General Biology 2: Exam 3
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
Green algae
Closest living relative to plants
Major land plant groups
Non-vascular, seedless vascular, seed, flowering/fruiting plants
Non-vascular plants
Lacks vascular tissue
Vascular tissue
Specialized groups of cells that conduct water or dissolved nutrients throughout the plant body. (Also gives support)
Moss
Type of nonvascular plant that uses spores, not seeds, for reproduction and dispersal
Seedless vascular plants
Have well developed vascular tissue but use spores for reproduction instead of seeds
Seed plants
Plants that have vascular tissue and make seeds
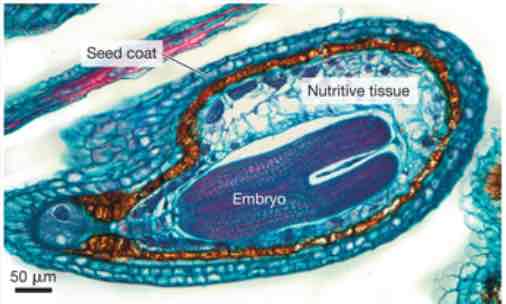
Seeds
An embryo and nutritive tissue, surrounded by a tough protective layer
Gymnosperms (naked seeds) and angiosperms or flowering plants (encased seeds)
Types of seed plants
Similarities between green algae and land plants
Same chloroplast structure, similar thylakoid arrangements, and similar structure and composition of cell walls, sperm, and peroxisomes
Gametophyte
Multicellular haploid phase
Sporophyte
Multicellular diploid phase
Alternation of generations
A phase all land plants undergo where they have gametophytes and sporophytes
Gametophyte-dominant life cycle
Found in nonvascular plants, which are largely dependent on gametophyte for nutrition while the sporophyte is small and short lived
Sporophyte-dominant life cycle
In ferns and other vascular plants, sporophyte is much larger and longer lived than gametophyte. The gametophytes of gymnosperms and angiosperms are microscopic
Sporophyte-dominated life cycle advantage
Diploid cells can respond to varying environmental conditions more efficiently than haploid cells can. This is especially true if individual is heterozygous at many genes
Pollen grains
Allow plants living in dry habitats to reproduce efficiently. (Tiny male gametophytes surrounded by tough coat of sporopollenin, can be exposed to air for long periods of time without drying out, carried to female gametophyte by win or animals)
Flowering plants (angiosperms)
Most diverse land plants living today. Reproductive success around the flower
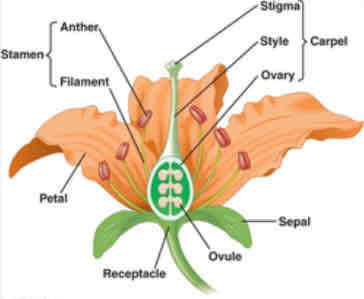
Anatomy of the flower
Stamen contains anther, where microsporangia develop, carpel contains ovary where ovules are found. Ovules contain the megasporangia
Pollinators
What helps fertilization by bringing the male gamete to the female egg (Flowers with different scents, shapes, and colors attract different ones)
Fruit
Structure derived from ovary and encloses one or more seeds (tissues are nutritious and brightly colored, makes efficient seed dispersal possible)
Plant form requirements
Light, carbon dioxide, water, nutrients
Shoot system (above ground)
Harvests light and carbon dioxide from atmosphere to produce sugars
Root system (below ground)
Anchors plant and takes in water and nutrients from soil, storage
Importance of high surface area/volume
More contact with the environment meaning there is higher ability to absorb nutrients like photons (leaves) and water (roots)
Phenotypic plasticity
Changes in an organisms phenotype depending on environmental conditions
Example of phenotypic plasticity
Oak tree leaves vary depending on the amount of sunlight they are exposed to
Nitrogen fixation (Important to symbiotic bacteria)
The plant provides sugars from photosynthesis that are utilized by the nitrogen fixing microorganism. The plant provides the microorganism a place to live
Parasitic plant
Plants that live on the host, obtaining water or nutrients and reduce the host’s fitness. Make their own carbohydrates during photosynthesis using carnivory to supplement nitrogen available in the environment
Carnivorous plants
A plant that traps insects and other animals: they kill their prey and absorb the nutrients
Multicellularity
An organism that consists of more than one cell
Heterotrophs
An organism that eats plants and animals (cannot make its own food)
Motility
The ability of an organism to move or get around
Bilateral symmetry
Left and right sides
Cephalization
Concentration of sensory organs in head region. Great deal of diversity of sensory abilities and structures among the animals
Radial symmetry
Symmetry around central axis (ex: sea star)
Coelom
An enclosed, fluid-filled body cavity between the tubes: provides space for oxygen and nutrients to circulate, enables the internal organs to move independently of each other
Acoelomates
Lack body cavity
Pseudocoelomates
“False” body cavity derived from both endoderm and mesoderm, still functional
Coelomates
Arises completely within mesoderm - body cavity and internal organs aligned with mesoderm, tissue holds organs in place, allowing motion

Detritivores
Feed on dead organic matter

Herbivores
Feed on plants or algae

Carnivores
Feed on animals
Omnivores
Feed on a combination of plants, animals, fungi, protists, archaea, and/or bacteria
Diversification of feeding strategies
Suspension feeders, deposit feeders, fluid feeders, mass feeders
Asexual reproduction
New offspring are produced by one parent (budding or parthenogenesis)
External fertilization
Occurs in the environment, extremely common in aquatic species, females lay eggs onto a substrate or release them into open water, males shed swimming sperm on or near the eggs or into open water
Internal fertilization
Fertilization that occurs within the female’s body
Viviparous
“Live-bearing species”
Oviparous
“Egg-bearing species”
Ovoviviparous
“Egg-live-bearing species”
Protostomes
Mouth developed first
Adaptations in transition from water to land
High surface area/volume, cuticle, some have spiracles for gas exchange, desiccation-resistant eggs
Traits of anthropods
Most abundant animals on earth, segmented bodies, exoskeleton, jointed appendages
Traits that make insects a diverse group
Wings, eat plants, co-evolution with angiosperms (flowering plants)
Deuterostomes
Developed anus first (three phyla)
Echinoderms
Organisms with pharyngeal gill slits
Traits of vertebrates
Vertebrae and cranium
Ray-fin fish
Dominant vertebrate group
Amphibians, reptiles, mammals
Key tetrapod groups
Key adaptations for vertebrates
Jaws, lungs, lobbed fins to limbs (tetrapods), amniotic egg, scales, feathers, placenta, fur, lactation, parental care
Types of mammals
Monotremes, marsupials, eutherians (placental)
Monotremes
Five known species that lay eggs and have no teeth
Marsupials
Embryo continues development in pouch, mainly in Australia, one species in North America (opossum)
Eutherians (placental mammals)
Most mammals, after development period (gestation), embryo emerges from mother’s body
Hemichordate
Dorsal hollow nerve chord
Chordate
Notochord; muscular post-anal tail