IB HL Biology: Enzyme Kinetics, Inhibition, and Reaction Graphs
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
What are the four variables that affect the rate of reaction?
Temperature, pH, enzyme concentration, substrate concentration.
How does temperature affect the rate of reaction?
As temperature increases, the rate of reaction increases until the optimum temperature is reached; beyond that, the enzyme denatures and the rate decreases.
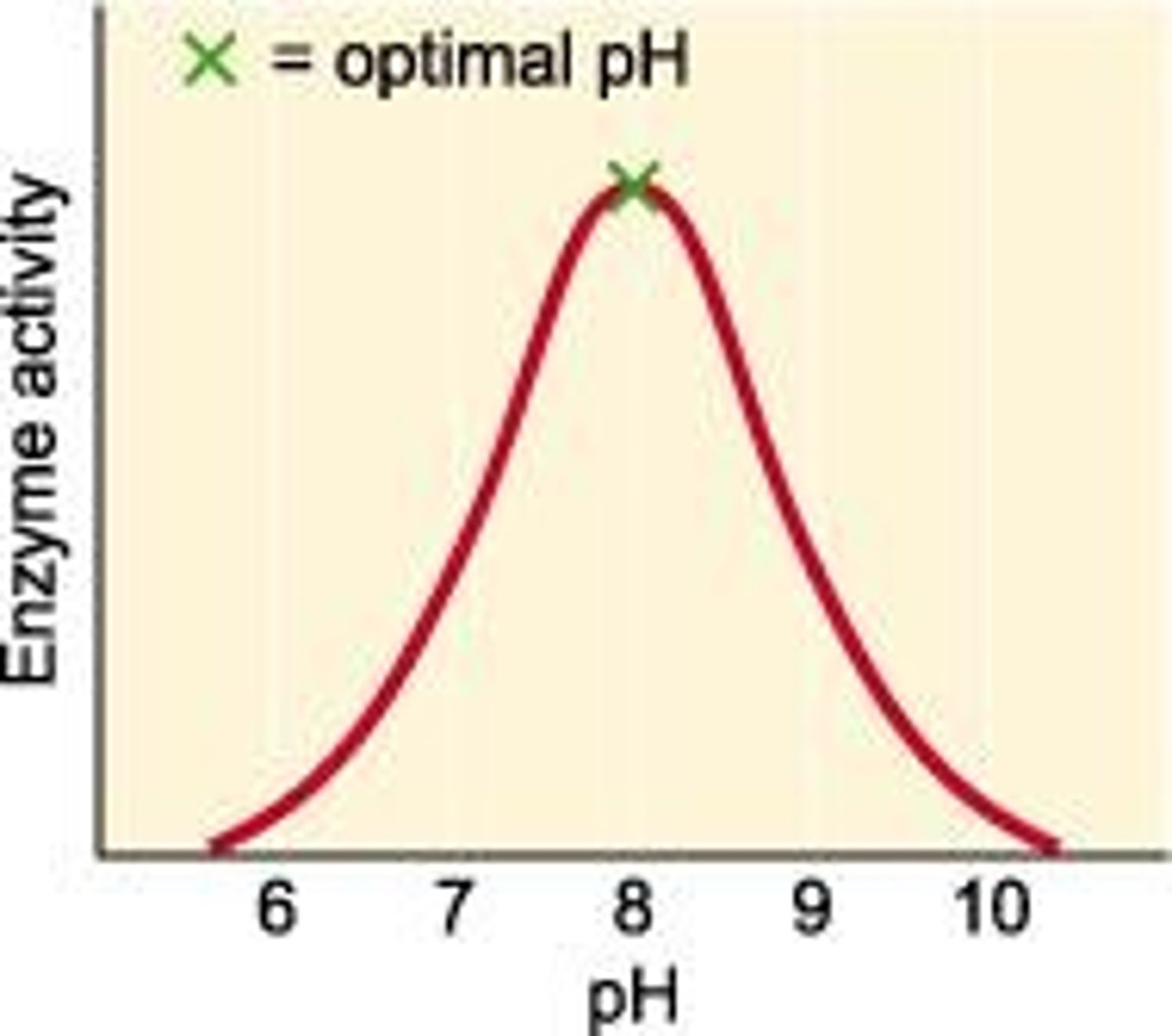
What happens to an enzyme at its optimum pH?
The enzyme functions best at its optimum pH, represented by the peak of the rate of reaction graph.
What is the effect of increasing enzyme concentration on the rate of reaction?
As enzyme concentrations increase, the rate of reaction increases due to more enzymes available for substrate collisions.
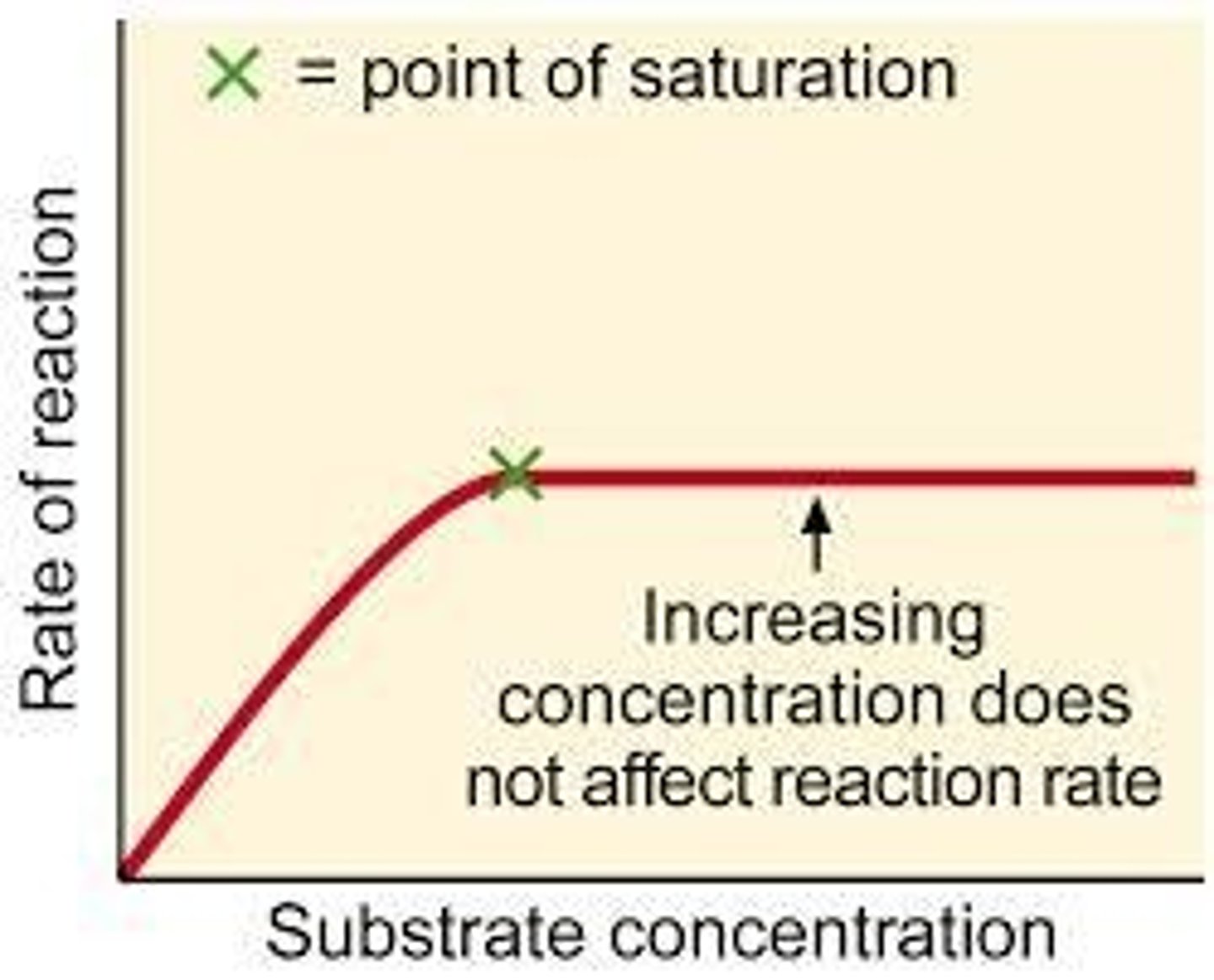
What is the point of saturation in enzyme activity?
It is the point where all enzymes are working at maximum efficiency, and further increases in substrate concentration do not increase the rate of reaction.
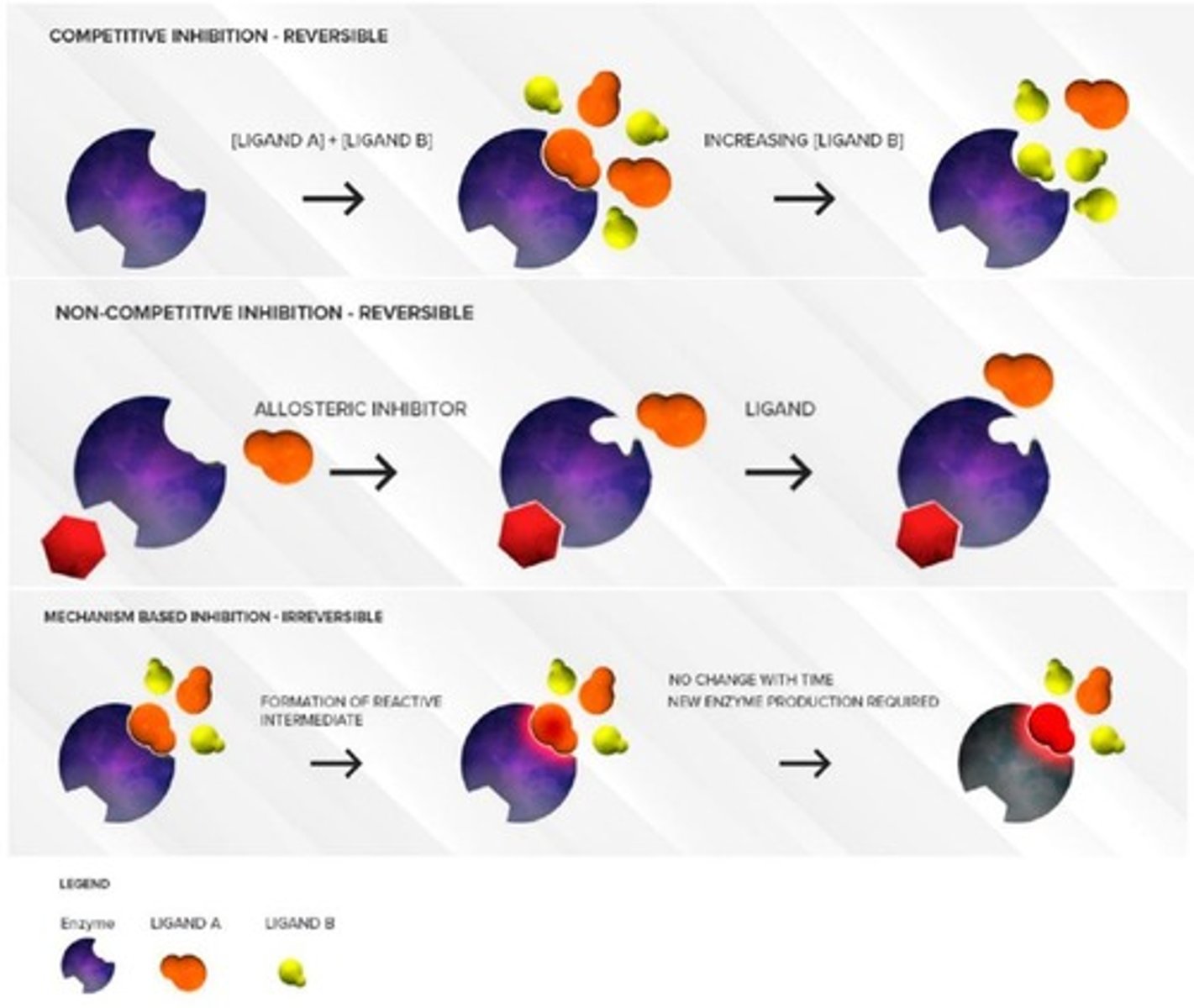
What is competitive inhibition?
It occurs when an inhibitor binds to the active site of the enzyme, blocking the substrate from binding.
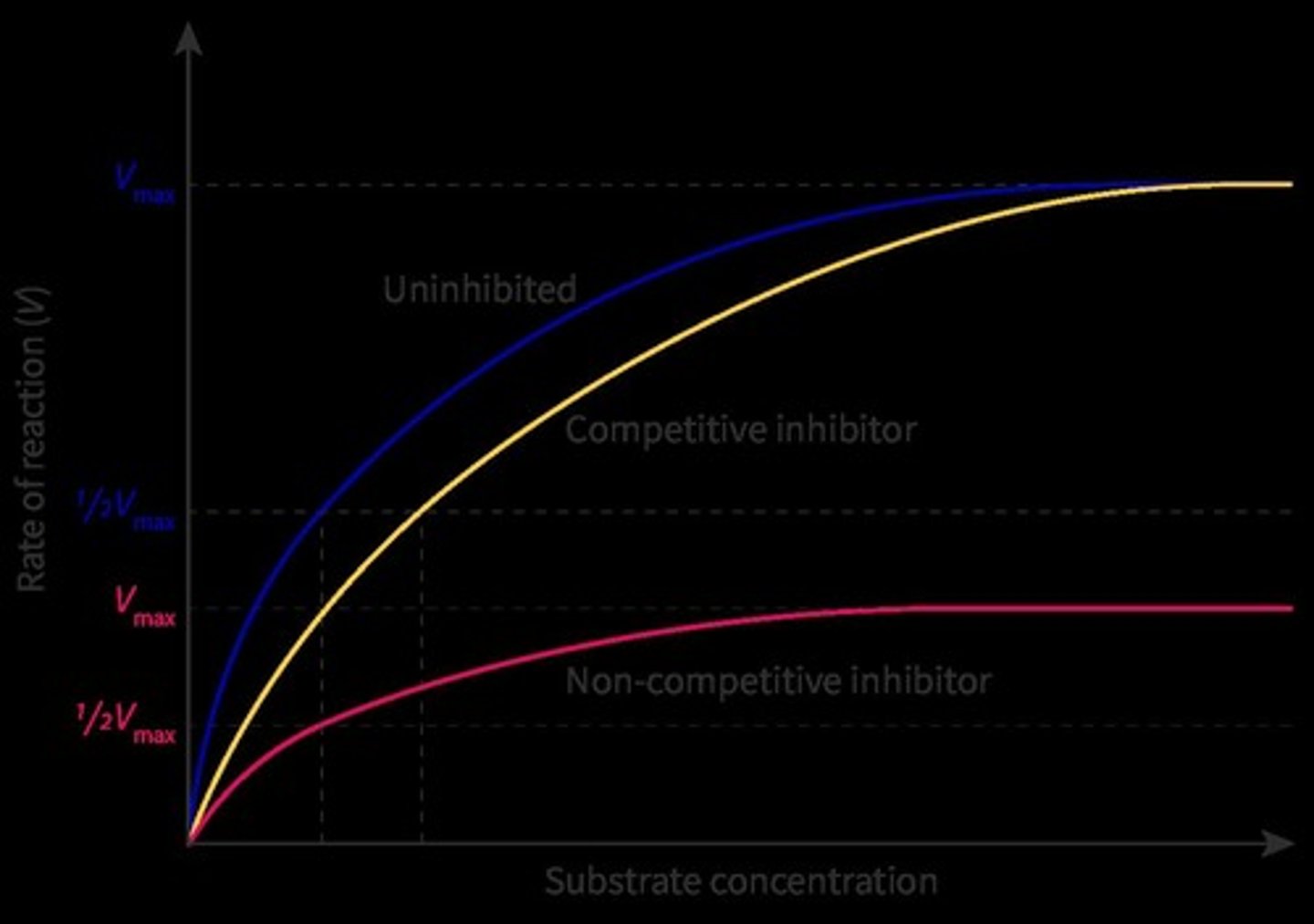
What is noncompetitive inhibition?
It occurs when an inhibitor binds to an allosteric site on the enzyme, changing the shape of the active site and preventing substrate binding.
How does substrate concentration affect competitive inhibition?
As substrate concentration increases, the impact of competitive inhibition decreases.
How does substrate concentration affect noncompetitive inhibition?
The impact of noncompetitive inhibition is not affected by increases in substrate concentration.
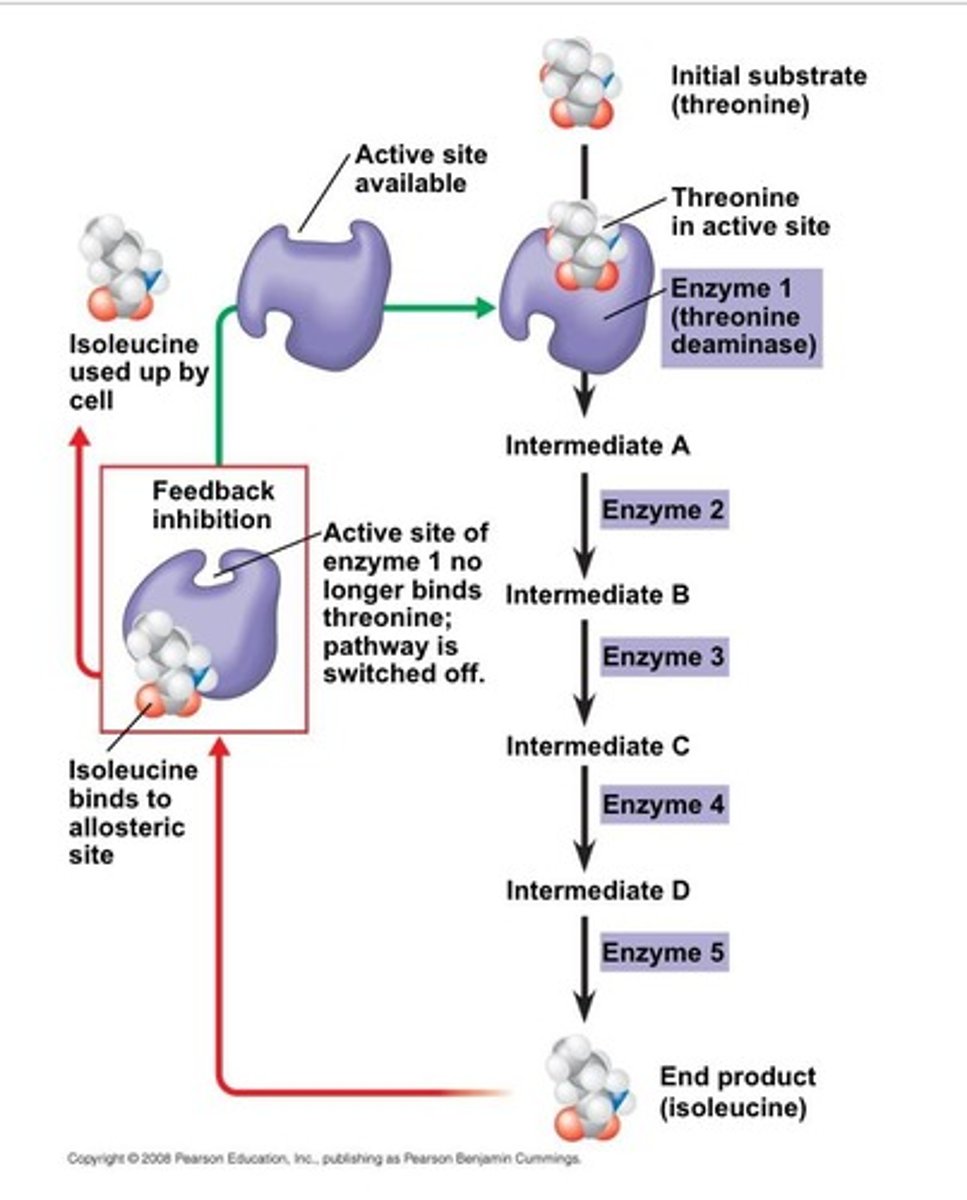
What is end product inhibition?
It is when the end product of a metabolic pathway inhibits the first enzyme in that pathway to prevent overproduction and reduce waste.
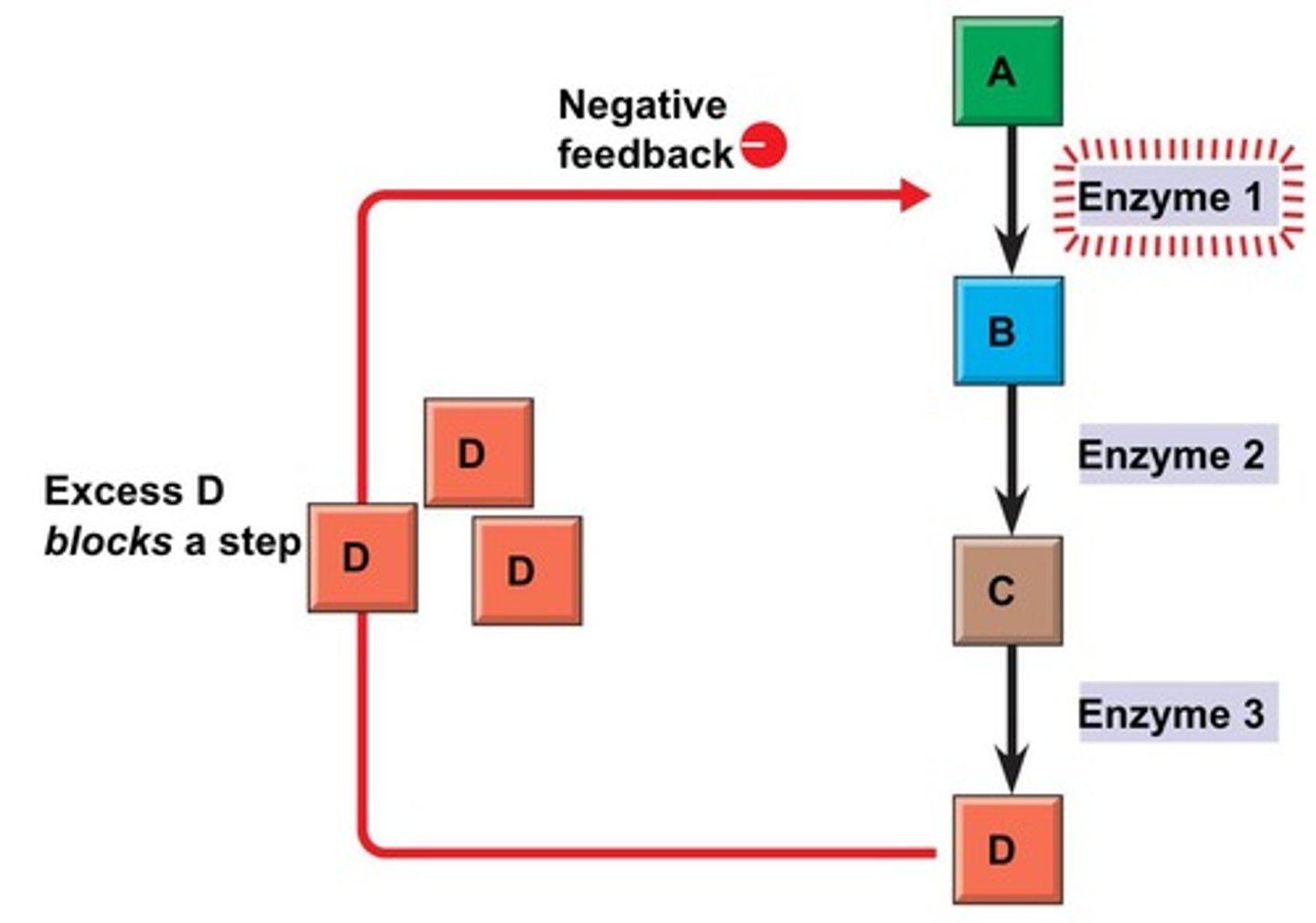
What happens when isoleucine is present in sufficient amounts in a cell?
It inhibits enzyme 1 in the metabolic pathway converting threonine to isoleucine.
What is mechanism-based inhibition?
It occurs when an inhibitor binds irreversibly to the active site of an enzyme, permanently disabling it.
How does penicillin act as a mechanism-based inhibitor?
Penicillin binds irreversibly to the transpeptidase enzyme, weakening the bacterial cell wall and causing bacterial cell death.
What is transpeptidase's role in bacteria?
It helps to build and maintain the structure of the bacterial cell wall.
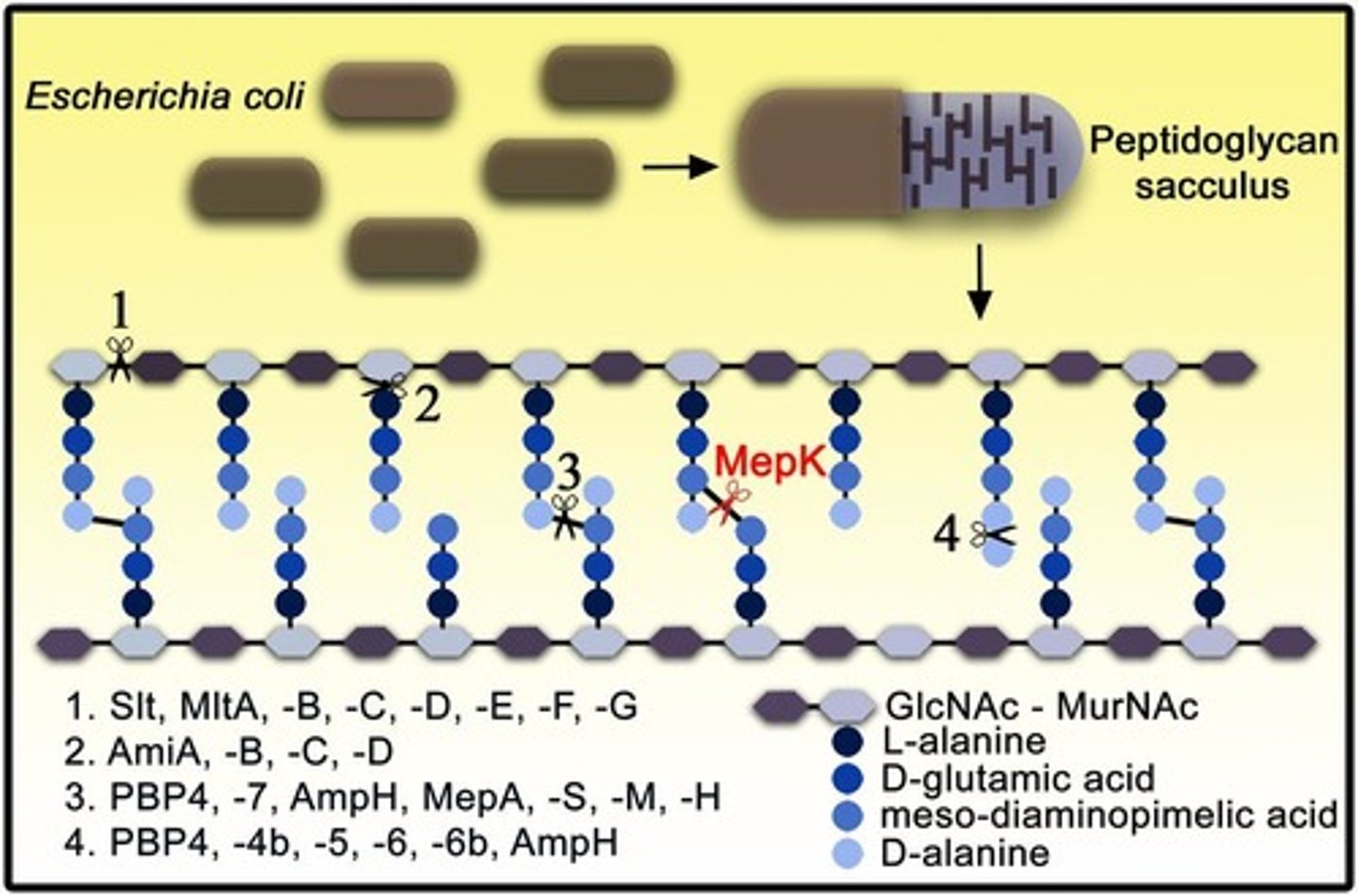
What leads to penicillin resistance in bacteria?
Changes in the shape of the transpeptidase enzyme prevent penicillin from binding, making it impossible for penicillin to deactivate the enzyme.
What is the relationship between enzyme activity and metabolic pathways?
Enzyme activity can be controlled to manage metabolic pathways and prevent chemical chaos in cells.
What is the significance of the optimum temperature for enzymes within an organism?
Most enzymes have the same optimum temperature which is crucial for their activity.
Why do different enzymes have different optimum pH levels?
Different enzymes may function best in different environments, leading to variation in their optimum pH levels.
What is the general effect of denaturation on enzyme activity?
Denaturation reduces enzyme activity, leading to a decrease in the rate of reaction.
What is the role of collision theory in enzyme reactions?
Collision theory explains that the rate of reaction increases with more frequent collisions between enzymes and substrates.