structure and bonding
1/38
Earn XP
Description and Tags
CHEM1302
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
What is the plum pudding model?
Who came up with it?
Homogenous positive mass with electrons inside it
Thomson
Limitations of the plum pudding model
Negatively charged things attract positively charged things = the protons and electrons would attract each other and the atom would collapse
What was Rutherford’s model of the atom?
Protons in the nucleus, electrons moving which stop atom from collapsing. Neutrons in the nucleus, gluing protons together
What does the gold foil experiment show?
Gold foil confirms protons are stuck together in nucleus, some alpha particles bounced back showing interactions with nucleus. Most went through showing atom is mainly empty space.
What is Bohr’s model of the atom?
What happens when energy is put in?
Electrons that circulate the nucleus can only take certain values of energy (energies are quantised) = energy levels.
When energy is put in, electrons move from one energy level to another. When they drop from high to low EL, they emit radiation. Energy can be emitted/absorbed according to fixed frequencies, equivalent to the energy difference between levels.
Limitation of Bohr’s model
Electrons are modelled as behaving as particles. Electrons are not particles
What does it mean that electrons are superpositions?
They can be particles or waves depending on how you look at them
What are probability clouds?
Electrons have probability densities of being in a certain place around the nucleus
What is n?
Principle Quantum Number = it determines which electron shell an orbital occupies r
which energy level
What is l?
Orbital Angular Momentum Quantum Number = determines the shape of an atomic orbital
it gives the number of nodal planes
What do the different values of l mean?
l = 0 is s orbital
l = 1 is p orbital
l = 2 is d orbital
What is ml?
Magnetic Quantum Number = determines the direction of an atomic orbital in space
orientation
What are the possible values for ml?
l = 0 (s orbital) = ml is 0
l = 1 (p orbital) = ml is -1, 0 or 1
l = 2 (d orbital) = ml is -2, -1, 0, 1 or 2
What is ms?
Electron spin
electrons can spin either clockwise or anticlockwise, either +1/2 or -1/2
What is an orbital?
A region of space that can be occupied by an electron
What is an orbital node?
A region of zero probability density
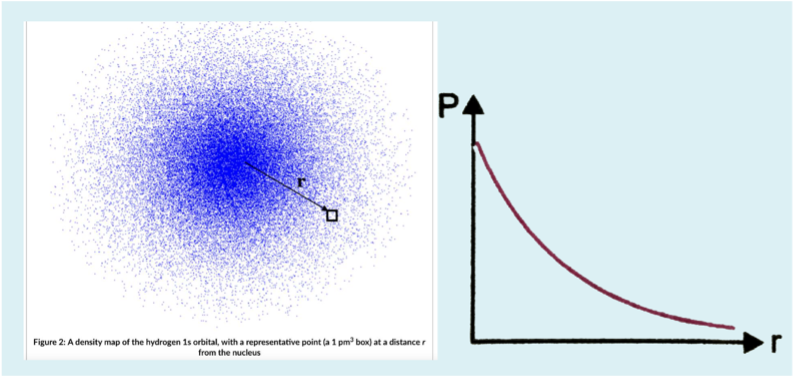
What is the limitation of this graph of electron probability density?
The probability of finding the electron at the nucleus is highest which would suggest the electron is in the nucleus
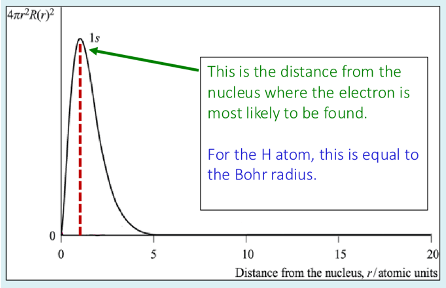
What is a radial probability plot?
It shows the probability of finding the electron in any given shell at a particular distance from the nucleus
probability is zero at the nucleus
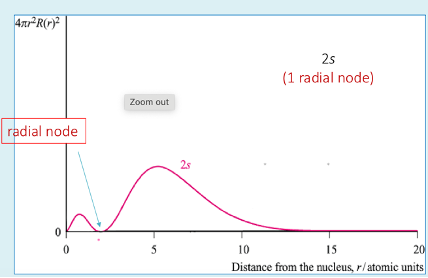
What happens as Principle Quantum Number increases for a given type of orbital?
Orbital shape stays the same
Radius of max probability increases (size of orbital)
Radius gives us size of an atom
Orbital develops radial nodes
What is the Aufbau principle?
Orbitals are filled with electrons in order of increasing energy
What is Pauli’s Exclusion Principle?
No two electrons in the same electrons in the same atom can have the same set of 4 quantum numbers
must have a different spin quantum number = spin pairs
What is Hund’s Rule of Maximum Multiplicity?
In a set of degenerative orbitals, electrons prefer to occupy them singly before pairing
What is Valence Orbital Energy?
the energy of an electron in a particular atomic orbital
the negative value of ionisation energy
What is the equation for VOE?
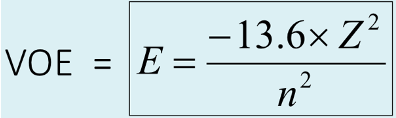
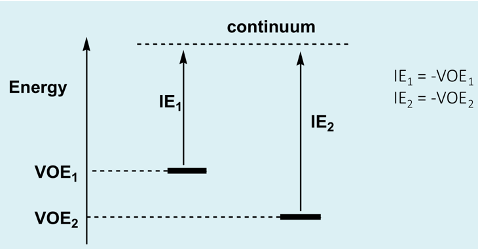
What is continuum?
Which VOE is more stable?
Continuum = the energy zero point; energy of an electron not interacting with anything in a vacuum (no kinetic or potential energy)
VOE2 is more stable as it is more negative
Order of VOE for the orbitals for same value of n (same EL)
s < p < d < f
What does a low Valence Orbital Energy mean?
The lower (more negative) the VOE, the more stable the orbital
How does VOE change with n?
How does VOE change across a period?
How does VOE change as you go down a group?
VOE gets less negative as n increases
VOE gets more negative across a period as Z (charge) increases = more protons
As you go down a group, n increases so VOE gets less negative
What is the first ionisation energy of an element?
What conditions?
The energy needed to remove the first valence electron at 0K and 1 atm from a gaseous atom
What is ionisation energy proportional to?
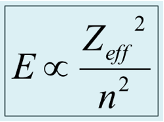
How does IE change across the periodic table?
Increases across a period
Increases up a group
What is Zeff?
Why is it lower than Z?
Effective nuclear charge
The amount of positive charge every electron feels from the nucleus taking into account shielding from other electrons
Explain changes in IE in terms of Zeff
Increasing Zeff with constant n means increase across a period
Smaller n and similar Zeff means smaller and tightly bound orbital = increase up a group
Highest and lowest values of IE
Highest = noble gases, filled shells
Lowest = alkali metals (single electrons outside full shell)
What is electron pairing energy and how does it affect IE?
Electron-electron repulsion means lower than expected IE
What is first electron affinity?
The internal energy released when an electron is added to a neutral gas phase atom
X (g) + e- → X- (g)
What is electronegativity?
The ability of an atom to attract electrons to itself in a molecule
What is electronegativity an indicator of?
general chemical behaviour
electron distribution in a bond
whether a compound will be ionic or covalent
What is the Pauling electronegative scale?
The difference between the average homonuclear bond energies and heteronuclear bond energy (in eV)