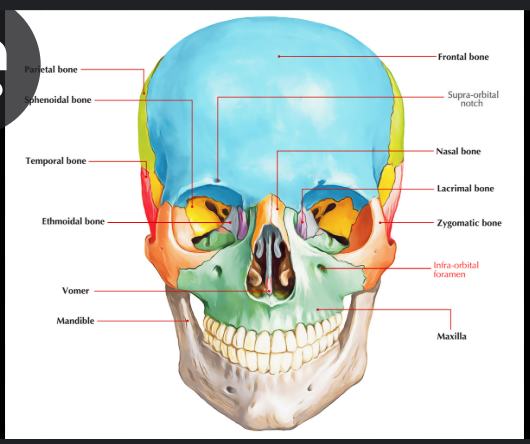
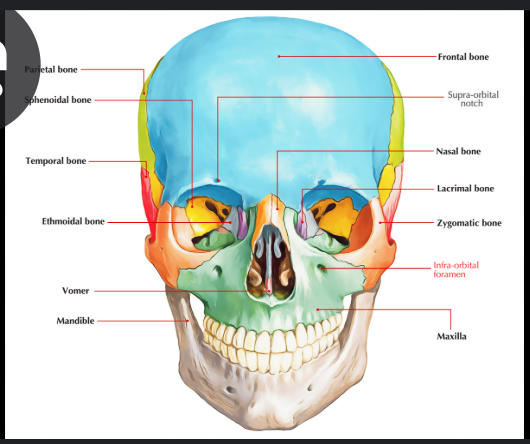
Maxilla and ethmoid bone
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
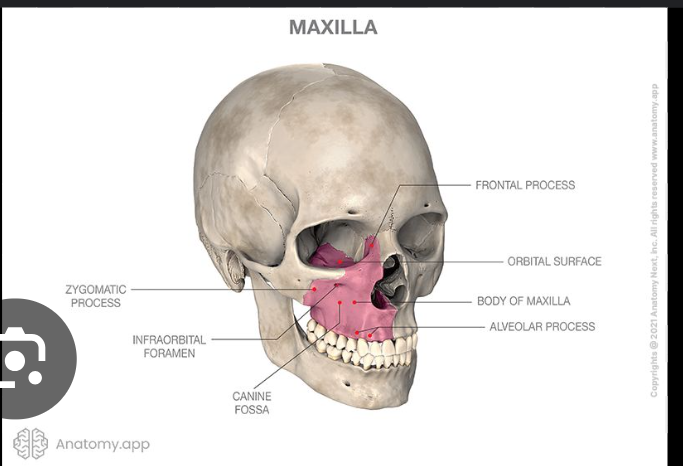
Maxilla
The maxilla is a paired bone.
It is made up from 2 symmetrical bones.
Each bone consists of a body and 4 processes which includes:
Zygomatic
Frontal
Alveolar
Palatine.
The maxilla articulates with 9 bones
Two bones of the cranium: frontal and ethmoid.
Seven of the face: the nasal, zygomatic, lacrimal, inferior nasal concha, palatine, vomer, and the adjacent maxillary bone.
The maxilla assists in forming the boundaries of three cavities:
Roof of the mouth
The floor and lateral wall of the nasal cavity
The roof of the mouth
The maxilla participates in the formation of 2 fossae:
Infratemporal fossa
Pterygopalatine fossa.
Two fissures:
The inferior orbital fissure.
Pterygomaxillary fissure.
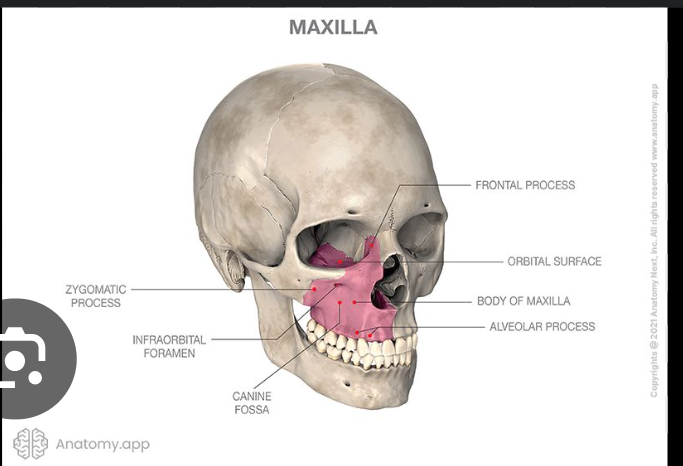
Body of maxilla
It has 4 surfaces:
Anterior surface
Posterior surface/infratemporal surface
Superior/orbital surface
Medial nasal surface
Anterior surface
Alveolar yokes
Incisive fossa
Canine fossa
Infraorbital foramen
Anterior nasal spine
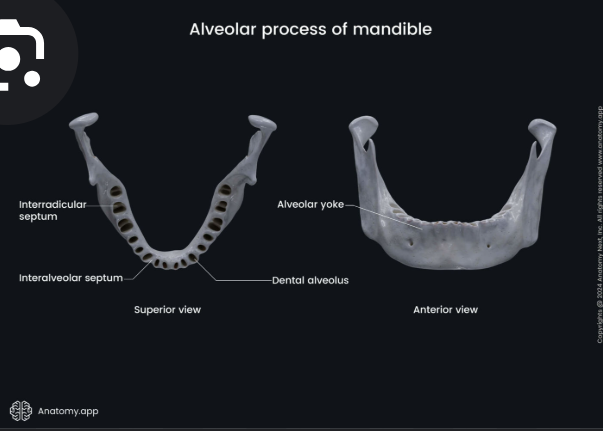
Alveolar yoke
Series of eminences corresponding to the positions of the roots of the teeth.
Incisive fossa
Just above the alveolar yokes of the incisor teeth.
Canine fossa
Lateral to incisive fossa, there is another depression, the canine fossa.
Infraorbital foramen
the end of the infraorbital canal
Anterior nasal spine
At the base of the nasal cavity
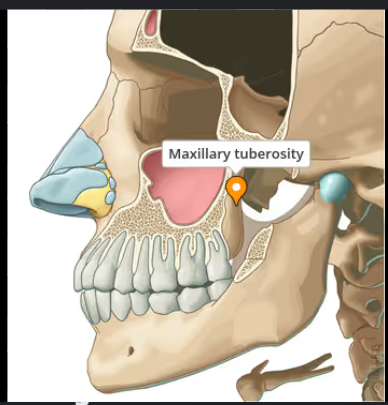
Posterior surface/infratemporal surface:
Maxillary tuberosity
Posterior superior alveolar foramina
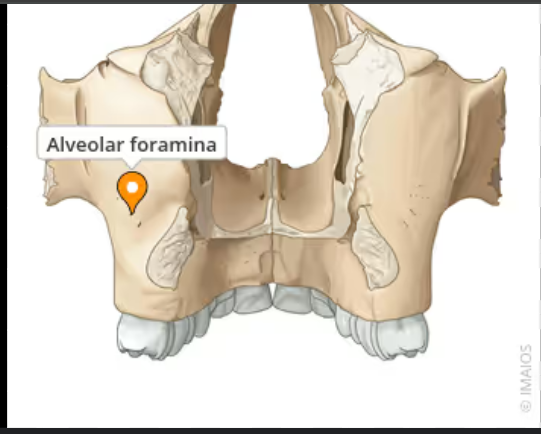
Posterior superior alveolar foramina
Content: Posterior superior alveolar nerve, vein and artery
Superior orbital surface
This forms the floor of the orbit:
Lacrimal notch- articulates with the lacrimal bone
Infraorbital groove, canal and foramen
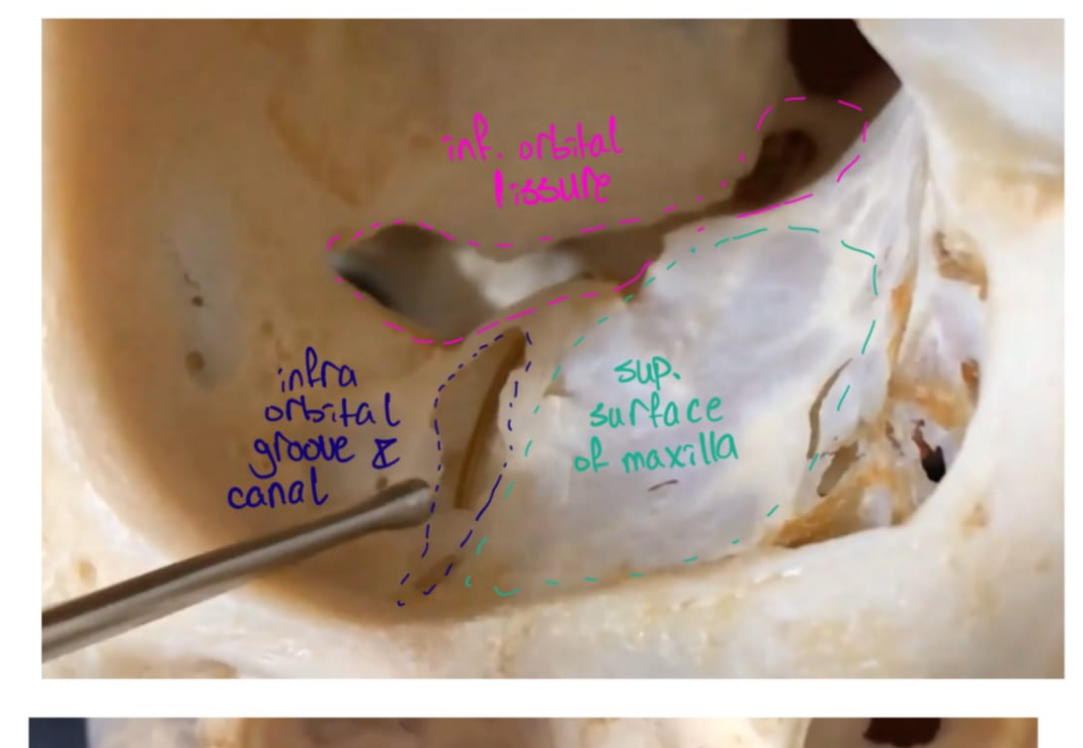
Infraorbital groove, canal and foramen
The infraorbital groove ends in a canal (infraorbital canal) for the passage of the infraorbotal vessels and nerve.
The infraorbital foramen is below the margin of the orbit.
Medial/nasal surface
This forms the lateral wall of the nasal cavity.
Opening of the maxillary sinus.
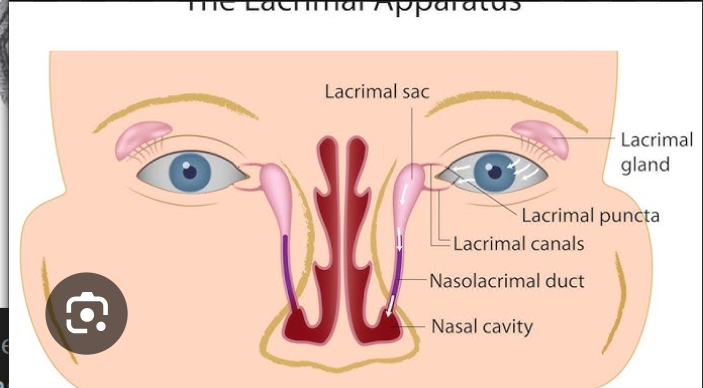
Nasolacrimal canal
Conchal crest.
Broken air cells
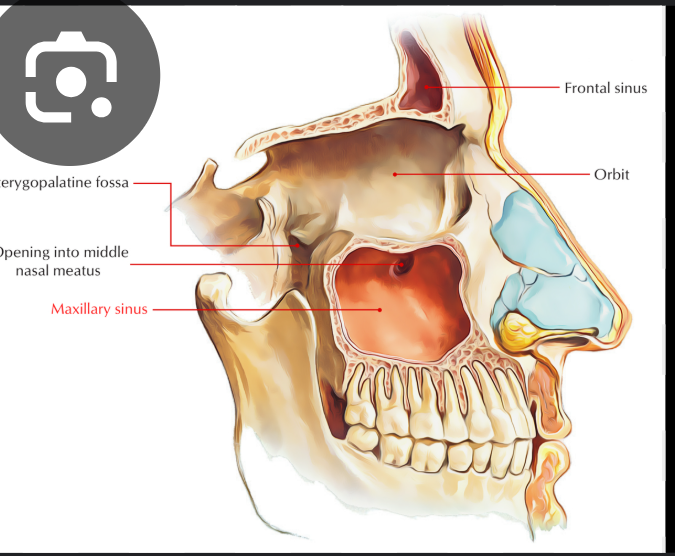
Opening of the maxillary sinus
The maxillary sinus opens into the nasal cavity through the maxillary ostium, also known as the maxillary hiatus or maxillary sinus ostium. This opening is located superoposteriorly on the lateral nasal wall
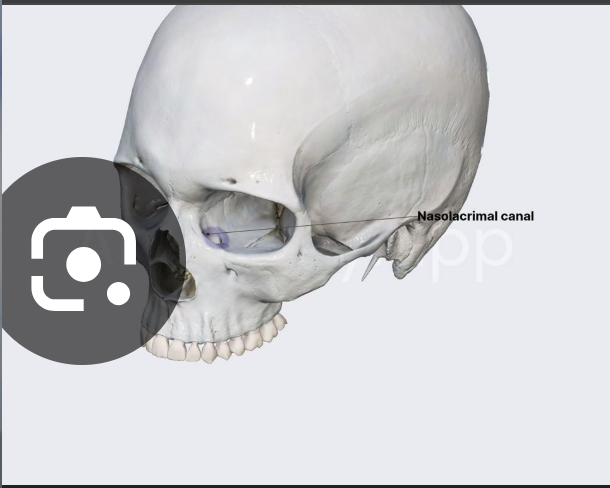
Nasolacrimal canal
Content: Nasolacrimal duct
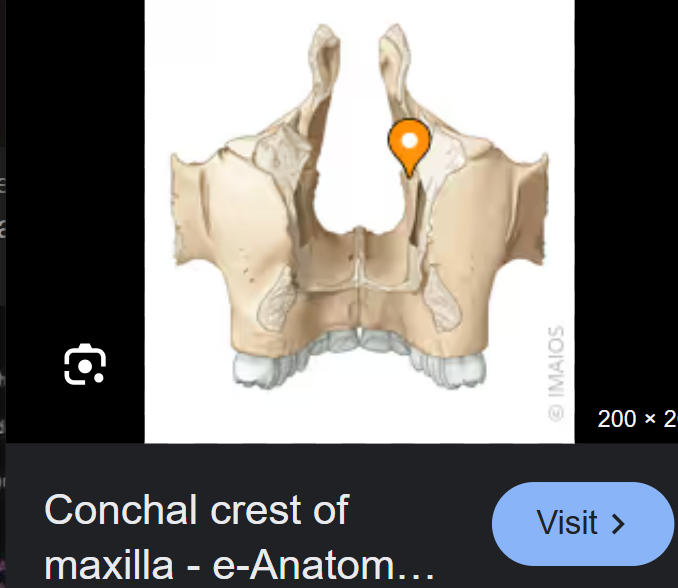
Conchal crest
For articulation of with the inferior nasal concha
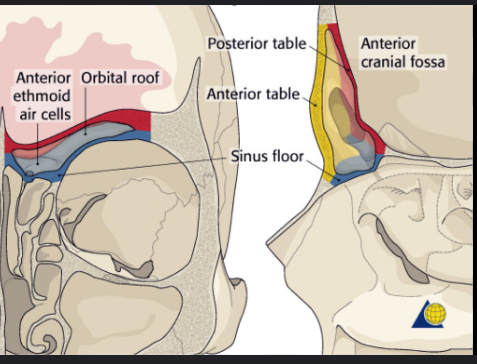
Broken air cells
at the upper border of the nasal surface are some broken air cells which in the articulated skull are closed in the ethmoid and lacrimal bone

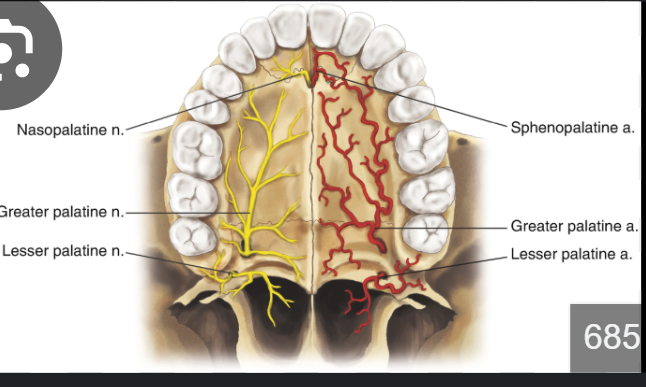
Incisive canal
It connects the oral cavity with the nasal cavity.
Content: Nasopalatine nerve, artery and vein.
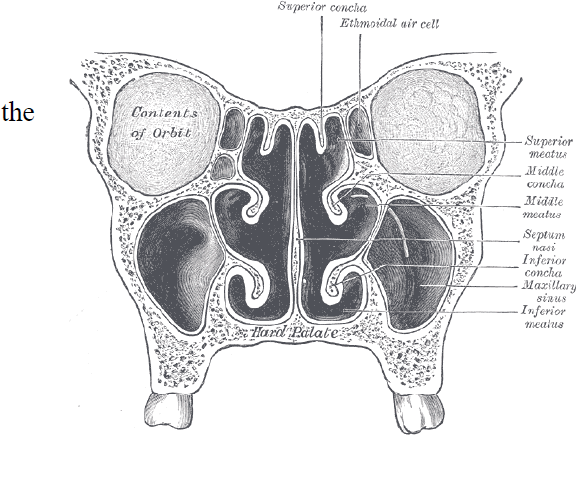
Ethmoid bone
This is an unpaired bone that creates the nasal cavity.
It is located at the roof of the nose between the two orbits.
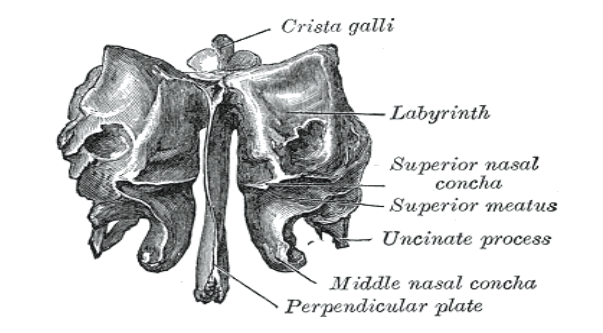
The ethmoid bone has 3 parts:
Cribiform plate.
Ethmoidal labyrinth.
Perpendicular plate
Articulation
The ethmoid articulates with 15 bones:
Neurocranium (frontal bone, sphenoid bone).
viscerocranium- 2 nasal bones, two maxillae, 2 lacrimal, 2 palatine bones, 2 inferior nasal conchae and the vomer
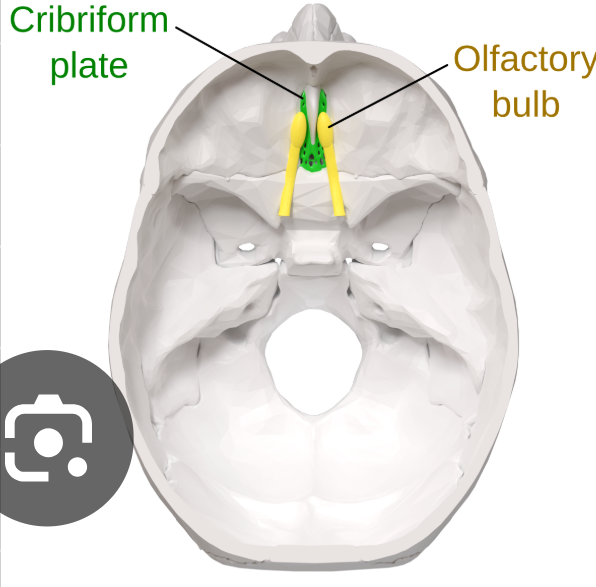
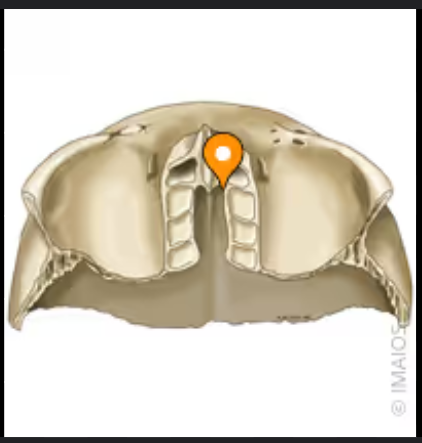
Cribiform plate
This articulates with the ethmoidal notch of the frontal bone.
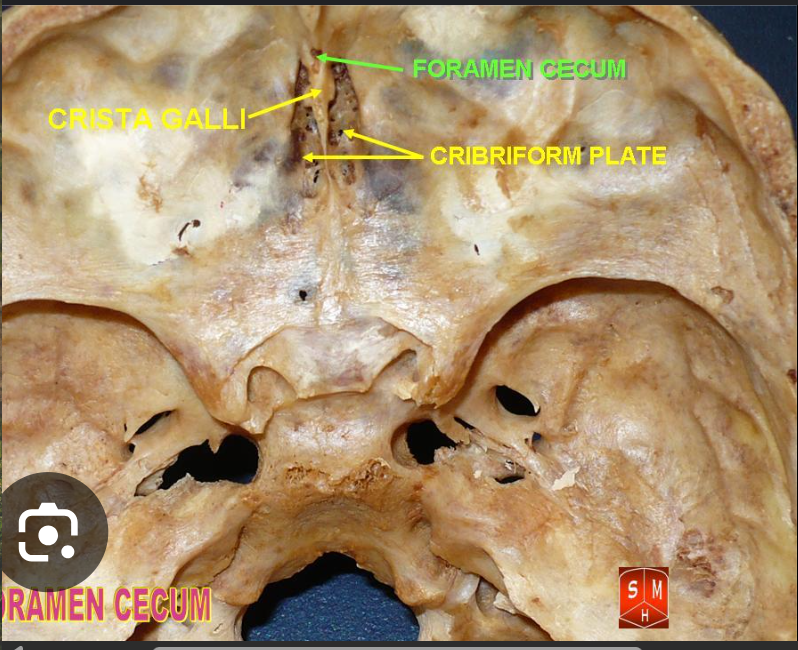
Contents of the ethmoid bone
Crista galli: dura mater anchors here.
Foramen Coecum: nasal emissary vein
Cribiform plate: 22 holes, 11 on each side of the crista galli. The olfactory nerve passes through.
Ethmoidal labyrinth (lateral masses)
Ethmoidal layrinth (lateral masses)
the ethmoidal labyrinth contains the ethmoidal air cell which are arranged in three groups: anterior, middle and posterior which all open into the nasal cavity.
Walls of the ethmoidal labyrinth
superior wall:
Posterior wall:
Lateral wall:
Medial wall:
Superior wall
broken air cells: this surface presents as number of half-broken cells that are completed in the articulated skull by the frontal bone.
Anterior and posterior ethmoidal foramen: opens into the inner wall of the orbit.
Posterior wall
Articulates with the body of the sphenoid and orbital process of the palatine bone.
Lateral wall
Forms the medial wall of the oribit
Artticulates:
superiorly with the orbital plate of the frontal bone.
Inferiorly: with the maxilla and orbital process of the palatine bone
Anteriorly: with the lacrimal bone
Posteriorly: with the body of the sphenoid
Medial wall of the labyrinth
Forms part of the lateral wall of the nasal cavity.
It contains:
Superior nasal concha
Middle nasal concha

The group of ethmoidal air cells
Ethmoidal air cells are also called ethmoid sinuses:
Posterior group
Middle group
Anterior group

Posterior group

Middle group

Anterior group
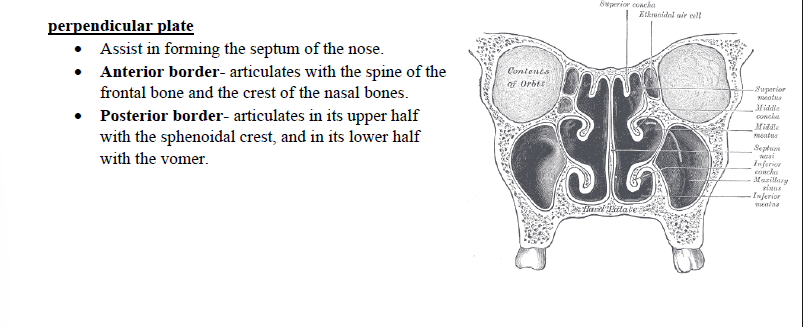
Perpendicular plate
It assists in the septum of the nose
Anterior border:
Posterior border: