Gene Regulation and Antigenic Variation in Trypanosomes
1/128
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
129 Terms
What is the main focus of the paper by Navarro and Gull published in Nature in 2001?
The regulation of gene expression at the level of transcription initiation.
How does estrogen activate transcription?
By recruiting RNA Polymerase II to an 'open promoter'.
What happens to the promoter when it is in a silent state?
It is in closed chromatin and does not activate transcription.
How many genes can be activated by the transcription process discussed in the paper?
Approximately 2000 genes.
What role does Activation-Induced Cytidine Deaminase (AID) play in gene regulation?
It is involved in regulating gene expression by DNA recombination.
Which chromosome contains the immunoglobulin gene mentioned in the notes?
Chromosome 14.
What is the consequence of a translocation event involving the C-Myc oncogene?
It can lead to cancer by disrupting the relationship between gene and enhancer, as seen in Burkitt's lymphoma.
What is phase variation in the context of gene regulation?
It is a process that allows genes to be expressed in different orientations, altering their expression, such as in the flagellin genes of Salmonella.
What is the significance of site-specific recombination in gene regulation?
It allows for the alteration of gene expression by changing the arrangement of genes and their promoters.
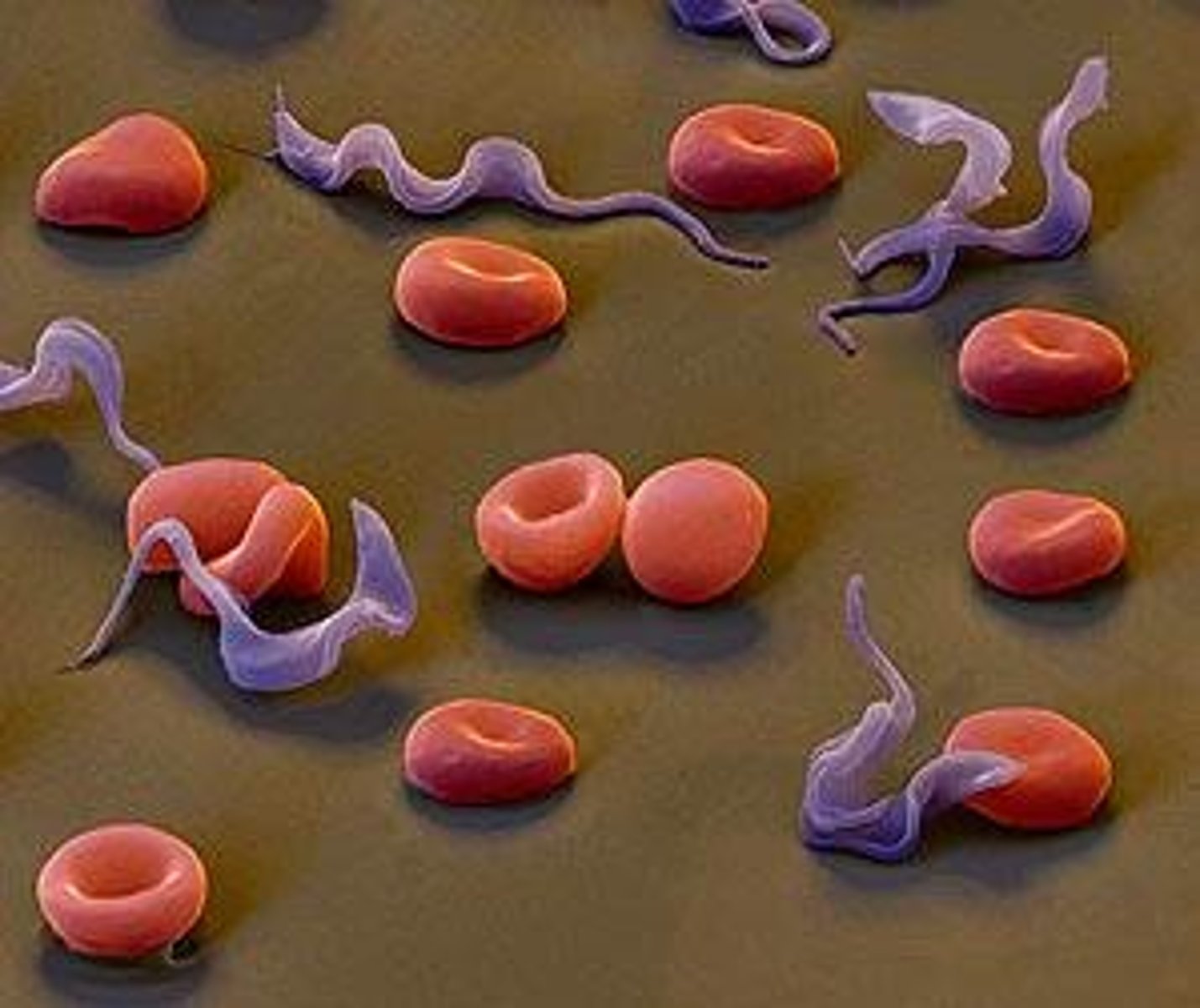
What organism causes African Sleeping Sickness?
Trypanosoma brucei.
How does Trypanosoma brucei evade the host immune system?
By long-term infection and telomeric regulation of Variant Surface Glycoprotein (VSG) expression.
What is the function of Variant Surface Glycoprotein (VSG) in Trypanosoma brucei?
It helps the parasite evade the host immune response.
What is the role of telomeres in the regulation of VSG expression?
They regulate the active and silent VSG arrays, contributing to immune evasion.
What is the relationship between the C-Myc oncogene and chromosome 8?
C-Myc is located on chromosome 8 and can be involved in translocation events leading to cancer.
What type of immune response does phase variation help evade in Salmonella?
The host immune response.
What is the outcome of a translocation event involving chromosomes 14 and 8?
It can result in the activation of oncogenes and contribute to cancer development.
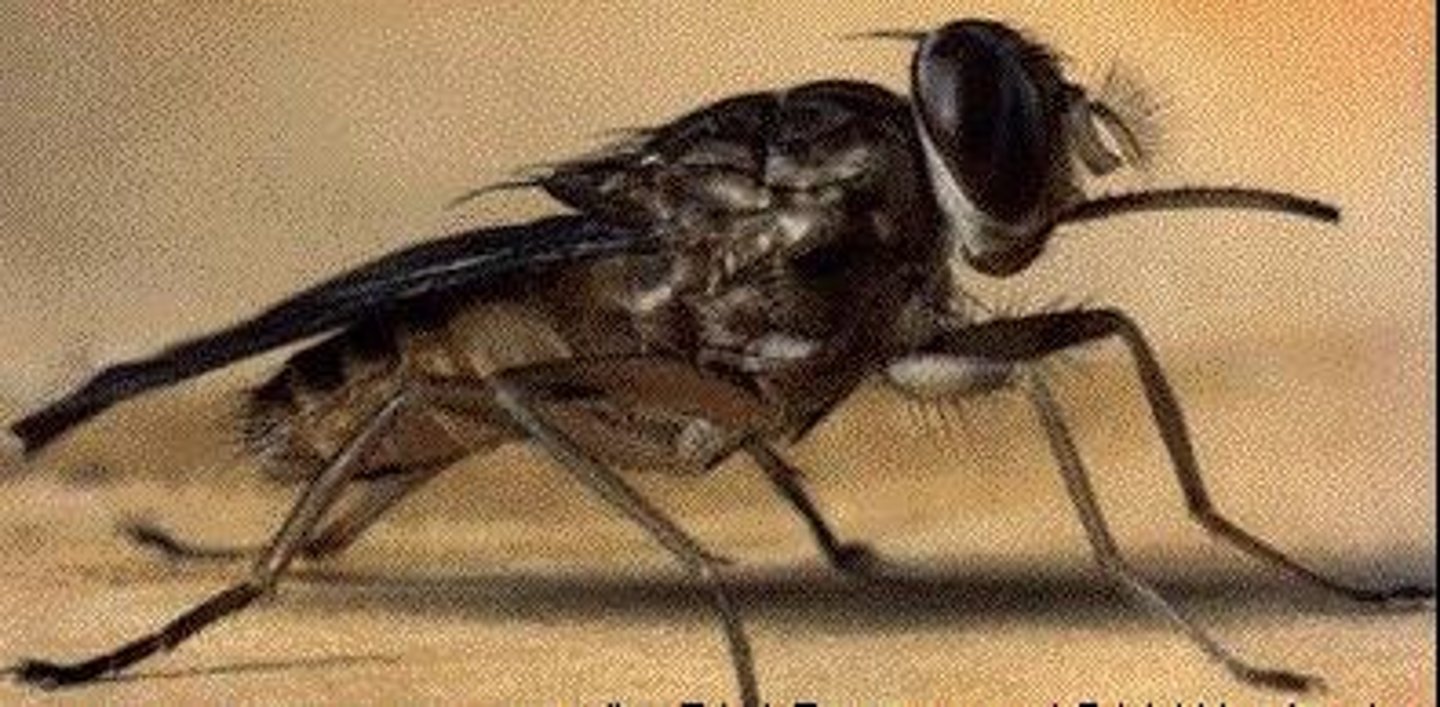
What is the primary method of transmission for Trypanosoma brucei?
It is transmitted by the Tsetse fly.

What is the significance of the 'silent VSG arrays' in Trypanosoma brucei?
They are inactive and help the parasite avoid detection by the host's immune system.
What is the effect of removing promoters relative to the coding sequence in gene regulation?
It can alter gene expression by changing how genes are oriented.
What disease is caused by Trypanosoma brucei?
Sleeping sickness in humans.
What is the Procyclic form (PF) of Trypanosoma brucei characterized by?
No Variant Surface Glycoprotein (VSG) expressed.
What is the primary form of Trypanosoma brucei found in mammalian blood?
Mammalian Bloodstream Form (BS).
What regulates the expression of Variant Surface Glycoprotein (VSG) in Trypanosoma brucei?
Telomeric regulation.
What is the significance of the Variant Surface Glycoprotein (VSG) in Trypanosoma brucei?
VSG is crucial for immune evasion as only one VSG is expressed at a time.
What is the approximate number of VSG genes in Trypanosoma brucei?
~1,000 VSG genes.
Where is the VSG gene expression site located in Trypanosoma brucei?
In the Bloodstream form.
What is the role of the kDNA in Trypanosoma brucei?
It is part of the mitochondrial DNA structure.
What is the surface coat of Trypanosoma brucei composed of?
Variant Surface Glycoproteins (VSGs).
What happens to VSG expression in the Procyclic form of Trypanosoma brucei?
VSG is not expressed.
What is the relationship between VSG and immune response in hosts?
VSG allows Trypanosoma brucei to evade the host's immune response.
What is the cellular location of the VSG in Trypanosoma brucei?
The VSG is located on the surface of the parasite.
What is the difference between active and inactive VSG expression?
Active VSG expression involves the expression of a specific VSG, while inactive means no VSG is expressed.
What is the function of the nucleus in Trypanosoma brucei?
It houses the genetic material and is involved in VSG gene regulation.
What is the significance of telomeres in VSG expression?
Telomeres regulate the switching of VSG expression.
What type of organism is Trypanosoma brucei?
A parasitic protozoan.
What does the term 'bloodstream form' refer to in Trypanosoma brucei?
The stage of the parasite that circulates in the blood of the host.
What does the 'X' notation signify in the context of VSG expression?
Indicates that a specific VSG is not expressed.
How does Trypanosoma brucei manage to avoid the host immune system?
By expressing only one VSG at a time, which changes frequently.
What is the role of the midgut in the life cycle of Trypanosoma brucei?
It is where the Procyclic form develops.
What is the primary challenge for the immune system posed by Trypanosoma brucei?
The ability to change VSGs and evade detection.
What is the primary research focus regarding VSG in Trypanosoma brucei?
Understanding the mechanisms of VSG expression and immune evasion.
What is the primary function of Variant Surface Glycoprotein (VSG) in Trypanosoma brucei?
VSG helps the parasite evade the host's immune response by varying its surface proteins.
How many VSG genes are present in Trypanosoma brucei?
Approximately 1,000 VSG genes.
Where is VSG expressed in the bloodstream form of Trypanosoma brucei?
In the VSG expression site (BES) located at the telomere.
What is the key regulation mechanism for antigenic variation in Trypanosoma brucei?
Only one VSG is expressed at a time.
What is nonreciprocal gene conversion in the context of VSG expression?
It is the process where genetic information is moved from a silent part of the genome to an expressed part.
What is the primary mechanism of VSG switching?
DNA recombination.
What is duplicative transposition in relation to VSG genes?
It is a mechanism that may contribute to the variation of VSG expression.
What is the significance of silent VSG genes in Trypanosoma brucei?
They provide a reservoir for antigenic variation by allowing the parasite to switch to different VSGs.
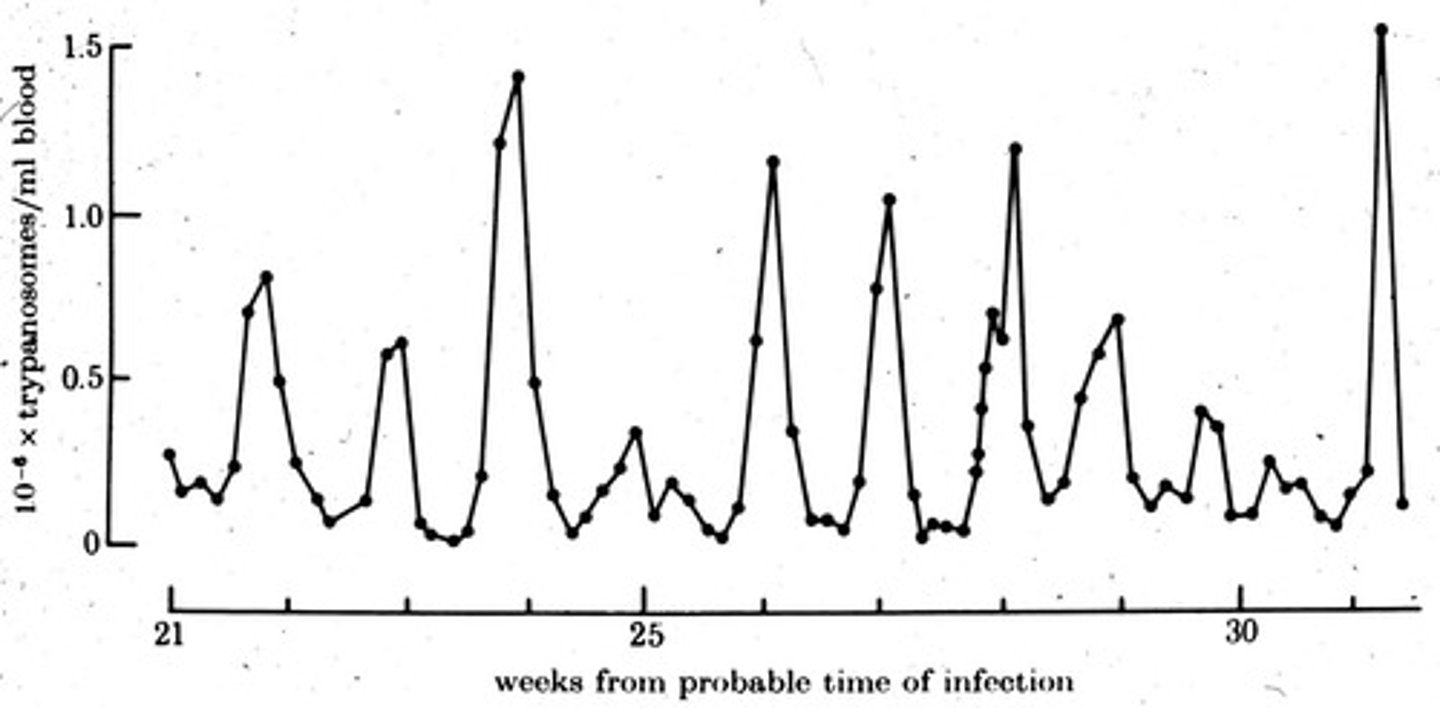
What happens to the immune response in relation to VSG expression over time?
The immune response can lead to the destruction of the parasite, prompting VSG switching.
What is the role of the chromosome core in VSG gene expression?
It contains silent VSG genes that can be recombined into an active VSG expression site.
How does Trypanosoma brucei achieve mono-allelic exclusion?
By ensuring that only one VSG is expressed at a time from multiple telomeric VSG expression sites.
What is the relationship between VSG expression and the immune response in the host?
The immune response targets the expressed VSG, leading to the need for the parasite to switch its VSG to evade detection.
What are the two main types of VSG switching mechanisms mentioned?
Recombination and nonreciprocal gene conversion.
What is the consequence of immune destruction by the host on Trypanosoma brucei?
It drives the proliferation of the parasite and necessitates VSG switching.
What is the significance of the VSG surface coat?
It protects the parasite from the host's immune system and is crucial for its survival.
How does the structure of VSG genes contribute to antigenic variation?
The presence of multiple VSG genes allows for a diverse range of surface proteins to be expressed.
What is the role of kDNA in Trypanosoma brucei?
kDNA is a unique mitochondrial DNA structure that plays a role in the parasite's energy metabolism.
What does the term 'antigenic variation' refer to in Trypanosoma brucei?
The ability of the parasite to change its surface antigens to evade the host's immune response.
What is the impact of VSG switching on the infection timeline in the host?
VSG switching can prolong the infection by continuously evading the immune response.
What is the relationship between VSG expression sites and telomeres?
VSG expression sites are located at the telomeres of chromosomes, where active VSG genes are expressed.
What is the importance of the immune response timeline in relation to VSG expression?
It influences the frequency and timing of VSG switching to maintain infection.
What does 'chromosome core' refer to in the context of VSG genes?
It refers to the part of the chromosome that contains silent VSG genes.
What is VSG in the context of Trypanosoma brucei?
VSG stands for Variant Surface Glycoprotein, which is expressed on the surface of the parasite.
What mechanism allows Trypanosoma brucei to express only one VSG at a time?
Mono-allelic exclusion allows only one VSG expression site (ES) to be active at any given time.
What is the role of Pol I in VSG transcription?
Pol I is exclusively localized within the nucleus and is responsible for high levels of VSG synthesis.
What is the significance of the 'Expression Site Body' in VSG expression?
The 'Expression Site Body' is where Pol I is localized, facilitating mono-allelic exclusion and VSG expression.
How does the localization of Pol I contribute to VSG expression?
Exclusive localization of Pol I within the nucleus allows for efficient transcription of a single VSG.
What happens to VSG expression in the procyclic form of Trypanosoma brucei?
In the procyclic form, all VSGs are repressed.
What is the function of silent VSG genes?
Silent VSG genes serve as potential alternatives for future VSG expression, allowing the parasite to evade the host's immune response.
What is the relationship between VSG expression and the nucleolus?
The nucleolus is involved in the localization of Pol I, which is necessary for VSG transcription.
What are the two main mechanisms involved in VSG switching?
Recombination and transcriptional silencing.
Why is Pol II not localized for VSG transcription?
Pol II is needed everywhere in the cell, unlike Pol I, which is specifically localized for VSG expression.
What is the role of the chromosomal core in VSG expression?
The chromosomal core contains multiple telomeric VSG expression sites that are involved in the regulation of VSG expression.
What is the significance of mono-allelic exclusion in antigenic variation?
Mono-allelic exclusion ensures that only one VSG is expressed at a time, allowing the parasite to change its surface antigens and evade the immune system.
How does Trypanosoma brucei ensure high levels of VSG synthesis?
By utilizing Pol I, which is a highly processive polymerase, for VSG transcription.
What is the role of the nuclear membrane in VSG gene expression?
Silent telomers are localized to the nuclear membrane, which may play a role in regulating VSG expression.
What is the significance of the non-canonical CTD in Pol I and Pol II?
Pol I and Pol III do not have C-terminal domains (CTDs), which means their transcripts lack 5' caps or polyA tails.
What is the relationship between VSG expression sites and telomeric regions?
There are multiple telomeric VSG expression sites that require mono-allelic exclusion for regulation.
What did Navarro and Gull (2001) investigate regarding VSG expression?
They explored how nuclear compartmentalization mediates the activity of only one VSG expression site.
What is the outcome of co-localizing Pol I with the active VSG expression site?
Co-localization may facilitate the transcription of the active VSG while keeping other sites inactive.
What is the primary question addressed in the study of VSG expression in Trypanosoma brucei?
How does the parasite allow only one VSG expression site to be active at a time?
What is the role of ribosomal RNAs in the context of Pol I?
Ribosomal RNAs are transcribed by Pol I and are part of the nucleolus, which is involved in VSG expression.
What is the significance of having silent VSG genes in the genome?
Silent VSG genes provide a reservoir for future antigenic variation, allowing the parasite to adapt to host immune responses.
What is the role of Pol I in the transcription of ribosomal RNAs?
Pol I is responsible for transcribing ribosomal RNAs in the nucleolus.
Where is Pol I localized when transcribing the active VSG expression site (ES)?
Pol I is co-localized with the active VSG ES.
What does DAPI stain in the context of procyclic forms of Trypanosoma brucei?
DAPI stains DNA and is used to visualize the nuclei of procyclic forms.
What is the significance of fibrillarin in the study of nucleolar markers?
Fibrillarin is a nucleolar marker used to identify nucleolar structures.
What does the presence of extranucleolar Pol I bodies indicate?
Extranucleolar Pol I bodies are transcriptionally active structures involved in RNA synthesis.
What method is used to detect nascent RNA in permeabilized bloodstream-form nuclei?
Br-UTP labeling is used to detect nascent RNA.
How does α-amanitin affect transcription activity in the study?
α-amanitin inhibits Pol II transcription, allowing the remaining signal to be attributed to Pol I.
What is the relationship between the active VSG ES and the extranucleolar Pol I body?
The active VSG ES co-localizes with the extranucleolar Pol I body.
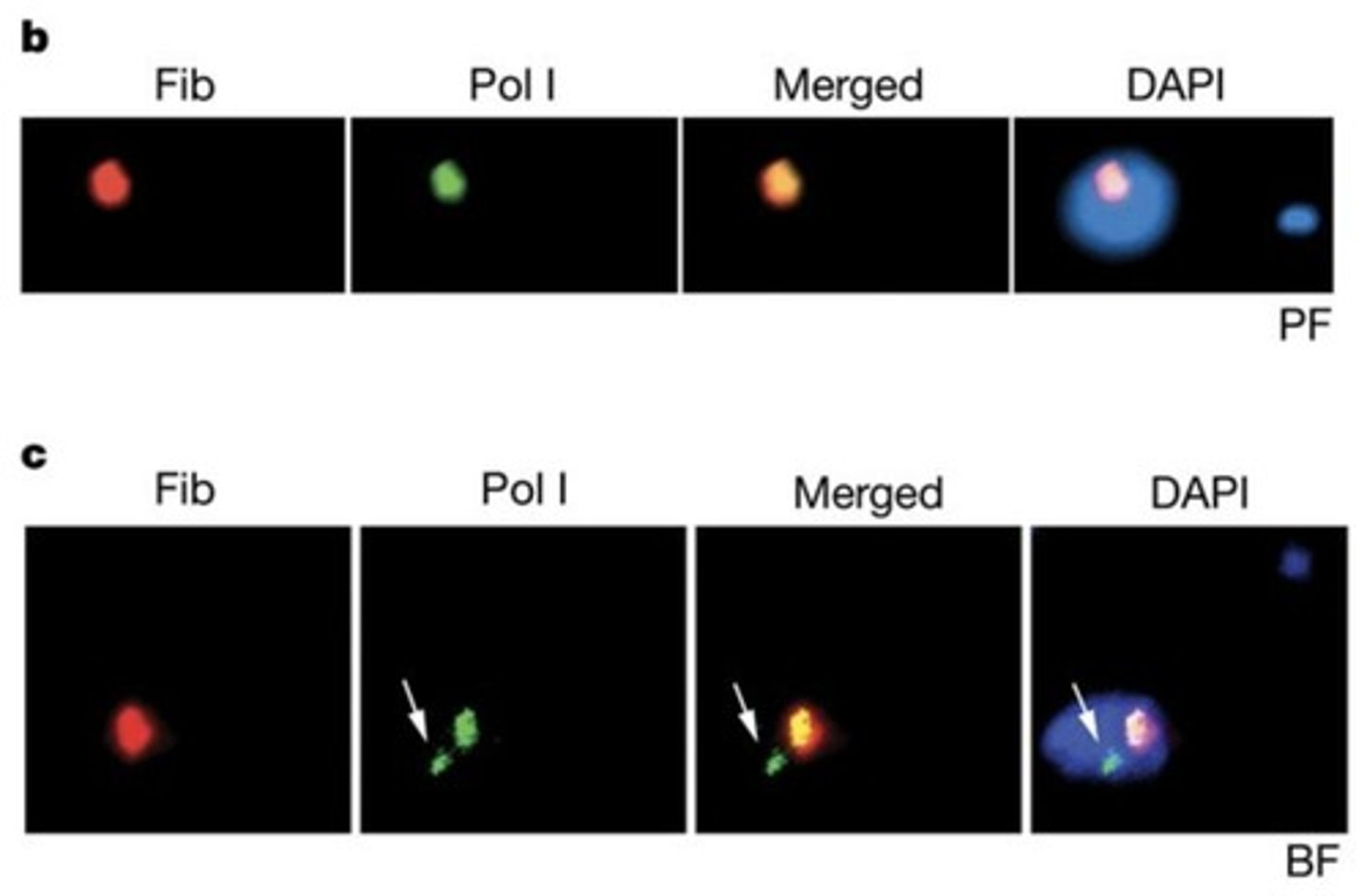
What technique is used to visualize active VSG ES tagged with GFP?
DNA FISH is used to localize active VSG ES by tagging with GFP.
What happens to inactive VSG ES in relation to Pol I ESB?
Inactive VSG ES does not co-localize with Pol I ESB.
What is the function of guide RNAs in the mitochondrial genome of Trypanosoma brucei?
Guide RNAs are involved in RNA editing within the mitochondrial genome.
What is the structure of the mitochondrial genome in Trypanosoma brucei?
The mitochondrial genome consists of 1,000 copies of kDNA.
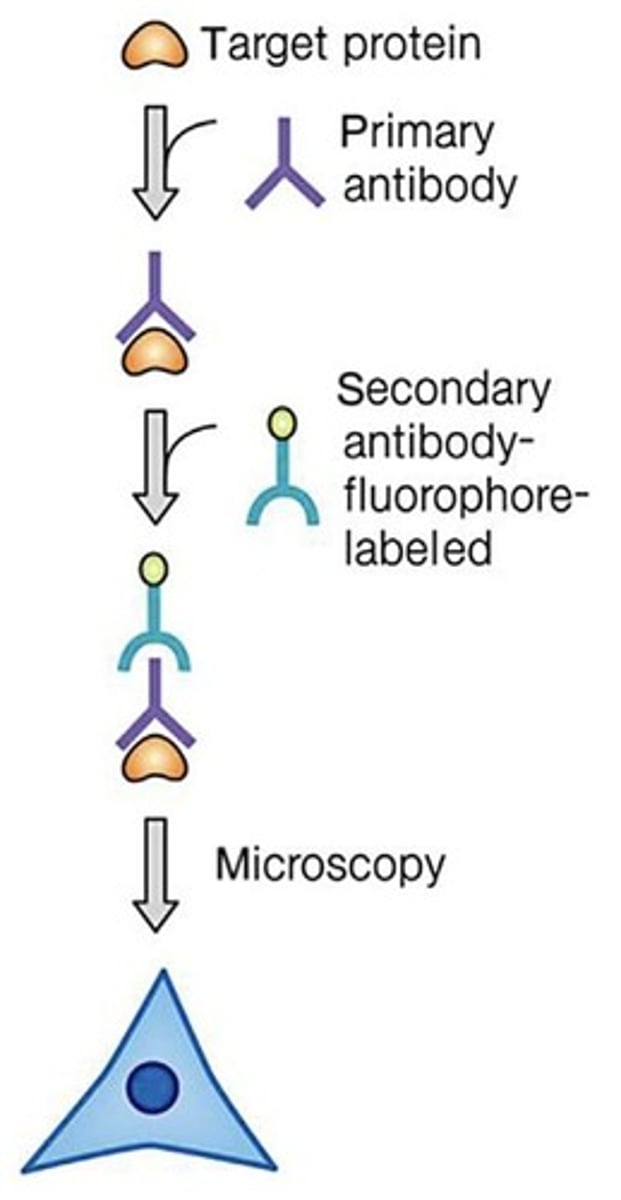
What does the immunofluorescence assay (IFA) detect in this study?
IFA detects the localization and activity of Pol I, Pol II, and Pol III.
What is the significance of using a labeled ssDNA probe in the study?
It is used to visualize telomeric VSG ESs and identify active expression sites.
What does the term 'uncondensed kDNA network' refer to?
It refers to the relaxed structure of the mitochondrial DNA network in vivo.
What is the role of the Lac repressor in the context of VSG expression?
The Lac repressor is used to tag active ES with GFP for visualization.