Critical care nutrition
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
what is nutritional support?
method to support metabolic status of hospitalised patients
what are the differences between enteral and parenteral nutrition?
enteral - methods utilising the GI tract
parenteral - feeding via IV
enteral nutrition is easier, has lower complications, more economical and more physiological —> preferred
Why is malnutrition significant in hospitalised patients?
healthy animals can reduce nutrient utilisation to compensate
sick animals cannot compensate —> nutritional deficiencies are magnified
when do we need to intervene and provide enteral nutrition?
recent weight loss > 10%
partial / complete anorexia for > 3days
diseases causing excess catabolism
how should we provide enteral nutrition in obese patients?
treat patient the same
what are the types of enteral nutrition?
encourage feeding
force feeding
drugs
tube feeding
what is essential for encourage feeding?
privacy and comfortable environment
favourite foods in small amounts
feed fresh and try warming
do not ‘overface’
record closely how much they have eaten
what diets should we feed during nutritional support?
highly digestible diet
cooked meat or fish
critical acre diet
what drugs are appetite stimulants?
diazepam
mirtazapine
cyproheptadine
capromorelin
what appetite stimulant would we usually use in dogs?
capromorelin (ghrelin agonist - liquid form)
= central appetite stimulant
only licensed in USA - import
3 mg/kg once daily
what appetite stimulant would we usually use in cats?
can use capromorelin but mirtazapine more common
well tolerated
only partial / short term anorexia
¼ tablet every 3 days
what are the types of feeding tubes?
naso-oesophageal tubes
(pharyngostomy tubes)
oesophagostomy tubes
gastrostomy / PEG tubes
enterostomy tubes
how would we use naso-oesophageal tubes?
short to medium term
small diameter tubes
what are contraindications for naso-oesophageal tubes?
disease of head, nose, pharynx and below
if they have no gag reflex
how would we use oesophagostomy tubes?
medium to long term support
well tolerated
GA required
what are indications for oesophagostomy tubes?
oral cavity, nasal or pharyngeal disease
what are contraindications for oesophagostomy tubes?
diseases of oesophagus and below
how would we use gastrostomy tubes?
long term support - minimum 7 days
well tolerated
GA required
what are contraindications for gastrostomy tubes?
gastric, intestinal or pancreatic disease
how would we use enterostomy tubes?
GA required
no gastric reservoir
need constant rate infusion
what are indications for enterostomy tubes?
good for pancreatitis
what are contraindications for enterostomy tubes?
diffuse intestinal disease
how do we decide what tube method we would use?
duration of treatment
illness
conditions and temperament
equipment and expertise
cost
use as proximal as possible
what equipment is needed for naso-oesophageal tubes? (recording)
how do we prep for placing naso-oesophageal tubes?
topical local anaesthetic solution in the nose
how do we place naso-oesophageal tubes? (recording)
how can we tell if we are in the oesophagus or the trachea in conscious patients when placing naso-oesophageal tubes?
oesophagus has no air in it - pull back on empty syringe to ensure negative pressure
use syringe with water in it - push some water into tube, if in the trachea, the patient will cough
how do we secure naso-oesophageal tubes in place? (recording)
what equipment would we use for placing oesophagostomy tubes?
long pair of carmalt forceps
may need mouth gags to protect hands - but may get in the way of placement
basic suture kit - material, scalpel, etc.
couple of sizes of tubes ready

what are pros and cons of bung on the end of tubes?
pros - shows up really well on radiographs - to check position
cons - can increase blockages, so better to cut off for long term placement
how are oesophagostomy tubes placed?
placed in the right or left lateral neck - left side better
patient in lateral recumbency
insert carmalt and push out laterally - so you can see the curved tip position through the skin
ensure you are well above the jugular vein
incsie the skin with scalpel to exposure the tip of the carmalt forceps
grab tip of tube with the foreceps and pull the tube through oesophagus, and out the mouth
reposition the foreceps on the tip of the tube, to redirect the tube down the oesophagus
how can we ensure the tube is in the oesophagus properly with oesophagostomy tubes?
as you are redirecting the tube down the oesophagus, gently pull the excess tubing back out the incision site - will see the tube flip directions
take radiograph to check position
can use endoscopy to check position - but not usually done
how do we secure the tube in place for oesophagostomy tubes?
using finger trap pattern
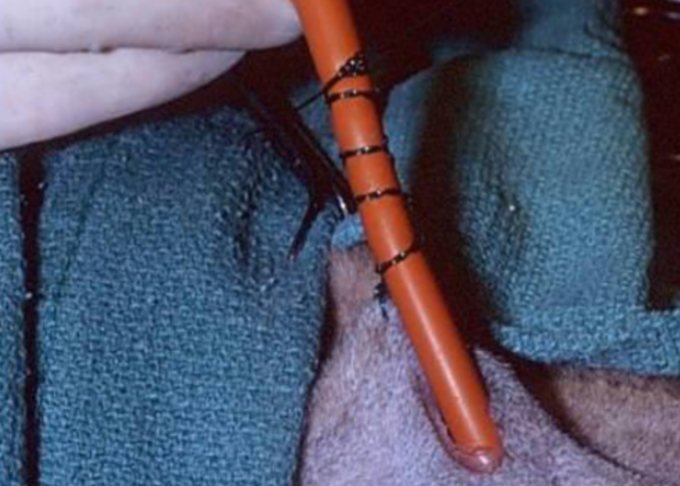

bandage in place
what equipment is needed for PEG tube placement? (recording)
how do we place PEG tube? (recording)
what energy requirement do we use for hospitalised patients?
resting energy requirement (RER) - reassess regularly
build up to this gradually - 1/3 on day 1, 2/3 on day 2, 3/3 on day 3
what is the aim for nutritional support in underweight patients?
stabilisation - don’t need to make them put on weight
if using a gastrostomy tube or enterostomy tube, when do we start feeding?
after the first 24 hours - for first 24 hours just allow them to adjust to the tube
how should we give food in tube feeding?
small, frequent meals (4-6 per day)
always aspirate first
warm the food
administer over several minutes
flush tube with warm water
what are the possible complications of tube feeding?
mechanical blockage
metabolic issues - GI upset, hypophosphataemia
tube dislodgement
stoma infection
tube removal by patient