Ad and Promo Test 1
1/102
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
103 Terms
How do we define advertising?
Structured and composed non personal communication of information, usually paid for and usually persuasive in nature, about products (goods, services, and ideas) by identified sponsors through various media.
Marketing and advertising are NOT the same thing
Also covers ideas and ideology
Persuasion is a critical part about advertising
What are the requirements for something to be considered advertising?
structured, non personal (not delivered interpersonally), paid for, usually persuasive, about products, and identified sponsors with various forms of media
What examples did we discuss in class regarding whether or not something is considered advertising?
we discussed:
TV commercials are advertising
Youtube ads are advertising
Telemarketing not advertising because of non personal
Tweets about products are advertising
NIL athletes
What celebrities wear is advertising because there is a value exchange technically is paid
What NFL coaches wear → Sean Payton wearing Jordans example is advertising
Pitfall buying the name rights for the Florida International stadium → sponsorship but is not technically advertising
What factors determine whether or not something is considered advertising?
A lot of things (the requirements for advertising) but especially the non personal element
What is promotion? How does it differ from Advertising? How is it related to advertising?
Is a more general category of marketing activities involving a broader range of persuasive communication related to companies, brands, products, services, and ideas.
Advertising falls under promotion as it is a subset.
Constitutes one of the main marketing pillars
Advertising is on form of……
Why do firms advertise?
no exposure means no perception
messaging
allow a brand to tell a story and communicate to the consumer
branding is a big element
What are the 2 main strategies?
brand ads (branding, equity, etc. ) or direct response (have a certain outcome: increase sales)
What is the brand building strategy?
long term strategy to use advertising as a tool to build or enhance brand equity and how people perceive the value of a brand. People will become familiar with things and it affects how we experience things like becoming brand loyal. Brand loyalty happens when we increase the brand building→ can take years to get people to become loyal.
What is the direct response strategy?
Stimulate immediate behavior from consumers: using a coupon, having a sale, want them to come in and make purchases or decisions immediately.
How do these strategies differ?
DR wants to create an immediate reaction or behavior like getting consumers to buy something asap with a sale or coupon (ex. a 3 day window sale on cars for Labor Day) but brand ads are in it for the long run. Trying to get consumers to become loyal, so you make ads for the loyalty long term.
Both are important priorities (DR 48% and BB 46%)
What types of knowledge and skills do we need to be able to produce effective Ad & Promo materials?
specialization/ ways to be niche and get into→ figure out the target industry
adapting quickly to trends
changes in culture also affects how we think about target audiences
Social media has shaped a lot of the changes that come
Technical skills
tracking metrics/ analytical skills
must understand markets, targets, who we are trying to pertain to
Think about the IMC components
What does an Integrated Marketing Communications (IMC) approach entail?
It entails the why and execution of an advertising campaign that is successful through a model that shows all the components that must work together to be truly effective
Iterative process trying to combine everything we have learned to leverage campaigns that are all they are worth to become successful with the IMC approach.
What are the components of an IMC approach to Advertising & Promotion (The Big Picture)?
(STP) → (Need communication and Consumer Behavior) → (Creative advertising, Processes, and Tools this step is elite)→ (Then we think about media choices ex. print, tv/video , digital, social media, influencers, mobile, or merging media, etc.)→ all of this goes to create effective and successful advertising campaigns
*We must fully understand these things to come all together
who do we answer to?→ target audience
(agency, clients, and consumers is all we serve→ sometime you have to pick 2/3)
What career building exercises and activities did we do as part of our introductory workshop?
We took time to reflect on important questions to help us look deeper within to see what we are naturally good at, what are our passions, how can those passions align with what we are good atto give us competitive advantage all through the power of thought and closing our eyes and reflecting on these questions with minimal distractions. Through the power of thought we look at thoughts→ intentions→ decisions→ behaviors → outcomes.
Thoughts shape what we become!
What questions did we consider to help us identify our passions?
We start with the challenge: how do we identify, develop, and choose to communicate our personal branding?
from there we ask ourselves:
what do you think about when you don’t have to think about anything at all?
If you were financially secure and you didn’t have to work, how would you spend your time? What would you do everyday?
What makes you excited to get up everyday? What do you look forward to most each day?
What questions did we consider to help us identify our competitive advantages?
What are you really good at?
When compared to others you know, what do you do really well?
What skills or abilities do you have that set you apart from others?
How do we use these questions to help provide direction for our career goals and plans?
The overlap between the things that excite us and our unique skills and abilities provides direction with how we might spend our effort and time working.
ex. Talked about Oprah and the podcast episode with having the greatest transformation when you own your power and the soul is where you have authentic empowerment.
Why should we try to identify our dream job as soon as possible?
We can then determine our path to obtaining that dream job and work towards it, but if that dream job does not exist we figure out what steps we can take to create it. If we know where we want to go then we can start taking baby steps closer to that goal (dream job).
What does the path to our dream job typically look like?
“life is a journey not a destination”, if we know what our dream job is we can start making a plan or a path to somehow eventually get to that dream job. (college→ internship→ job 1→ job2→ ….Dream job!
Because it is rare to land our dream job right away, how should we approach the process of working toward our dream job?
We should always try to take baby steps toward our dream jobs rather than just get discouraged.
What should we do if the jobs currently available to us don’t meet our personal job search criteria?
Create your own role! A lot of companies will create positions or roles for people because of their specialization and qualifications for a role that does not currently exist but should!
What is segmentation?
dividing a market into distinct groups
have similar needs and wants
respond similarly to marketing efforts and communications
we cut this into segments and across the segments they might have different needs, and different segments respond differently
What are the characteristics of market segmentation?
markets typically consist of multiple segments
firms can have a different strategy for each segment
firms can choose their efforts on only one or two segments
can use one strategy (shotgun Strat) for all the segments, but usually does not work as successfully
ex. the cigarette ads→ camel
Why do marketers employ segmentation?
To create successful advertising and promotion across different groups as we all are different but can share similarities.
What are the different ways that firms can implement segmentation?
They can implement segmentation into how they construct ads and operation to the audiences of different segments like the camel ad pertaining to women, men, and Lowkey children with the animated camel. → look at what segments have in common or how they are different in terms of wants or needs.
What are the different segmentation strategies? When are each appropriate?
shotgun (all segments) , focus on one, focus on 2 strategies
How do we characterize the different segmentation strategies?
we categorize them through geographic, demographic, behavioristic, and psychographic segmentation
What is geographic segmentation?
When is it most appropriate?
What examples of geographic segmentation did we discuss?
What are the challenges to geographic segmentation?
it is segmentation based off where people live, can be region wise, country wise, state, city, a town, etc. A way we define a market by geography or physical location
when people in certain areas of the country have preferences that cluster or have similar preferences
ex. McDonalds in Santiago Chile, they love avocados and hotdogs and also have grilled chicken sandwiches
surfboards vs snowboards, where do we advertise things, how will surfboards perform in FL or how do surfboards sales perform in Omaha?
the simplest form of segmentation and also could be the least productive form. → can tell us some things but not much
What is demographic segmentation?
When is it most appropriate?
What are the challenges to each of the demographic segmentation strategies?
Census→
includes: age, gender, race, education, income, occupation, religion, socioeconomic status.
a way to define pop groups by statistical characteristics
how is age used in demographic segmentation?
ex. age→ McDonalds with the happy meal → some places are now anti-child no kids allowed movement → potty training kid at a restaurant table. Living with your parents ex. how acceptable is it?→ Dr. J’s dad moving in with him.
how is gender used in demographic segmentation?
ex. now challenging gender norms and becoming more fluid. making Home Depot ads targeted towards women. ex. men looking into skincare vs the stereotype of the Marlboro man image. ex. 31-52% men who use skincare products
how is income used in demographic segmentation?
ex. income low middle high, ads targeted towards income (cars) proxy→ travel sites will charge people more if you are on an apple computer.
can be deceptive→ savers vs spenders, cash vs credit, or loans unobservable financial resources that makes problems.
how is race/ nationality used in demographic segmentation?
ex. race/ nationality→ both different things but realization, why would we segment with nationality- people can move and still have the same ideologies of the place they grew up in. ex. the Giselle ad covering her up to be more modest. ex. McDonalds also Remember the Titan’s and then in a team environment there is more variability in racial groups is different, this can tell us just a little bit
What is behavioristic segmentation?
When it is it most appropriate?
What are the challenges to behavioristic segmentation strategies?
We categorize users by their user status, usage rate, purchase occasion, and Benefits sought.
talked about how this shows in political ads→ they are trying to pertain to the people who are in the middle with user status
Challenges: assumptions that previous behavior is future behavior→ not a bad rule of thumb but not great.
what are the benefits users are seeking
price, quality, status, taste, health
purchase occasion buyers
can be distinguished by when people buy the products (ex. silly bands) or even by seasons (affected by: Frequency, Fads, Seasons)
User status
how we define the loyalty or openness of users and certain products
includes: Sole, semi-sole, discount, aware, trial/rejectors
Sole user
- Brand loyal; require little advertising or promotion
Semi-Sole user
- Semi-loyal, but will buy other brand if discounted
Discount users
- Will buy focal brand if discounted
Aware non-triers
-Use products in the category, but not focal brand
Trial/Rejectors
- Have tried focal brand, but didn’t like the product
usage rate
20% of the market consumes 80% of the product ex. of the US or the show top gear and pivoted his whole life to being a farmer
we want to target the 20% of users. ex. Hardy’s or Carls Junior call their 17-34 year old HFFU - Heavy Fast Food Users
What is Psychographic Segmentation?
When is it appropriate?
What is required for effective psychographic segmentation?
What examples of psychographic segmentation did we discuss in class?
What do we learn from the Cambridge Analytica case?
How was psychographic segmentation used by Cambridge Analytica to segment voters?
What are the challenges to psychographic segmentation?
Values, attitudes, lifestyles. (VALS)
Marketers group people by their values, attitudes, personality, and lifestyle
enable marketers to understand consumers as living,
breathing people with feelings and inclinations (rather than as mere statistics)
To use this we need working knowledge of CB and the cognitive CB psychology
Remember: Exposure Attention Perception, MAO, Attitude formation and changes, Judgement and decision making, heuristics, and this all goes into Values, lifestyles and personalities.
Cambridge Analytica: They collected and used users data to target them political ads→ how not to do stuff in terms of unethicalness. looked at things people liked and used that data to identify all these different things like race, gender, sexual orientation, political status and could predict political parties 85%.
Looked at Meyers Brigg and Big 5 → they tricked people after scraping data and then created a personality test, they used the personality test data to then combine it with previous data to target them.
Openness (imagination, insight, curiosity)
Conscientiousness (impulse control)
Extraversion (sociability, expressiveness)
Agreeableness (trust, kindness, cooperation)
Neuroticism
Accounts for the human element→ can use fears and what they like to segment to people.
Challenges: how do you get the data ethically and morally & you have to have a lot of skill to leverage that data→ ex. amazon, google, etc.
we can use other browsers so people can’t segment you
What is a target market?
a group of segments the company wishes to appeal
to, design products for, and tailor its marketing activities toward.
Firms typically have primary and secondary markets and allocate
resources to them accordingly.
What is the target marketing process? What are the steps involved?
identify markets with unfulfilled needs
determine market segmentation
strategically select segments to market
position through marketing strategies
How does target marketing work?
works through bringing segments together to pertain a strategy to and hopefully gain their attention
What is the difference between a “shotgun” strategy and a “targeted” strategy?
shotgun is aiming it and hoping you hit your target markets( ex. napolean dynamite slapping up posters around school)→ sometimes we use shotgun because we do not have the data but the risk is pertaining to a diverse market, you relate to less people.
and targeted is pertaining to a specific group with a strategy that hits the bullseye (the nerdy kid in napolean getting protection from the bully)
What examples did we discuss in class to evaluate target marketing effectiveness?
Napolean Dynamite vote for Pedro → posters vs the protection for geeks
Ruckus → competitor of Napster and was free, was used for college students and ads would pop up. ex. ford super duty maybe motivate students to get a job to one day own a ford super duty (planting the seed, brand equity building), college students are opinion leaders telling parents about ads they saw.
prostate formula
also talked about micro targeting → breaking down the jury by tampering their feed. ex. Facebook and Cambridge analytics
What is brand/product positioning?
a marketing process used to create cognitive
schemas in consumers’ minds.a marketing strategy used to stake a claim, with the goal of owning a specific space in consumer’s minds.
what comes to mind when we say a brand or product in consumers minds. (think about it as owning real estate in someone’s mind)
ex. Sears→ appliances and tools
What is a cognitive schema?
taking up real estate in peoples minds→ a mental structure that guides how consumes perceive and interpret information about a product or a brand.
Why do firms use brand/product positioning?
Upflation→ repositioning products etc. Take old products and call them something new (ex. all over body deodorant and costs 4x more) change the schema in consumers mind to charge more money.
What are the different positioning strategies we discussed in class? How do we characterize them?
price or quality→ name brand vs store brand (cereals)
use of application→ Baking soda is now used for air freshener, using it to wash things, the same product used differently.
product class→ ex. the butter category
product user→ ex. Dr.pepper 10 is for men (women don’t think about drinking it)
competitor → pc vs Mac commercial showing contrast between products
attributes & benefits→ mad men example positioning the cigarettes “its toasted” → ex. limit the calories or minimize the portion and calling it less calories
What are positioning statements?
target, concept, point of difference, and reason to believe it.
format: to (target)
our brand is the (concept)
that (point of difference)
because (reason to believe)
What are the different components of positioning statements? What does each component entail?
target→ the market/ who we are pertaining to
concept→ what a brand is/ stands for/ mission
point of difference→ what separates them from competitors/ individualize
reason to believe→ evidence backing up the points
ex. chevy truck
Why is the STP framework so important for Advertising & Promotion?
foundation for affective promotional marketing activities
STP helps to identify the needs, wants, desires, values, and dreams of consumers in the target audience.
It provides structure for communicating effectively with members of the target audience.
It guides branding (and brand building over time) to create proper schemas in consumers’ minds.
Because it determines successful advertising campaigns, it should underlie and guide our advertising and promotional strategies.
STP forms the foundation of effective advertising and promotion.
It helps to identify the portion of the market that will respond favorably to marketing efforts.
What are the main components of the communication process?
Source (sponsor) -> encoding (consumer understands what is being communicated-> channel (computing ads/ medium)-> decoding-> (consumer interpreting with noise) receiver (through these we get messages) then we repeat the chain after receiving context and feedback.
We have a message that will travel through a channel (the message must be encoded by the sender or source, goes through a channel, then it has to be decoded to be received)
*Usually in a marketing context the source is a sponsor of the product service idea
-> feedback: when a communication is communicated, and it gets miscommunicated, who’s fault is it? (Probably the sender)
Source, message, channel, receiver, feedback (Communication process in ad and promo)
In what sequence do these elements occur in the process?
source→ encoding→ channel→ decoding→ receive (and then feedback and getting context repeats the process)
How do each of these components map on to advertising and promotional communications?
This is the entire process of communicating in advertising and promotion and trying to get a message to consumers and then reflecting on the effectiveness of an ad or promotion.
What factors facilitate successful communication?
over communicating and making sure a message is effectively received
Why does communication typically break down?
Not having shared understanding or having alternative meanings (ex. makeup exam)
different world, moderate commonality- shared experiences and then high commonality→ know what others are thinking and looking at what people are doing and know immediatley what to do.
What impact do fields of experience have on communication?
they affect how we encode and decode messages to others and our understanding of what is being communicated.
What examples did we discuss to highlight differences in fields of experience?
different worlds (ex. makeup exam), moderate commonality- shared experiences (ex. waterboy scene were guy can’t be understood but sort of is understood) , and then high commonality (step brothers) → know what others are thinking and looking at what people are doing and know immediatley what to do.
How do consumers and marketers sometimes differ regarding their fields of experience?
Firms sometimes mistakenly view and market products as simply a bundle of attributes or
characteristics → example apple product users being lumped.
How do these differences impact communication between marketers and consumers?
Marketers see things as just their attributes.
Consumers oftentimes see products as a set of possible outcomes,
which can be functional, psychological, social, and/or symbolic.
What examples of successful and/or unsuccessful communication did we discuss in class?
apple products vs competitors and their spec counts but people do not think about how apple makes consumers feel.
ex. Humphrey yang giving advice on financial topics on TikTok → he is a great source for gen z, can communicate effectively, knows who to market towards→ communicates to those channels and has owned the gen z finance mentor role.
What are the keys to successful communication?
Select an appropriate source*
Properly encoded the message
Identify channels used by target audience
Communicate in the proper channel
Obtain feedback & revise message
How do we define consumer behavior?
The mental and emotional processes and activities of people who purchase goods and services to satisfy particular needs and wants
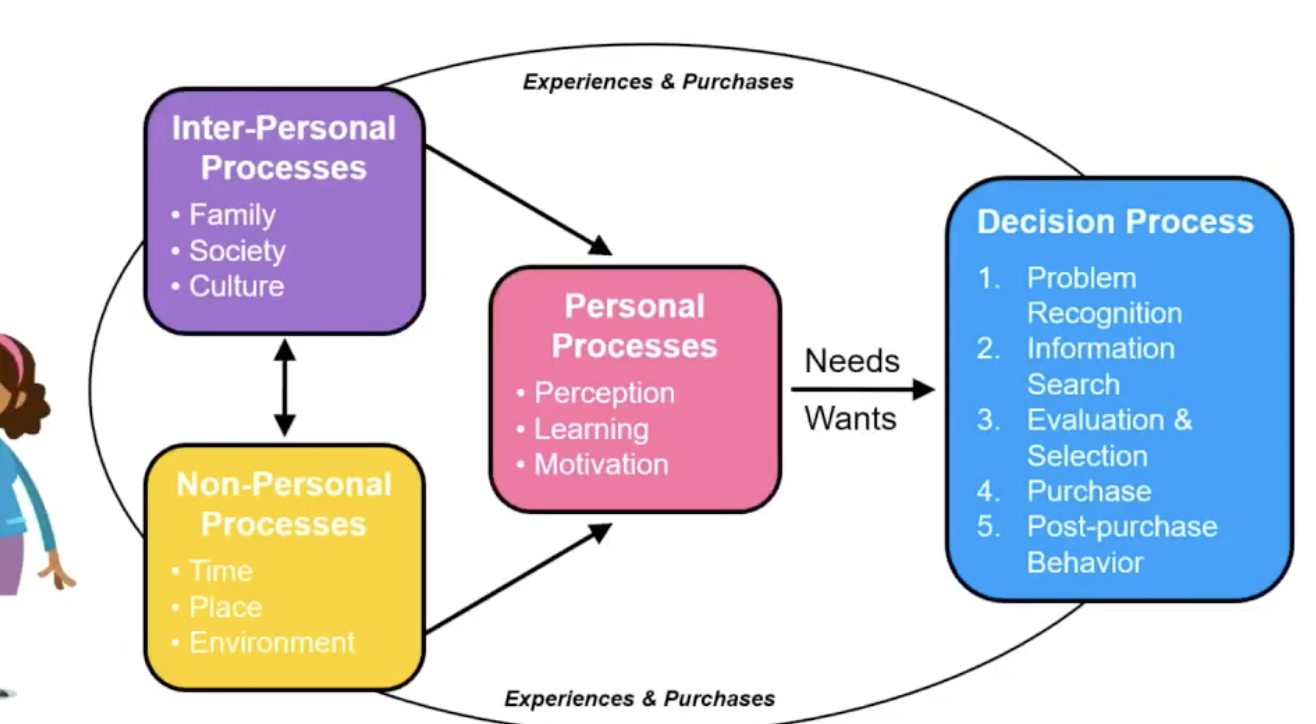
what are the different influences on consumer behavior?
decision processes→ Consumers follow a predictable path for many purchase decisions Ad & Promo activities can impact consumer decision making at all stages( prob recognition, info search, evaluation and selection, purchase, and post purchase behavior)
personal processes→(perception, learning, motivation, needs and wants)(are influenced by interpersonal and non personal processes
interpersonal processes→ ( family, society, culture)
non-personal processes→ (time, place, environment)
experiences and purchases→ impact everything (inter, non, personal, and decision processes)
What is problem recognition?
the perceived difference between actual and ideal state.
Discrepancy between these two states -> advertising is so good driving car and heard commercial about mothers day and bought flowers
How does advertising impact decision making?
We can change the decision makers of the actual state or make it change perceptions of an ideal state. (Manipulation and then every competitor needs to meet that bar)
Advertising is a kickstarter for prob recognition.
Then consumers move through the decision making process
Advertising can impact all the stages and provide relevant and meaningful resolutions to help in decision making.
What are the 5 steps of the decision making process?
1.) problem recognition
2.)info search proce
3.) evaluate and select
4.) purchase
5.) post purchase evaluation
What is perception?
the way we sense interpret and comprehend stimuli
What are examples of common stimuli used in advertising and promotion?
loud our catchy sounds or jingles, using influencers or notable figures, playing on emotions, utilizing trends or even asking a question that relates to a problem consumers might be facing.
What are perceptual screens?
What examples of screens did we discuss in class?
Physical stimuli-> ads, promos, products, stores, influencers)
physiological
Psychological Screens
Make it past all the resistance attitudes for what?-> once we get through the resist we are heading towards trying to get things through cognition
what is a psychological screen?
(emotional attitudes, beliefs, habits, personality, self-concept) things we like and don’t like
Ex. The kids not paying attention in ferris beuler’s day off
what is a physiological screen
detect incoming info and data and measure the intensity using 5 senses
(sensory-> sight sound touch taste smell) (sensory is where things need to break through a threshold, something needs to be bright enough or smell strong enough)
Ex. The chalk on the chalkboard waking up the kid from Ferris beliers day off in economics class
What is selective perception?
When we only perceive certain things because they break through the stimuli barrier, or we have a preconceived notion of not liking something so it does not grasp our attention.→ process of focusing on some info and data while ignoring others
What is cognition?
involves comprehending, processing, and understanding the stimuli
has to pass both perceptual (physiological and psychological) into awareness)
(Awareness or non awareness Cognition thoughts awareness)
What are mental files?
autobiographical, experiences, semantic, info, wants/ needs
What is tricky about mental files: think about a folder system on your compute, can resist making a new folder because it feels like a lot. We resist cognitive work.
Stimuli that make it into awareness are deemed important and consistent with our memories and are stored in mental files. We avoid info that is inconsistent with existing mental files.
What barriers must stimuli pass through to ultimately be stored as mental files?
People do not like to store stuff that they do not have folders for already. (how lazy we are as consumers (cognitive-mizers), it can be hard to pass through peoples attention, ad must be: good enough, personally relevant, meaningful, important enough to make it into the mental files? Is it worthy to store as a mental file. Most stuff does not make it through to mental files
What role does feedback play in perceptual processes?
Once there is something in a mental file this is where we receive feedback for whatever we store for next time→ can be positive or negative ex. remembering an ad you did not like so next time you do not store it (not pay attention to it)
What is persuasion?
occurs when a change in belief, attitude, or behavioral intention takes place→ goes 2 ways central or peripheral
What is the central route to persuasion?
we pay attention to the content of the message→
High ability and motivation
to process messageAttention is paid to
message contentInvolvement is high
What is the peripheral route to persuasion?
People are not paying attention to the message→ all the other things (like the packaging)
Low ability and motivation
to process messageAttention is paid to
peripheral cuesInvolvement is lo
care but do not have the cognitive ability to process it.
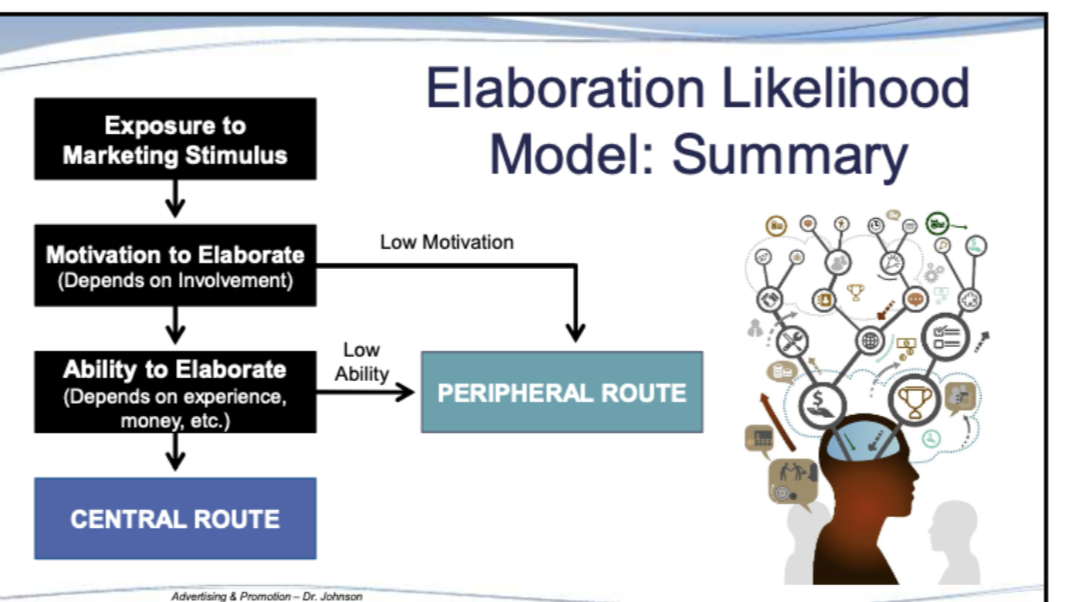
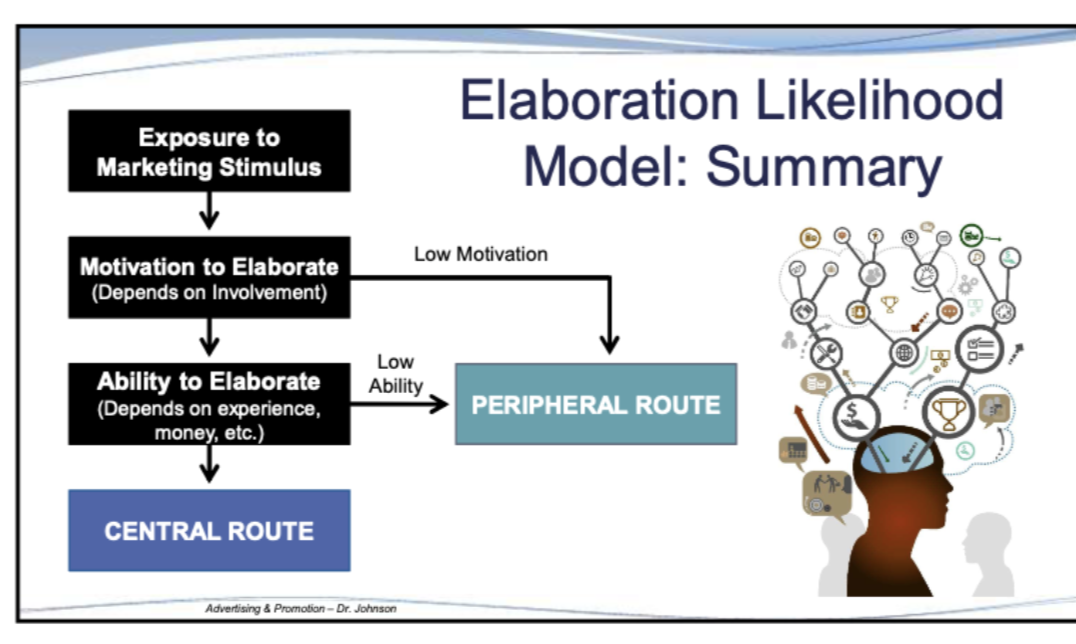
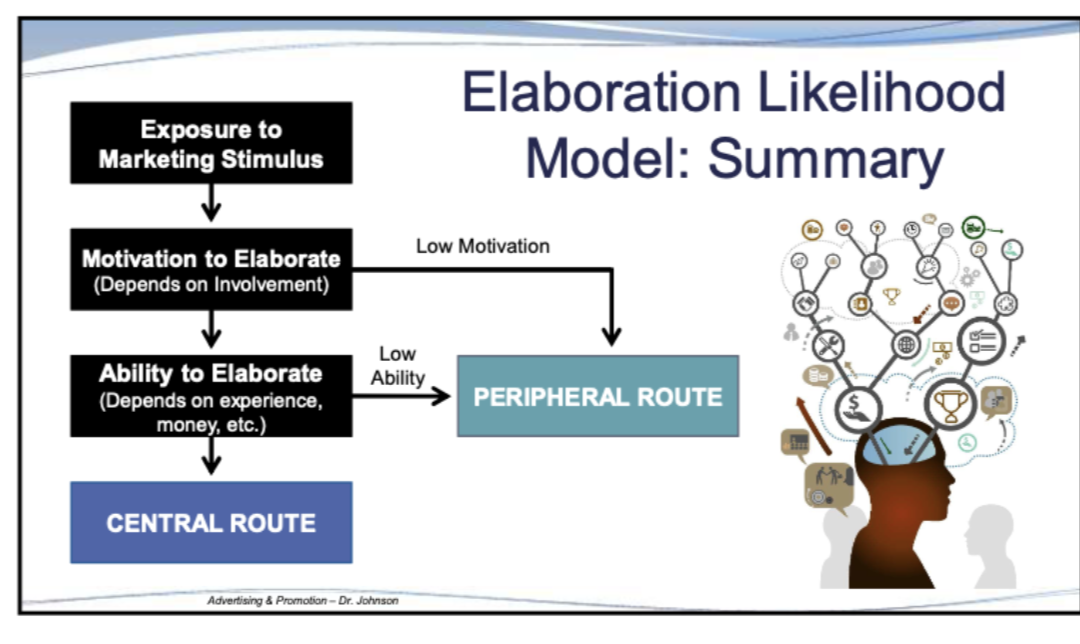
What is the Elaboration Likelihood Model (ELM)?
The way in which we process things and are persuaded with our attention (how much motivation and ability we have to process things and be persuaded)
Based on ELM, when are consumers likely to process using the peripheral route?
If the have high motivation or low ability, or both low motivation and low ability
Based on ELM, when are consumers likely to process using the central route?
High motivation and high ability to elaborate
What are attitudes?
An acquired mental position regarding some idea or object
The positive or negative
(valence) evaluations or feelings that we holdIs it possible to change consumers’ attitudes? How?
How do source factors influence persuasion?
Our attitudes are influenced by: message factors (content of message) or Source factors (who delivers the message)
What is source credibility?
Influencers who are viewed by consumers
as credible are more persuasive.
Credibility is derived from the influencer’s reputation(skill and expertise) and their objectivity(trustworthy and honest)
redline example of the energy drink→ choose Oprah
What is source attractiveness?
impacts their ability to
persuade consumers.
This is often determined by
their likeability (pleasant and agreeable) and how
similar/dissimilar(similarity→ audience and reference) they are
from consumers.
What are source associations?
Influencers who elicit positive reactions and other emotional responses are more persuasive.
How do we use source factors to select Marketing spokespeople and/or influencers?
We use them to tap into how it makes others feel and to find a target audience and how that can also determine who is needed for specific products and being the right fit for a product or campaign→ who’s values and what they stand for
(Ronaldo is the highest paid influencer)
What is motivation?
refers to the underlying forces
(or motives) that contribute to our actions.
forces to get us to act that stem from conscious or unconscious goals of satisfying needs
and wants.
What are needs?
basic human forces that motivate us to do
something
What are wants?
things that we desire, but we can
live without, if needed
What needs does Maslow identify?
physiological (ex. food, health), safety( car ads highlighting safe features), social or love (ex. coke ad based on finding love), egoistic/ self esteem (ex. dove ads), then top of the pyramid is self-actualization (ex. leader based ad)
In what order are these needs typically sought?
Bottom to top→ physiological, safety, social, self esteem, self actualization (top)
What influence does family have on consumption?
affect our attitudes toward
many products and our purchasing habits.
- generations of brand loyalty
-generations of service loyalty
-food consumption trends