Phylum Arthopoda
1/99
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These are just key terms and orders. Actually study your notes
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
Mutable connective tissue
ability to alter rigidity of the dermis in a few second
→ udner direct neurual conntrol
Dipleurula
larval stage of echniodermata that contains bilateral symmetry
Amubulacrum
furrows of asteroidea, echinoidea, holothuroidea, and crinoidea that extend radially along each arm
→ contains 2-4 podia

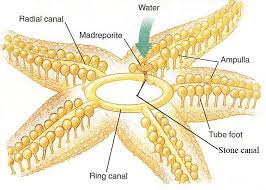
Maderporite
cpnnection between the water vascular system and the exterior eenviroment
Xiphosura
class of horseshoe crabs
apart of subphlyum chelicerata
Chelicera
hook shaped legs that tend to altch onto femaels during mating
present in Xiphosura and Piconogondia
Acon
the head and first 5 segments of crusteans
Pereon
Thorax of crusteaceans consisiting of the carapace
Pereopods
appendages attached to the pereon
Pleon
abdomen of crusteceans
Pleopods
appendages on the pleon
Cheliped
large defenisve claw taht is a pereopod
Maxillipeds
anterior throaxic appendages
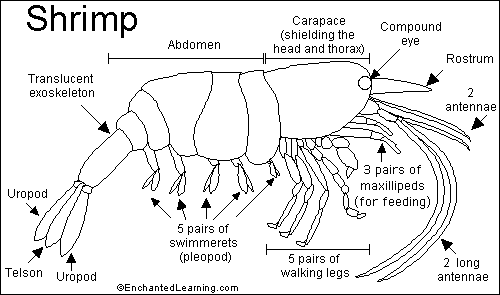
carapace
fused exoskeleton covering the head and throax
Aesthetascs
sensory setae on crusteceans
Proprioreceptors
sensory system that provdes the central nervous system with information needed to coordinate locomotion and posutre
→ detects and reprots degree of contraction of muscles and angle of felxion of body joints
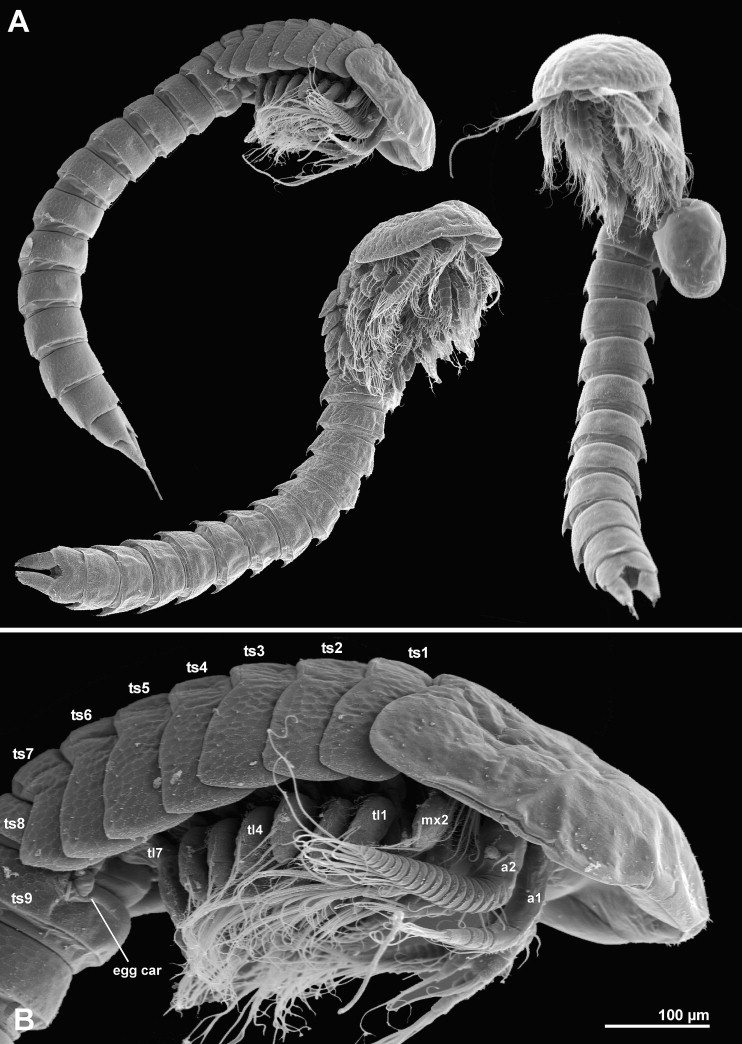
Nauplis
basic crustean larvae
use large anteane to swim
single naupilar eye
Copeopodites
larval stage that is between nauplis and adult copeopod
zoeae
crab larvae

Megalope
crab post larvae; full set of appendages
Gonopods
modified appendages in crusteans used for sperm transfer into the female
Class Rimipedia
class of blind crustaceans found in saline aquifers
→ live in udner sea caves
→ NOT polychaetes
Class Cephalocardia
Horseshrimp
epibenthic depoist feeders with undifferentied trunk appenages

Class Branchipoda
class of fairy shrimp, brine shrimp, and bivalved shrimp
→ no abdominal appendages
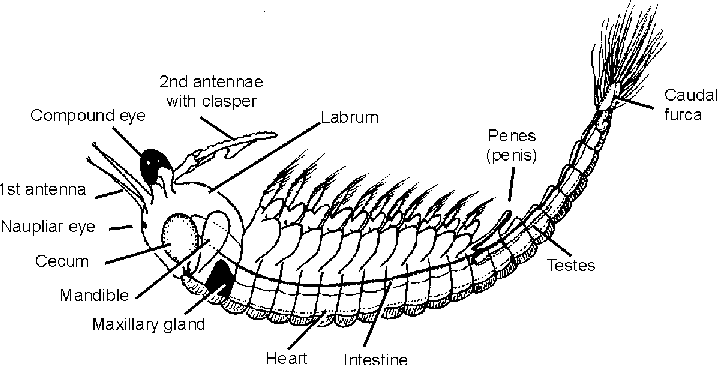
Caudal Rami
in class branchipoda, the extension of the telson
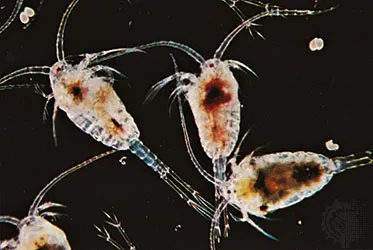
Class Copepoda
class copepoda
→ tapered cylindrical body
→ compound eyes absent, have a median naupilar eye instead
→ primary link between producers and higher-level consumers
Class Theocostraca
Barnacles
→ inhabit a rigid, calcerous skelton
→ grows without molting, instead adds additiona layers to the base plate to molt
Cirri
modified appendage on Theocostraca that is used to sweep through the water and collect food
Cypris
secondary larval stage of Theocostraca that settles and attaches to the subtrate
Class Ostracoda
Class of ostracods or seed shrimp
→ compeltled enclosed in a 2 valved carapace

Telson
posterior segment of arthopods with uropods
Cephalization
the development of anterior tagma responsible for sensory reception, integration and feeding
gills
in arthopods, this organ is a like a stack of flare paltes with llots of blood flow; it is located n the espace between the exoskelton and the throax
Ecydosone
hormone that target epidermal cells in arthopods and controls the molting process
→ secreted by the alpha organ in crustean and is distbruted in the blood
molting inhbiting hormones
hormones that supress production of ecdysone, secreted by the X organ/sinus gland complex
Hemocyanin
respiratory pigment in arthopods that is in the blood as a solute
Dorsal supraesophagel ganglion
Brain of arthopods
Ommatidia
light receving units in arthopod eyes
→ each has its own lens and cornea
→ senses light itnensity and charazterizes wavelength to make one compelte image
Distal pigments
screen each ommatidium from the surronding ommatidia
Superficial cleavage
fused nuclei will undergo cleavges within the the egg→ begin migration to the outer edge of the cell→ cellular blastoderm forms→ yolk replaces where nuclei once wehre
mechanoreceptors
hollow seta with one or more sensory neurrons insided
Class Malacostraca
class of crabs, lobsters, crayfish, and shrimp
3 tagmata, 18 segments total
8
amount of segments in a thorax(pereon) of a malacosteran
6
amount of segments in a pleon of a malacosteran
Order Stomatopoda
class malacostracan; order of mantis shrimp

Rapotorial claw
2nd thoracic appendage in Stomatopoda that can be spear or club like
Order Decapoda
class malacostrean
→ order shrimps, lobsters, crabs
Cardiac stomach
anteiror stomach in decapods that cotnains cuticualr gastric mill to grind fill and seal screen guarding enctrances into the pyloric stomach
Pyloric stomach
dorsal channel in decapods that leads direclty to intenstive for indigestiable particles
→ filter press, gland filter which both further sorts food particles
cephalothroax
in crab like decapods, the abdomen is reduced and flexed under the
Epipods
modfieid portions ot he throacic appendages for O2 uptake in epiobodies
Branchiostegites
lateral extensions of the carapace that enclose the branchial chamber in decapods
Infraorder Peneidea
infraorder of decapods differentiated from Caridea by not brooding eggs
prawns, commercial shrimp

Infraorder Caridea
infraorder of decapods that brood eggs
snapping shrimp, glass shrimp, cleaner shrimp

Infraorder anumura
type of decapod with a reduced 5th pereiopod on the throax
can dig themselves into sediements
→ hermit crabs, procelain crabs, kingcrabs, mole crabs

Infraorder Brachyura
apart of order decapoda where the abdomen is fulled folded under the carapace
→ all 5 pairs of pereiopods are functional
Order Euphausiacea
class Malacostraca, order of krill
→ carapace does not extend ventrally beyond the base of the legs
→ gills are exposed
Order Mysidacea
class malacostraca
→ opossum shrimp
→ The carapace covers entire cephalothorax, but is only attached to the first three segments
→ statocyst present in the endopod of each uropod
→ marsupium pouch

Maruspium
brood pouch in order Mysidacea, Isopoda, Amphipoda
Manca
post-larval/pre juv stage lacking the last pair of legs in order Mysidacea Order Cumacea and order Isopoda
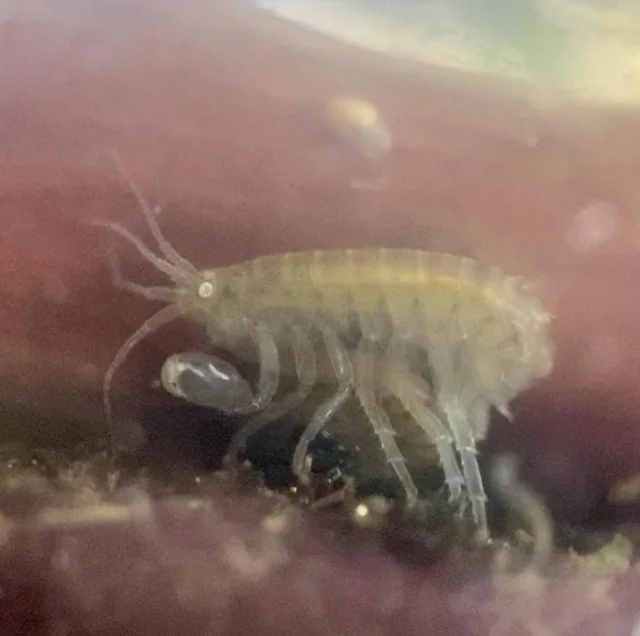
Order Amphipoda
order of laterally compressed malacostreans with no carapace
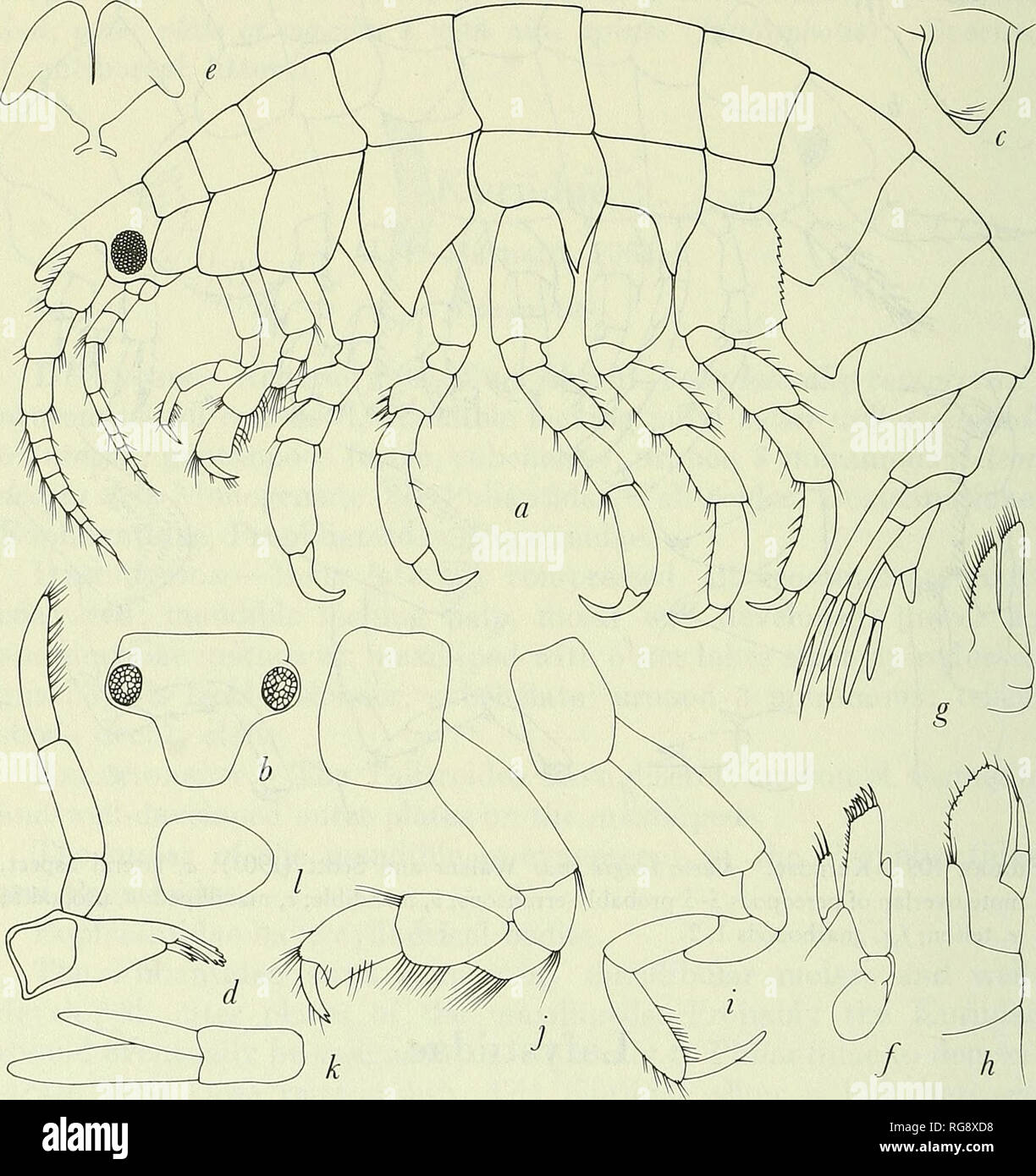
Coxal plate
in amphipoda, coxae of pereiopods forms protective space ventral to the throax
contains the gills and brachial chamber bound(internal gill palcement)
Gnathopods
Speciasied claw like appenaged in order Amphipoda that are sexually dimoprhic, used in copulation

Order Isopoda
dorso-ventrally flattened malacoestrean with non specialzied appendages
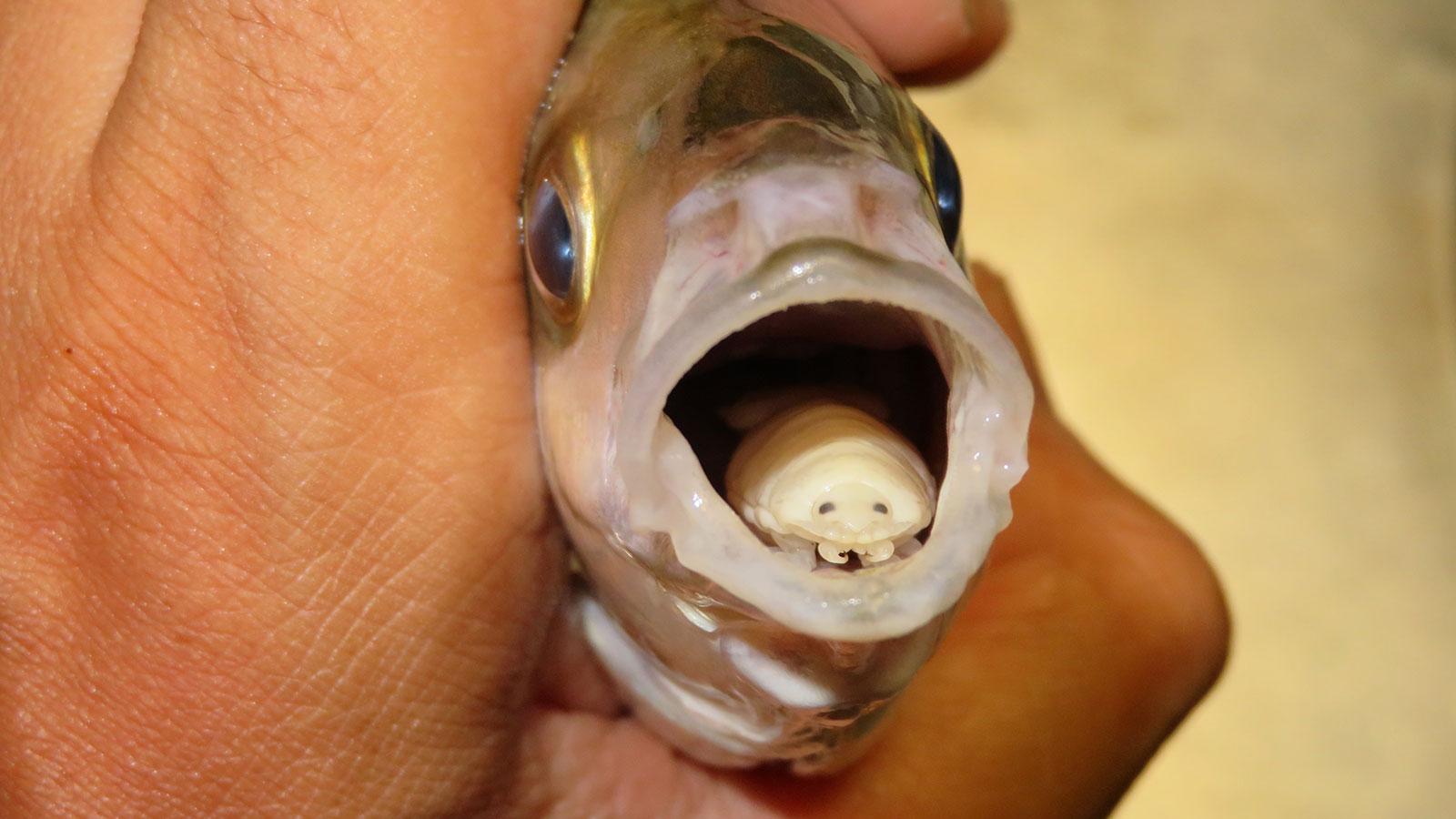

Cymothoa exigua
parasitic isopod that can enter through the gills of the fish and eats their tongue
females are found in the mouth, while males take up residency in the gills
display protandry when females cie
common in croakers
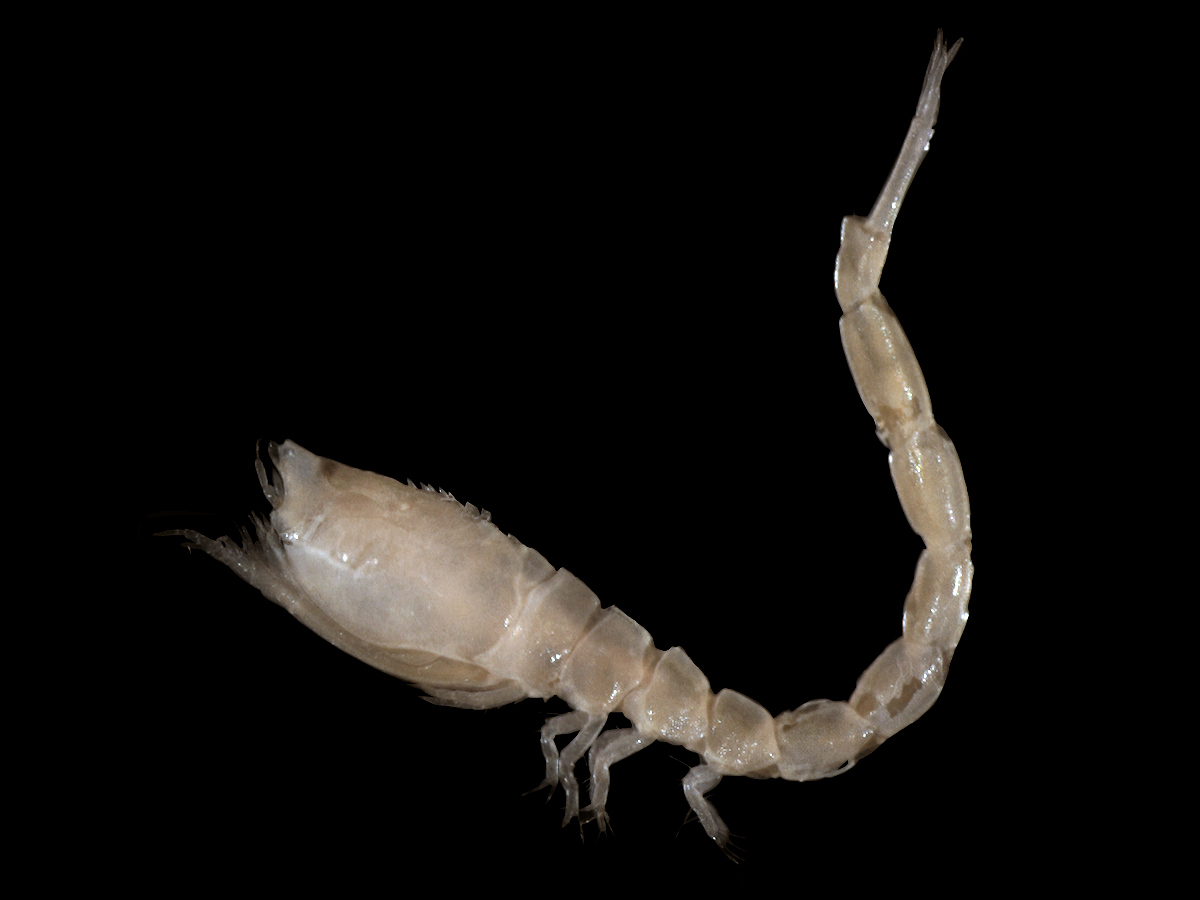
Order Cumacea
order of infaunal malacostracan with a large carapace that covers the entire cephalothorax
infual, lives in sandy and mud bttoms

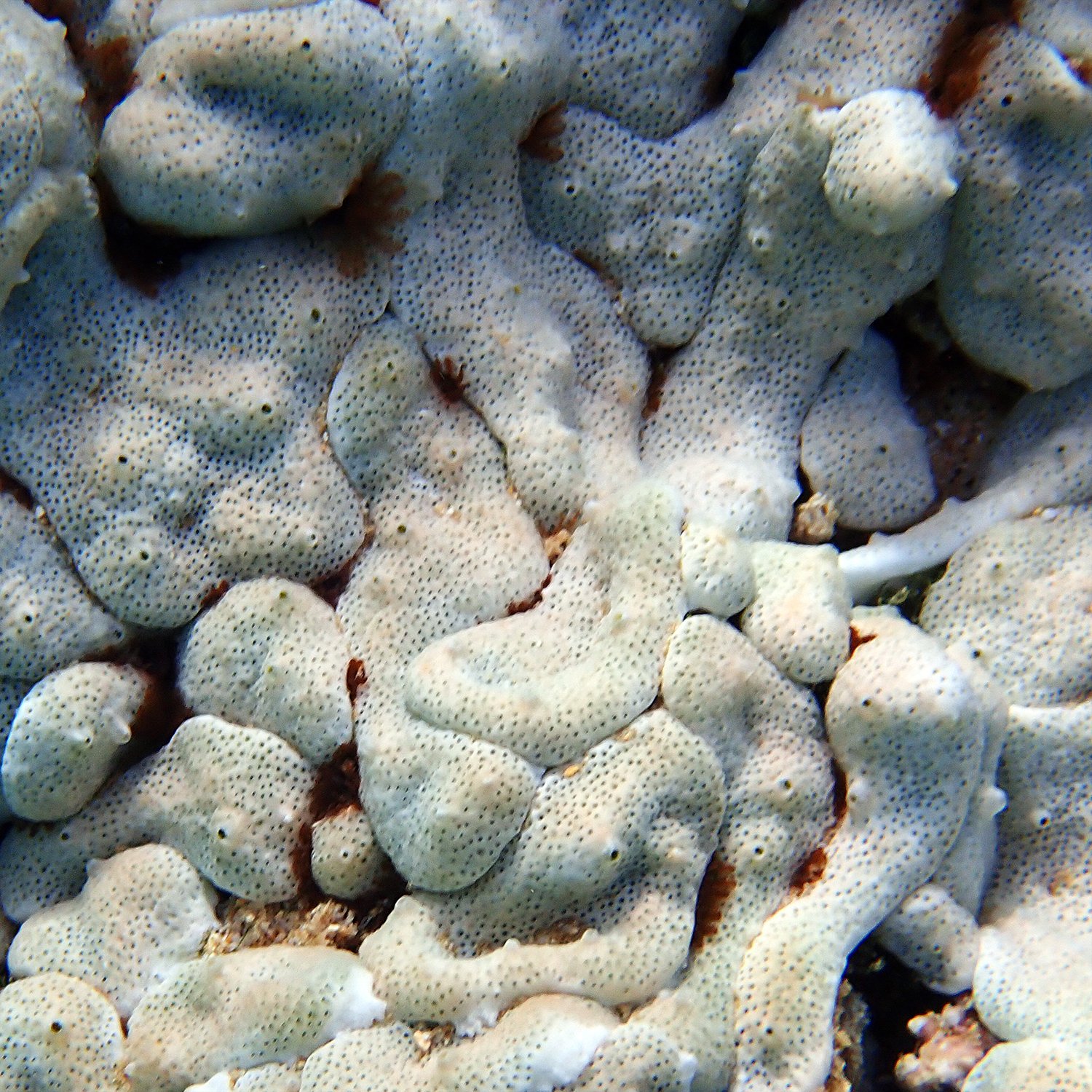
Ossicles
calcerous skeletal elements of Echinodermata that form a 3-D lattice strucutre
formed in the dermis by scleocytes
held together by collagenous connective tissue
make up the spines of ecnhidermata c
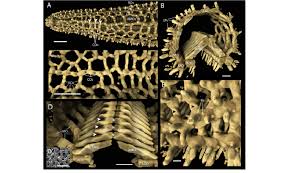
Paxillae
ossciels that cover the aboral surface of some asteroids, used for burrowing
Pedicellariae
moveable, compound ossicles that function as forceps; used to defend the aboral surface aganist settling larvae and other small organisms

Stone Canal
apart of the water vascular system that ascends aborally from the ring and opens into the madreporite
High concentrationof K+ ions, proteins, and extra coelomocytes
components of Water Vascular System Fluids
podia
tube feet
Cardiac stomach
this stomach comparment is everted during feeding to release digestive enzymes and engluf prey
Perivisceral coeloem
in-between coloemoic cavity with its own gills (Papula)
nutrition
the hemal system is mainly used to transport this in Echnidoermata
autonomization
ability to voluntarily release limb if thereanted
→ possible if 1/5 of the disc is present, or if madreprotie is present
Class Ophiuroidea
Brittlestars and basket stars
Class Asteroidea
Class of sea stars
Class Echinoidea
sea urchins, heart urchins, sand dollars
test
fussed ossicles in Echnioidea
Ambulcaral area
area in Echnioidea with 5 sections of 2 feet, and 2 rows of ambularal plates
interambulacral areas
5 sections without tube feet, composed of 2 rows of interambularal plates
Bucca podia
5 pairs of short tube feet around the mouth of Echinoidea
Aristotle’s lantern
specialzied protrusible jaw
→ musles extend and retract the lantern through the mouth
→ other muscles control the teeth
Class Holothuroidea
class of sea cucumbers
Cuvierian tubules
defense from Holothuridea where stickly tubules are ejected from ainus at predators. Toxic (Holothurnin) and regenreated after ejection
holothurnin
toxic produced by Holothuridea that is attached to Cuvierian tubulues
Evisceration
occurs when the posterior or anterior end of Holothurideas ruptures and part of the gut is forciblty expelled
→ confsued predators
→ regenrated following
Class Crinoidea
Class of sea lillies and feather stars
Aboral Calyx
calcified up in Crinoidians that contains visvera
tegmen
membranous oral wall that covers calyx like a drum head
Pentamerous
type of symmetry in Echniodermata
Notochord
flexible, but incompressible axial rod that causes the body to bed
Post-anal tail
extension of the body after the anus used for locomotion
Dorsal hollow nerve cord
centralzied nerval system, open at the aanteror enter in invertebrate chordates at the neruopore
gill slits
features used for feeding and gas exhange in chordates
Subphlyum Cephalochordata
consists of Amphiformes
Subphylum Tunicata
Sea squirts and planktonic relatives
Class Ascidacea
apart of subphlyum tunicata, sea squirits

Tunic
covering of the body wall in AScidacea
dense fibrous outer layer, similar to cartialge
middle layer contains spicule elements