A&P 1 Lab Exam 3: Skeleton
1/258
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
259 Terms
skeleton is composed of
206 bones, cartilages, joints, and ligaments
the skeleton is divided into the
axial and appendicular skeleton
axial skeleton
composed of 80 bones segregated into three major regions: skull, vertebral column, and thoracic cage
function of the axial skeleton
support the head, neck, and trunk and protect the brain, spinal cord, and the organs in the thorax
how many bones are in the skull
22 (28 including ear bones)
skull consists of two sets of bones
cranial bones and facial bones
cranium
top portion of the skull that encloses and protects the brain and furnish attachment sites for head and neck muscles
2 major areas of the cranium
cranial dome and cranial floor
cranial dome (Calvaria)
forms the superior, lateral, and posterior walls of the skull
cranial floor (base)
forms the skull bottom
three fossae of the cranial floor
1) anterior cranial fossa
2) middle cranial fossa
3) posterior cranial fossa
how many cranial bones are there
8
name the 8 cranial bones
frontal bone, 2 parietal bones, 2 temporal bones, occipital bone, sphenoid bone, and ethmoid bone
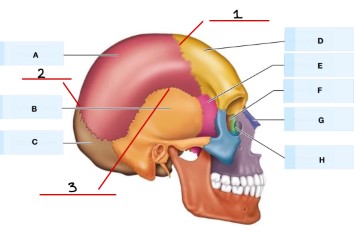
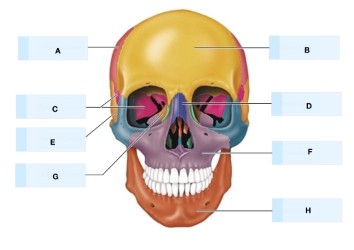
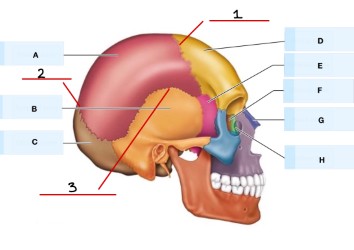
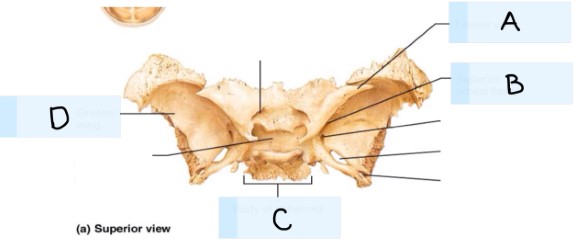
Refer to the image, what is A?
parietal bone
what is B?
temporal bone
what is C?
occipital bone
what is D?
frontal bone
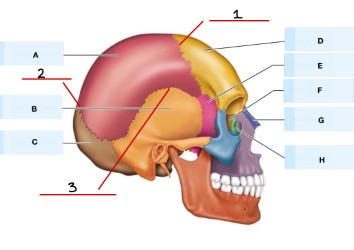
What is E?
sphenoid bone
what is F?
Ethmoid bone
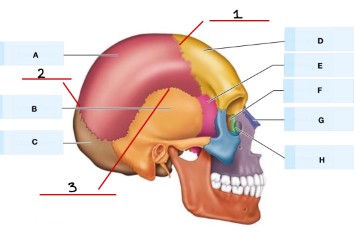
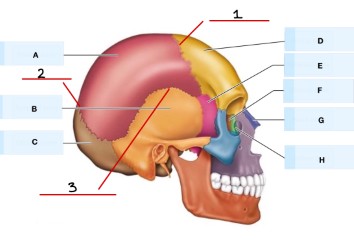
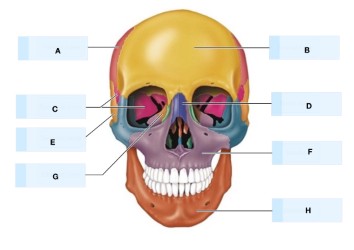
what is A?
parietal bone
what is B?
frontal bone
what is C?
sphenoid bone
What is E?
temporal bone
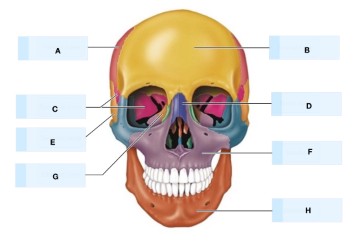
what is G?
ethmoid bone
how many facial bones are there
14
name the 14 facial bones
2 maxillae, 2 palatine, 2 zygomatic, 2 lacrimal, 2 nasal, 2 inferior nasal conchae, vomer, and mandible
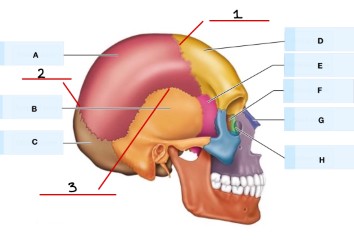
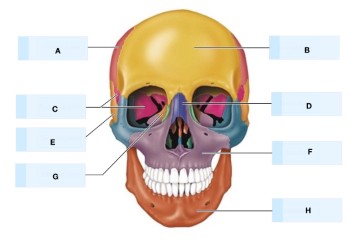
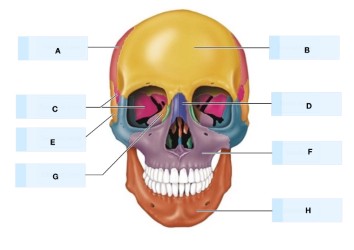
what is G?
Nasal bone
What is H?
Lacrimal bone
what is D?
nasal bone
What is F?
maxilla bone
What is H?
mandible bone
sutures
interlocking joints that connect the bones of the cranium
major sutures of the skull
coronal suture, sagittal suture, lambdoid suture, and squamous suture
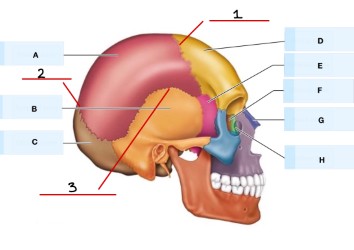
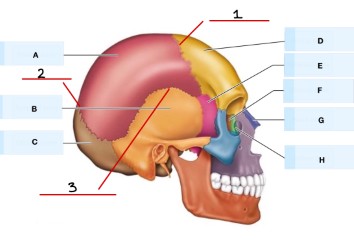
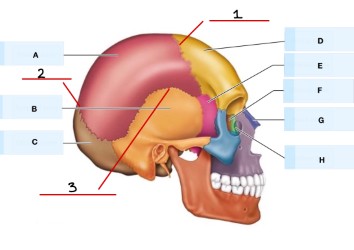
What is 1?
coronal suture
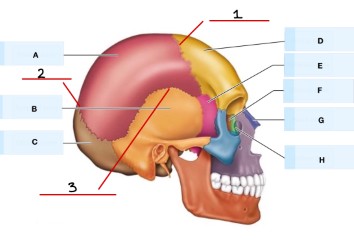
What is 2?
lambdoid suture
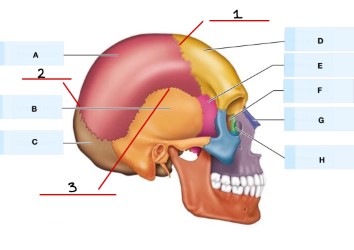
What is 3?
squamous suture
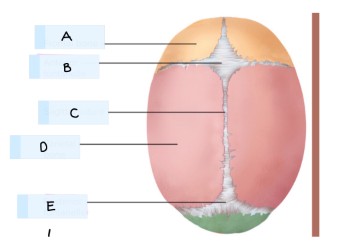
What is C?
sagittal suture
coronal suture
connects the parietal and frontal bones
sagittal suture
connects the right and left parietal bones
lambdoid suture
connects the occipital and parietal bones
squamous suture
connects the temporal and parietal bones
fontanelle
soft spot on skull because the bones have not yet fused
anterior fontanelle
diamond shaped spot that forms at the junction of the frontal and parietal bones
posterior fontanelle
triangular shaped spot located at the junction of the occipital and parietal bones
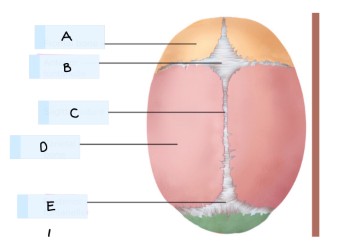
What is B?
anterior fontanelle

what is E?
posterior fontanelle
what bone is this?
sphenoid bone
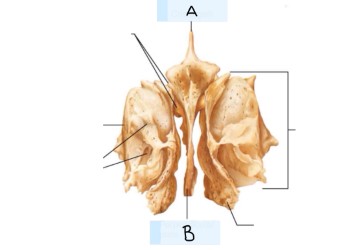
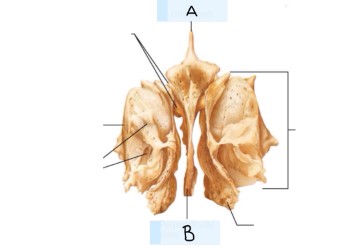
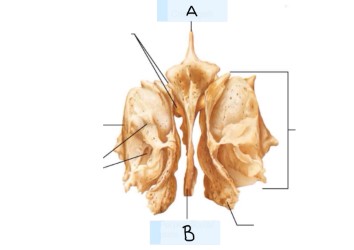
what is A? (landmark)
lesser wing
What is B? (landmark)
Superior orbital fissure
What is C? (landmark)
body of sphenoid
what is this bone?
ethmoid bone
what is A? (landmark)
crista galli
What is B? (landmark)
perpendicular plate
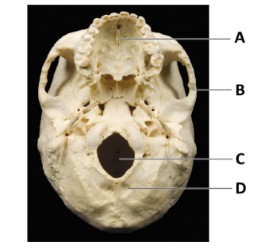
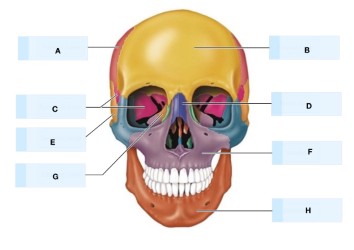
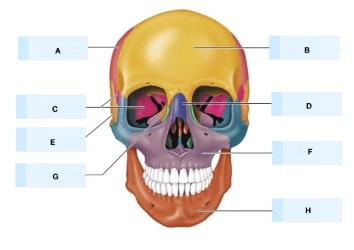
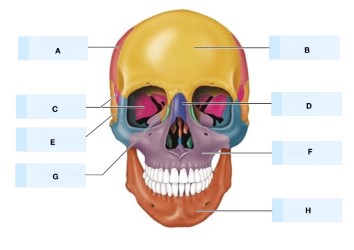
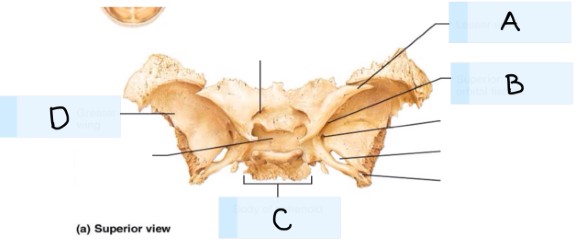
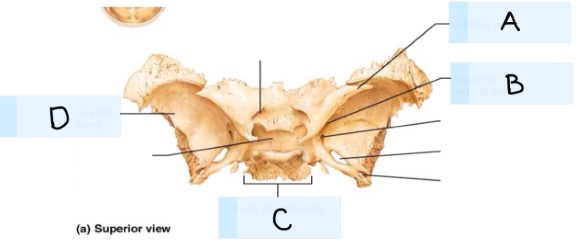
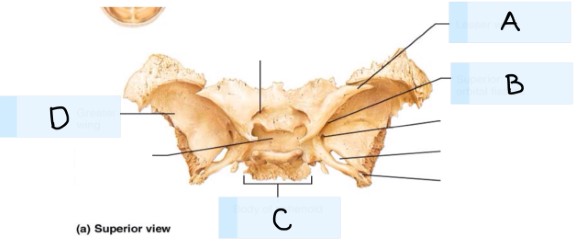
What is A?
maxilla bone
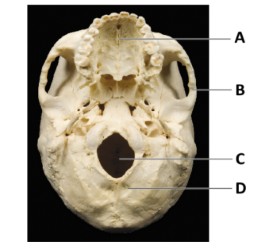
What is B?
temporal bone
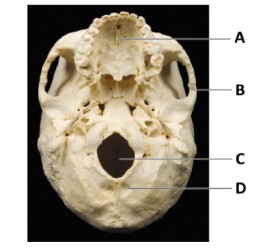
What is C?
magnum foramen
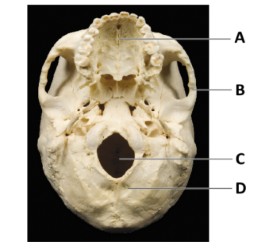
What is D?
occipital bone
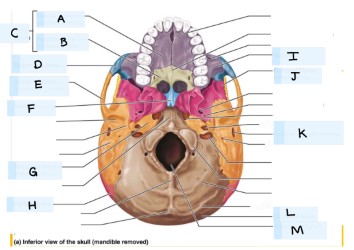
What is A?
maxilla bone
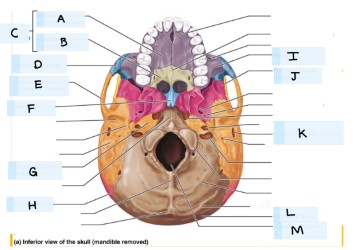
What is B?
palatine bone
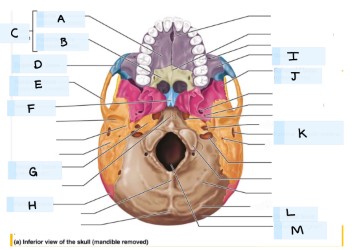
what is C?
Hard palate
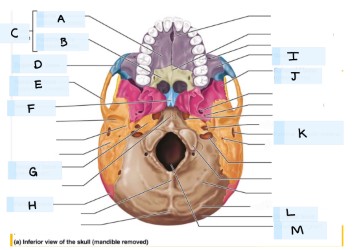
What is D?
zygomatic bone
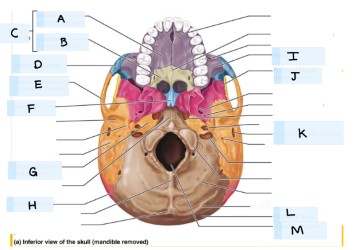
what is E?
temporal bone
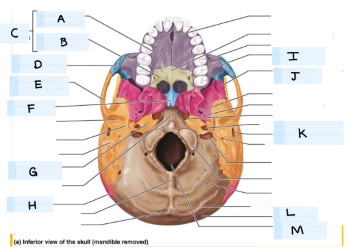
what is F?
vomer
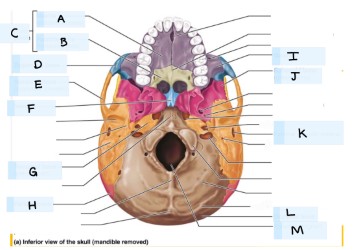
what is H?
parietal bone
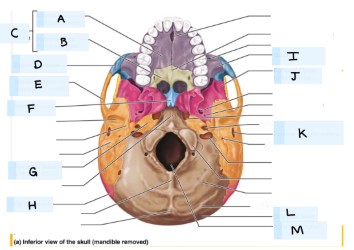
what is I?
maxilla bone
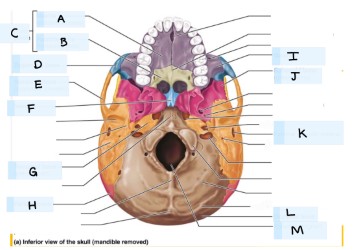
what is J?
sphenoid bone
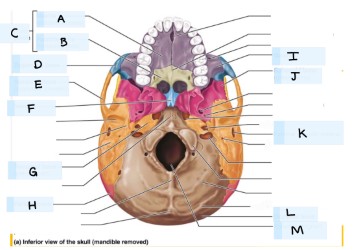
what is K?
external acoustic meatus
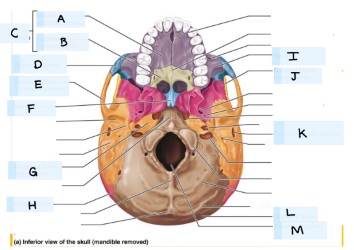
What is L?
occipital bone
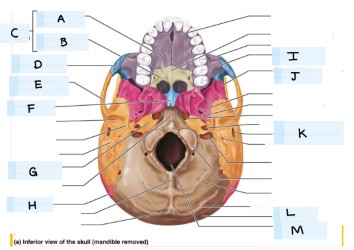
what is M?
magnum foramen
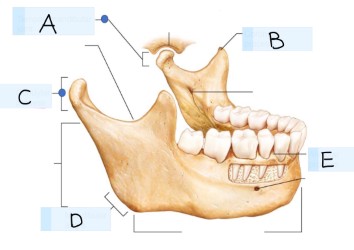
what bone is this?
mandible bone
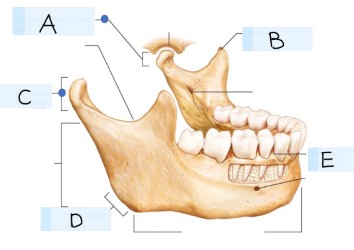
what is A?
Temporomandibular joint
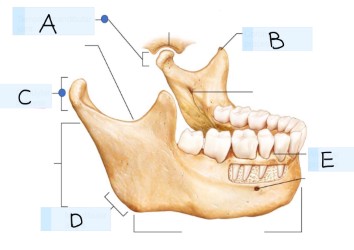
what is B? (landmark)
coronoid process
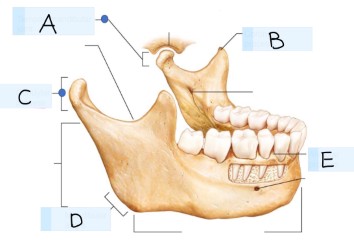
what is C? (landmark)
condylar process
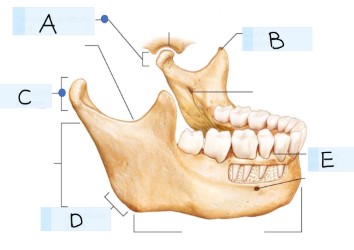
what is D? (landmark)
mandibular angle
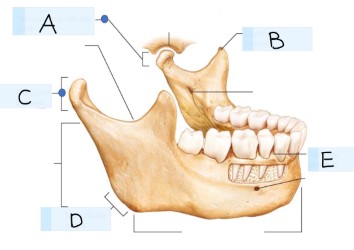
what is E? (landmark)
alevolar process
maxillary bones
form the upper jawbone and part of the orbits and the anterior hard palate
hard palate
bony roof of the mouth
lacrimal bone
passageway for tears
sinuses
cavity or hollow space in bone with mucus lining
hyoid bone
U-shaped bone located in the neck that serves as a point of attachment for many tongue and neck muscles (only bone that does not articulate with any other bone)
vertebral column consists of
26 bones (24 vertebrae, sacrum, and coccyx)
sacrum
consists of 5 fused sacral vertebrae
coccyx
consists of 4 fused vertebrae
cervical vertebrae
first 7 vertebrae (C1-C7)
characteristics of cervical vertebrae
smallest vertebrae with transverse foramina (holes) and bifid (divet) in the spinous process
thoracic vertebrae
12 vertebrae that articulate with 12 pairs of ribs (T1-T12)
characteristic of thoracic vertebrae
medium sized vertebrae with sharp spinous processes slant downward
lumbar vertebrae
last 5 vertebrae (L1-L5)
characteristic of lumbar vertebrae
large vertebrae with short, thick spinous processes (point straight out)
intervertebral discs
cushion-like pad that absorbs the shock and provides flexibility to the spine
atlas
first vertebra that supports the skull with no vertebral body or spinous process (saying yes)
axis
second vertebra with a dens (projection) that allows for head rotation (saying no)
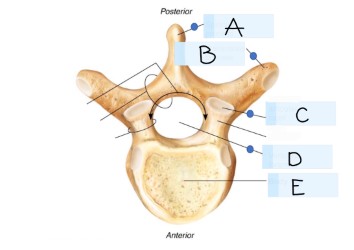
what kind of bone is this?
vertebra
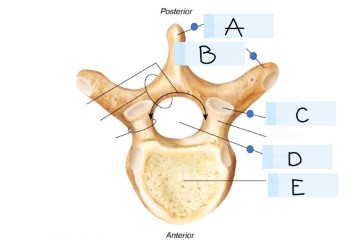
what is A?
spinous process
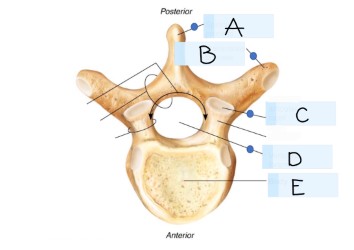
what is B?
transverse process
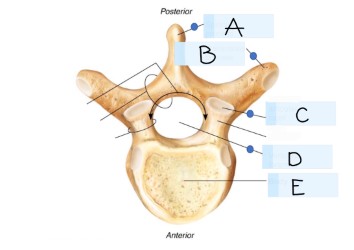
what is C?
superior articular faucet
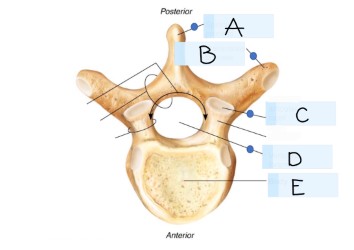
what is D?
vertebral foramen
vertebral foramen
passageway for the spinal cord
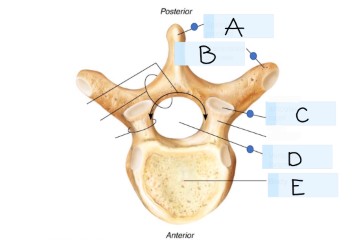
what is E?
vertebral body
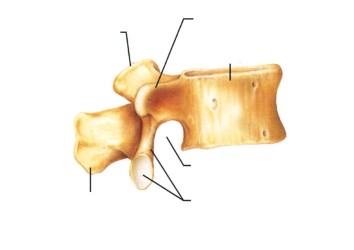
what vertebra is this?
lumbar vertebra