BIOL 111 Lab 7: seed plants
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
Seed plants
gymnosperms and angiosperms
- have vasculaqra tissue (xylem & phloem)
- most productive/successful bc of seeds and pollen
Gymnosperms
"Naked seeds" - do not have an ovary
- not protected by fruit tissue
-do not produce flowers
Angiosperms
"Covered seeds" - do have an ovary (covering) that becomes fruit
Advantage of pollen and seeds
- remove the need for water for reproduction (fertilization)
- seeds provide protective covering (survival harsh environments)
- seeds store food (boost growth following germination)
- can disperse widely and survive in new areas
Homosporous plants
Mosses and ferns
- male and female spores appear the same
Heterosporous plants
Gymnosperms and angiosperms
-male and female spores are different
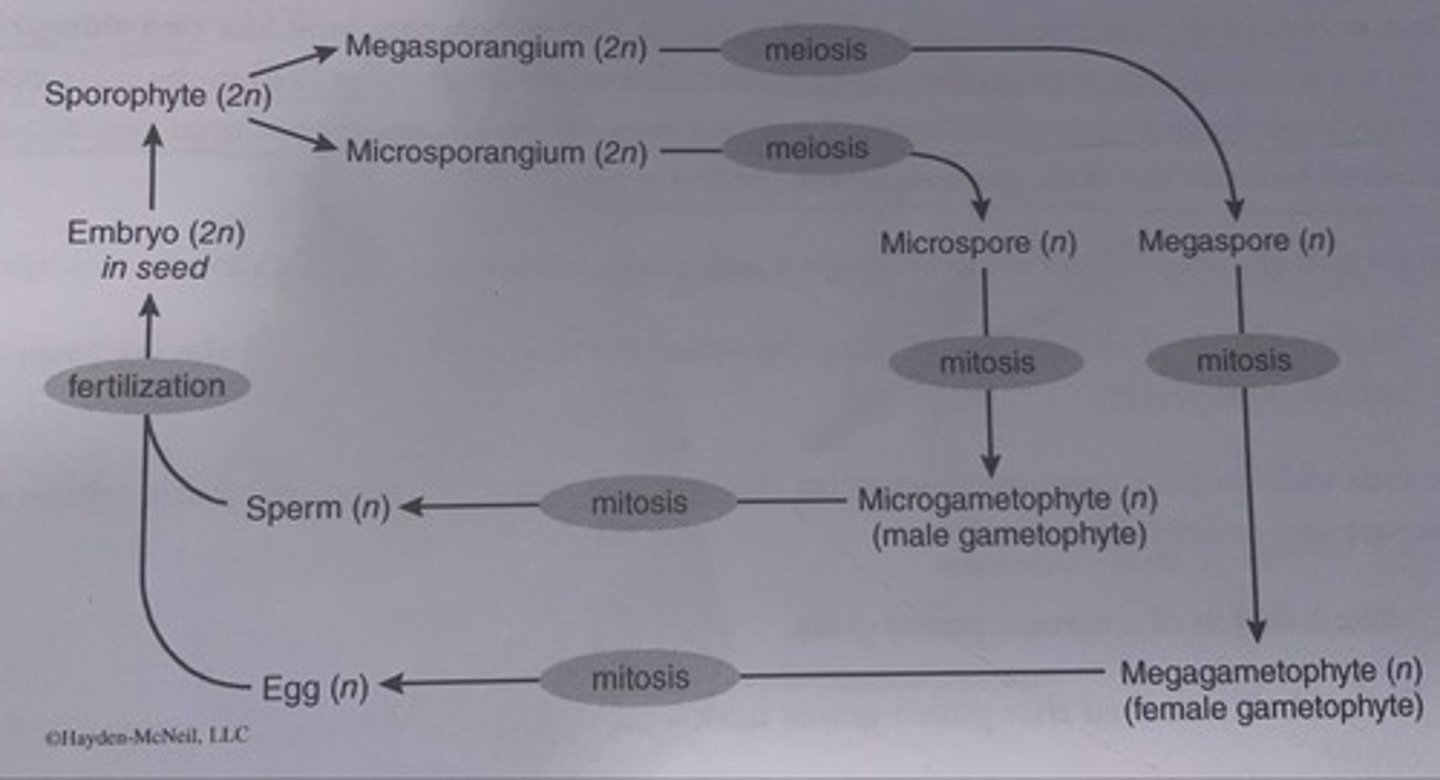
Microspores
Produced in microsporangia (develop into male gametophyte= pollen)
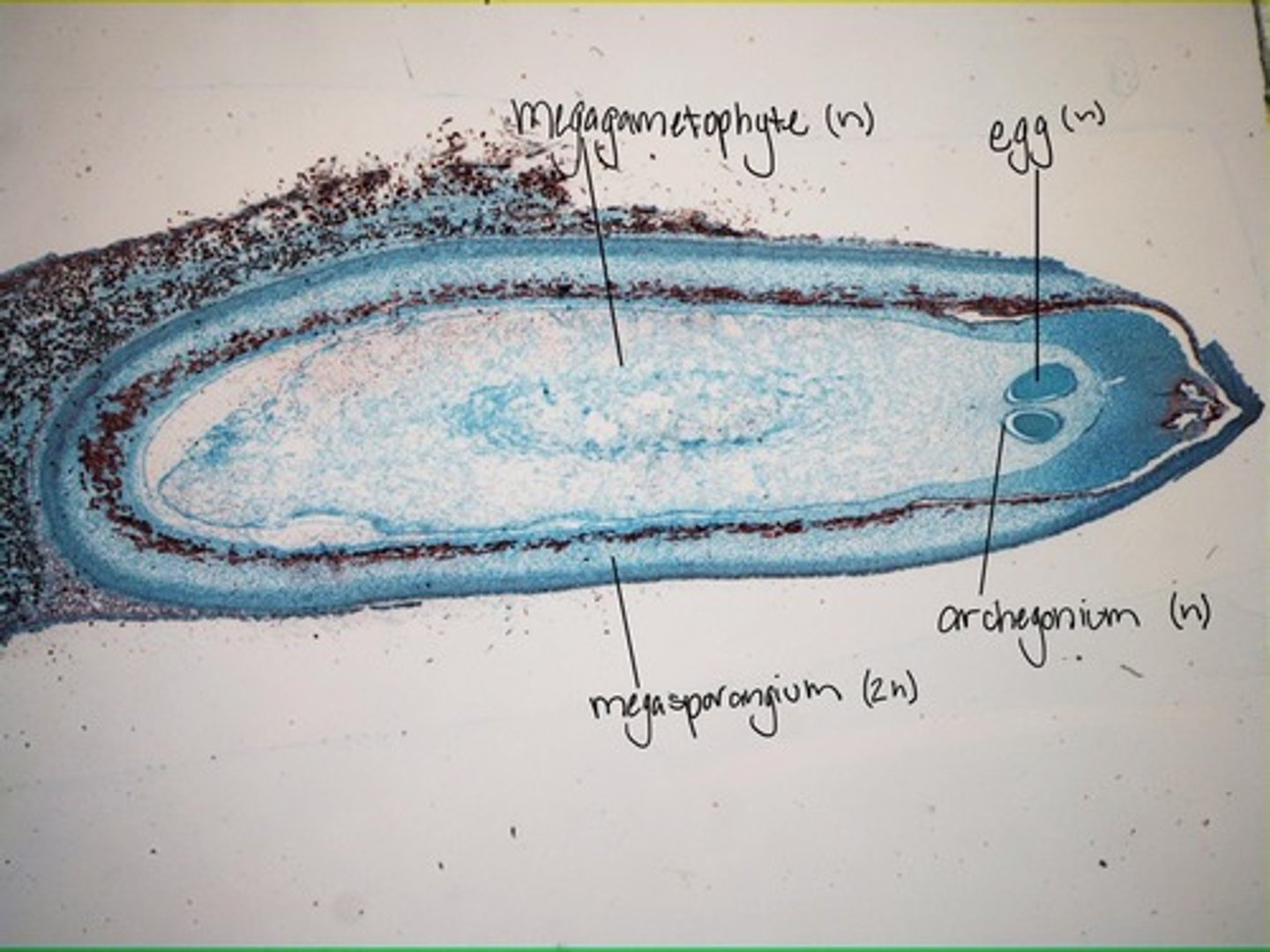
Megaspores
Produced in megasporangia (develop into female gametophyte which releasing in megasporangium)
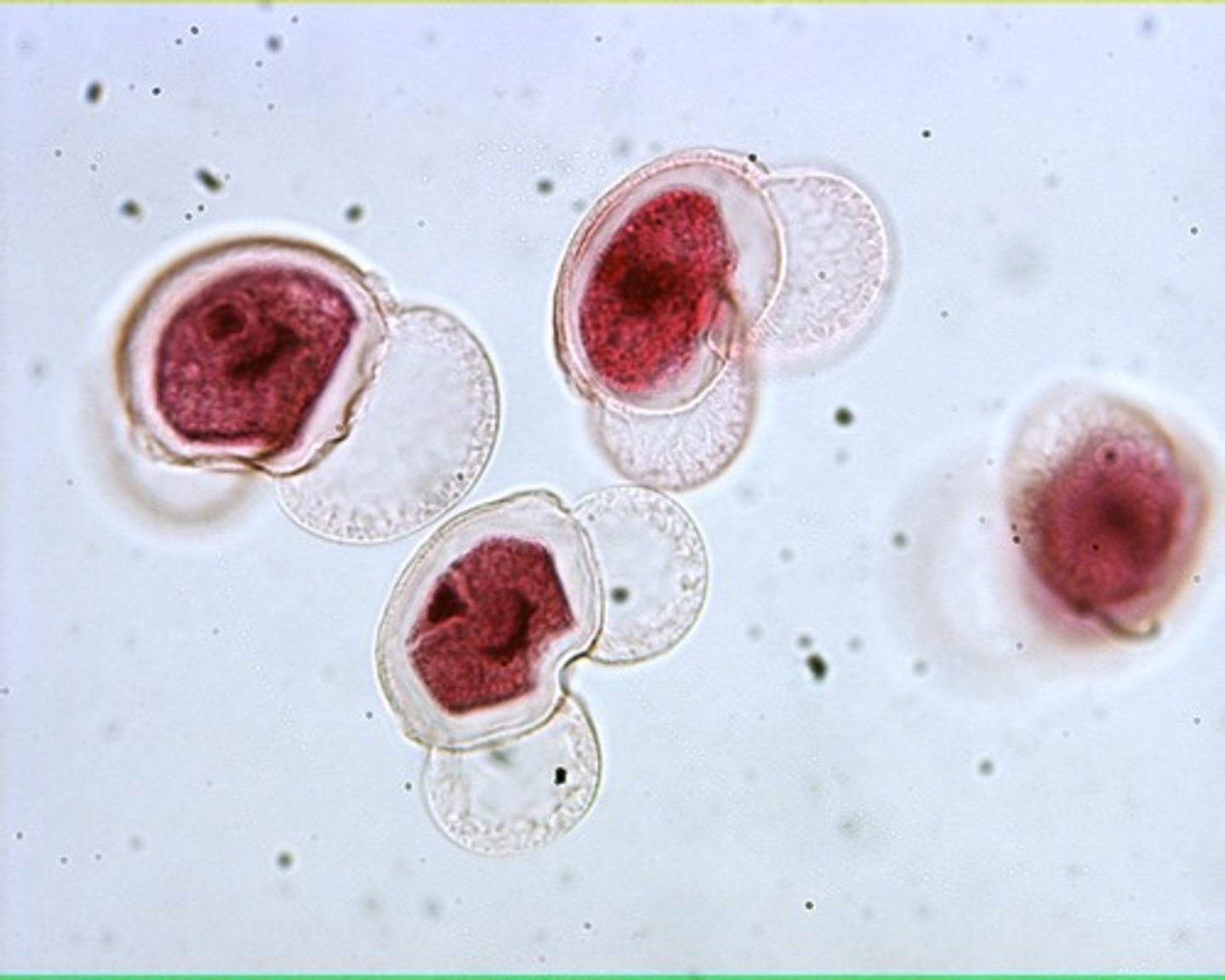
Pollen grain
- microgametophyte (produce sperm)
-contains 2-4 cells
- highly reduced compared to other gametophytes
- dos not need water for fertilization
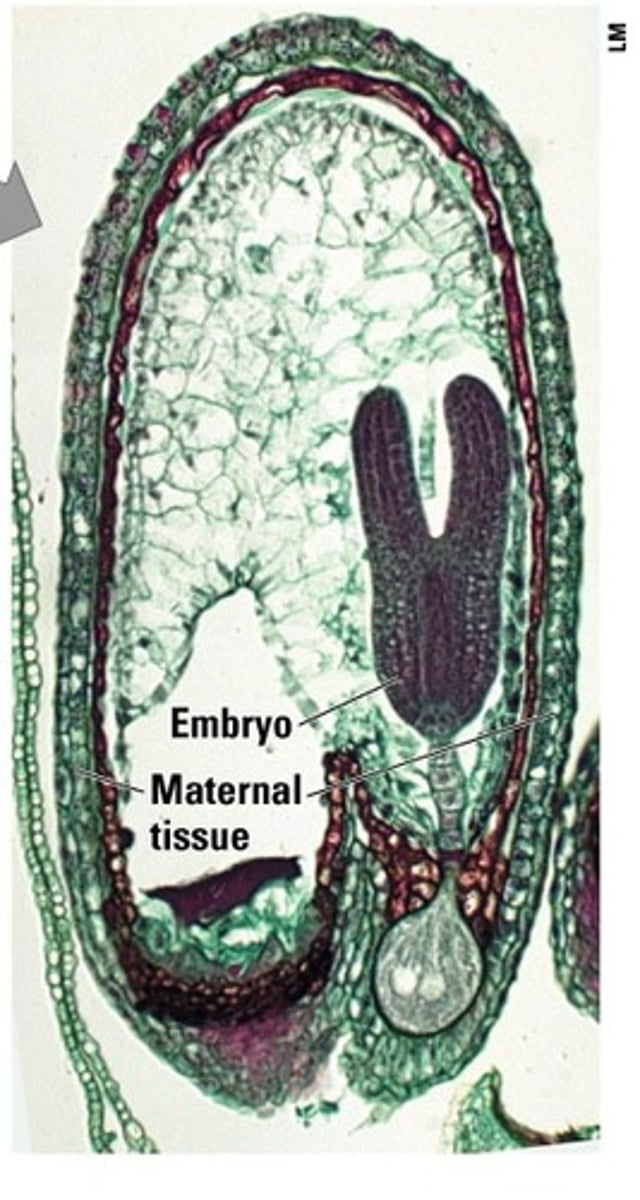
Seeds
Seed coat- gives enhanced survivability
Food source - (endosperm in angiosperms) tissue from parent (gameophyte) when developing into an embryo
Tissue generations:
1. Sporophyte (seed coat)
2. Gametophyte (food source)
3. New sporophyte (embryo)
Primary growth
growth in length

Secondary growth
pattern of plant growth in which stems increase in width

Female cones
A.k.a ovulate/seed cones