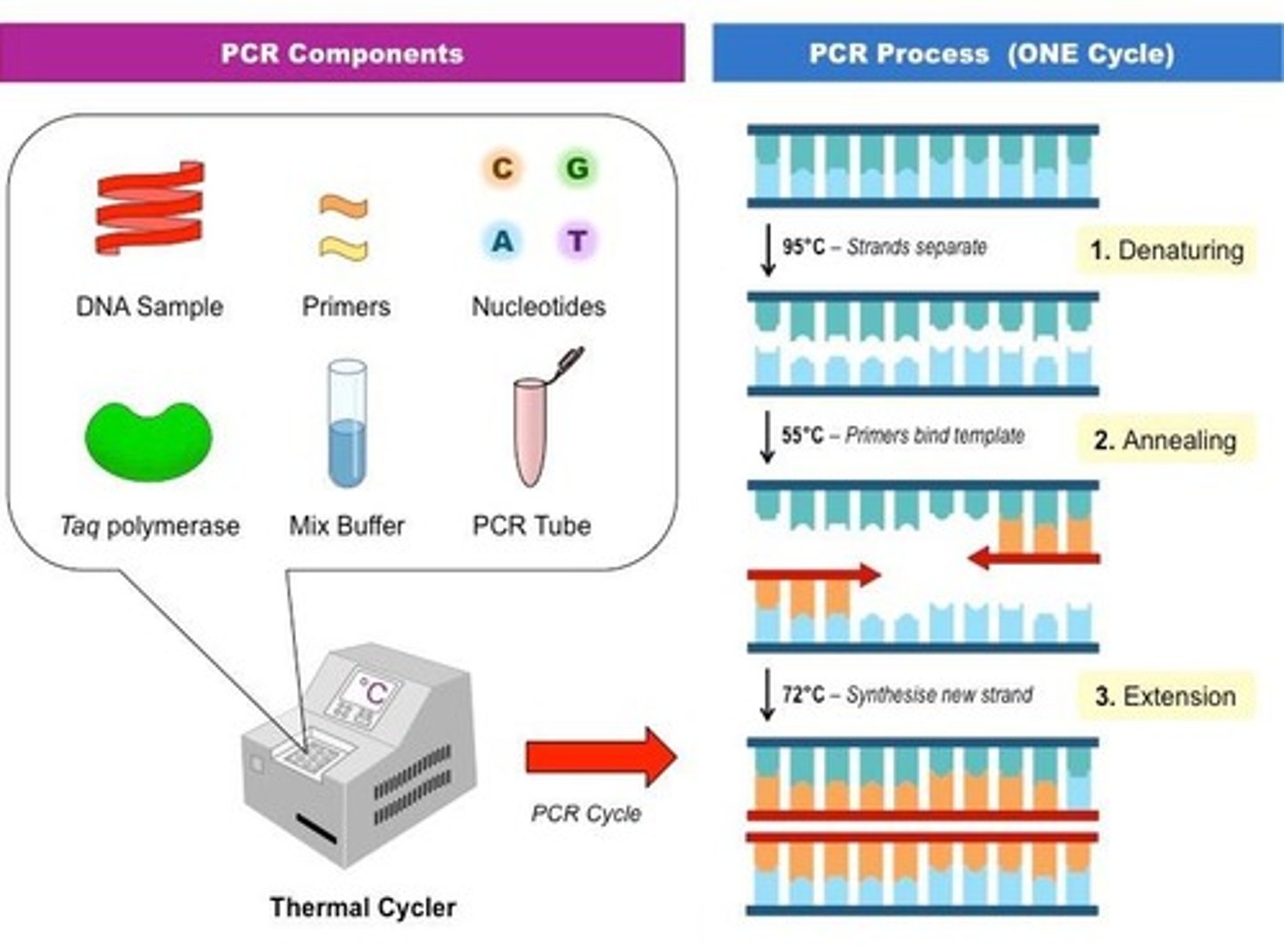
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
Technique to amplify specific DNA sequences.
RNA Processing
Modifications to RNA before translation.
Codons
Three-nucleotide sequences in mRNA coding for amino acids.
Anticodons
tRNA sequences complementary to mRNA codons.
Stop Codons
Codons signaling termination of translation.
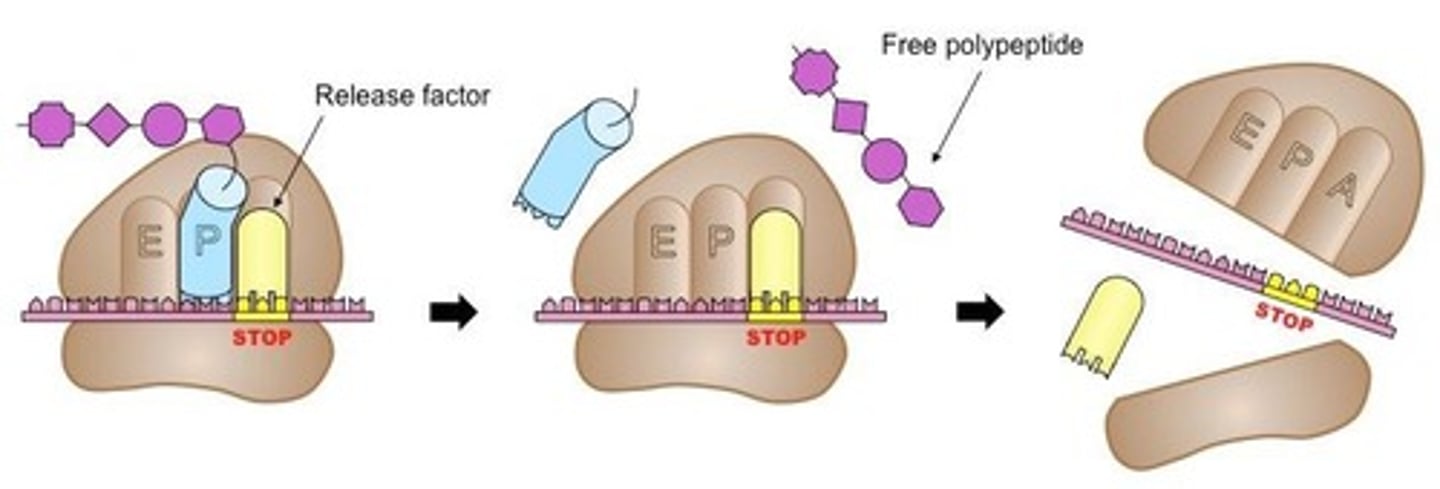
Peptide Bonds
Covalent bonds linking amino acids in proteins.
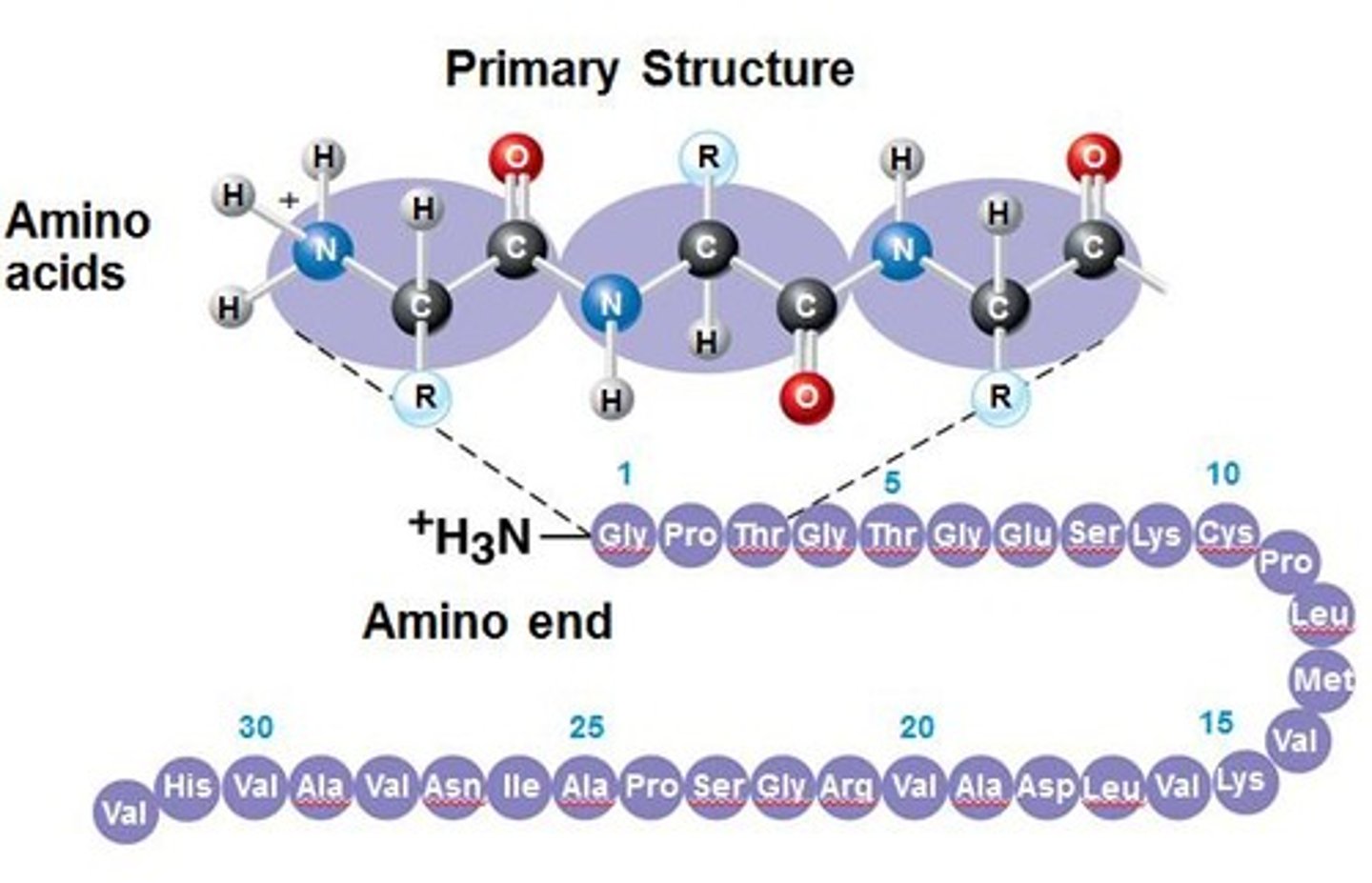
Primary Structure
Unique sequence of amino acids in a protein.
Secondary Structure
Coils and folds formed by hydrogen bonds.
Tertiary Structure
3D shape of a protein from R group interactions.
Quaternary Structure
Complex of multiple polypeptide chains.
Allosteric Proteins
Proteins that change shape to regulate activity.
Point Mutation
Change in a single nucleotide in DNA.
Silent Mutation
Nucleotide change with no effect on amino acid.
Missense Mutation
Nucleotide change resulting in a different amino acid.
Nonsense Mutation
Nucleotide change creating a premature stop codon.
Protein Modifications
Post-translational changes affecting protein function.
Gene Families
Groups of related genes in the genome.
Pseudogenes
Nonfunctional gene duplicates in the genome.
Transposons
DNA sequences that can move within the genome.
Nucleosome
Basic unit of DNA packaging with histones.
Chromatin Remodeling
Process allowing gene expression by uncoiling DNA.
Mendelian Inheritance
Patterns of inheritance based on dominant and recessive alleles.
Autosomal Dominant
Requires one copy of a dominant allele to express phenotype.
Autosomal Recessive
Requires two copies of a recessive allele to express phenotype.
Sex-Linked Inheritance
Inheritance patterns associated with X or Y chromosomes.
Genetic Anticipation
Worsening of a disorder in successive generations.
Founder Effect
Reduced genetic diversity from a small population.
Heterozygote Advantage
Benefit of carrying one copy of a recessive allele.
Dysmorphology
Study of physical features for syndrome identification.
MicroRNAs
Small non-coding RNAs regulating gene expression.
Clinical Correlation
Linking genetic findings to clinical symptoms.
Phenotype
Observable traits resulting from gene expression.
Reverse Transcription
RNA converted back to DNA by reverse transcriptase.
Prokaryotic Cells
Cells without a nucleus; transcription and translation simultaneous.
Eukaryotic Cells
Cells with a nucleus; transcription and translation separate.
Splicing
Removal of introns from mRNA, leaving exons.
mRNA
Messenger RNA; carries genetic information for protein synthesis.
tRNA
Transfer RNA; brings amino acids to ribosomes.
rRNA
Ribosomal RNA; component of ribosomes.
Replication Fork
Y-shaped region where DNA is unwound for replication.
PCR
Polymerase Chain Reaction; amplifies specific DNA sequences.
Transcription Initiation
RNA polymerase binds to promoter to start transcription.
Translation Initiation
Ribosomal subunits assemble at start codon (AUG).
Codons
Three-nucleotide sequences on mRNA coding for amino acids.
Anticodons
Three-nucleotide sequences on tRNA complementary to codons.
Stop Codons
Codons that signal termination of translation.
Primary Protein Structure
Unique sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide.
Secondary Protein Structure
Coils and folds formed by hydrogen bonds.
Tertiary Protein Structure
3D shape formed by interactions of R groups.
Quaternary Protein Structure
Complex of multiple polypeptide chains.
Allosteric Proteins
Proteins that change shape upon binding of effectors.
Point Mutation
Change in a single nucleotide in DNA sequence.
Glycosylation
Addition of carbohydrates to proteins post-translationally.
Phosphorylation
Addition of phosphate groups to proteins for regulation.
Autosomal Dominant
One copy of an allele causes phenotype expression.
Autosomal Recessive
Two copies of an allele required for phenotype.
X-linked Inheritance
Traits linked to genes on the X chromosome.
Founder Effect
Reduced genetic diversity from a small founding population.
Gene Family
Group of related genes within an organism's genome.
Pseudogenes
Nonfunctional gene remnants; may arise from mutations.
Transposons
DNA sequences that can change positions in the genome.
Chromatin Remodeling
Modifications allowing access to DNA for transcription.
Dysmorphology
Study of congenital abnormalities and their patterns.
Gene Regulation
Mechanisms controlling gene expression levels.
Environmental Impact
External factors influencing gene expression and phenotype.