Physical Geography
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
regions
areas of places that have more similarities than they have differences.
Physical regions
share similar physical features
Functional regions
serve as a central location for a service.
Cultural regions
identified by shared human characteristics such as language, religion, tradition, or economy. do not have firm borders, they have transition zones, areas which exhibit characteristics similar to multiple regions around it.
Rust Belt
central New York; western Pennsylvania; the entirety of Ohio; northern Indiana; south-central Michigan, including Detroit and Grand Rapids; major cities in Illinois; and the area surrounding Milwaukee, Wisconsin.
suffered economically following the outsourcing of many factory jobs abroad, resulting in the de-industrialization of these states and subsequent economic downturn.
least culturally driven
Bible Belt
states south of Virginia (excluding Florida) and east of Oklahoma. States such as Mississippi, Alabama, Tennessee, and Arkansas are often referred to as part of the Bible Belt due to their conservative and religious populations.
steady population growth since the mid-20th century, driven by its lower cost of living and increased job opportunities in industries like manufacturing, energy, and technology.
Midwest
Indiana, Illinois, Kansas, Iowa, Minnesota, Michigan, Ohio, Missouri, North Dakota, Nebraska, Wisconsin, and South Dakota
relatively flat landscape and culturally conservative population,
slower population growth and even population decline in some areas since the mid-20th century, driven by the loss of manufacturing jobs and by economic shifts that have led to out-migration to regions with more job opportunities, like the Sun Belt
New England
Maine, New Hampshire, Vermont, Massachusetts, Connecticut, and Rhode Island.
Protestant values
slower population growth compared to other U.S. regions, partly due to a higher cost of living and limited job opportunities in some industries,
Sun Belt
It spans from the Southeast (Florida, Georgia, and Alabama) to the Southwest (Texas, Arizona, and New Mexico) and incorporates portions of other states like California, North Carolina, and Tennessee.
region in the southern and southwestern U.S., known for its warm climate, economic growth, and cultural diversity.
The Sun Belt has thriving industries, such as technology, aerospace, and energy, and a lifestyle centered around outdoor activities, unique cuisines, and Southern and Western traditions.
population growth
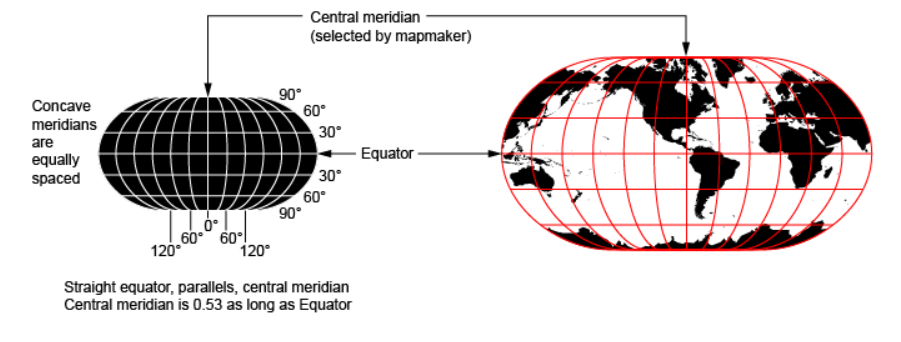
Robinson projection
designed to show the entire world at once, but in doing so compromises both trueness to area and the angle.
the global poles are represented as long lines rather than points – resulting in large distortion of land areas near the poles. Despite these weaknesses, the Robinson projection is considered one of the best single-image global map projections.
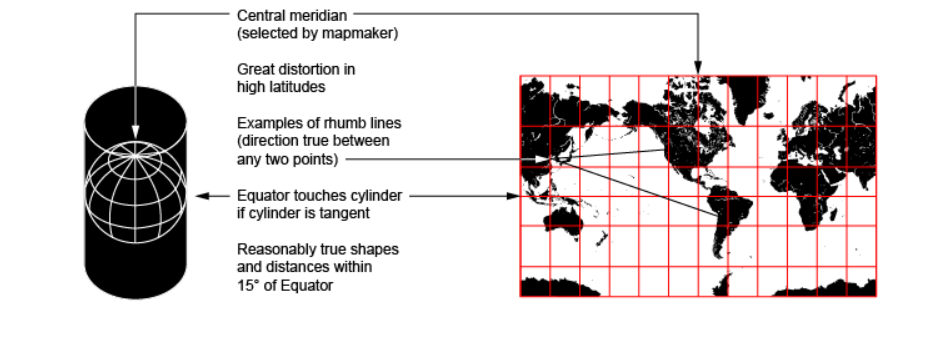
Mercator projection
cylindrical map used mainly for navigation, as its key strength lies in its ability to represent the route between any two points as a straight line.
endency to inflate objects at an increasing rate the farther they are from the equator – resulting in areas such as Greenland and Antarctica to be represented as many times their actual size.
Cassini projection
depiction of the rotated globe on a flat surface and presents it as an ellipsoid shape.
surveying
Armadillo projection
is an example of a perspective-maintaining map projection.
In this image the round shape of the earth is shown as land masses curl away from one another, providing a perspective approximately true to form.
sacrifices trueness to both area and angle, and the ability to show all of the globe in a single image.
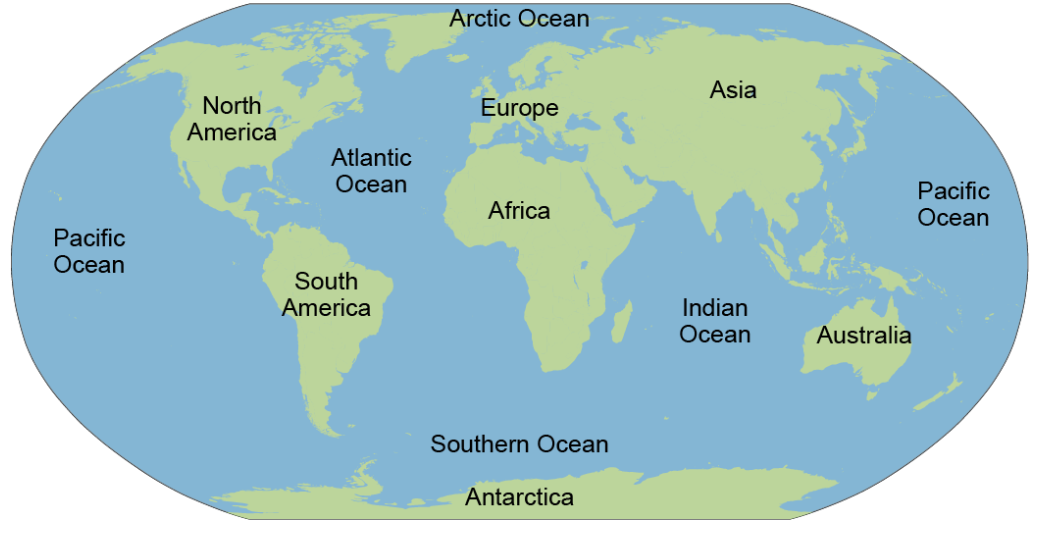
major continents and oceans
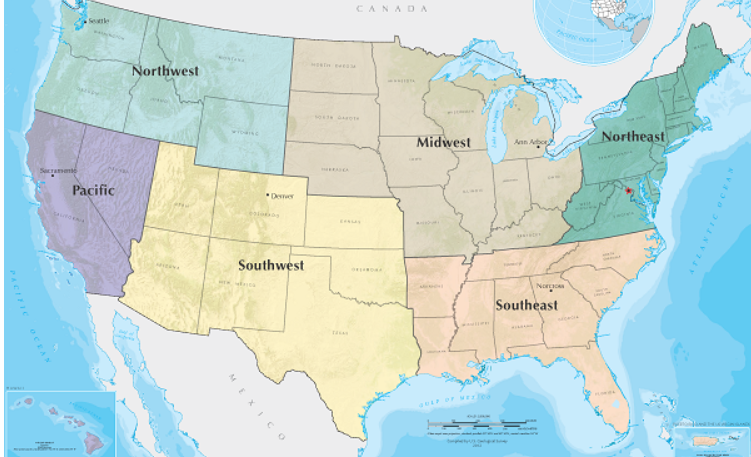
Major USA region
Rain Shadow Effect
the phenomenon in which desert-like conditions appear on the leeward side of a mountain or mountain range.