Abiotic Factors
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
What are the 6 abiotic factors that affect productivity:
• Temperature
• Light intensity, day length
• Water availability
• Soil fertility
• Topography
• Relief
What is the 5 important reasons of temperature?
Length of thermal growing season - Temperatures must be warm enough not only for survival but also for growth (e.g. grass doesn't grow below 5°C).
Frost-free period - Some crops can be damaged by frost, so these cannot be grown where late frosts are likely.
Impact on evaporation - Higher temperatures increase the rate of evapotranspiration which increases.
Biochemical reactions - Higher temperatures increase rates of chemical reaction e.g. for photosynthesis.
Thermoregulation - Keeping animals warm reduces the need for them to use energy for thermoregulation, increasing the amount of food energy put into growth.
How to control temperature?
Using greenhouses during cooler months.
Avoiding low-lying valley bottoms - It's more likely to have frost due to cold dense air sinking and collecting there.
Utilising south-facing slopes - They receive more solar insolation and tend to be warmer
Laying protective materials over fields to insulate them.
Keeping livestock in shelters during the winter.
What is the importance of suitable light levels?
Brighter light enhances the rate of photosynthesis and plant growth.
What is photoperiodism?
The physiological response of organisms, particularly plants, to the relative lengths of day and night.
It affects:
Growth and development of crops
The reproductive function of some livestock species

How does photoperiodism affect growth and development of crops?
Some plants require longer periods of light each day for flowering (e.g. oats), others require less daylight (e.g. maize).

How does daylength affect cows?
Long day length increase milk production

How does daylength affect poultry?
Poultry grow best with short days while egg production is greatest when days are long.

How does daylength affect sheep?
Sheep mate when days are getting shorter in the autumn, and reproduce (lambs are born) as days get longer in spring.

How to manage light levels?
Artificial lighting

How can artificial lighting be used?
Can be used in greenhouses to extend the growing season for crops.
Artificial recreation of autumn light conditions can result in an additional mating season for sheep in spring
CO₂ can be a limiting factor in the rate of photosynthesis. Methods to manage carbon dioxide levels:
Crop growth rates in greenhouses can be increased by burning carbon-based fuels.
Expensive, but balanced by the higher value of greenhouse gases
What does topography mean?
Undulations of the land
Methods to manage topography
It is not practical to alter land topography, but terracing can be used to make hillslopes more suitable for cultivation.
Areas that are nearly flat can be levelled by machinery to reduce runoff and help to produce flooded fields for rice cultivation.
What is relief?
Relief describes the variation in elevation of the Earth's surface
The altitude of an area (height of above sea level) controls other abiotic factors (like temp), meaning some species may not be suited for that area
Why don't cattle survive at higher altitudes?
Their pulmonary arteries thicken at higher altitudes, restricting blood flow to their organs.
Methods to control relief in agroecosystems
This cannot be controlled, but management involves selecting suitable species for the relief of farmland. Goats and llamas survive at higher altitudes.
Importance of water
- Physiological functions
- Cell water produces turgidity
- Nutrient absorption
Physiological functions
Water is a key solvent in many cell reactions.
Cell water producing turgidity
Provides support to the plant
Why is water important?
Nutrient absorption from soil often involves ions dissolved in water e.g. nitrate, phosphate
Water is needed to replace water lost during transpiration
Water is needed to transport materials e.g. glucose, oxygen, nutrients.
Methods to increase water levels
Crop irrigation.
Adding soil organic matter
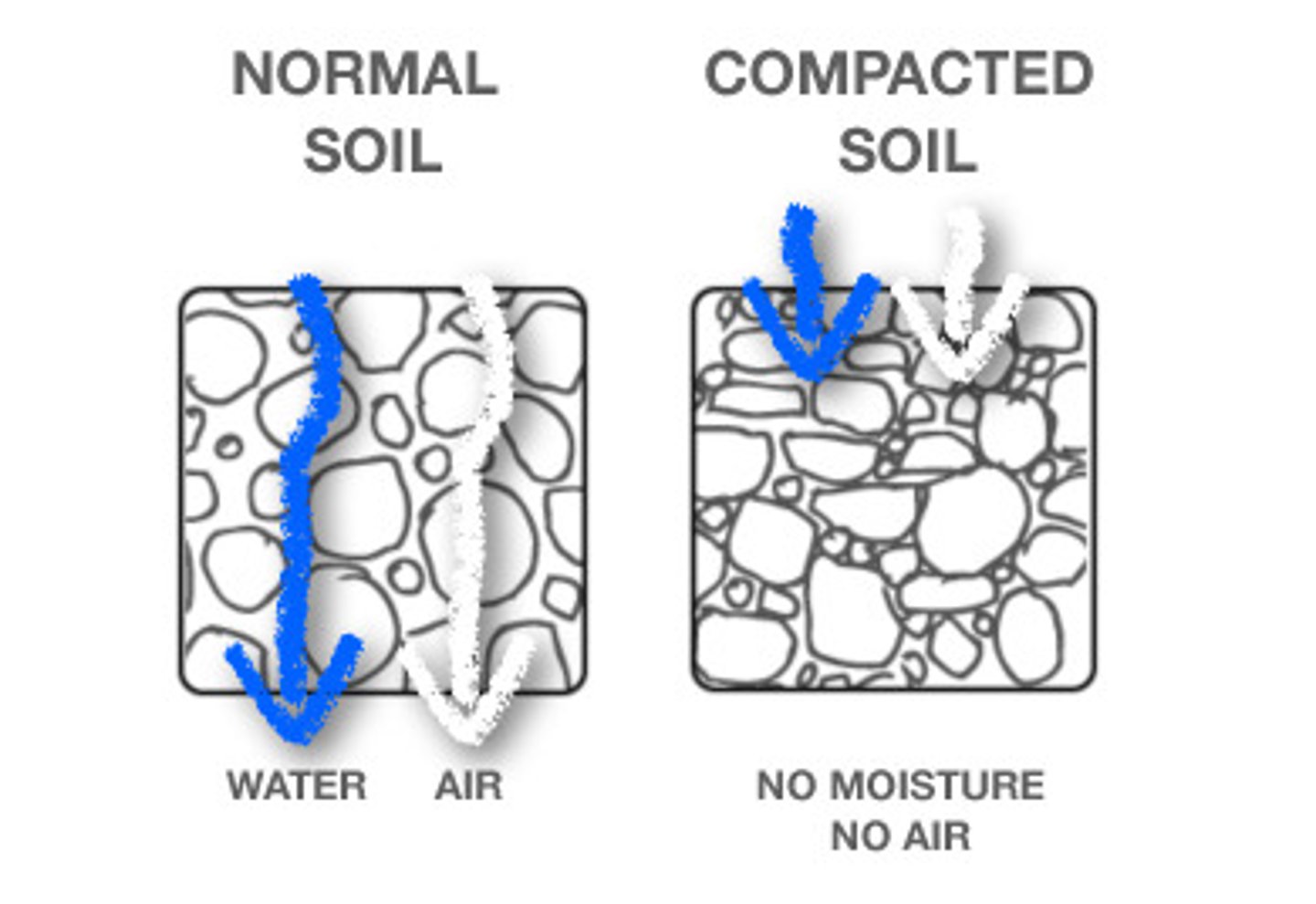
Reducing soil compaction
Provision of suitable conditions for worms
How does adding soil organic matter increase water levels?
It increases water retention

How does reducing soil compaction increase water levels?
It increases infiltration
What do worms do to increase water levels?
They increase infiltration and reduce runoff losses
What are some issues caused by waterlogged soils?
Higher risk of fungal diseases (e.g. root rot)
Soil becomes anaerobic and creates ideal conditions for denitrifying bacteria, reducing soil fertility as nitrates are lost from soils more rapidly and replaced more slowly due to lack of nitrifying bacteria.
How to reduce waterlogged soils
Excavation of drainage ditches or installation of drainage pipes
Avoidance of soil compaction by machinery or livestock
Provision of conditions to encourage worms e.g. by adding soil organic matter

What is the importance of soil fertility?
A measure of the ability of soil to support plant growth. It is the result of availability of nutrients & water, aeration, texture & structure.
Soil nutrients include macronutrients and micronutrients
What is nitrogen used for?
Protein synthesis
What is phosphorous used for?
Root growth
ATP manufacture
What is iron used for?
Chlorophyll manufacture
What is zinc & copper used for?
Enzyme activation
How to manage soil fertility?
Application of organic and inorganic fertilisers
Hydroponics
Pros of Organic fertilisers
Derived from organic waste, which can be locally available
Increases the soil humus content
Increases soil biota populations

Cons of Organic fertilisers
The nutrient composition cannot be controlled
Nutrients are released slowly as the material decomposes, so they must be used as part of a long term cultivation plan
Many are bulky with a high water content, so transport is expensive
Pros of Inorganic fertilisers
The nutrient composition can be controlled to meet specific crop requirements
The nutrients are released rapidly
Cons of Inorganic fertilisers
Cause eutrophication
Expensive to manufacture
Hydroponics
Involves the growth of crops in a nutrient solution, rather than a solid growth medium.
It is usually carried out in greenhouses as part of an intensive system.
Productivity is maximised by controlling limiting factors as much as possible.
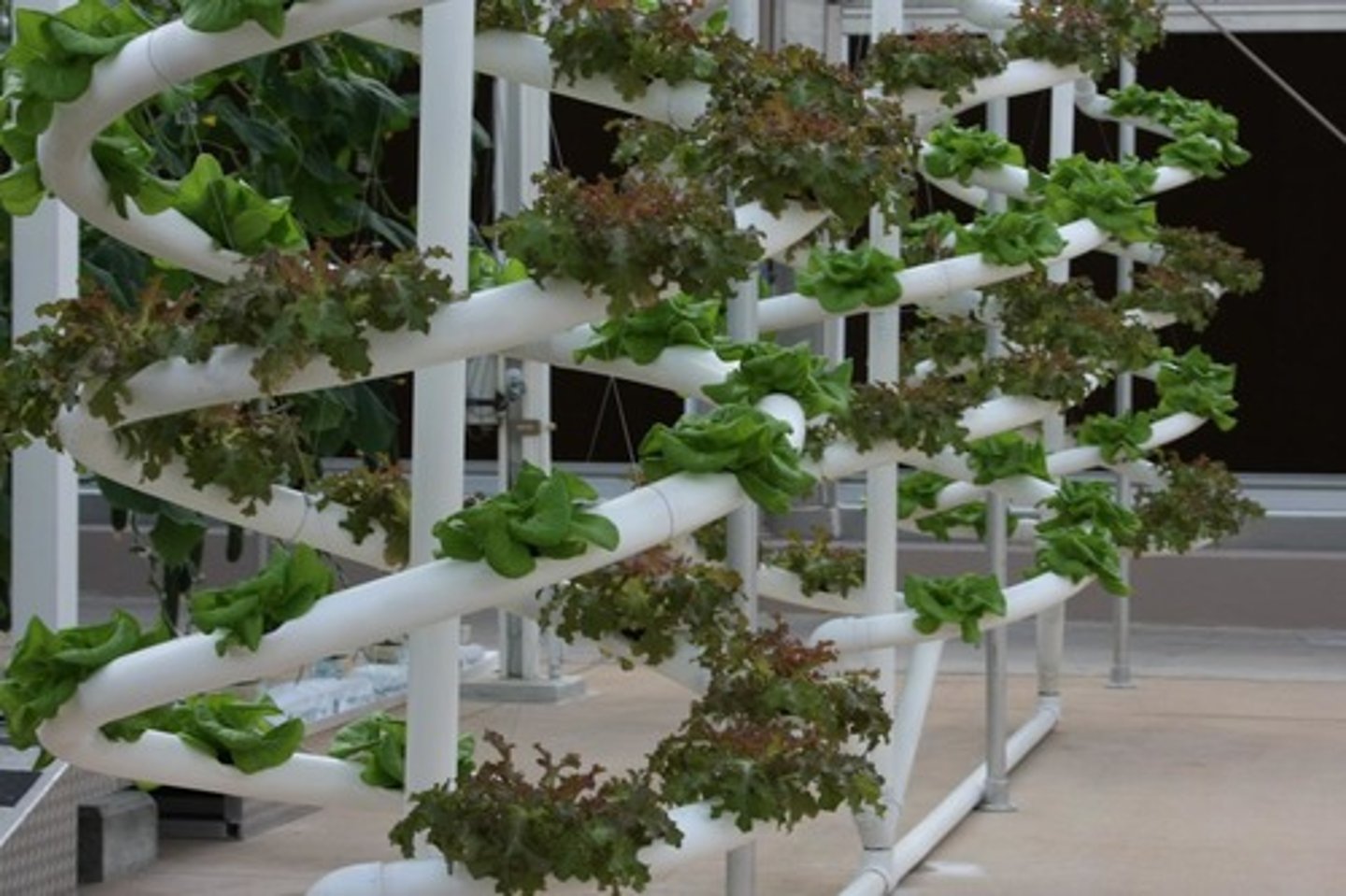

Pros of Hydroponics
Nutrient supply is optimal so it is not a limiting factor for growth
All roots are in contact with the nutrient medium, so roots are smaller and more growth is directed into the harvestable crop
No soil needed
No weeds
Cons of Hydroponics
Intensive production involves high inputs of nutrients and energy
A high level of technical knowledge is needed
Importance of soil salinity
Dissolved salts in soil water are essential for plant growth as they include soil nutrients.
Excessive salinity can kill plants due to dehydration of roots (though osmosis).
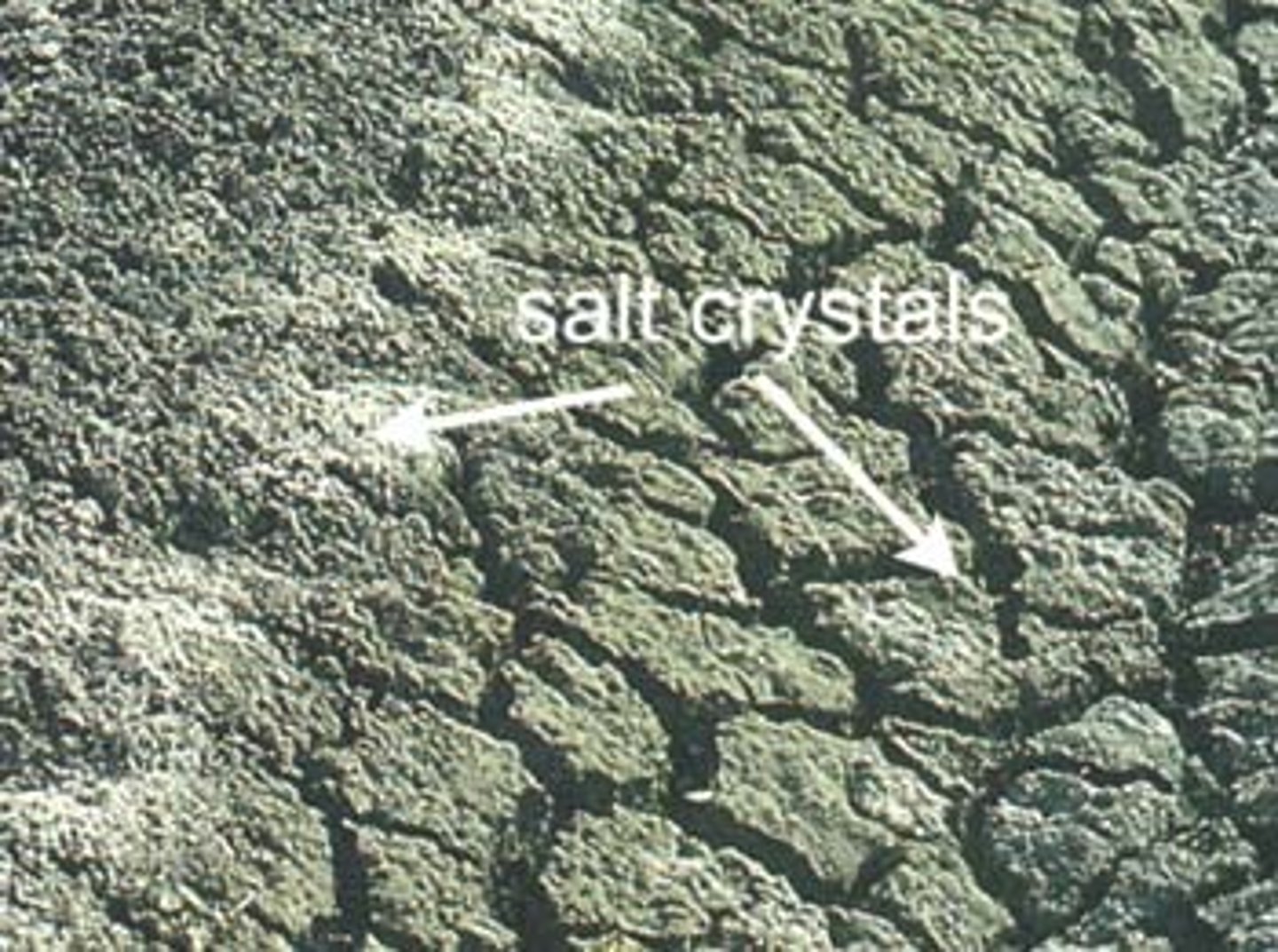

How to manage soil salinity?
Avoid farming methods that increase salinity.
Use freshwater irrigation to wash salts out of the soil
Importance of soil pH
All plant species have a specific range of tolerance for soil acidity (usually between pH 5 and 7)
What can a high pH do?
Inhibit nutrient solubility
What can a low pH do?
Cause leaching of nutrients and inhibit nutrient uptake.
It can also mobilise toxic ions in the soil, like lead
How can soil pH be increased?
Adding crushed lime (CaCO₃)
How can soil pH be decreased?
Spreading powdered sulphur
Importance of soil aeration
Uncompacted soil has larger pore spaces between soil particles, increasing aeration.
Many soil processes are aerobic and require oxygen such as root respiration, nitrogen fixation & decomposition.
What farming practices actually reduce aeration?
- Use of farm machinery or livestock trampling.
- Ploughing & crop removal
- Most commercial crops have shallow roots.
How does ploughing & crop removal reduce aeration?
It reduces soil organic matter content/topsoil.
Ploughing also kills soil organisms by moving them too deep in the soil for survival.
Methods to increase soil aeration
- Removing trampling livestock from damp fields.
- Low tillage methods
- Adding organic matter to increase suitability for worms.
What are low tillage methods?
Methods that do not require machinery or ploughing of soil
