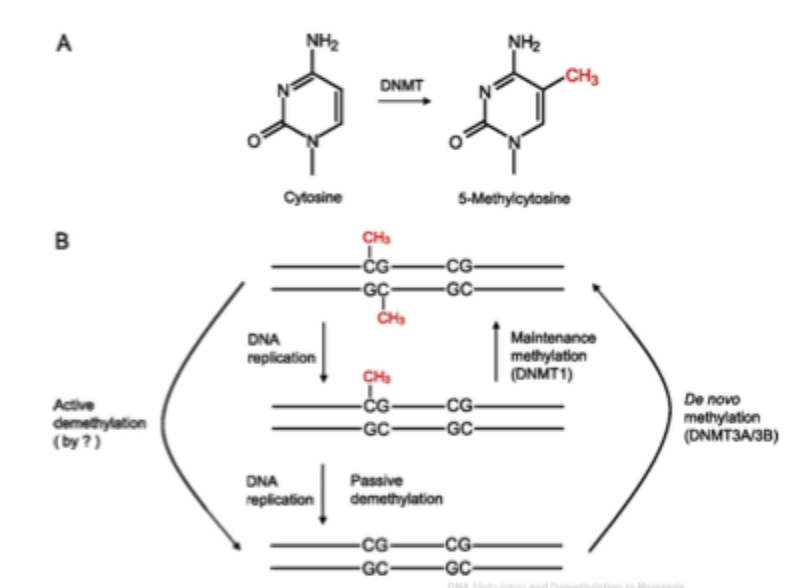
DNA modifications
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
Early life environment- adult phenotype
Influence on DNA methylation patterns and ageing?
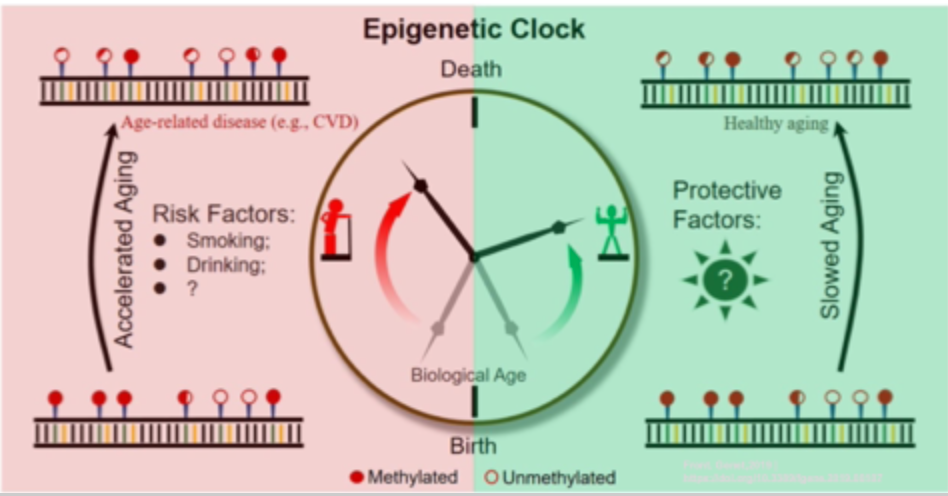
Genetic clocks
Age estimates in years resulting from a mathematical algorithm based on the methylation state of specific CpGs in the genome
Cytosines of CG(CpG) Dinucleotides:
Sites of DNA methylation
The human genome has about 28 million CpG sites (potential for cytosine methylation)
Microarrays for cytosines methylation analysis
2-3% of the CpG sites can currently be analysed by microarrays
Ideal for surveying thousands of DNA samples
Widespread global adoption
Consistent data sets/ huge data sets
Such data sets can be used to generate epigenetic clocks
Some epigenetic clocks are tissue specific
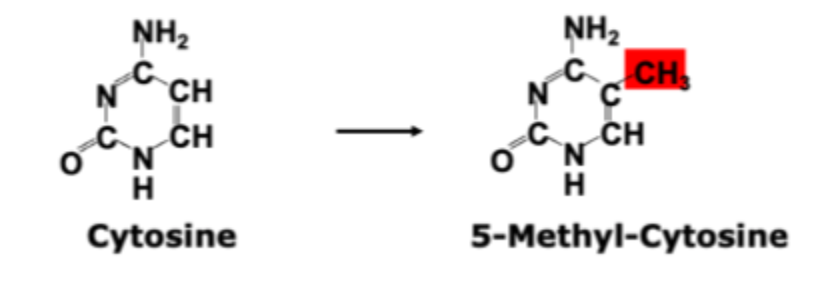
Cytosine methylation
A common form of post- replicative DNA modification
Adds information without changing of the actual DNA sequence
Donor of methyl group: S- adenosyl- L- methionine (SAM)
Mammalian DNA methylation
CpG dinuclotides are the predominant sites of cytosine methylation (there are exceptions)
*DNA has a polar direction
*Palindromic sequence- reads the same both ways

How does DNA become methylated?
Replication fork
Semiconservative replication
5’ to 3’
De novo- add methyl to DNA where there previously wase’t any
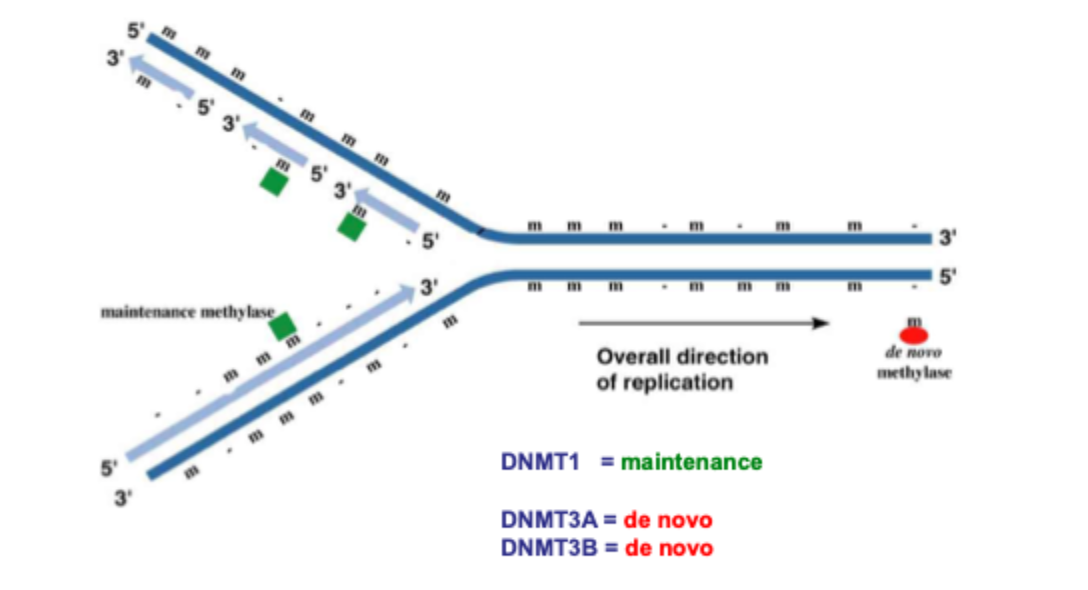
3 known mammalian DNA Methyltransferases: DNMT1, DNMT3A, DNMT3B
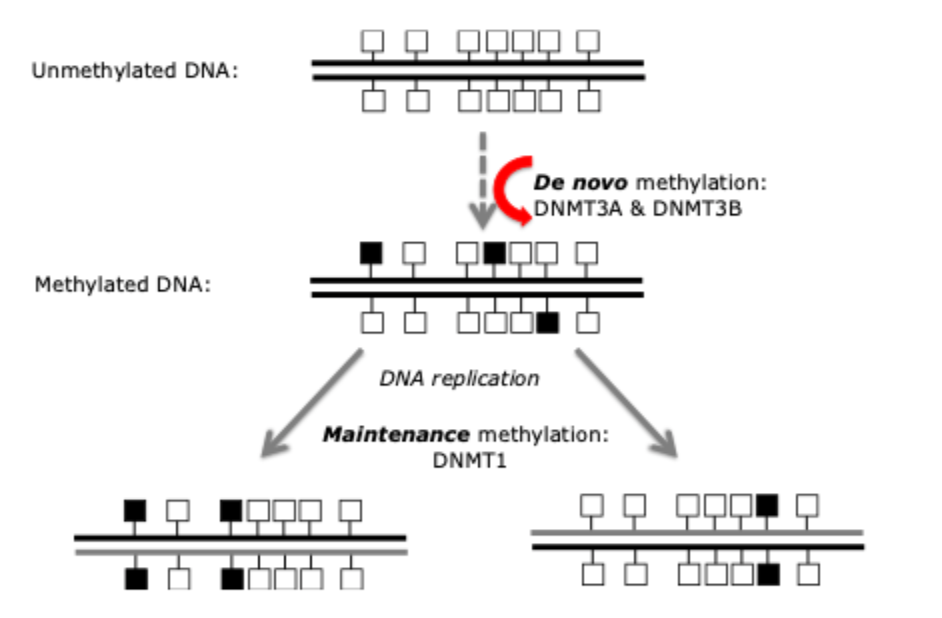
DNA methyltransferases are essential for normal mammalian development
Deletion of these genes in mice results in embryonic or postnatal lethality
What triggers DNA methylation?
repetitive DNA
histone modifications
certain RNAs
metabolites4
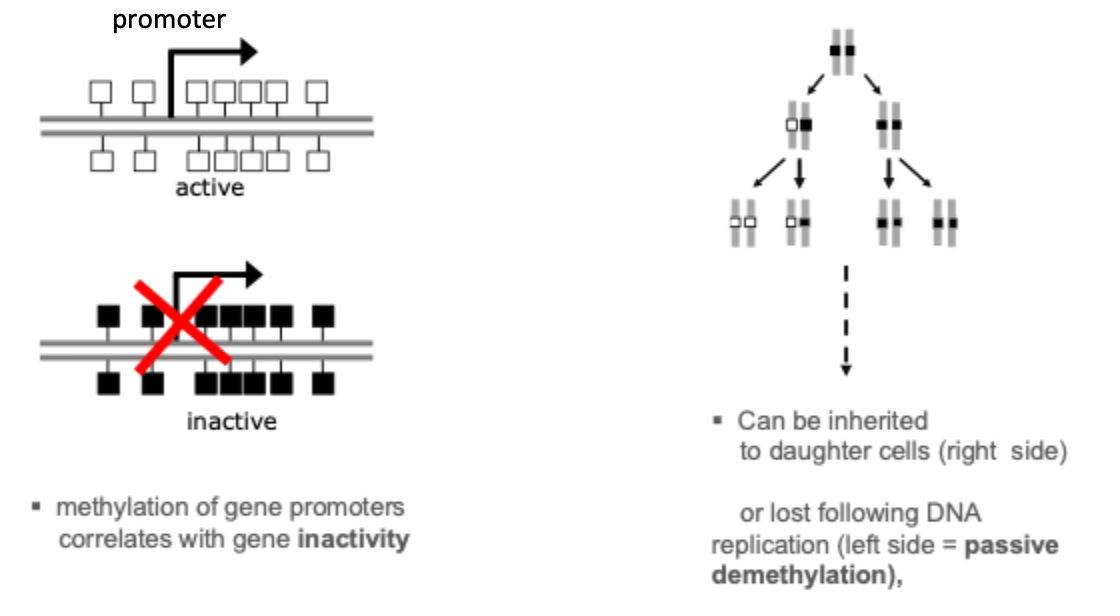
Cytosine methylation: gene silencing and passive demethylation
*X chromosomes in women 1 active and 1 inactive
Cytosine methylation: active versus passive demethylation
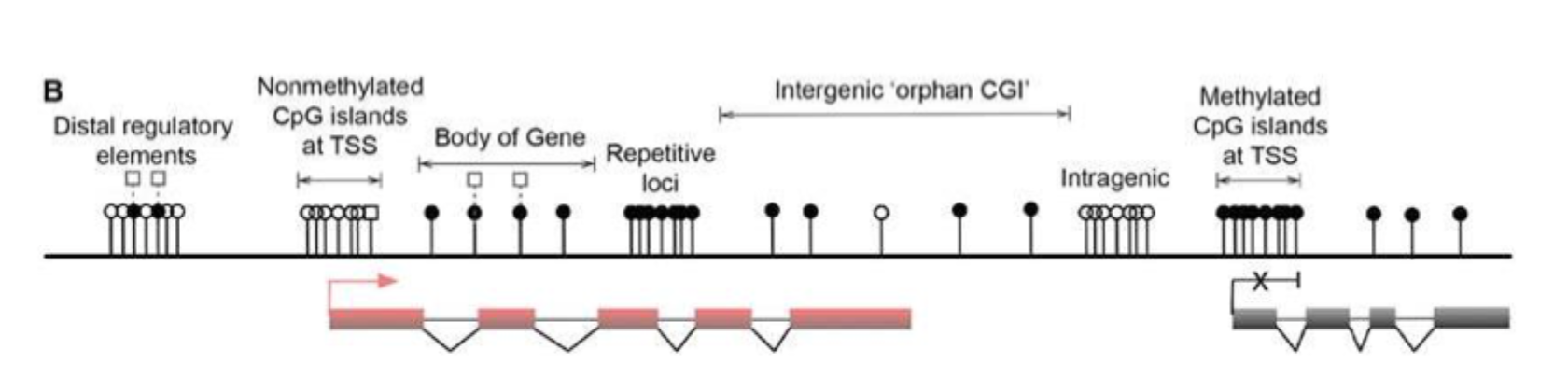
Uneven distribution of CpG dinucleotides in mammalian genomes- and their modification states
Gene bodies are often methylated with higher DNA methylation at exons than introns
5hmC is present at expressed gene bodies (white square at body of gene)
key:
white circles: nonmethylated CpGs
black circles: methylated CpGs (5mC)
white squares: hydromethylated CpGs (5hmC)
red boxes: active and transcribes exons
grey boxes: inactive and silenced exons
red arrow: active transcriptional state
black cross: inactive transcriptional state
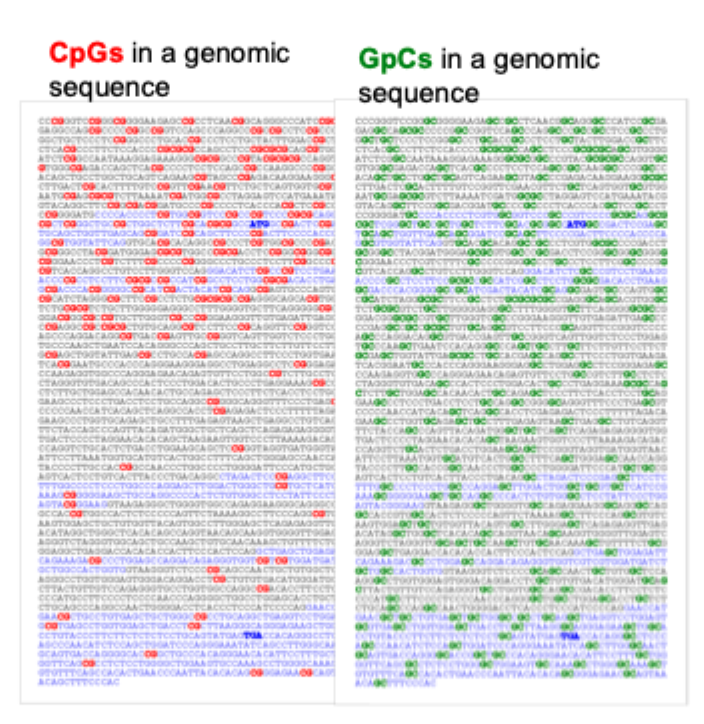
CpG islands
CpG- rich areas in the genome
Defined as >0.5 kb stretches of DNA with a G + C content >/ 55%
CpG islands are typically located in the promoter region, 5’ to the TSS
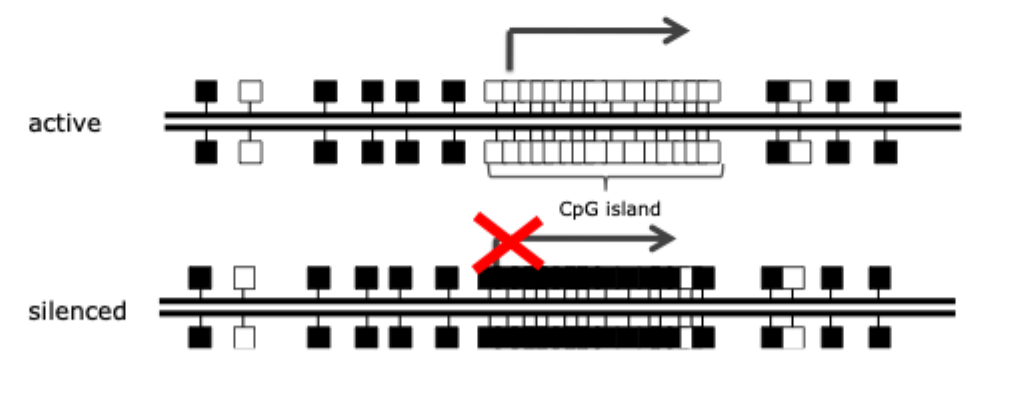
CpG islands
CpG islands are regions of high CpG density that often lack methylation
These “islands” are found at promoters of the most human genes
Long- term silencing of the gene can be established by methylation of the CpG island region. E.g. genes on the inactive X chromosome and certain imprinted genes are silenced in this way. In cancer cells, certain genes are aberrantly silenced by CpG island methylation. Methylation of gene promoters generally correlates with gene inactivity
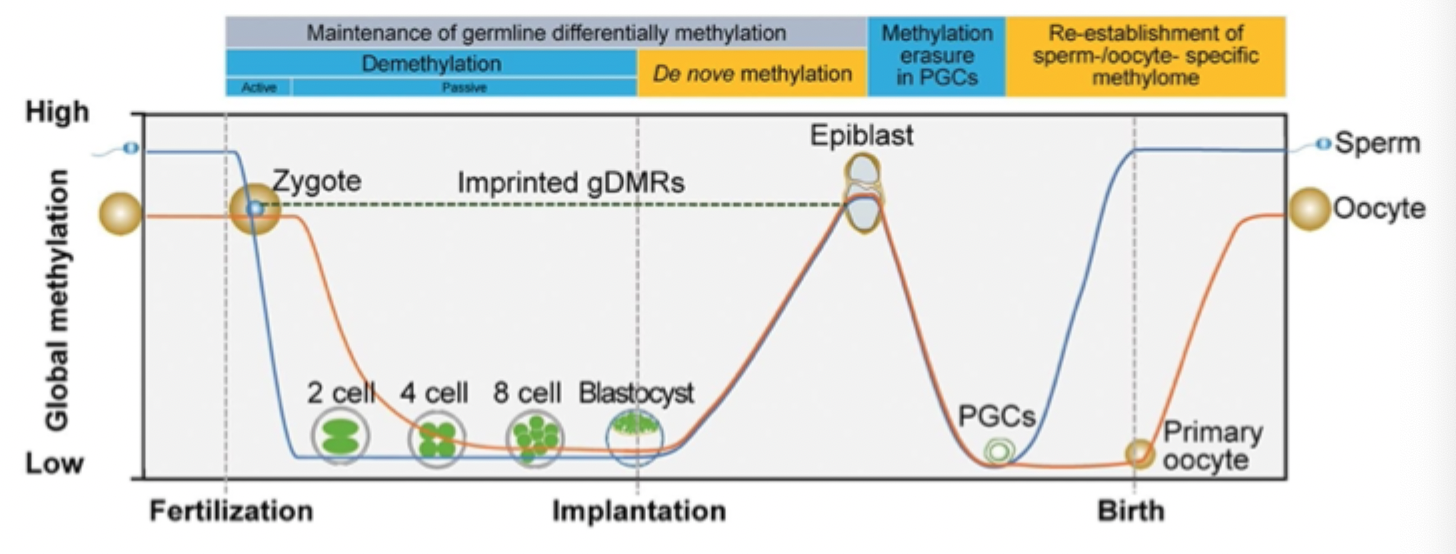
Genome- wide DNA methylation: dynamic during development
Developmental epigenetic reprogramming during mouse pre- implantation and germ cell development
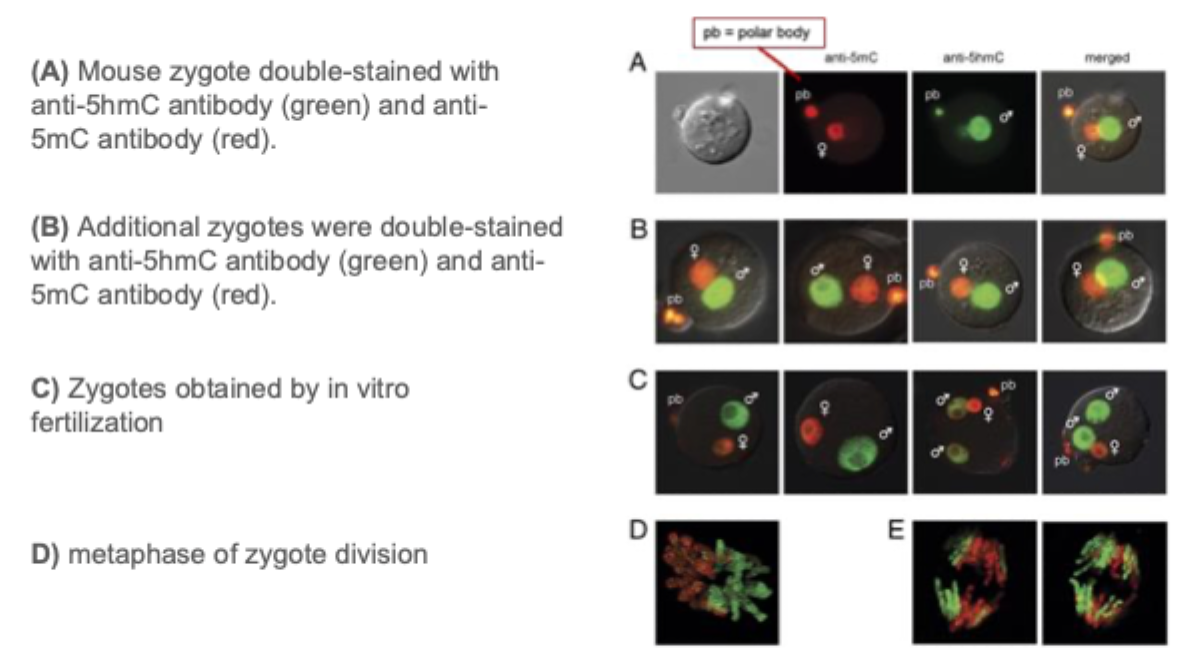
More cytosine modifications

5hmC is present in the male pronucleus of mouse zygotes
5- hydroxymethly- cytosine (5hmC) known biological roles
5hmC can be a stable modification enriched with gene bodies, concentrated at transcriptional regulatory elements and positively associated with transcriptional activity
5hmC recruits transcriptional regulators, splicing factors, DNA repair proteins and chromatin regulators that are distinct from those recruited by 5mC
5hmC plays an essential role in embryonic development, cellular differentiation and stem cell reprogramming
5hmC is a strong prognostic indicator in cancer and other diseases
5hmC is implicated in the regulation of neurological plasticity, immunology and other dynamic systems by the TET enzyme family
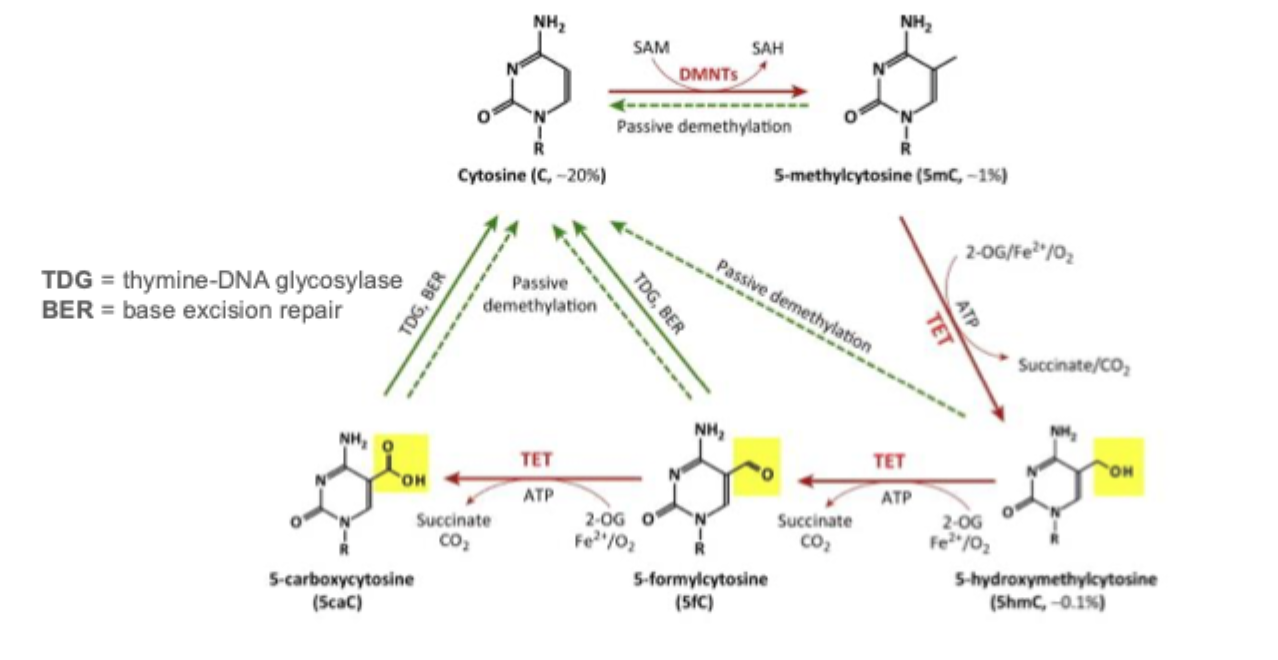
5hmC is an intermediate during the process of demethylation
DNA demethylation: passive and active mechanisms
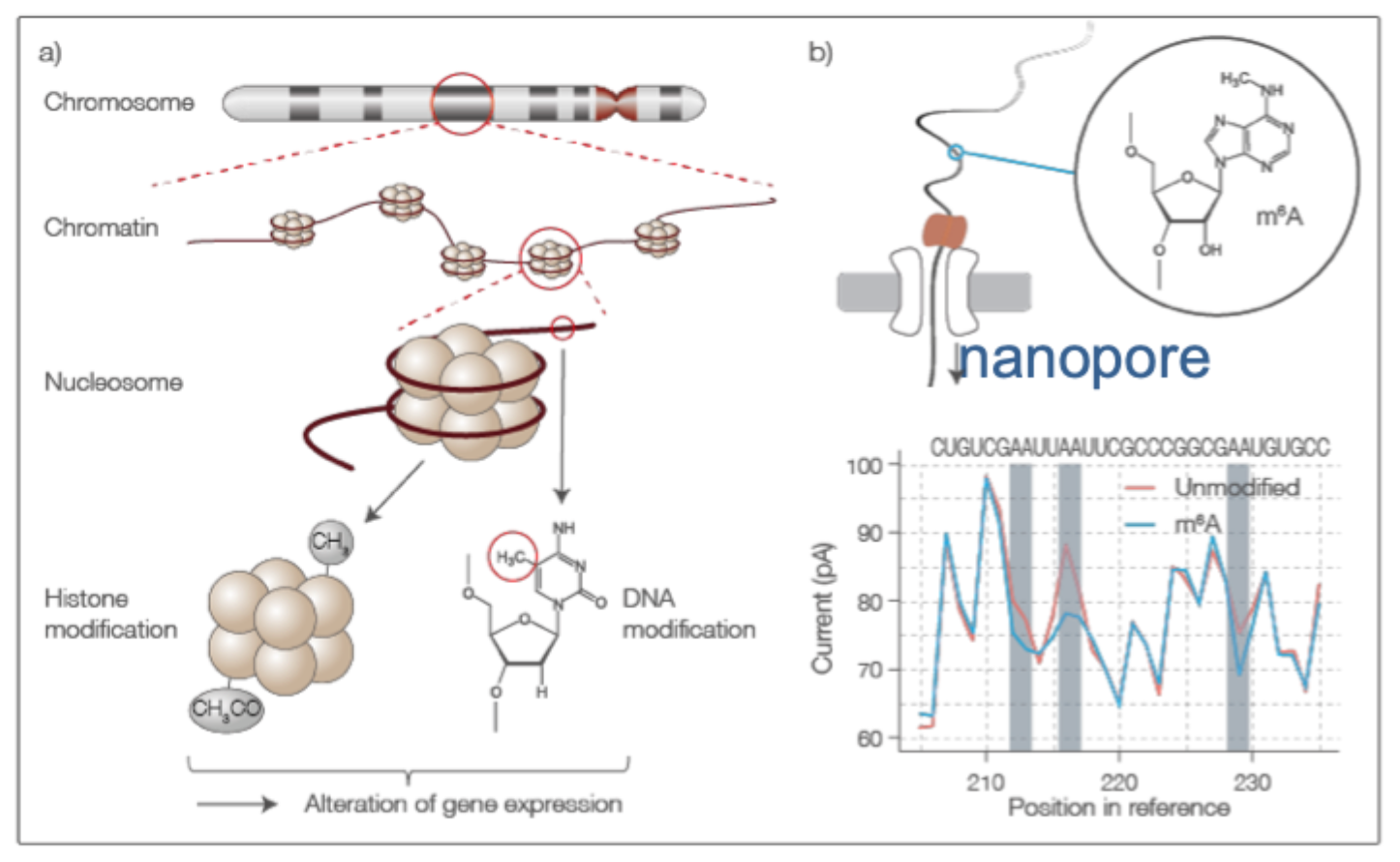
Detection of DNA methylation
Methylation- sensitive restriction enzymes
Antibodies (dotblot/ immune precipitation)
Nanopore sequening
Bisulfite sequencing (targeted, whole genome, microarrays)
Bisulfite sequencing: detection of cytosine methylation in DNA
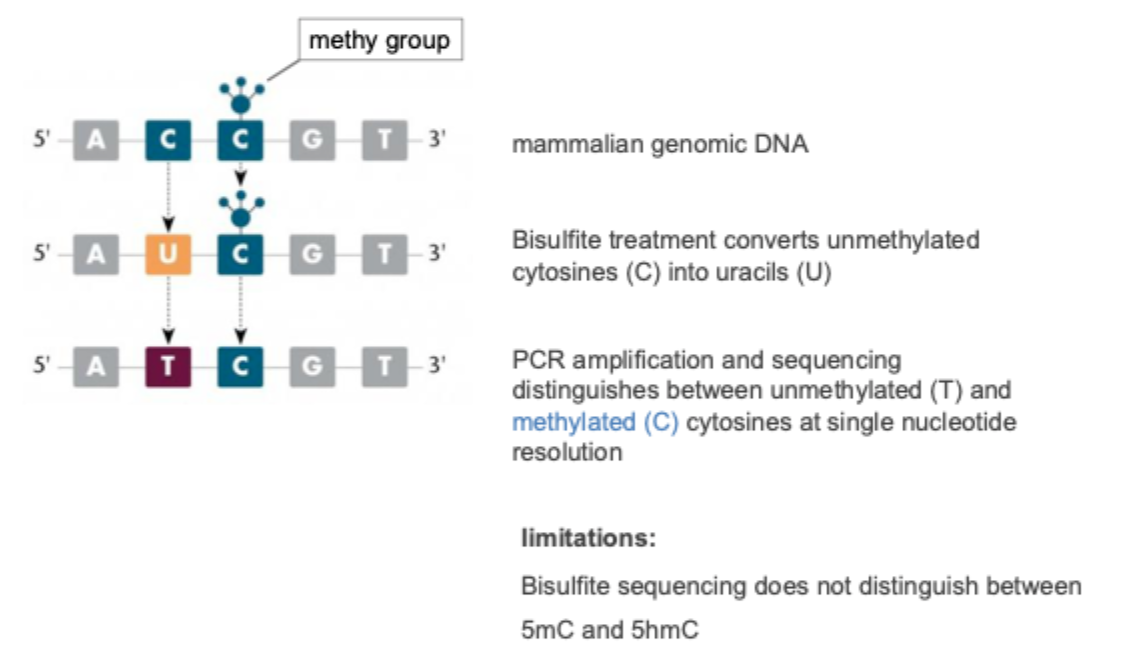
Environmental influences: metal programming
Poor nutrition (the environment) in early life leads to “epigenetic programming” of certain organs and tissues:
a factor in the aetiology of type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease and related health problems
Example of how environmental factors may influence the epigenome
The dutch hunger winter 1944- 1945
daily rations: 400-80- calories
~20 years after dutch hunger winter children started to experience obesity
~54 years after DNA methylation differences after exposure to prenatal famine are common and timing- and sex- specific
A type of cellular memory system
Biological memory can be defined as a sustained cellular response to a transient stimulus
The ability of a daughter cell to retain a memory of the gene expression patterns that were present in the parent cell is an example of epigenetic inheritance
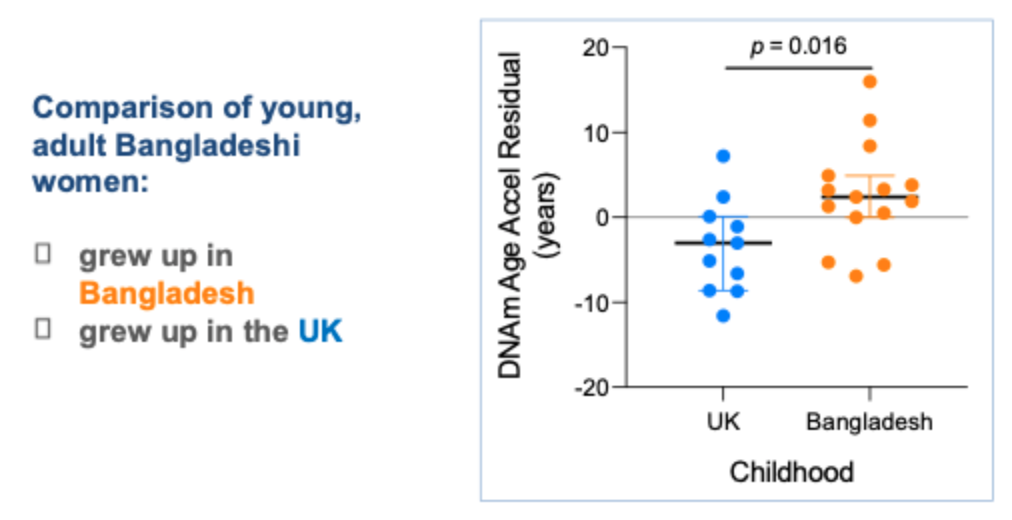
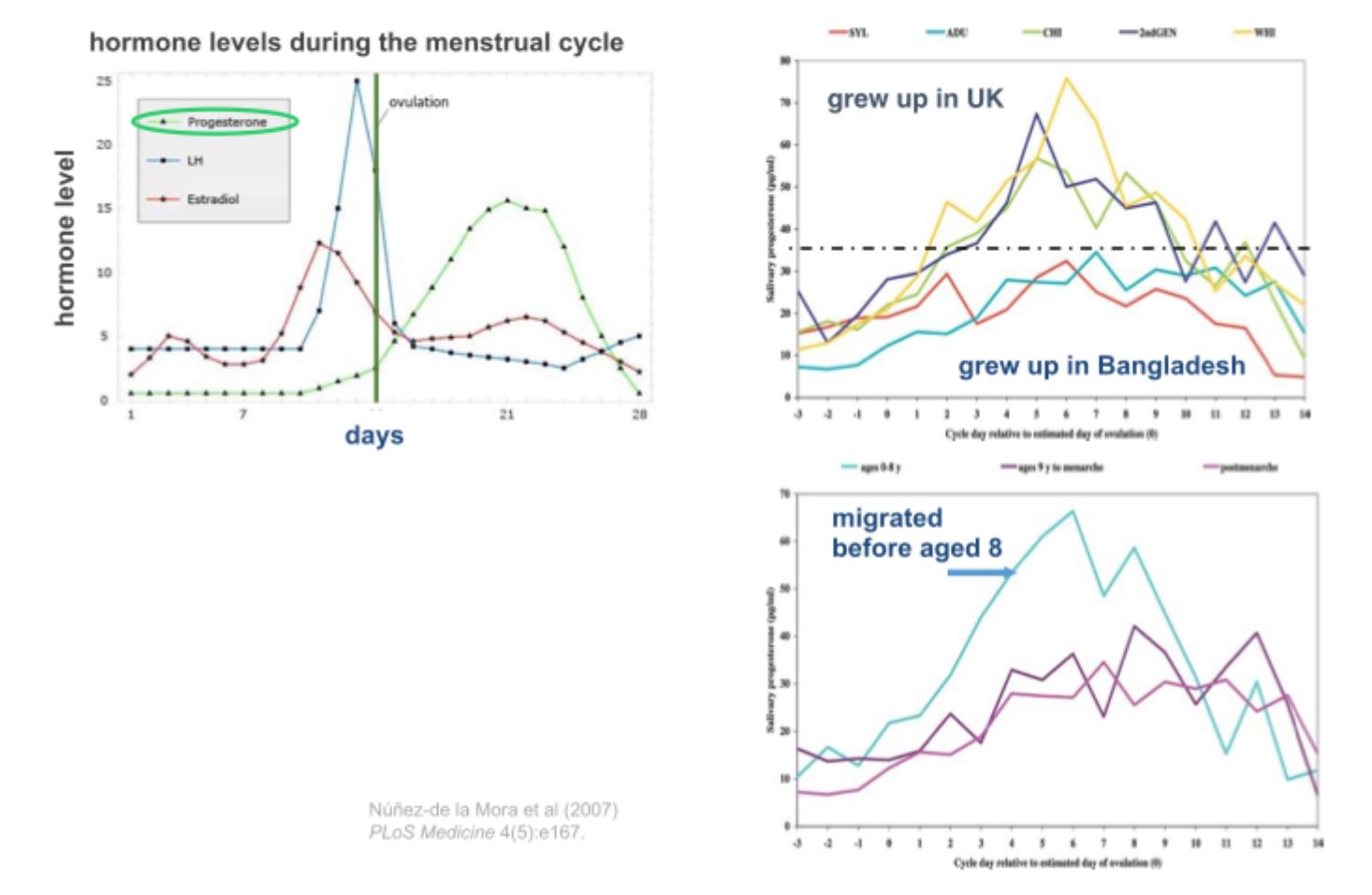
Migrant model (changing enviornment) at different points in the life course
Bangladesh/ UK
Childhood environment influences levels of reproductive steroid hormones
Comparing mouse and human data
Question: what is early life stress?
Hypothesis: early life immunological stress (gastrointestinal infection)
Experimental work: compare DNA methylation patterns between mouse and human samples, gene expression in mouse
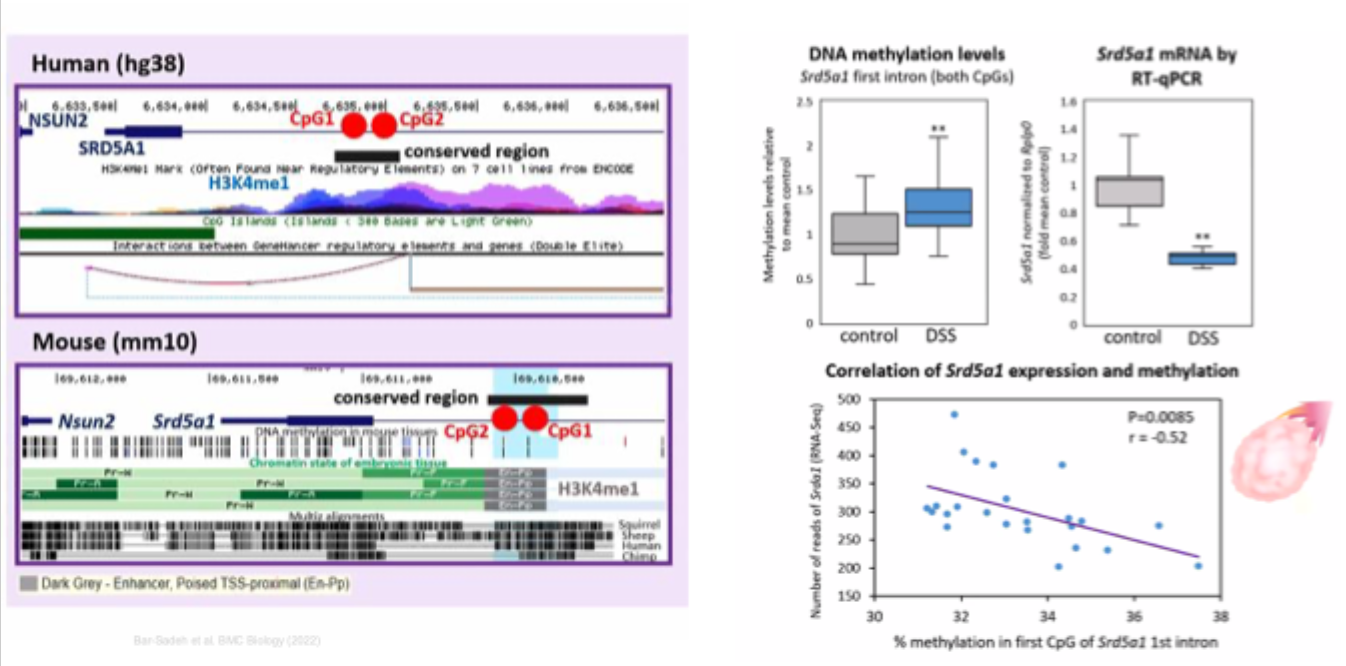
Differential gene expression in mouse ovaries
13 genes in mice ←→ differential DNA methylation in human orthologs
Correlation with altered DNA methylation levels in woman?
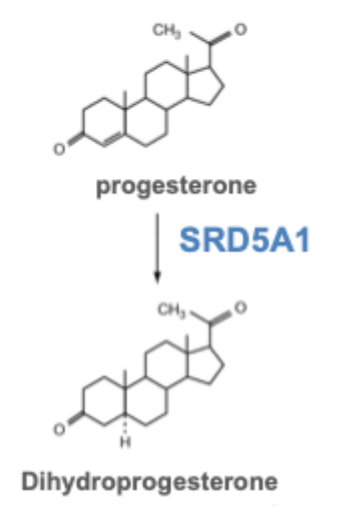
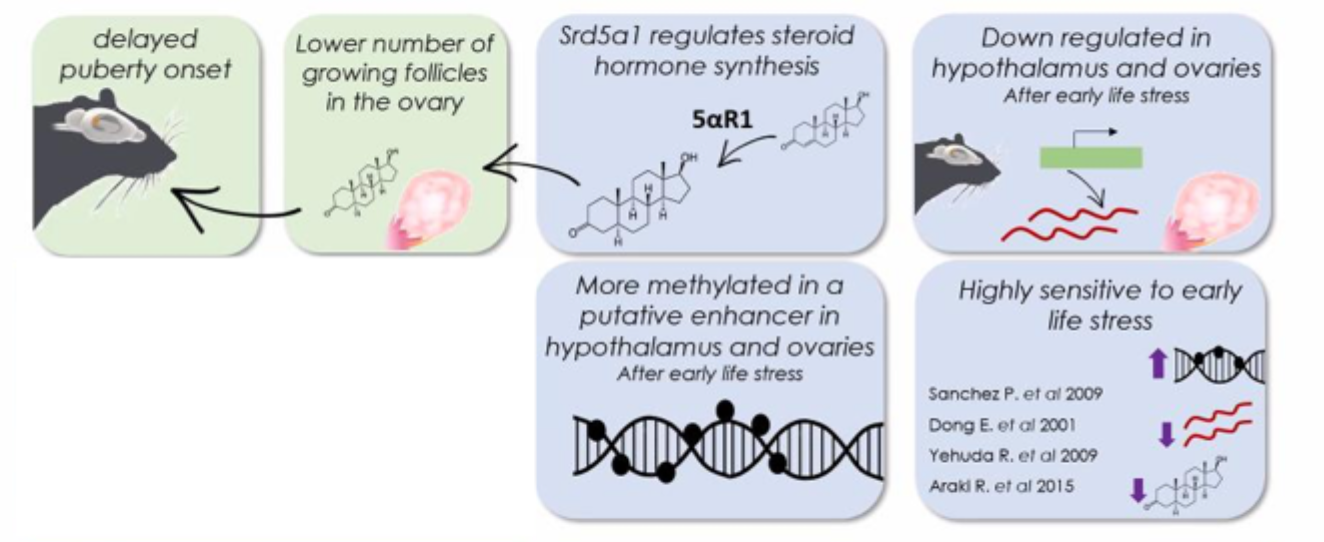
1 of the down- regulated genes in mouse ovaries: steroid 5 alpha- reductase 1 (SRD5A1)
SRD5A1 processes steroid hormones
e.g. progesterone → dihydroprogesterone
reduced SRD5A1 expression reported:
in adult rodents
humans after early- life stress
survivors of the Holocaust
Altered SRD5A1 methylation in a putative enhancer in mouse and human
Summary
Early life immune challenge alters reproductive phenotype
SRD5A1 is a strong candidate mediating long- term effects of reproduction
2 classic cellular memory (epigenetic) systems
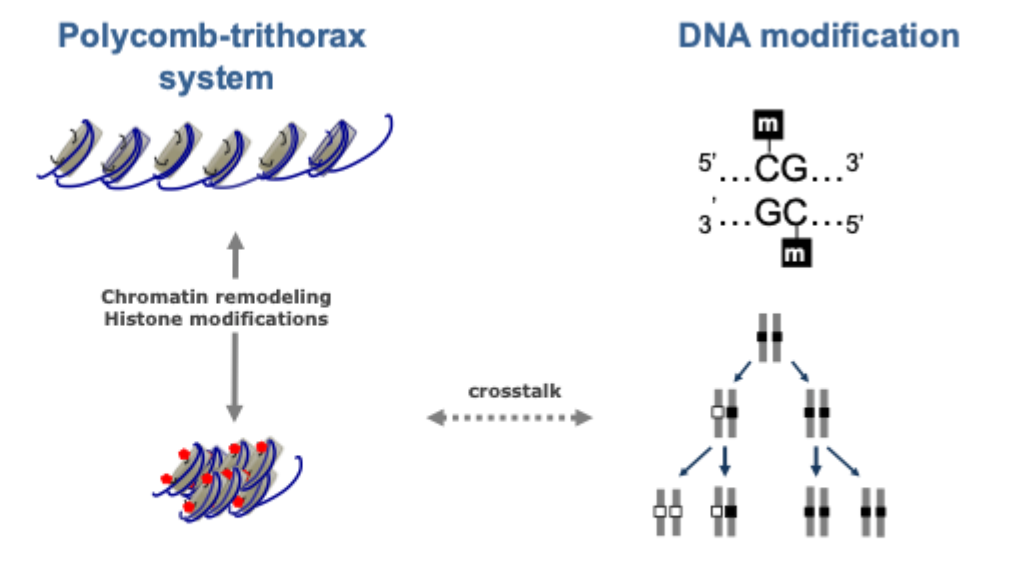
Polycomb- trithorax system
DNA modification