CFB 14: Obesity and Bariatric Surgery (Nutrition)
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
Obesity is a ______________ disease.
Multifactorial
Obesity is caused by an excess accumulation of what?
Adipose tissue
Increase in size and #
According to the WHO, how many people are obese vs. overweight in the world?
Obese: >600 million
Overweight: >billion
What percent of the US population is overweight?
65%
What are the BMI categories?
Underweight <18.5
Healthy 18.5-24.9
Overweight 25-29.9
Obese >30
Co-morbid conditions of obesity
Chronic inflammation
Respiratory compromise
Critical care limitations
Immune Disregulation
Co-morbid complications
Endocrine Disfunction
Impaired pulmonary perfusion
The risk of hypertension increases by _% for every 1kg of extra weight gained above a normal weight.
5%
What greatly increases the risk of Type II Diabetes?
BMI > 30
Increased body fat can influence _______ sensitivity and _______ secretion --> factors that. can contribute to the development of _____.
Insulin; T2DM
What is periodontitis?
Inflammation and infection of the ligaments and bones that support the teeth
How does obesity cause periodontitis?
Inflammatory products released from adipocytes contribute to gingival inflammation and bacterial growth in the oral cavity
The concentration of what in the gingival fluid is positive correlated with BMI?
TNF-α
How does TNF-α contribute to periodontitis?
Triggers ECM breakdown
How does obesity impact dental practice?
-Standard dental chairs and operatory units used in clinics have weight limitations (308 lbs)
--Chairs limited with armrests
-Excess fat:
--Smaller oral cavity opening
--Increased volume of the tongue
-Effectiveness of anesthesia:
--Redistributed into fat
--Stored for a longer duration
Weight loss treatment options
Dietary modification
Behavioral therapy
Pharmacotherapy
Bariatric surgery
Education and behavioral therapy
Alter eating habits and response to food stimuli
Monitor daily meal intake; food diary
Can lose up to 3-7kg alone or up to 10% weight loss with pharmocotherapy
Pharmacotherapy treatment
E.g. phentermine, topiramate, and metformin
Qualifications: BMI > 30 or BMI >27 with medical conditions, are unable to lose 5-10% weight, and cannot sustain the behavioral therapy approach
T/F: If medication is ceased, majority regain the weight they lost.
True
What is the most effective long term weight loss treatment?
Bariatric surgery
Qualifications for weight loss surgery
Patients with class III obesity
Class II obesity with medical conditions may qualify
What are the surgical techniques that alter gastrointestinal anatomy?
Can induce malabsorption (e.g. Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass or Sleeve Gastrectomy)
Can promote restriction (e.g. gastric band)
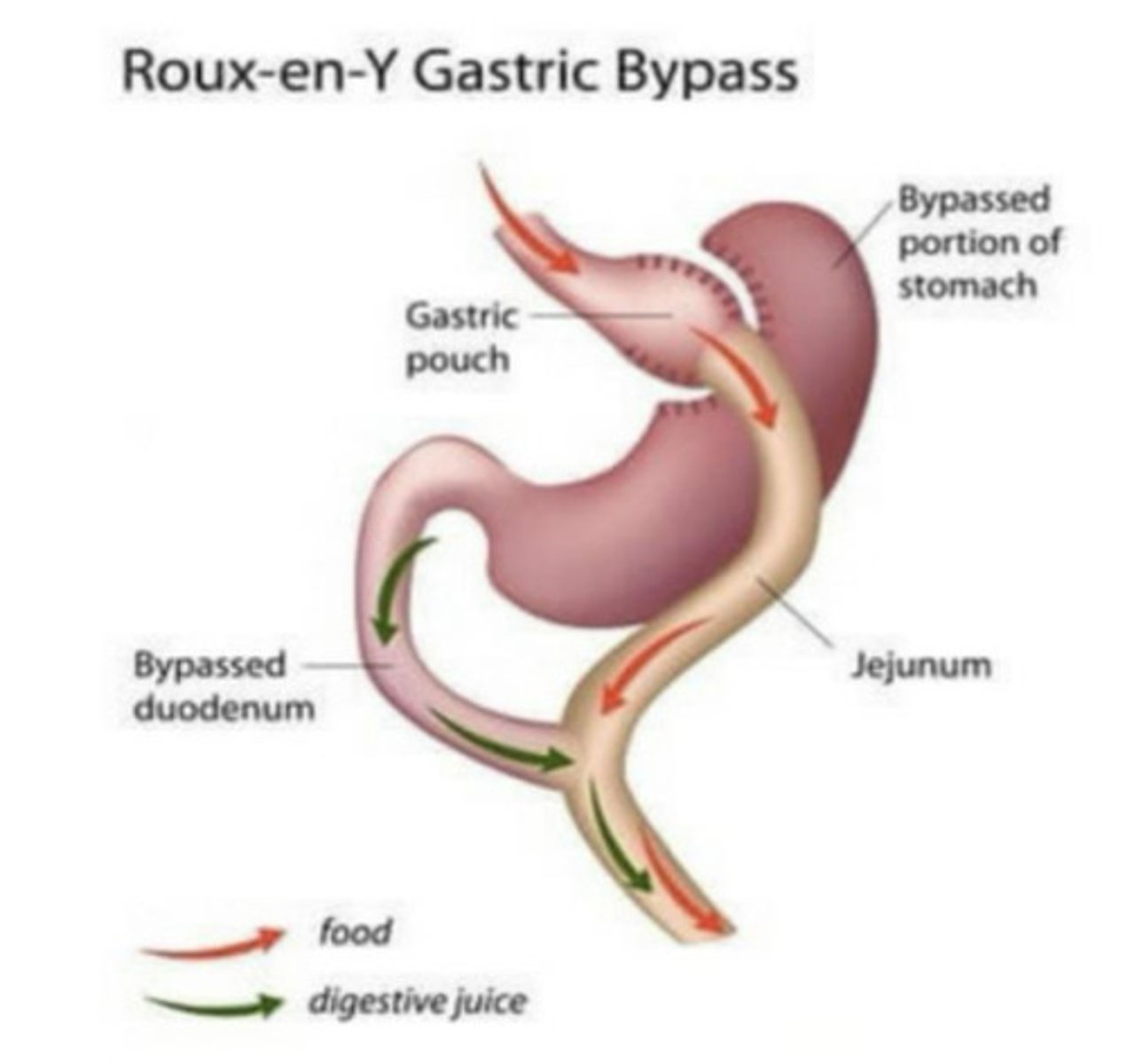
Roux-en-Y gastric bypass
Bariatric surgery that involves stapling the stomach to decrease its size
Shortening the jejunum and connecting it to the small stomach pouch, causing the base of the duodenum leading from the nonfunctioning portion of the stomach to form a Y configuration
Decreases the pathway of food through the intestine, thus reducing absorption of calories and fats
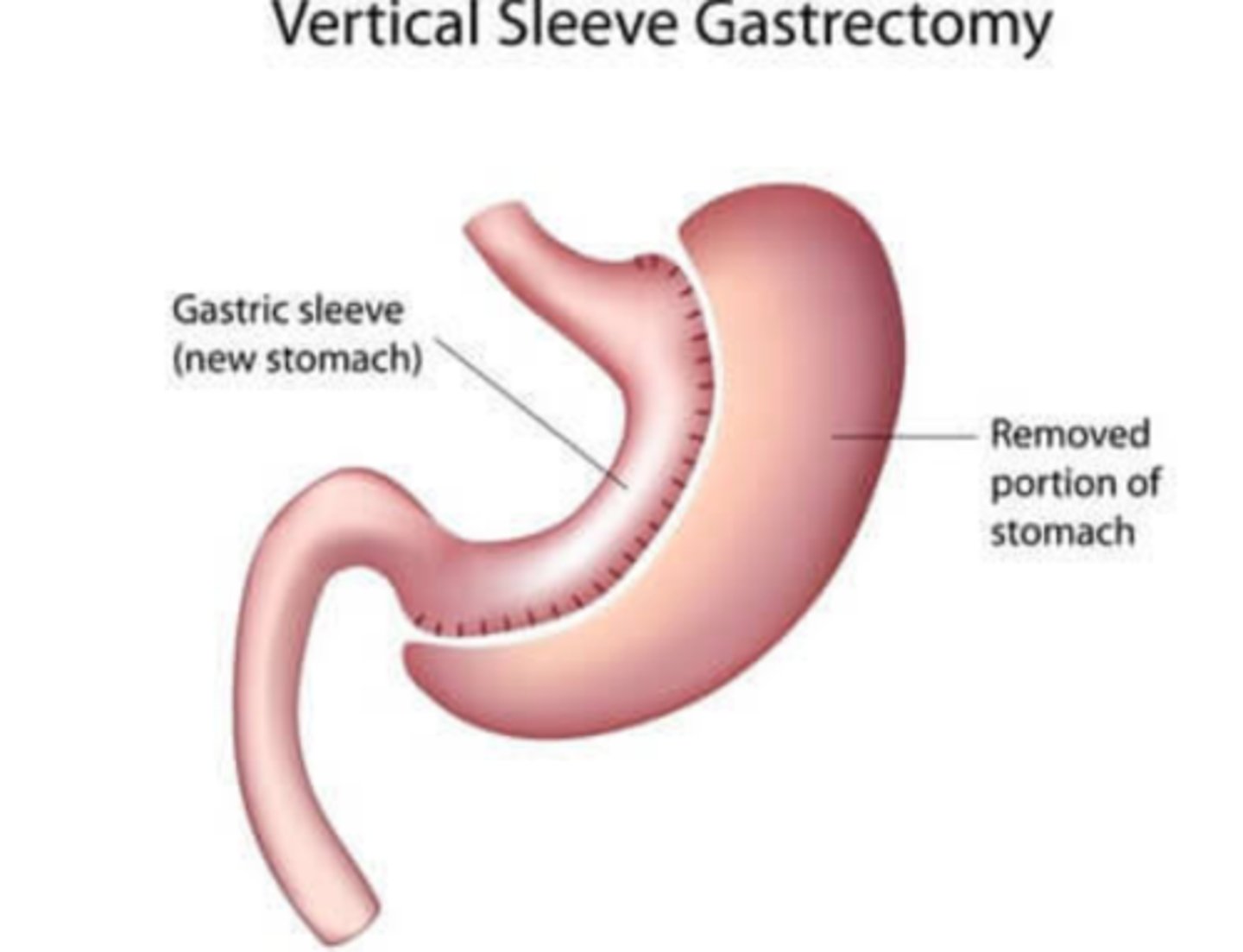
Vertical Sleeve Gastrectomy
Part of stomach removed
Small stomach = less room for food (restriction)
What bariatric surgeries induce malabsorption?
Roux-en-Y
Sleeve Gastrectomy
How can surgery impact oral health?
Meal pattern recommendations
Oral pH change
Change in salivary flow rate
Vitamin deficiencies
Oral microbiome transformation
Periodontal disease
Examples of symptoms that can result from surgery
Dental erosion
Caries
Hypersensitivity
What is the post-operative meal plan?
Eat more frequent smaller portions (4-6 20 min meals daily)
Benefits of post-op meal pattern
Helps with digestion
Allows satiety
Maintains weight loss
Reduces vomiting, nausea, and dumping syndrome
Bariatric patients are at increased __________ potential.
Cariogenic
T/F: RYGB and SG allow proper absorption of micronutrients.
False; they are malabsorptive, inadequate absorption of micronutrients
What vitamins might a post-op patient be at risk of deficiency of?
Vitamin B12
Iron
Vitamin D
Vitamin C
Vitamin E
Folate
Calcium
Zinc
RYGB patients are deficient in which vitamin?
B12
What can Vitamin B12 deficiency result in?
Megaloblastic anemia
Neuropathy
Oral health complications: stomatitis, glossitis, angular cheilitis, xerostomia, burning tongue
Where is iron absorbed?
Duodenum and proximal jejunum
Bariatric surgery patients are at risk of ______.
Anemia
Anemia oral side effects
Angular cheilitis
Atrophic glossits
Glossodynia
Deficiency in Vitamin D increases risks for...
Osteoporosis and its complications
Periodontal disease, alveolar bone loss, eventually tooth loss
Common symptoms of pH change in oral cavity
Acid reflux, regurgitation, and vomiting
What can endogenous aids cause?
Enamel erosion and demineralization
Exposes dentine and increases hypersensitivity
Occlusal surface of molars and maxillary anterior teeth
Bariatric surgery patients are at increased risk of ____ exposure.
Acid
What is our role as dental providers?
1. Inter-professional and intra-professional collaborations (collaborate with registered dieticians)
2. Dental care pre-operatively and continue post-op
3. Educate on how to maintain oral health after acid exposure or vomiting
4. Frequent counseling on vitamin compliance and nutrition
How to maintain oral health after acid exposure or vomiting
Sugar free antacids
Rinsing with sodium bicarbonate and water
Sugar free xylitol gum