Understanding Corrosion: Types, Mechanisms, and Control
1/299
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
300 Terms
Corrosion
Destructive attack of metals by the environment.
Electrochemical Theory
Mechanism explaining corrosion via electrochemical interactions.
Galvanic Series
Ranking of metals based on corrosion potential.
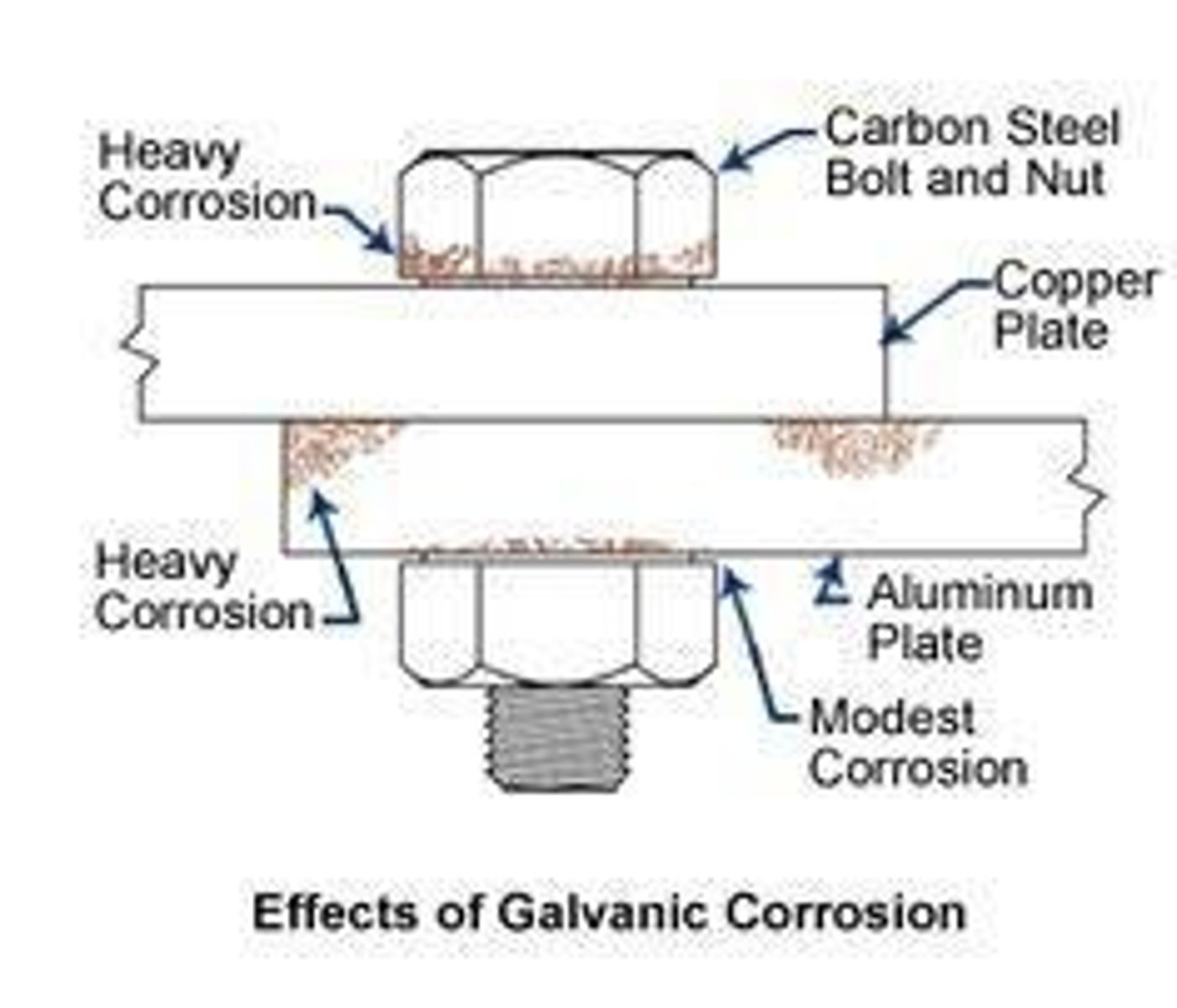
Galvanic Corrosion
Corrosion due to two different metals in contact.
Pitting Corrosion
Localized corrosion forming small pits on metal.
Intergranular Corrosion
Corrosion along grain boundaries of metals.
Stress Corrosion
Cracking due to tensile stress and corrosive environment.
Corrosion Inhibitors
Substances that reduce the rate of corrosion.
Cathodic Protection
Technique using a sacrificial anode to prevent corrosion.
Anodic Protection
Method to protect metals by making them anodes.
Metal Coating
Applying a protective layer to prevent corrosion.
Dry Corrosion
Corrosion occurring in the absence of moisture.
Wet Corrosion
Corrosion occurring in the presence of moisture.
Galvanizing
Coating steel with zinc to prevent corrosion.

Tinning
Coating iron or steel with tin for protection.
Organic Coatings
Protective layers made from carbon-based materials.
Inorganic Coatings
Protective layers made from non-carbon materials.
Rusting of Iron
Formation of Fe2O3.H2O from iron and oxygen.
Tarnishing of Silver
Formation of Ag2S from silver and sulfur compounds.
Scales on Copper
Formation of Cu2(OH)2CO3 from copper and compounds.
Corrosion Cost
Annual losses due to corrosion, 3-4% of GDP.
Human Safety
Corrosion-related failures can lead to loss of life.
Material Conservation
Corrosion affects supply of earth's material resources.
Corrosion Science
Study of corrosion mechanisms and processes.
Corrosion Engineering
Application of scientific knowledge for corrosion prevention.
Interdisciplinary Area
Combines chemistry, materials science, and mechanics.
Corrosion Mechanisms
Processes explaining how corrosion occurs.
Corrosion-resistant Alloys
Alloys designed to withstand corrosion effects.
Surface Treatments
Methods to enhance material resistance to corrosion.
Corrosion Control Measures
Strategies to mitigate corrosion impacts.
Maintenance Costs
Expenses incurred for repairing corrosion damage.
Plant Shutdowns
Temporary halts in production due to corrosion.
Contamination Loss
Loss of products due to corrosion-related leaks.
Environmental Pollution
Pollution caused by dumping contaminated products.
Dry Corrosion
Corrosion without the presence of moisture.
Electrochemical Corrosion
Corrosion involving electron flow in conductive solutions.
Oxidation Corrosion
Corrosion from direct reaction with dry oxygen.
Stable Oxide Film
Protective layer preventing further oxidation.
Unstable Oxide Film
Decomposes, allowing continued oxidation.
Volatilization of Oxide
Oxide layer evaporates, increasing corrosion rate.
Corrosion by Gases
Corrosion caused by gases like SO2 and Cl2.
Liquid Metal Corrosion
Corrosion from molten metals at high temperatures.
Anodic Area
Electrode where oxidation occurs in corrosion.
Cathodic Area
Electrode where reduction occurs in corrosion.
Conducting Medium
Substance allowing electron flow in corrosion.
Corrosion Consequences
Negative effects of corrosion on structures and safety.
Corrosion
Degradation of metals due to environmental reactions.
Electrochemical Theory
Corrosion occurs via coupled electrochemical half-cells.
Anodic Area
Site of oxidation where metal dissolves.
Cathodic Area
Site of reduction where electrons are consumed.
Microgalvanic Cells
Small electrochemical cells formed on metal surfaces.
Driving Force
Potential difference causing electron flow between areas.
Anodic Reaction
Metal oxidation releasing electrons into solution.
Cathodic Reaction
Reduction processes consuming electrons from anodic area.
Hydrogen Evolution
Production of hydrogen gas in acidic conditions.
Oxygen Reduction
Reduction of oxygen in neutral environments.
Electrolytic Conduction
Current conduction through dissolved ions in solution.
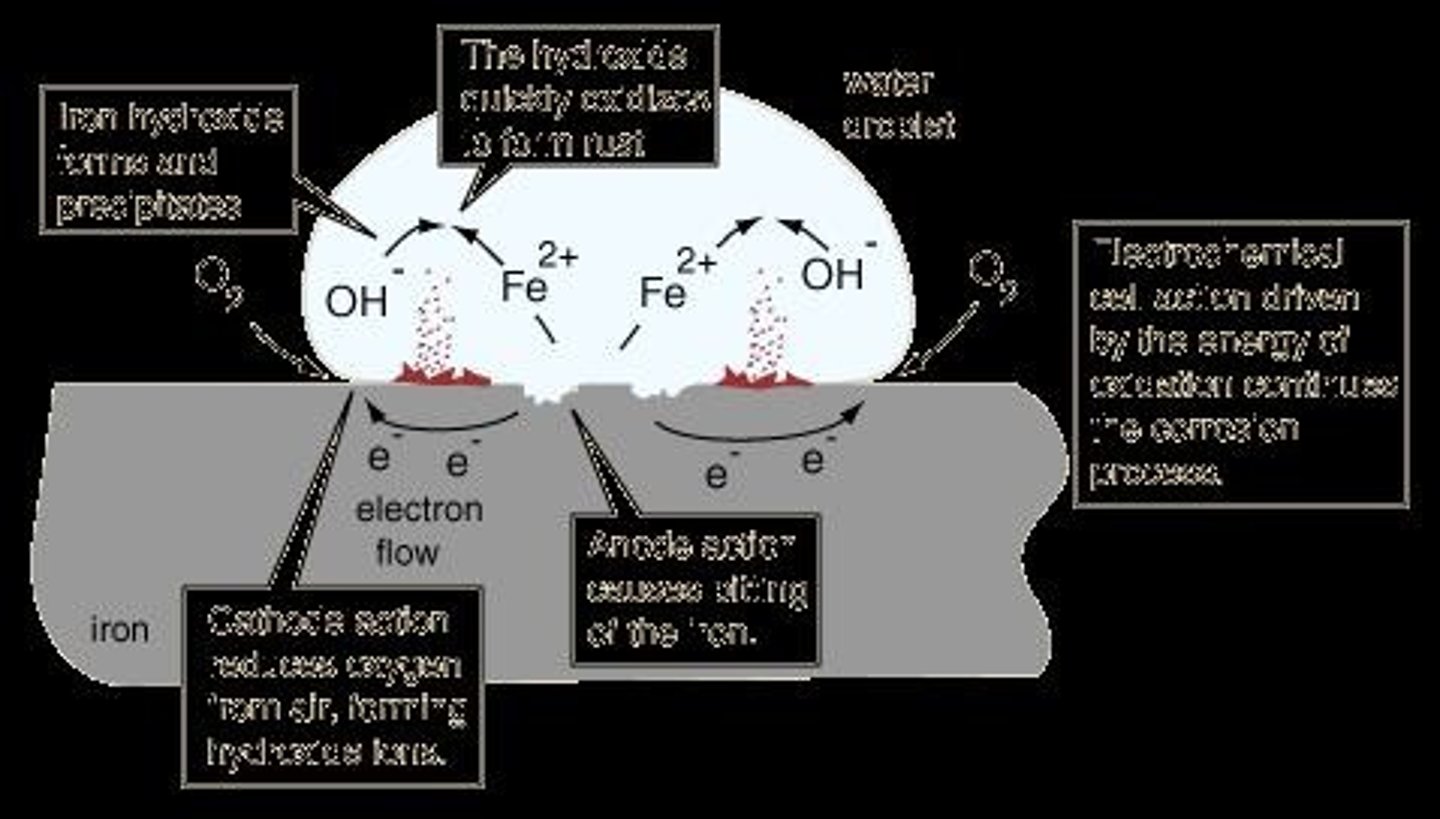
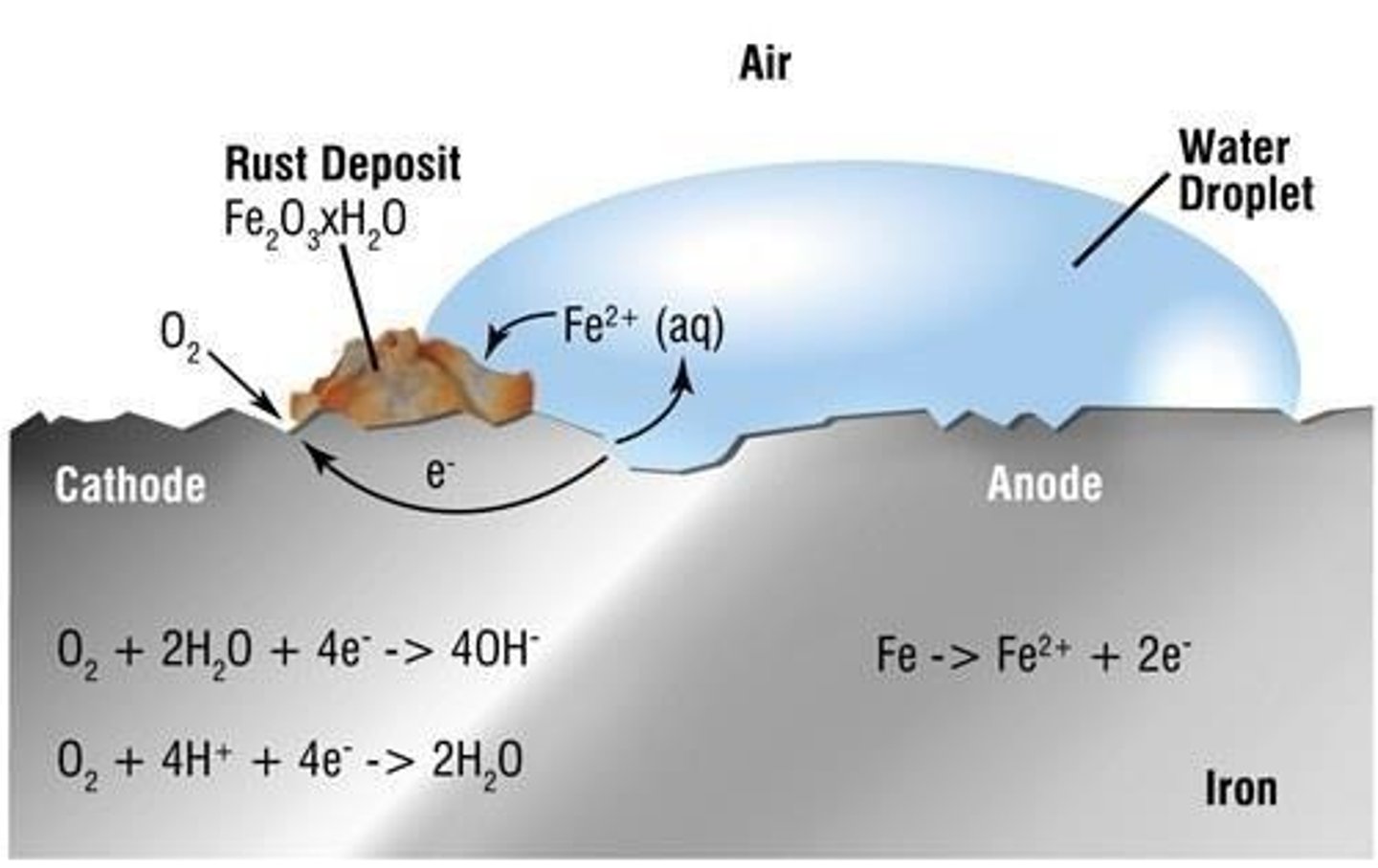
Rusting
Corrosion of iron in moisture and oxygen presence.
Ferrous Hydroxide
Corrosion product formed from Fe2+ and OH−.
Yellow Rust
Hydrated ferric oxide formed with sufficient oxygen.
Black Magnetite
Anhydrous corrosion product formed with limited oxygen.
Overall Rusting Reaction
2Fe + O2 + 2H2O → 2Fe2+ + 2OH−.
Anodic Oxidation Reaction
Fe → Fe2+ + 2e− at anodic sites.
Cathodic Oxygen Reaction
O2 + 2H2O + 4e− → 4OH− at cathodic sites.
Corrosion Current
Electron flow from anodic to cathodic areas.
Conducting Medium
Solution facilitating electron transfer between sites.
Metal Ion Reduction
Rare process involving deposition of metal ions.
Dissimilar Metals Corrosion
Corrosion occurring when different metals contact.
Conducting Solution
Liquid medium allowing ionic movement for corrosion.
Yellow Rust
Hydrated iron(III) oxide, Fe2O3.3H2O.
Black Rust
Anhydrous magnetite, Fe3O4.3H2O.
Dry Corrosion
Corrosion from atmospheric gases without moisture.
Wet Corrosion
Corrosion requiring a corrosive medium.
Galvanic Series
Ordered list of metals' corrosion potentials.
Electrochemical Series
Ranking of metals by electrode potential.
Oxidation Corrosion
Corrosion due to oxidation reactions.
Liquid Metal Corrosion
Corrosion caused by liquid metal contact.
Pitting Corrosion
Localized corrosion forming small pits.
Stress Corrosion
Cracking due to tensile stress and corrosion.
Intergranular Corrosion
Corrosion along grain boundaries in metals.
Corrosion Resistance
Material's ability to withstand corrosion.
Corrosive Medium
Substance that promotes corrosion, like water.
Corrosion Product
Material formed as a result of corrosion.
Passivity
State where metal becomes resistant to corrosion.
Electrode Potential
Voltage difference at an electrode in solution.
Dissimilar Metals
Metals with different corrosion potentials.
Aqueous Electrolyte
Liquid solution that conducts electricity.
Copper-Steel Corrosion
Galvanic corrosion example with copper and steel.
Corrosion Behavior of Alloys
Alloys' response to corrosion in environments.
Hydrated Iron Oxide
Iron oxide containing water molecules.
Galvanic Corrosion
Corrosion due to two dissimilar metals in contact.
Zinc-Coated Screws
Screws protected by a layer of zinc.
Copper Sheet
A flat piece of copper metal.
Stainless Steel Screw
Corrosion-resistant screw made of stainless steel.
Cadmium Plated Steel Washer
Steel washer coated with cadmium for protection.
Steel Propeller Shaft
Shaft made of steel for propelling mechanisms.
Bronze Bearing
Bearing made from bronze, used for support.
Moisture Effect
Corrosion severity increases with moisture presence.
Coastal Corrosion
Higher corrosion rates near coastal areas.
Conductive Electrolyte
Substance that facilitates electrical conductivity in corrosion.