BIOLOGY (CH 2)
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
What's classification?
the organization of living organisms into groups, based on similarities in their characteristics & evolutionary basis
Who's Carolus Linnaeus?
the founder of taxonomy.
he classified living organisms into groups based on their morphology & behavior
he also developed the binomial naming system
What's the binomial naming system?
it's a formal system of naming living organisms by giving each one a name composed of 2 parts of Latin origin (Genus & Species)
What are the rules we must follow when using the binomial naming system?
1. the first letter of the first word (ex: 'Genus') must be uppercase while the rest is in lowercase
2. if the name is printed in a scientific magazine or in a book, the whole name is italicized
3. if the name is written by hand, then the whole name must be underlined
What's taxonomic classification?
a hierarchical system used to categorize organisms to the species level (based on similar characteristics or common ancestors)
What are the 8 taxonomic classification levels (in descending order = largest to smallest)
1. Domain (domains)
2. Kingdom (kingdoms)
3. Phylum (phyla)
4. Class (classes)
5. Order (orders)
6. Family (families)
7. Genus (genera)
8. Species (species)
What are the 8 taxonomic classification levels (in ascending order = smallest to largest)
1. Species (species)
2. Genus (genera)
3. Family (families)
4. Order (orders)
5. Class (classes)
6. Phylum (phyla)
7. Kingdom (kingdoms)
8. Domain (domains)
What are some mnemonics to memorize the taxonomic classification levels?
- Dumb Kids Prefer Cheese Over Fried Green Spinach
- Did King Phillip Come Over For Good Soup?
The word "phylum" is used to describe... while the word "division" is used to describe...
animals
plants/bacteria
What's a domain?
largest group & it contains 1 or more kingdoms
What's a kingdom?
composed of smaller groups called phyla (or divisions if we're referring to plants/bacteria)
What's a phylum?
includes 1 or more related classes of animals (or divisions of bacteria/plants)
What's a class?
contains related orders
What's an order?
comprised of families sharing a set of similar nature or character
What's a family?
a group of 1 or more genera, especially sharing a common attribute
What's a genus?
a group including closely related species
What's species?
comprises related organisms that share common characteristics & can produce a fertile offspring
Modern taxonomy: according to more recent classifications, all living organisms can be classified into..
3 domains and 6 kingdoms
What are the 3 domains?
1. bacteria
2. archaea
3. eukarya
Describe bacteria
1. includes the kingdom Eubacteria
2. cell wall is made up of peptidoglycan
3. membrane bound organelles are absent
Describe Archaea
1. includes the kingdom Archaebacteria
2. cell wall does not contain peptidoglycan
3. can survive in harsh conditions (ex: heat & acidity loving, salt loving, & those that produce methane)
4. membrane bound organelles are absent
Describe Eukarya (main domain)
1. has 4 kingdoms (Animalia, plantae, Fungi, Protists)
2. membrane bound organelles are present (so they have things like nucleus, mitochondria)
3. large in size
[Eukarya] Describe Animalia (animals)
1. multicellular (made up of at least 2 or more cells)
2. absent cell wall
3. express heterotrophic nutrition (can't produce their own food)
[Eukarya] Describe Plantae (Plants)
1. multicellular
2. cell wall made up of cellulose
3. stores carbohydrates in the form of starch
4. autotrophic = can produce their own food by using energy from sunlight
[Eukarya] Describe Fungi
1. cell wall made up of Chitin
2. do not photosynthesize
[Eukarya] Describe Protists
1. do not possess highly specialized tissues or organs
2. classified into 3 groups based on their modes of nutrition
Are viruses considered living or non-living? And why?
Non-living. Because they CANNOT survive on their own, it needs a host.
What's HIV and what does it cause?
Human immunodeficiency virus: it's a virus that causes AIDS (acquired immunodeficiency syndrome)
What are prokaryotes?
unicellular, microscopic, organismsthat do NOT possess membrane bound organelles (such as nucleus & mitochondria).
they contain DNA & ribosomes
their cell types are found in bacteria & archaea
What are prokaryotic cells made up of?
- Chromosomes (made up of DNA)
- Capsule (prevents dessication of the cell = prevents cell from drying out)
- Pili (for attachment to other surfaces)
- Flagellum (for movement)
- Cell wall
What are the 3 types of archaea?
1. Halophiles
2. Thermoacidophiles
3. Methanogens
What are halophiles?
aerobic (need oxygen) organisms that live in very salty environments
What are thermoacidophiles?
organisms that live in hot and acidic environments.
they grow at high temperatures (greater than 80℃) & in acidic conditions (pH 1-2)
in nature, they are mainly found in acidic hot springs and sulfur springs
What are methanogens?
microorganisms that consume carbon dioxide & produce methane (gas) as a byproduct of metabolism
they are found in seweage treatment plants & sabkhas (area of low-lying salty ground)
What's gram staining?
it's a method of staining used to classify bacterial species into 2 large groups:
1. Gram Positive
2. Gram Negative
What are gram positive bacteria?
Bacteria appears dark PURPLE when stained with gram stain. This is because of the presence of a thick layer of peptidoglycan in the bacterial cell wall.
Summary:
- dark purple
- thick peptidoglycan
What are gram negative bacteria?
Bacteria appears PINK when stained with gram stain. This is because of the bacterial cell wall having a thin layer of peptidoglycan & high lipid content
Summary:
- pink
- thin peptidoglycan
- high lipid content
Why is gram staining important?
Medical doctors use it to identify the most suitable medication for use against disease causing bacteria.
What are the types of reproduction (in prokaryotic, asexual reproduction)
1. Conjugation
2. Binary Fission
What's conjugation?
sexual reproduction for bacteria
bacterial cells come in contact next to each other and using the sex pilus, they transfer genetic material to another
What's binary fission?
a type of asexual reproduction
the parent cell is split into 2 identical daughter cells
most prokaryotic organisms follow this method of reproduction
The benefits of bacteria include...
- Normal Flora
- Production of food & medicine
- Nitrogen fixation
What's normal flora? (benefits of bacteria)
a large number of bacteria live on the inside & outside of the body such as Escherichia coli
E. coli lives within the intestines & produces vitamin K which is used in coagulation (blood clotting)
What's production of food & medicine? (benefits of bacteria)
Bacteria is used in the production of food such as yogurts, cheeses, and chocolates
It's also used in the production of antibiotics such as Streptomycin, Tetracycline, & Vancomycin
What's nitrogen fixation? (benefits of bacteria)
certain types of bacteria found on the roots of plants convert gaseous nitrogen found in the atmosphere to a form of nitrogen that is usable by plants
the root nodules found on the roots of plants develop a symbiotic (beneficial) relationship with nitrogen fixing bacteria especially in legumes (ex: soybeans, peas, clovers, & alfalfa)
What are the diseases caused by bacteria?
- Respiratory diseases: Pneumonia, Whooping cough, Tuberculosis, & Anthrax
- Skin diseases: Acne
- Digestive tract: Cholera
- Nervous system: Tetanus
- Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs): Syphilis (affects many organs)
Viruses are...
nonliving microorganisms made up of genetic material contained within a protein coat
How are viruses classified?
based on the genetic material they possess
A virus is made up of...
- protein coat
- genetic material : either DNA or RNA
Do all viruses have an envelope?
No, some of them have the envelope (similar to a membrane) but others do not. The general makeup is protien coat & genetic material
If they have an enevlope they're called enevloped viruses
If they don't, they're called non-enveloped viruses
What are retroviruses?
- their genetic material is made up of RNA
- uses the enzyme reverse transcriptase to form DNA from RNA
- example: human immunodeficiency virus
What are viral diseases?
- Sexually Transmitted Diseases: AIDS, genital herpes
- Respiratory Diseases: Influenza, Common cold
- Childhood Diseases: Measles, Mumps
- Nervous System: Polio Myelitis, Rabies
- Other: Chickenpox, Hepatitis
What are Prions?
They are proteins called "protinaceous infectious particle" that cause infection or disease
What are diseases caused by prions?
- Mad Cow Disease
- Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease: affects the nerve cells in the brain, resulting in their rupture
What are the 4 types of viruses?
- helical
- polyhedral
- spherical
- complex
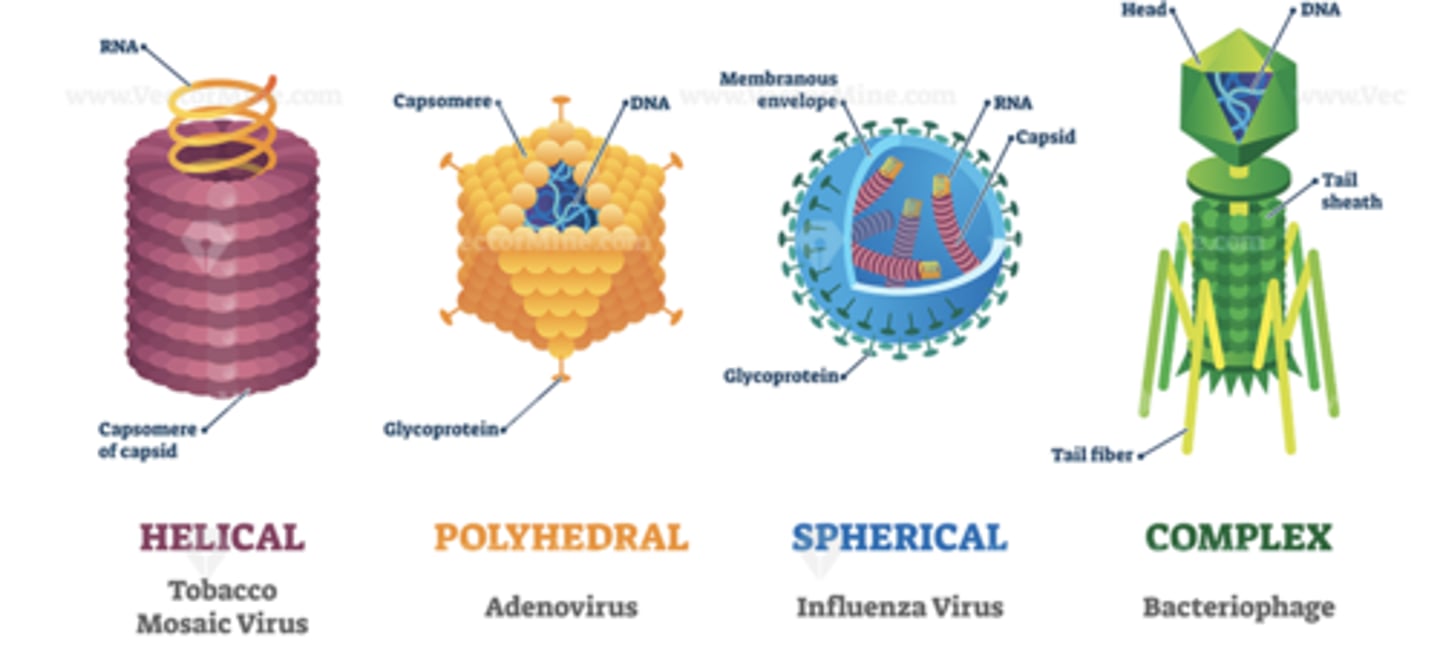
What's an example of a helical virus?
tobacco mosaic virus
What's an example of a polyhedral virus?
adenovirus
What's an example of a spherical virus?
influenza virus
What's an example of a complex virus?
bacteriophage (virus that infects bacteria)