L1. Introduction to Bacteriology
1/161
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
162 Terms
Linnaean Taxonomy
A classification system for organisms based on hierarchical ranks.
Bacteriology
The study of single-celled microorganisms that lack a true nucleus.
Domain
Bacteria.
Kingdom
Prokaryotae.
Division or Phylum
Gracilicutes.
Class
Scotobacteria.
Order
Eubacteriales.
Family
Enterobacteriaceae.
Genus
Escherichia.
Species or Epithet
coli.
Subtype
Escherichia coli O157:H7.
Subspecies (subsp)
A further division of species.
Serovarieties (serovar)
Based on serologic test result differences.
Biovarieties (biovar)
Based on biochemical test result differences.
Binomial system
A two-part naming system for species.
Koch's Postulates
A series of criteria to establish a causative relationship between a microbe and a disease.
Phenotypic characteristics
Readily observable traits of an organism.
Genotypic characteristics
Genetic make-up of an organism based on their DNA and RNA structure and homology.
Prokaryotes
Cells that lack a true nucleus and membrane-encased organelles.
Eukaryotes
Cells with a true nucleus and membrane-encased organelles.
Archaebacteria
Bacteria that grow under extreme environmental conditions.
Father of Medicine
Hippocrates.
Father of Microbiology
Antonie van Leeuwenhoek.
Father of Immunology
Edward Jenner.
Aseptic Surgery
Founded by Joseph Lister, important in Bacteriology.
Gram's Staining
A method employed for microscopic bacterial cell differentiation.
Bordetella pertussis
Causative agent for whooping cough discovered by Jules Bordet.
Kleb's Loeffler's bacilli
Cultivated by Friedrich Loeffler.
Penicillin
Discovered from mold 'Penicillum nolatum' by Alexander Flemming.
Genome
Located in the nucleoid at the mesosome.
Taxonomy
Orderly classification and grouping of organisms into 'taxa' or categories.
Taxon
Means 'arrangement'.
Nomos
Means 'law'.
Nomenclature
The naming of microorganisms according to established rules and guidelines set forth in the International Code of Nomenclature of Bacteria.
Reproduction
Can be asexual or sexual and asexual.
Identification
The process by which a microorganism's key features are delineated.
Membrane-bound organelles
Present in all eukaryotic cells; absent in prokaryotic cells.
Lysosomes
Contain hydrolytic enzymes and are absent in all prokaryotic cells.
Endoplasmic Reticulum
Present in all eukaryotic cells; absent in all prokaryotic cells.
Mitochondria
Present in all eukaryotic cells; present in most prokaryotic cells.
Ribosomes
Sites of protein synthesis; present in all cells.
Ribosome Size
70S = 50S and 30S; 80S = 60S and 40S.
Flagella
Made up of a protein called flagellin; classification according to number and arrangement of the flagella on bacterial cell.
Glycocalyx
Present as capsule or slime layer.
Pili
Non-motile, long, hollow protein tubes made up of pilin that connects two bacterial cells.
Fimbriae
Non-flagellar, sticky, proteinaceous, hair-like appendages that aid in adhesion to tissues and surfaces.
Cilia
Present in some eukaryotic cells; absent in prokaryotic cells.
Plasmids
Small circular molecules of DNA commonly found in Gram Negative bacteria.
Cell Wall
Composed of peptidoglycan in bacteria.
Sterols
Absent except in the mycoplasma; present in eukaryotic cells.
NUCLEUS
has chromosomes which contains DNA. They are covered with basic proteins called histones. It is bounded by a bilayered lipoprotein membrane known as the nuclear membrane.
NUCLEOLUS
round, refractile body which is the site of ribosomal RNA synthesis. It is located within the nucleus.
ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM
A system of membranes that occur throughout the cytoplasm.
ROUGH ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM
Covered with ribosomes which gives it a "rough" appearance. It is the site of protein synthesis.
SMOOTH ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM
No ribosomes. It doesn't synthesize proteins but it synthesizes phospholipids.
GOLGI APPARATUS
Modify and package proteins sent by the rough endoplasmic reticulum.
RIBOSOMES
Where protein synthesis occurs.
MITOCHONDRIA
Main site of energy production.
LYSOSOME
Contains hydrolytic enzymes for degradation of macromolecules and microorganisms within the cells.
MESOSOMES
point of attachment of chromosomes.
PEROXISOMES
Break down hydrogen peroxide.
PLASMA MEMBRANE
phospholipid bilayer.
CILIA
Short projections that extend from the cell surface and used for locomotion.
COCCI
Spherical in shape. Singular: Coccus.
CELL WALL (MUREIN LAYER)
Provides rigidity and strength to the exterior of the cell.
DIPLOCOCCI
Cocci in pairs.
STREPTOCOCCI
Cocci in chains.
STAPHYLOCOCCI
Cocci in clusters.
SPIROCHETES
Spiral/helical with a long axis that bends when in motion.
FUSIFORM BACILLI
Bacilli in short rods or ovals.
VIBRIO
Curve rod-shaped, comma shaped.
PLASMOLYSIS
A cell in a saline solution shrinks because water passes out.
PLASMOPTYSIS
A cell in distilled water bursts.
CALCIUM DIPICOLINATE
A composition of their inclusion bodies.
Gaffkya tetragena
Representative organism of Tetrads.
Sarcina lutea
Representative organism of Sarcina.
Cocci
All cocci are gram positive except Neisseria, Veillonella, and Moraxella group.
Bacilli
All bacilli are gram negative except Bacillus, Clostridium, Mycobacterium, Corynebacterium, and Listeria.
Bacillus
Singular form of bacilli; rod shaped.
Nocardia
A type of bacilli.
Erysipelothrix
A type of bacilli.
Lactobacillus
A type of bacilli.
Kurthia
A type of bacilli.
Rothia
A type of bacilli.
Spiral organisms
Very hard to stain but they are gram negative.
Non-sporing snapping diplobacilli
If the organism appears in V-shaped.
Non-sporing slipping diplobacilli
If the organism appears parallel to each other.
Lactobacillus acidophilus
Acid-loving; requires pH 3.0; tomato juice agar is used.
Vibrio
Alkali-loving; requires pH 8-10; use Alkaline Peptone Water as a culture medium.
Bacterial replication
Bacteria multiply by binary fission, producing 2 identical daughter cells.
Lag phase
Involves little or no growth.
Log/Exponential phase
Maximum rate of bacterial multiplication; most susceptible to antimicrobials.
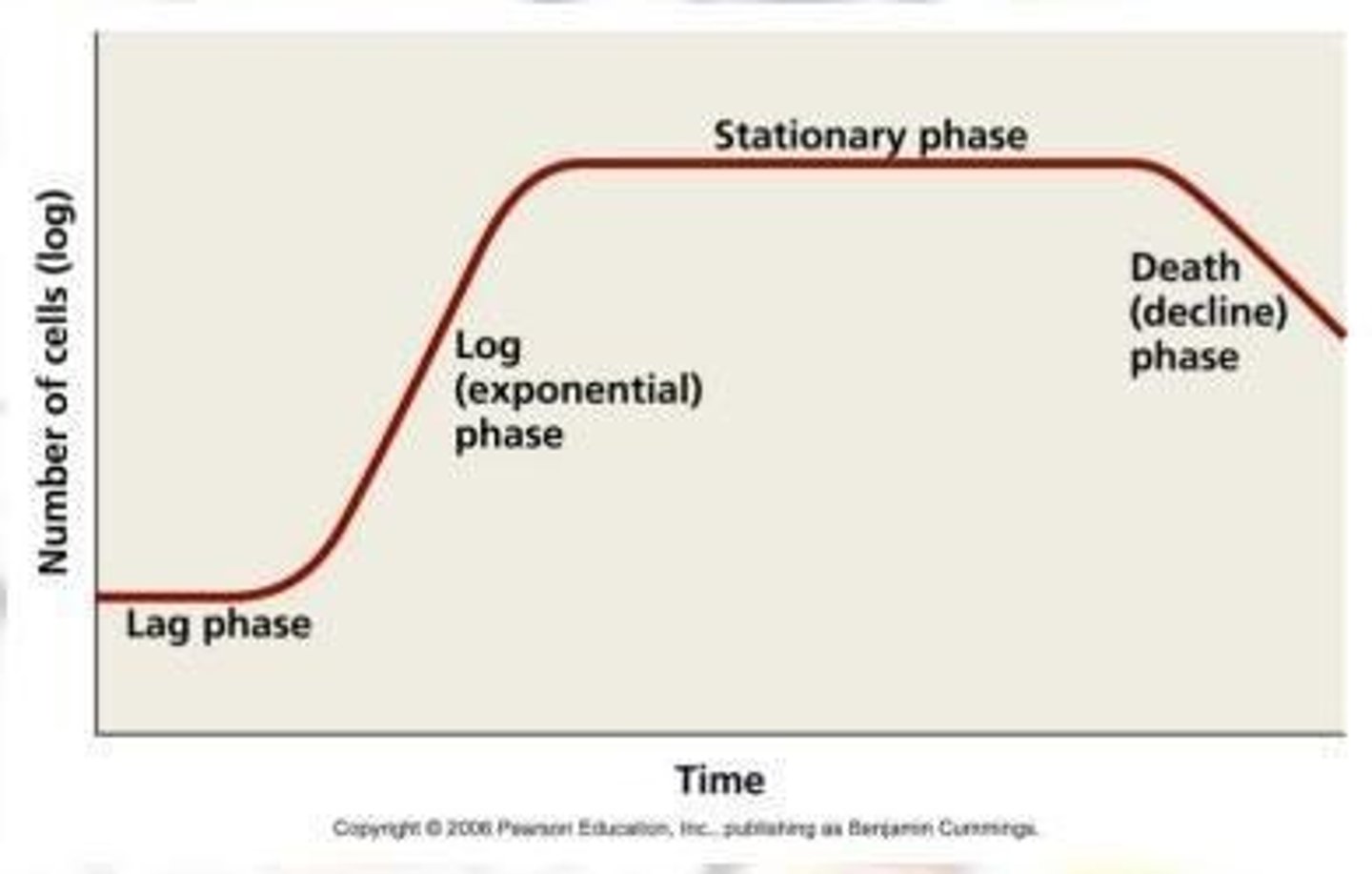
Plateau/Stationary phase
Number of bacteria alive is equal to the number of dead bacteria.
Decline phase
Increase in number of dead bacteria.
Bacterial transformation
Free or naked DNA found in the environment is taken up by a bacterial cell.
Bacterial transduction
A virus injects DNA into the bacterial cell.
Lytic cycle
The replication of the bacterial chromosome is disrupted.
Lysogenic cycle
The bacteriophage DNA is incorporated into the bacterial genetic material.
Bacterial conjugation
DNA is transferred from one cell to another via sex pili.
Lithotroph/Autotroph
Carbon source is from Carbon dioxide.