Week 5B: Patient Safety
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
Define patient safety
The avoidance of unexpected or unintended harm to people during the provision of healthcare
The absence of harm does not mean _______
Care is safe
True or False: Everyone contributes to patient safety?
True
1 multiple choice option
Define harm
An unexpected outcome for the patient, resulting from the care and/or services provided, that negatively affects the patient's health and/or quality of life
Define a clinical adverse event
An event that reasonably could or does result in an unintended injury or complications
Arising from health care management, with outcomes that may range from death, disability, or require a change in patient care
What is the leading cause of injury and avoidable harm in health care systems?
Medication errors
What is one of the most common and preventable causes of patient harm ?
Venous thromboembolism (blood clots)
What medical condition contributes to one third of the complications attributed to hospitalization?
Venous thromboembolism (blood clots)
List the top 10 patient safety concerns for healthcare organizations
1. Risks of Dismissing Patient, Family, and Caregiver Concerns
2. Insufficient Governance of Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare
3. Wide Availability and Viral Spread of Medical Misinformation: Empowering Patients through Health Literacy
4. Medical Error and Delay in Care Resulting from Cybersecurity Breaches
5. Unique Healthcare Challenges in Caring for Vulnerable groups and Vetrans
6. The Growing Threat of Substandard and Falsified Drugs
7. Diagnostic Error: The Big Three—Cancers, Major Vascular Events, and Infections
8. Persistence of Healthcare-Associated Infections in Long-Term Care Facilities
9. Inadequate Communication and Coordination during Discharge
10. Deteriorating Community Pharmacy Working Conditions Contribute to Medication Errors and Compromise Patient and Staff Safety
Is error always present?
Error is all around us, ever present, and attempts to eliminate it are fruitless (James Reason)
Error itself is _________ and __________
Neutral, Boring (James Reason)
It is how we _________ and _________ to error that shapes whether harm may later result
Understand, Respond (James Reason)
What is the swiss cheese model?
Used for risk analysis and management
The holes in each slice represent weaknesses or flaws in that layer. On their own, each slice might catch most errors. However, when the holes in multiple slices align, a hazard can pass through all layers — resulting in an adverse event or system failure
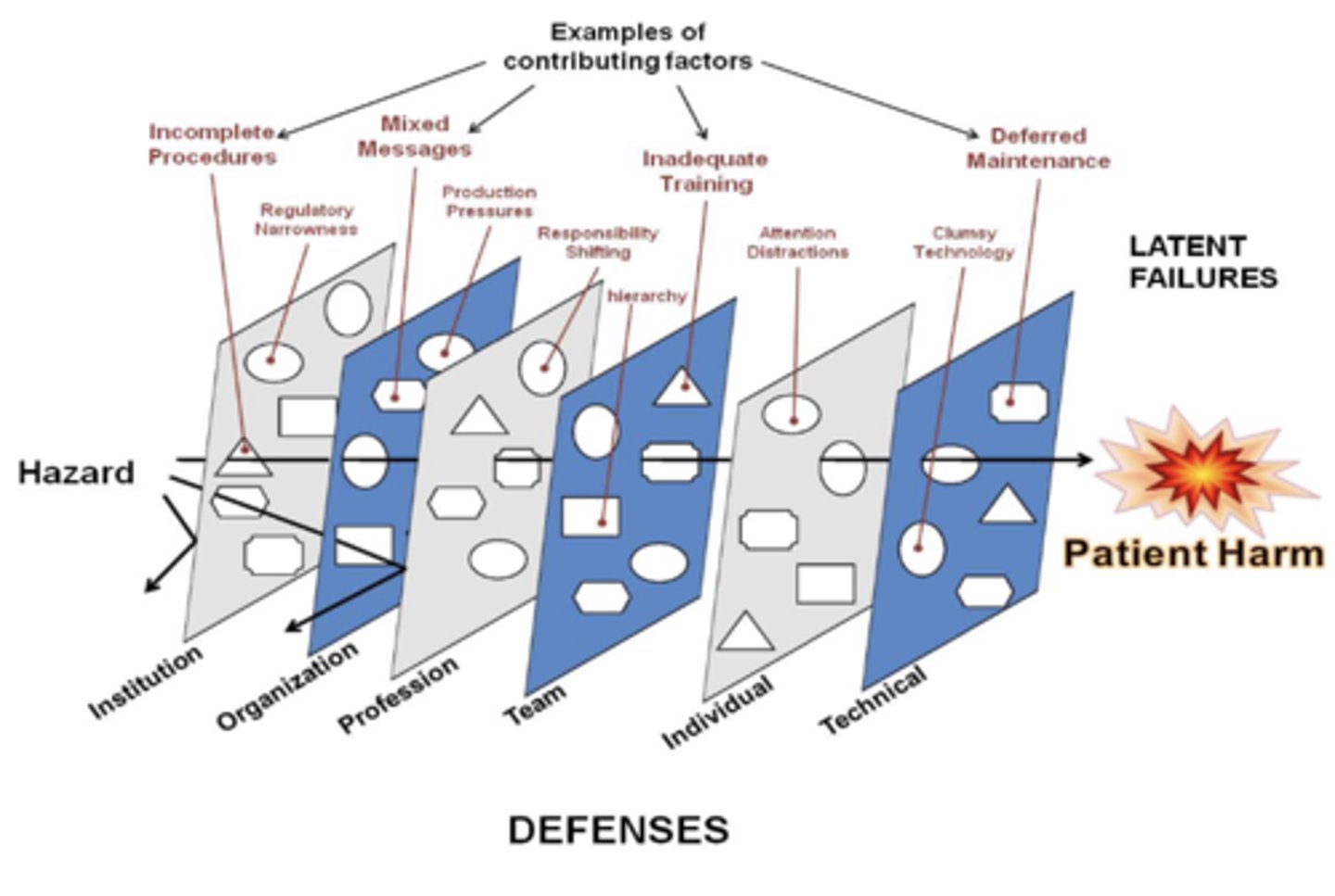
What causes holes in the swiss cheese model?
Latent conditions and active failure
What are latent conditions?
-Organizational: Management decisions and processes
-Workplace: Working conditions
What are active failure?
People (human)
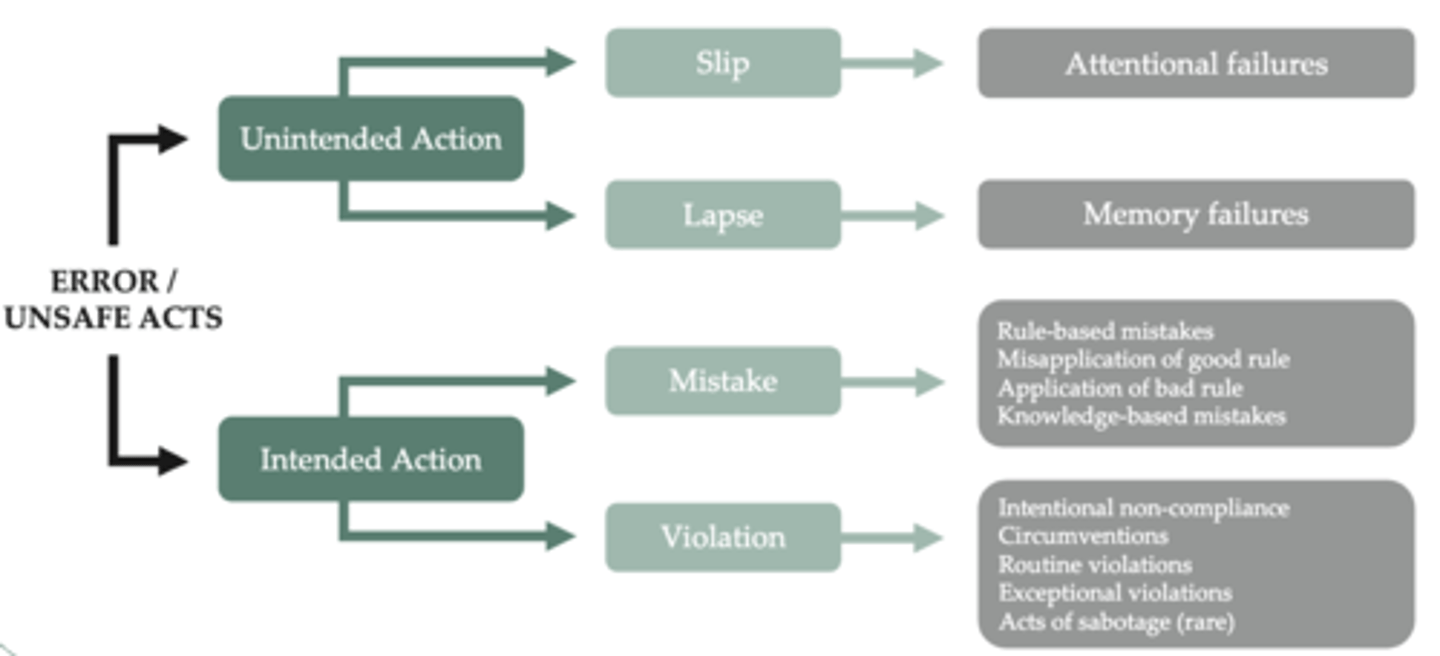
Categories of Human Error
Define culture
The shared values, beliefs, attitudes and behaviours (the way we do business)
What does culture help define?
What the team is willing to accept as 'normal' and directly impacts organizational functions and outcomes
What is a culture of patient safety?
The shared values, beliefs, behaviours, and attitudes within a healthcare organization that prioritize patient well-being and safety
And minimizes harm by fostering a work environment where safety is valued, and errors are openly discussed and addressed
Define organizational culture?
The implicit knowledge, values, or beliefs within the organization that reflect the norms and traditions of the organization
What is a just culture?
A culture that is:
-Respectful in how they engage with those involved
-Transparent in the evaluation process used
-Hold the system, themselves, and others accountable
-Learn from mistakes and close calls to improve safety and performance
True or False: Everyone contributes to a patient safety culture?
True
1 multiple choice option
Mistakes are a matter of _______ not ______
When, If
How do you make sense of an adverse event?
You have two choices:
1. Human error as the cause: Leading to human error as the conclusion to the investigation
2. Human error as the symptom of deeper trouble: Leads you to look for ways error is systematically connected to factors such as tools, tasks, and the operational/organizational environment
What are human factors in healthcare?
Scientific studies for how health-care providers work and then design processes and equipment that contribute to a high-quality and safe healthcare system
List the components of human factors in healthcare
-Workspace Design
-Device Evaluation
-Medication Safety
-Information Design
-Human Error Management
Define workspace design
Evaluate new and existing spaces and provide recommendations
Define device evaluation
Enable the purchase of user-friendly equipment
Define medication safety
Improve the storage and labelling of medications and supplies
Define information design
Accessing the right information at the right time
Define human error management
Study the causes of human error and the best mitigation strategies
Define digital health
Refers to the use of technology in healthcare
What are the pros and cons of digital health
Pros: Can improve patient safety and quality of care
Cons: Introduce risks when poorly designed, implemented, or used
What is an eSafety event?
Any event related to a patient safety hazard, close call, or adverse event where technology contributed to, or triggered the event
E.g. A computer update failure that caused patient lab results to go to the wrong provider
Historically what approach has healthcare taken to adverse events?
Person centred approach
What is person approach?
Focuses on individual mistakes, often attributing errors to forgetfulness, inattention, or negligence.
Often leads to blame and punishment of the person involved
What is a systems approach?
Focuses on why the system allowed the error to happen, not just who made the mistake
Aims to improve processes, environments, communication, and tools to prevent errors
What is a person to system approach?
Contrasts blaming individuals for errors with understanding how systemic factors contribute to those errors
What are the causes of error in a person approach?
-Forgetfulness
-Inattention
-Negligence
-Poor motivation
-Carelessness
-Recklessness
-Distraction
What are the reactions to error in a person approach?
-Procedure review
-Disciplinary action
-Threat of litigation (taking legal action, e.g. suing)
-Retraining
-Naming, blaming, and shaming
What are the causes of error in a systems approach?
-Conditions within the workplace (e.g. Pressures, understaffing, equipment, fatigue, inexperience)
-Weaknesses (e.g. Unworkable procedures, design deficiencies, equipment failure)
What are the reactions to error in a systems approach?
-Error is generalized rather than isolated
-System is reviewed to limit the incidence of error
-System is reviewed so that if an error occurs it's damaging effects are minimized
Outline the following levels within a systems approach:
-Mega
-Macro
-Meso
-Micro
-Mega: External systems
-Macro: AHS
-Meso: Hospital/Zone
-Micro: Individual/Provider/Local unit/Program
What does a systems approach (systems thinking) consider?
-Patient
-Personnel
-Equipment
-Environment
-Organization
-Regulatory agencies
When is the threshold for disclosure met?
1. A patient has suffered any degree of harm
2. Potential for future harm
3. A change in care or monitoring
What is involved in a leaders plan?
-Build capacity
-Walk the talk
-Establish an open climate and encourage reporting
-Provide "lessons learned" opportunities
Healthcare is a __________ system
Complex
Patients depend on many individuals doing the _____________ at the _____________. They depend on a system of care (WHO).
Right thing, right time
What should you ask yourself when assess personal accountability?
-Am I doing the right thing?
-How could I do this better?
-Am I using the right assumptions?
What does systems thinking not exclude?
Accountability
What are the five key functions of a team?
-Results
-Accountability
-Commitment
-Effective communication
-Trust
How is an effective team measured?
As one that accomplishes the results they set out to achieve
What is needed to ensure effective implementation of patient safety?
-Effective teamwork and communication skills
-Strong clinical leadership at the microsystem level
-Quality improvement capability
-Ongoing learning and reflection about performance
-Support from senior leadership
SIDE NOTE: Review the Unit Manager Presentation