Building Utilities
1/115
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
116 Terms
backpressure
a suction created by the flow of liquids in a pipe;
a pressure less than the atmospheric pressure
ball valve
(type of valve)
the flow of liquid is controlled by a rotating drilled ball that fits tightly against a resilient (flexible) seat in the valve body
battery of fixtures
any group of two or more similar adjacent fixtures which discharge into a common horizontal waste or soil branch
branch interval
a vertical length of soil or waste stack at least 8 feet in height (one storey high) within which the horizontal branches from one story or floor of the building or structure are connected to the stack
building sewer
(part of drainage system)
extends from the end of the building drain and conveys its discharge to the public sewer, private sewer, individual sewage disposal system or other appropriate point of disposal
building supply pipe
(part of drainage system)
located between the water main and water meter
cesspool
a loosely lined excavation in the ground which receives the discharge of septic tank and designed to permit the effluent from the septic tank to seep through the bottom and sides of the pit
drainage fixture unit
a common measure of the probable discharge into the drainage system by various types of plumbing fixtures on the basis of one unit of this being equal to a discharge rate of 7.5 gallons per minute or one cubit foot of water per minute
drainage, waste, vent
DWV
globe valve
a valve in which the flow of water is cut off by means of a circular disk
gooseneck
a p-shaped trap commonly used on most plumbing fixtures except for a fixture having an integral trap
gooseneck
a kind of return bend of small-sized faucet;
one end of which is about one foot long and the other end is about three inches
gooseneck
commonly used as a faucet for pantry sink and drinking fountain;
the lead connection between the service pipe and the water main
fixture
a receptacle attached to a plumbing system wherein water and wastes may be collected
full bath
a bathroom containing a water closet, lavatory, and bath tub
plumbing
the art and science of installing pipes, fixtures, and other apparatus for bringing in water supply and removing water and waterborne waste in buildings
privy
an outhouse or structure used for the deposition of excrement
riser
a water supply pipe that extends vertically one full storey or more to convey water to fixture branches or group of fixtures
septic tank
a watertight receptacle which the discharge of sanitary plumbing system or part thereof, designed and constructed to retain solids, digest organic matter through a period of detention and to allow the liquids to discharge into the soil outside of the tank through a system of open jointed subsurface piping or seepage pit
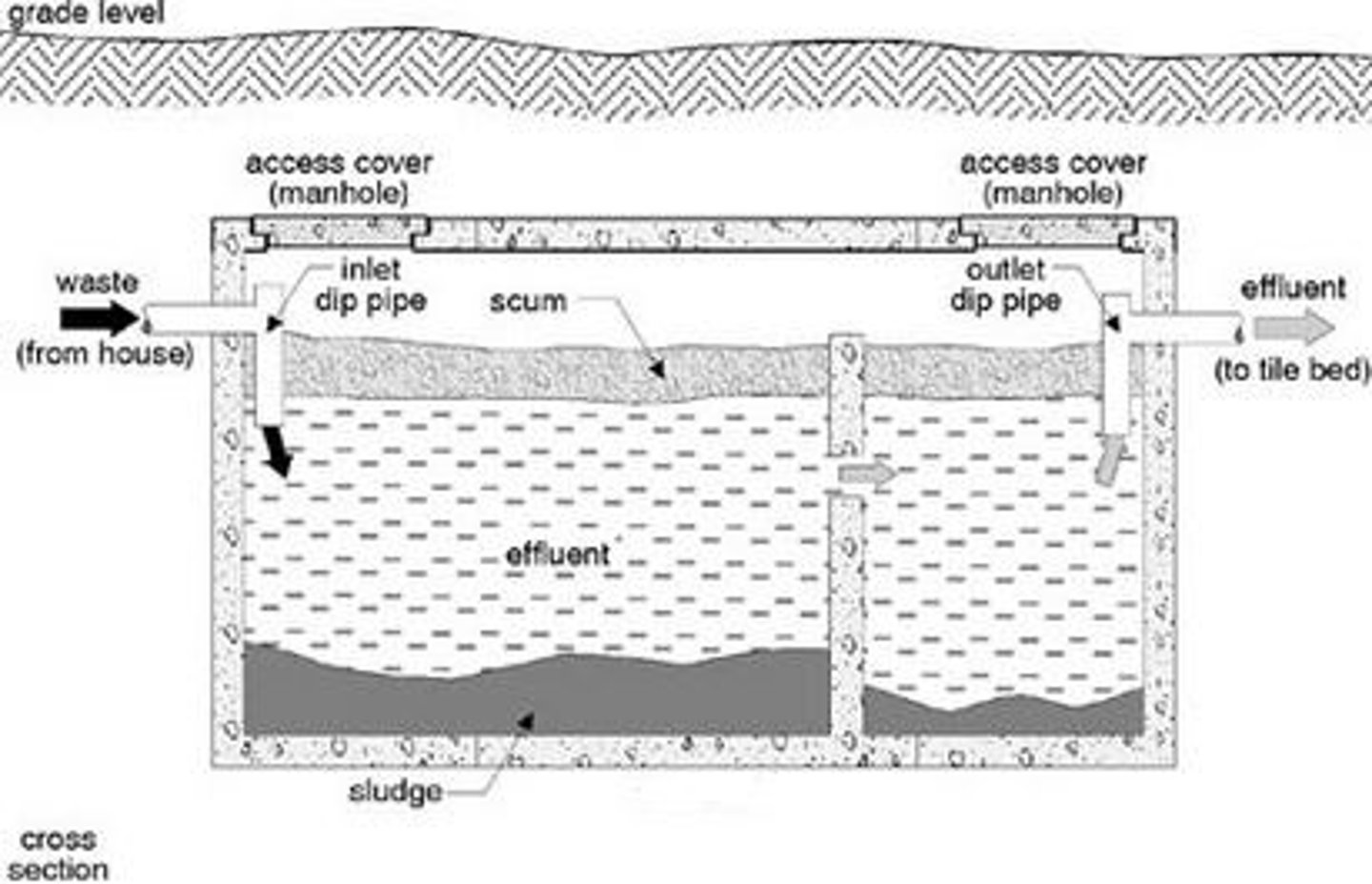
soil pipe
any pipe which conveys the discharge of water closets, urinals, or fixtures having the similar function, with or without the discharge from other fixtures, to the building drain or building sewer
trap
a fitting or device designed and constructed to provide, when properly vented, a liquid seal which prevents back flow and passage of foul air and gases without materially affecting the flow of sewage or waste water through it
waste stack
a vertical pipe which conveys only waste water or liquid waste free of fecal matter
water distributing pipe
first section the water supply piping in a building after the water meter
water distributing pipe
a pipe which conveys potable water from the building supply pipe to the plumbing fixtures and other outlets
water supply system
consists of the water service pipe, water supply line, water distributing pipes, and essential branch pipes, valves and all other appurtenances for the supply of potable water
yoke vent
a pipe connecting upward from a soil or waste stack below the floor and below the horizontal connection to an adjacent vent stack at a point above the floor and higher than the highest spill level of fixtures for preventing pressure changes in the stack;
vent to vent
ampere
unit of electrical current
farad
unit of capacitance
horsepower
unit of mechanical power
mho
reciprocal of ohm
ohm
unit of resistance
tesla
unit of magnetic flux
volt-ampere
unit of volt-electrical potential
watt
unit of electrical power
cables
conductors that are larger than wires and stranded (no. 6 AWG and larger)
cable tray
a unit or assembly units or sections and associated fittings forming a rigid structural system used to support cables
conductors-on-insulator wiring
concealed knob and tube; open wiring on insulators
conduit
a cylindrical conduit or conductor;
the wall thickness is sufficient to receive a standard pipe
copper
has the property of being ductile and malleable
current
analogous to pressure in water flow
heat resistant thermoplastic
THHN;
insulated conductor
Hermholtz resonator
named in honor of a German physicist;
consists of a hollow material with a small hole on one side;
used to detect individual frequency of complex acoustic wave configuration
impedance
used in transformers and other devices in AC;
combination of resistance and reactance
individual resonator
a type of resonator made from empty clay vessels of different sizes;
absorption ranges from 100-400 hertz
metal clad cable
type MC;
a factory assembly of one or more conductors, each individually isulated and enclosed in a metallic sheath of interlocking metal tape, or a smooth corrugated metallic tube
multi-outlet assembly
a type of surface flush raceway designed to receive conductors and receptacles assembled in the field or in the factory
non-metallic sheathed cable
type NM and NMC;
a factory assembly of two or more insulated conductors having an outer sheath of moisture resistant, flame retardant, non-metallic material
panel board
also known as the electric panel or load center
rigid metal conduit (RMC)
a type of raceway specially constructed for the purpose of pulling in or the withdrawing of wires or cables after the conduit is in place
roughing-in
the installation of parts of the plumbing system which can be completed prior to the installation of fixtures or finishing;
includes drainage, water supply, and vent piping, and necessary fixtures
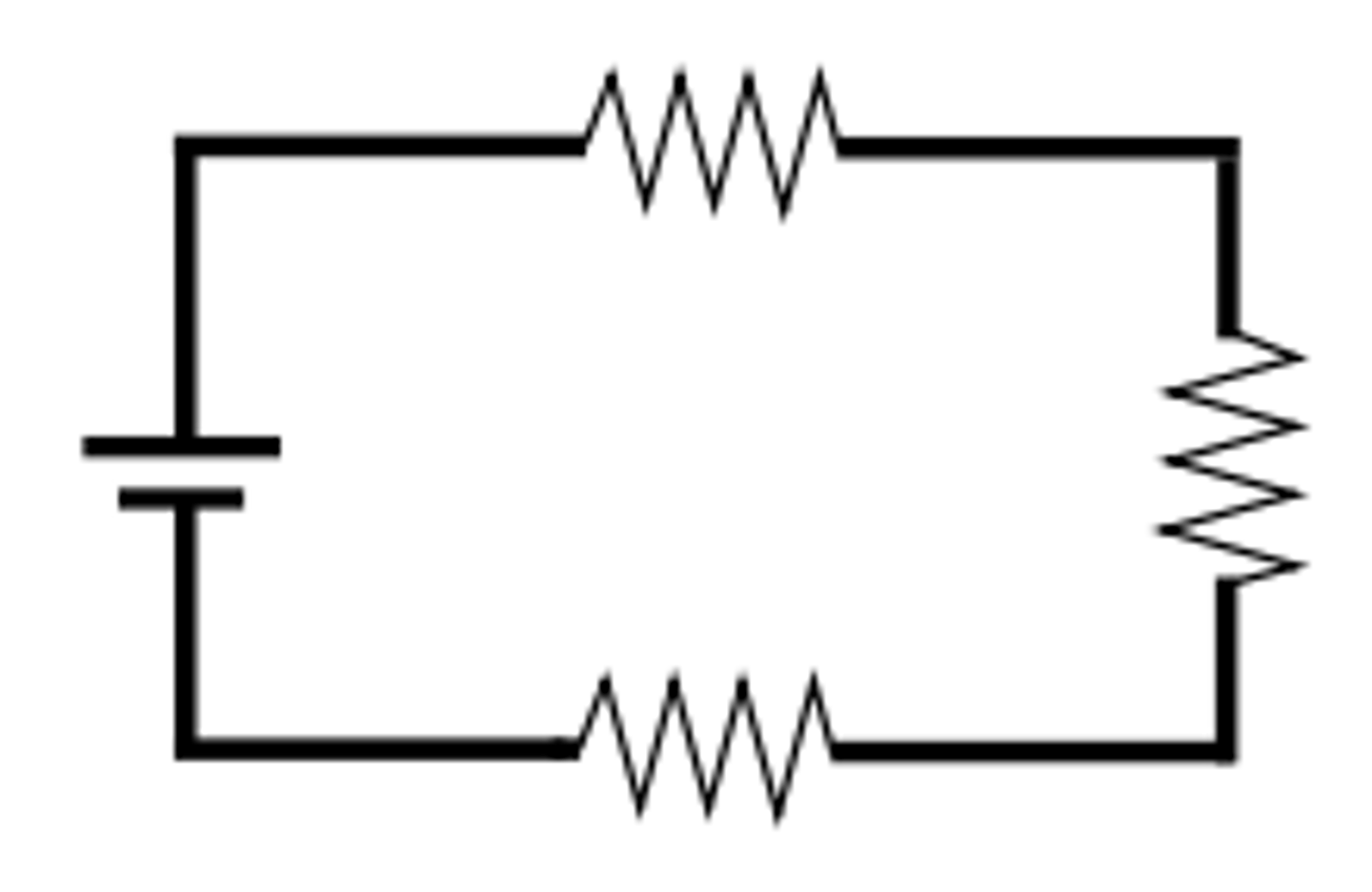
series circuit
(circuit type)
components are electrically connected end to end
parallel circuit
(circuit type)
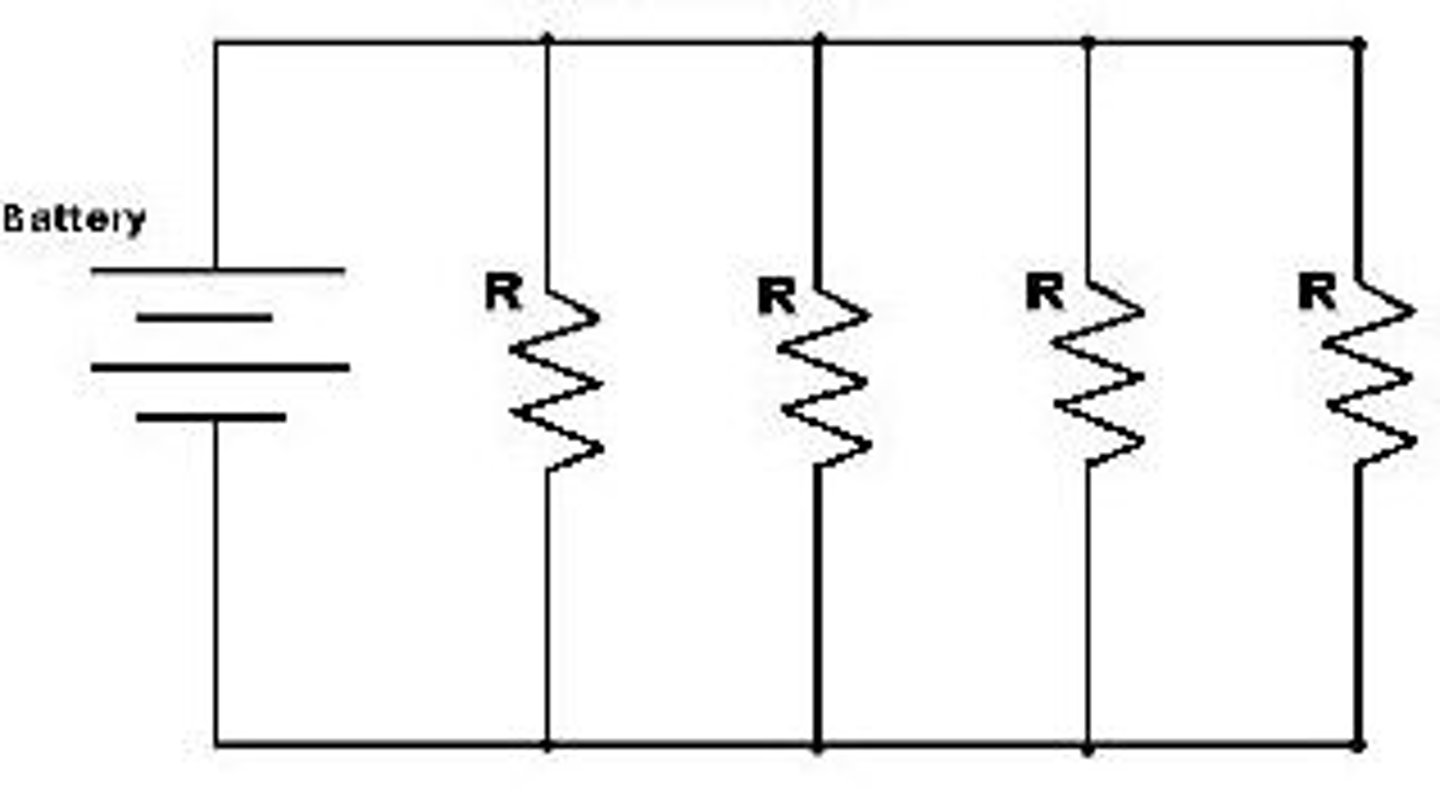
transfer switch
a type of switch used for transferring one or more load conductor connections from one power source to another
transformer
a mechanical device used to step up or step down voltage in AC
Nikola Tesla
"Let the future tell the truth and evaluate each one according to his work and accomplishment. The present is theirs, the future for which I really worked for is mine."
Wallace Clement Sabine
an American physicist who pioneered work on sound;
father of architectural acoustics
act as a switch, open or close position easily detected, can be used again after correcting fault
advantages of a circuit breaker over a fuse
2-s3w and 1-s4w
a switch combination used in order to control a lamp or group of lamps in three different locations
low resistance, high current
characteristics of a short circuit
positive and negative polarity, average value is zero, has frequency
characteristics of an alternating current
lead, iron, tin
fusible materials in a fuse
length, area, temperature
factors that affect the resistance of a conductor
source, conducting path, electrical load
basic elements of an electric circuit
fungus and corrosion resistant
over-all covering of underground feeder and branch circuit cables
hydraulic elevator
(type of elevator)
supported by a piston at the bottom of the elevator that pushes the elevator up
2-8 stories
(hydraulic elevator)
scope of floors serviced
200 feet per minute
(hydraulic elevator)
speed
lowest level adjacent to elevator shaft
(hydraulic elevator)
location of machine room
traction elevator
(type of elevator)
lifted by ropes, which pass over a wheel attached to an electric motor above the elevator shaft
mid and high-rise
(traction elevator)
scope of floors serviced
faster than hydraulic
(traction elevator)
speed
counter weight
makes traction elevators more efficient
balustrade assembly, continuous belt, step assembly
basic components of an escalator
558 mm
minimum distance between the handrails of escalators
90-120 fpm
recommended speed for escalators
4 section truss
typical truss configuration for escalators
3 ropes required for traction type elevator
example of a violation of all provisions in the Mechanical Code on Elevator Design and Installation
British Thermal Unit
BTU;
the quantity of heat required to raise the temperature of one pound (0.4 kg) of water 1F
R12
(type of refrigerant)
dichlorodifluormethane
R22
(type of refrigerant)
recommended for residential, commercial, and industrial application using split type air conditioning system
seasonal energy efficiency ratio
total cooling output of an air conditioner during its annual usage, in BTU/hr, divided by the energy input during the same period, in watt-hours
thermal load
a factor used in calculating cooling load that includes heat transferred from walls, doors, ceilings, etc.
air handling unit, control equipment
elements of centralized air-conditioning systems
temperature of the surrounding air, motion of air
air-conditioning system for human comfort
uses ducts, has a cooling tower, has an air handling unit
characteristics of a centralized air-conditioning system
conduction, convection, radiation
methods of transferring heat
acoustics
transmission of sound;
effect of sound waves;
generation of sound
creep
the phenomenon whereby sound travels in a curved surface
environmental acoustics
a branch of acoustics that involves the control of noise pollution, environmental noise;
e.g. motor vehicles, aircraft noise, etc.
gold
the best conductor of electricity among copper, aluminum, and iron
inverse square law
sound intensity varies inversely with the square of the distance from the source
sound
doesn't travel in a vacuum;
aural sensation;
caused by an oscillation in an elastic medium;
caused by the vibration of particles which move in an infinitesimal amount causing particles to impart motion and energy to them
sound absorption
the product of surface area (sq. ft.) and sound absorption coefficient (SAC);
has the unit sabin
structure-borne sound
when sound impinges on a surface such as walls, floor, ceiling, etc.
threshold of hearing
e.g. the rustling of leaves in breeze
transondent facings
transparent facings with holes;
10% opening will reflect more sound compared to 20%, 30%, and 40% opening
acoustical tile
manufactured from rock wool, glass fibers, hair felt;
generally installed on wood or metal framing system
bonded acoustical panel
BAP
carpet
any of a variety of soft floor finishes made of synthetic materials such as nylon or natural material such as wool;
either glued directly to the floor or installed over n underlayment of hair felt or foam rubber
carpet
exhibits the highest sound absorption coefficient (SAC) value among:
(marble, wood, carpet, plastic)