BUS 202 - Ch.16-20 Study Guide
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
A key idea in process costing that refers to the number of whole units that could have been started and completed given the costs incurred in a period is known as:
equivalent units of production
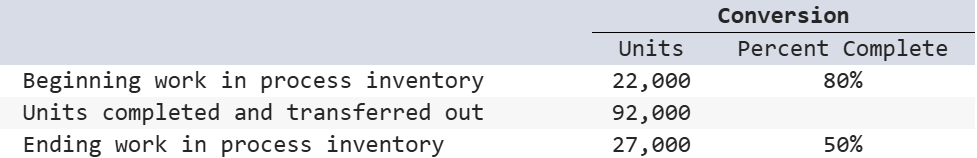
A process manufacturer that uses the weighted-average method reports the following. Equivalent units of production for conversion are:
105,500
A manufacturer used $100,000 of direct materials in its Roasting department. The journal entry to record the use of direct materials consists of a:
Debit Work in Process Inventory—Roasting for $100,000; credit Raw Materials Inventory for $100,000.
Which of the following products is least likely to be produced in a process operation?
Custom cabinets
A manufacturer used $67,000 of indirect materials in production. The journal entry to record this transaction includes a:
Credit to Raw Materials Inventory for $67,000.
Which of the following products is most likely to be produced in a process operation?
cereal
A production department's output for the most recent month consisted of 9,300 units completed and transferred to the next stage of production and 6,300 units in ending Work in Process inventory. The units in ending Work in Process inventory were 50% complete with respect to both direct materials and conversion costs. Calculate the equivalent units of production for the month, assuming the company uses the weighted average method.
12,450 units
Clarksen Company uses a process costing system. The company requisitioned $93,000 of materials for Department A and $67,000 of materials for Department D. The entry to record the use of the direct materials by these two departments is:
Debit Work in Process Inventory—Department A $93,000; debit Work in Process Inventory—Department D $67,000; credit Raw Materials Inventory $160,000.
The combined costs of direct labor and factory overhead per equivalent unit used by many businesses with process operations is called:
Conversion cost per equivalent unit
Bryant Manufacturing produces its product in two sequential processing departments. During October, the first process finished and transferred 330,000 units of its product to the second process. Of these units, 75,000 were in process at the beginning of the month and 255,000 were started and completed during the month. At month-end, 55,000 units were in process. Using the FIFO method, compute the number of equivalent units of production for direct materials for the first process for October assuming that beginning work in process inventory is 30% complete for direct materials cost and ending inventory is 80% complete for direct materials cost.
351,500

GSP Manufacturing uses machine hours to allocate overhead costs to products. Budgeted information for the current year follows:
The plantwide overhead rate based on machine hours is:
$85.00 per MH.
The use of departmental overhead rates will generally result in:
The use of a separate cost allocation base for each department in the factory.
Water Sports Company budgets overhead cost of $840,000 for the year. The company manufactures two types of boats: Pontoons and Speedboats. Budgeted direct labor hours per unit are 16 for the Pontoon model and 24 for the Speedboat model. The company budgets production of 200 units of the Pontoon model and 200 units of the Speedboat model for the year. The plantwide overhead rate using budgeted direct labor hours is:
$105.00 per DLH.
_____________ costs support the company as a whole.
Facility-level
Overhead costs:
Cannot be traced to units of product in the same way that direct labor can
From an ABC perspective, what causes overhead cost to be incurred?
Activities.
Water Sports Company budgets overhead cost of $840,000 for the year. The company manufactures two types of boats: Pontoons and Speedboats. Budgeted direct labor hours per unit are 16 for the Pontoon model and 24 for the Speedboat model. The company budgets production of 200 units of the Pontoon model and 200 units of the Speedboat model for the year. What is the total number of budgeted direct labor hours for the year?
8,000 direct labor hours.
A method of assigning overhead costs to a product using a single overhead rate is:
Plantwide overhead rate method.
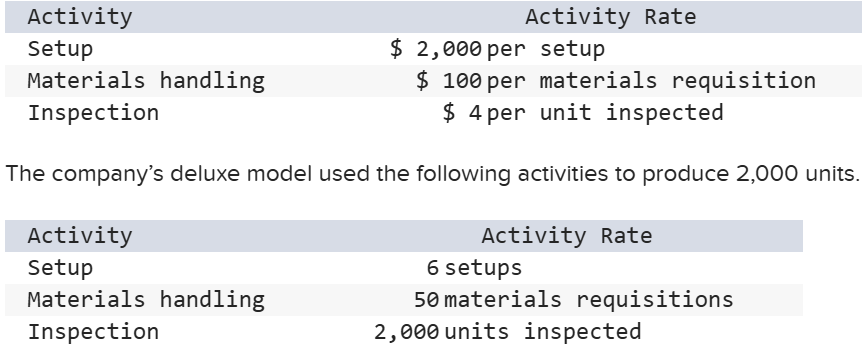
A company computed the following activity rates using activity-based costing.
The company’s deluxe model used the following activities to produce 2,000 units. Compute the overhead cost per unit for the deluxe model using activity-based costing.
$12.50
When calculating the departmental overhead rate, the numerator should be?
The budgeted departmental overhead cost.
The margin of safety is the excess of:
Expected sales over break-even sales.
The contribution margin ratio:
Is the percent of each sales dollar that remains after deducting the unit variable cost.
A cost that includes both fixed and variable cost components is called a:
Mixed cost.
A cost that remains unchanged in total despite variations in volume of activity within a relevant range is a:
Fixed cost.
A cost that changes in total in proportion to changes in volume of activity is a(n):
Variable cost.
In cost-volume-profit analysis, the contribution margin per unit is:
Selling price per unit less variable costs per unit.
The difference between selling price per unit and variable costs per unit is the:
Contribution margin per unit.
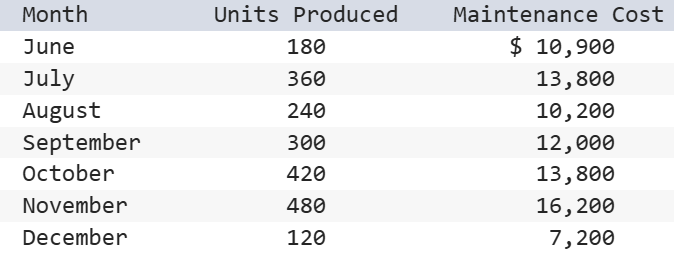
The following information is available for a company’s maintenance cost over the last seven months.
Using the high-low method, the variable component of its maintenance cost is:
$25.00 per unit.
Contribution margin divided by income is the:
Degree of operating leverage.
The contribution margin per unit expressed as a percentage of the product's selling price is the:
Contribution margin ratio.
Which of the following costing methods charges all manufacturing costs to its products?
Absorption costing
Which of the following is not a product cost under variable costing?
Fixed overhead.
Using absorption costing, which of the following manufacturing costs are assigned to
products?
Variable overhead, direct materials, direct labor, and fixed overhead.
Which of the following statements is true regarding absorption costing?
It assigns all manufacturing costs to products.
Which of the following statements is true regarding variable costing?
It includes direct materials, direct labor, and variable overhead costs in product costs.
Which of the following statements is true?
Absorption costing treats fixed overhead as an expense in the period it is incurred.
Which of the following would be reported on a variable costing income statement?
Contribution margin
When evaluating a special order, management should:
Only accept the order if the special-order price exceeds total variable product costs.
A company had income of $500,000 based on variable costing. Beginning and ending
finished goods inventories were 100,000 units and 96,000 units, respectively. Assume the
fixed overhead per unit was $1.50 for both the beginning and ending finished goods
inventory. The income under absorption costing is:
$494,000
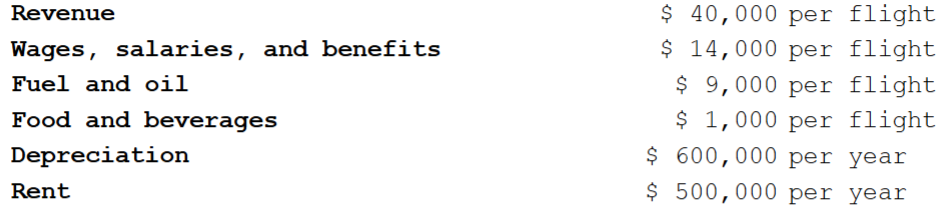
Eastern Airlines reports the following cost data for the year. The company flew 100 private
flights during the year. A group has offered Eastern $22,000 for a private flight to Chicago
for its members. What is the contribution margin from accepting this offer?
$(2,000).
Income __________ when there is zero beginning inventory and all inventory units produced
are sold.
Will be the same under both variable and absorption costing
A formal statement of a company’s plans in dollars is a:
budget
The process of planning future business actions and expressing them as formal plans is called:
budgeting
Which of the following is not necessary for budgets to be effective?
all budgeted amounts must be spent to ensure that budgets aren’t reduced for the next period.
Which of the following is a benefit derived from budgeting?
Budgeting provides a basis for evaluating performance.
Which of the following is not a step in the budgetary control process?
communicate differences to supervisors to facilitate promotion decisions.
Budgets that are revised by adding a new quarterly budget to replace the quarter that just elapsed are called:
rolling budgets
A company budgets 640 hours of direct labor during July. The company applies variable overhead at the rate of $18 per direct labor hour. Budgeted fixed overhead equals $92,000 per month. Budgeted total factory overhead is:
$103,520
The practice of continually revising budgets as time passes is called:
continuous budgeting
The usual budget period for most companies is:
an annual period separated into quarterly and monthly budgets
A company budgets sales of $800,000 for June. The company pays a sales manager a monthly salary of $4,000 and a commission of 8% of that month’s sales. Total selling expenses for the month of June equal:
$68,000