Bio Invaders Midterm
1/100
Earn XP
Description and Tags
PCB2441 - UF Fall 2023 [scored 89.25% on exam]
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
101 Terms
What are invasive species?
non-native to the ecosystem and whose introduction (likely spreads rapidly) causes/is likely to cause economic, environmental, or human health harm
Where did the term “invasive species” come from?
Ecology of Invasion by Animals and Plants
Who coined the term “invasive species”
Charles Elton
When did the term “invasive species” start?
1958
How old is the study of invasive species?
relatively young
Are all non-native species invasive?
no
What is water hyacinth classified as?
non-native and invasive
What is striped bass classified as?
native to NE America but non-native to SE America
What is maize/corn classified as?
non-native but non-invasive
What are Carolina, Cattail, Eastern Red Cedar classified as?
native and invasive
How many species are invasive globally?
4-44%
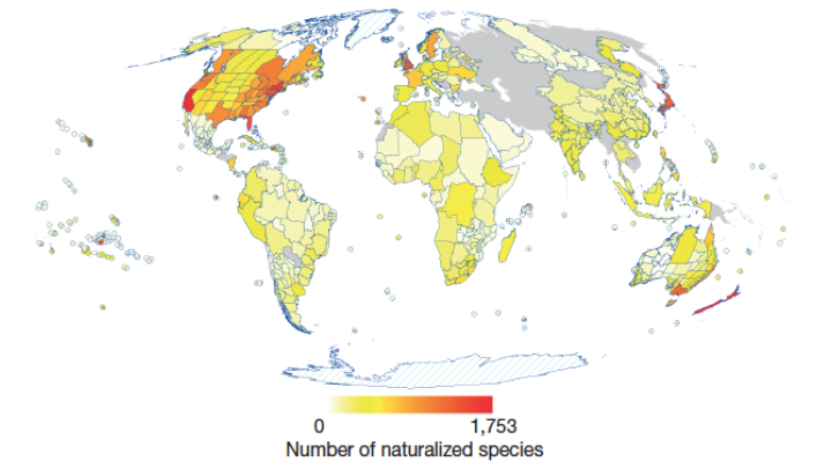
Why is there a large discrepancy in invasive ecology knowledge?
Most studies are done in first-world countries
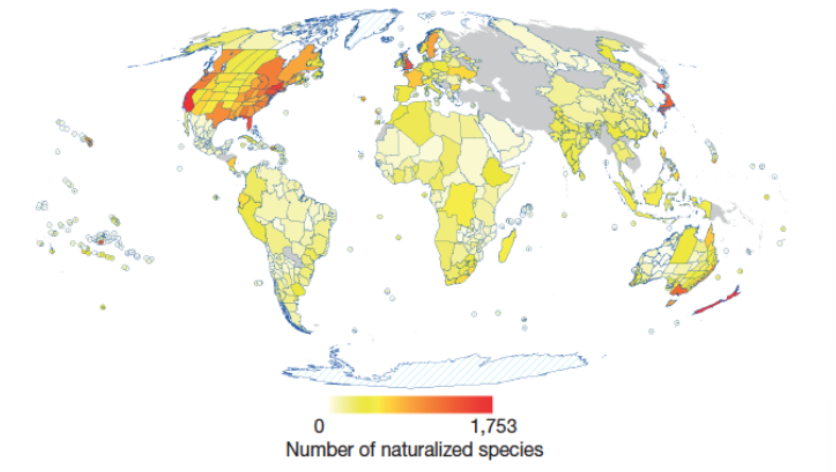
How many non-native species are in the US?
50,000
Are all non-native species accidental?
NO - some species are cultivated and domesticated
What are some other terms for invasive species?
alien species, noxious weed, exotic, non-native, non-indigenous, introduced species, naturalized
Are other terms for invasive species synonyms?
NO - they are related terms
What does the Blackburn Model present?
the barriers and stages needed to overcome for successful invasions AND the types of management needed for each stage
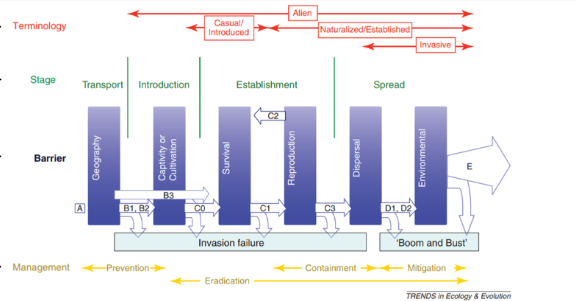
What is the first stage of the Blackburn Model?
transport and introduction
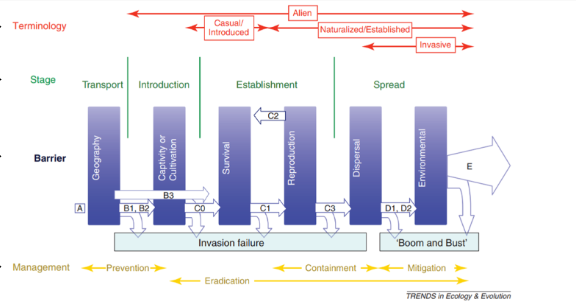
How are invasive species introduced and transported?
1) usually by humans
2) can be intentional or unintentional
3) species escapes captivation
What is the second stage of the Blackburn Model?
establishment
Why do some species fail to establish?
factors associated with the species (biotic factors) or location (abiotic factors)
What are some biotic factors that affect the establishment of a species?
species reproduction, predators, competition, disesases
What are some abiotic factors that affect the establishment of a species?
location, climate
What is the third stage in the Blackburn Model?
spread
What are some factors that affect the spread of a species?
limiting abiotic factors OR adaptation to spread farther
What is the fourth stage of the Blackburn Model?
impact
What is considered a successful impact for invasive species?
species population dominates
What is impacted by invasive speces?
community and ecosystem
What are the 4 types of management?
1) prevention
2) eradication
3) containment
4) control/management
When is prevention most impactful?
prior to invasion
What is ecological biodiversity?
variation in ecosystems in a region or globally
What is species biodiversity?
variation in species in an area or region
What is genetic biodiversity?
variation in genetics within a species
What is perpetual change?
all species and continuously changing
What are the rules of nature?
combined influences of physical and biological limiting factors action upon organisms
What controls evolution/natural selection?
nature, its NOT goal-oriented or anticipatory
What are limiting factors?
any biological or physical factors which regulate the welfare of an organism
What are some types of limiting factors?
disease, competition, predation, environmental change
What is evolution?
gene pool of the population changes over time
How long does evolution take?
usually over a long period of time
What is the first step of evolution?
mutation
What does mutation do to a species?
leads to changes in the phenotype
What is the second step of evolution?
genetic variation through mutation
What does genetic variation do to a species?
changes the genotype
What is the third step of evolution?
natural selection acts upon the phenotype
What is the fourth step evolution?
individuals more suited to the environment produce more offspring
When does speciation occur?
if geographic and reproductive isolation mechanisms exist
Who is affected by evolution?
populations NOT individuals
What are the 3 types of natural selection?
1) directional
2) stabilizing
3) disrupting/diversifying
What is directional natural selection?
when allele frequencies shirt to favor individuals at one extreme of the normal range
What happens during directional natural selection?
one side of the distribution reproduces more than the other
What is the result of directional natural selection?
population looks different ( → → | )
What is stabilizing natural selection?
when a population favors individuals with an average genetic makeup
What happens during stabilizing natural selection?
only the middle of the distribution reproduces
What is the result of stabilizing natural selection?
the population looks more similar ( → | ← )
What is disrupting/diversifying natural selection?
when environmental conditions favor two groups at the same time
What is the result of disruption/diversifying natural selection?
population splits into two groups ( | ← → | )
What is speciation?
two species arise from one
Why does speciation occur?
there is reproductive isolation
What the 4 types of reproductive isolation?
1) geographic
2) temporal
3) behavioral
4) anatomical
What are the 2 types of speciation?
1) allopatric
2) sympatric
What is allopatric speciation?
members become so different that they can no longer interbreed
When does allopatric speciation occur?
when two groups of the same species are geographically isolated
Why does allopatric speciation occur?
allele frequencies change over time
Why does sympatric speciation occur?
behavioral barrier, hybridization, or polyploidy
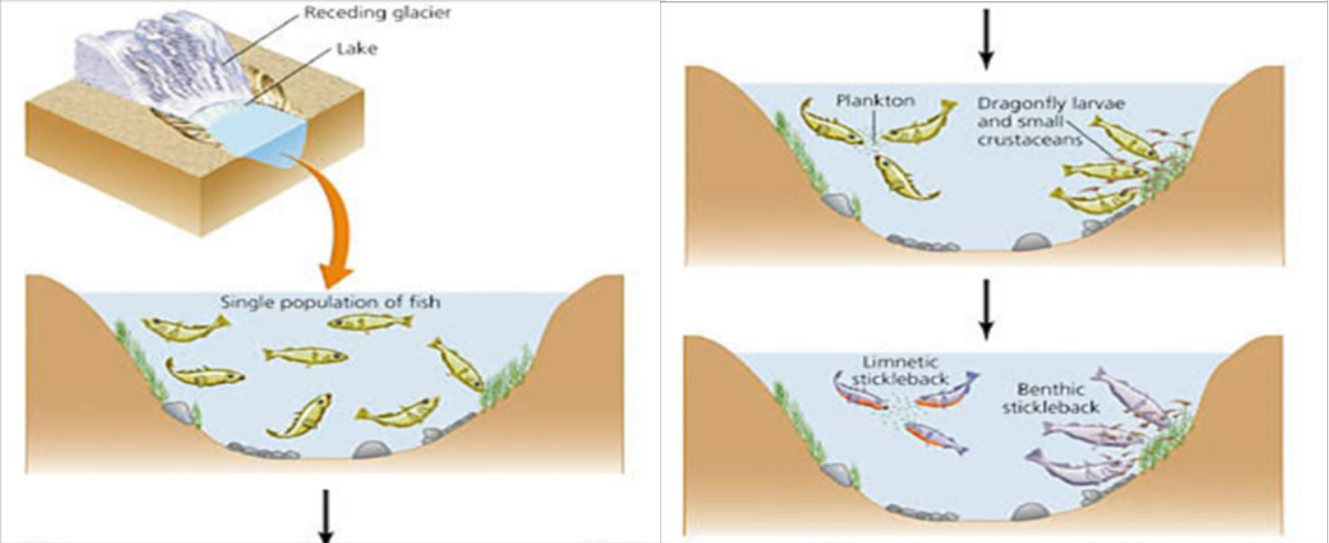
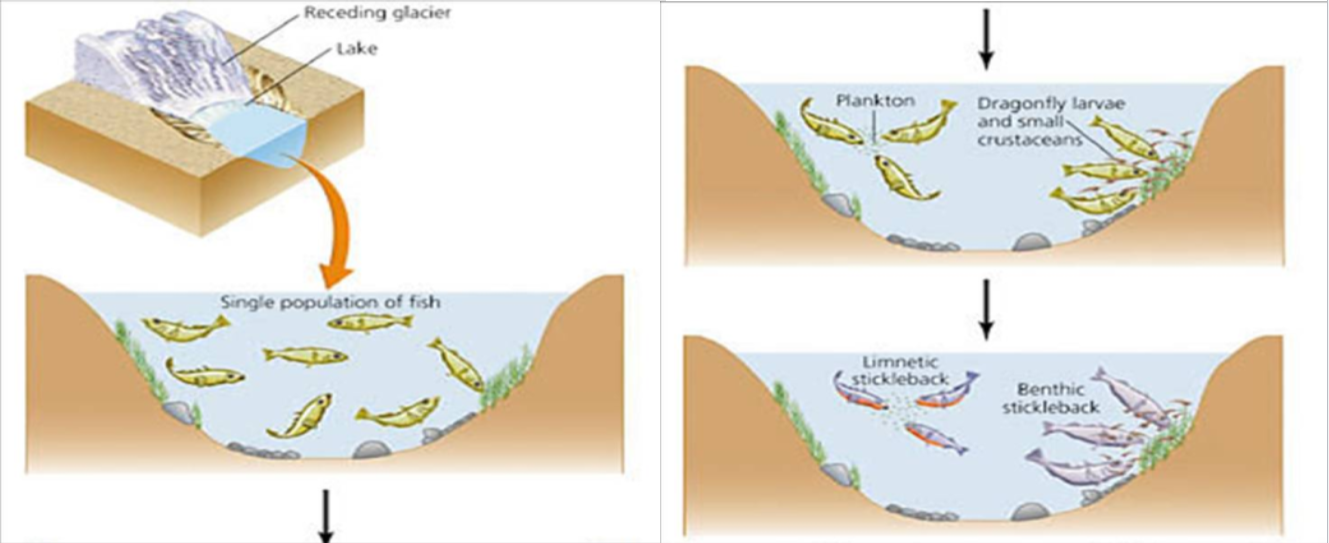
When does sympatric species occur?
population evolves with overlapping ranges
Why should we preserve biodiversity?
genetics, bio-control agents, food sources, natural products, environmental services, enjoyment, scientific interest, self-perpetuation, future/potential uses
What is an endemic species?
those that occur in a particular area or region but nowhere else?
What are the 4 scales of isolation?
1) macroscale
2) mesoscale
3) microscale
4) bio-scale
What is macroscale isolation?
isolation from different continents
What is the result of macroscale isolation?
mammals can not move freely and compete with similar species, preventing major extinction
What is mesoscale isolation?
islands or habitats that function as islands
What is microscale isolation?
semi-isolation habitats within an area
What is bio-scale isolatino?
isolated areas of the same organism
Why are islands more vulnerable to invasions?
1) Evolved in isolation from competitors, predators, and pathogens
2) Highly disturbed by human use
3) Humans discount the value of native species and introduce species from other areas
4) Initial invasion can enable or facilitate additional invasions (invasion meltdown)
Why are continents less vulnerable to invasions?
1) Species on continents are more resilient to disease and predation
2) If an invasion causes a species extinction in one area, it is likely that the species has persisted elsewhere on the continent
What are some factors to the distribution of biodiversity?
1) old habitats = rich habitats
2) diversity is self-reinforcing
3) isolated places are more likely to have unique species
4) divided landscapes create more species
What is convergent evolution?
when a population/species is in isolation and can independently evolve similar traits
What is happening to the species introduction rateto Hawaii?
increasing quickly (1 species every few months v. 1 species every 5-7k years)
What has had the greatest impact on native species?
global invasion of humans
What did the global invasion of humans cause?
megafauna extinctions
Why was Africa not affected by megafauna extinctions?
the coevolution of humans and African species prepared them for threats
What are the 3 types of transport technology?
1) speed of travel
2) cargo capacity
3) conditions during transport
What did multiple-sail ships change about transport?
caused regular trips across the Atlantic
What 3 types of introductions did Atlantic trips cause?
1) intentional agricultural/livestock species
2) unintentional hitchhikers (insects, pathogens, rats)
3) unintentional ballast (sources of weeds, insects)
What was the net flow of species introduction from Atlantic trips?
Europe → Americas
What are 5 examples of mechanization that altered transport?
1) large boats
2) railroads
3) containerization
4) air travel
5) Panama Canal
How did large boats affect transport?
haul more, haul faster, travel upstream, affordable transport, haul raw goods → survival for sensitive species
What risk does containerization pose for introductions?
lack of inspection
What does air travel change for introductions?
increased speed of travel
Why is invasion happening more than its prevention?
1) technology/globalization increased rapidly
2) policies/funding has not kept up
What are the 7 traits of invasive animals?
1) fast growth rate
2) high fecundity (offspring)
3) reproductively mature quickly
4) few predators or diseases
5) tolerate a wide range of conditions
6) broad diet
7) high competitive
What are the 8 traits of invasive plants?
1) fast growth rate
2) high fecundity (seeds)
3) few predators/diseases
4) thrive under disturbed conditions
5) habitat generalists
6) extended phenology (photosynthetic period)
7) some exhibit allelopathy
8) alter soil conditions
What are the 5 mechanisms of invasions?
1) propagule pressure
2) abiotic factors
3) biotic factors
4) human modification
5) interactions between P, A, and B
How is propagule pressure measured?
size x frequency
What is propagule size?
number of individuals released at any one time
What is the frequency of propagule introductions?
how many introductions
What is important for invasion success?
high quality and propagule pressure
What are 3 reasons why high propagule pressure positively affects invasion success?
1) increases genetic diversity
2) increases the probability that propagules will encounter favorable environmental
3) results in seeds swamping
What are 2 hypothesizes for propagule pressure?
1) null hypothesis - simplest explanation
2) acts as a prerequisite for invasions