Normal Postural Control
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
71 Terms
Define postural control
involves controlling body's position in space for:
- postural orientation
- postural stability
- postural control = dynamic balance
Postural orientation
ability to maintain appropriate relationship between body segments and between body and environment for a task
- think: orient thyself in space
- ex: bent posture = slouched - not suited for movement
Postural stability
ability to control COM in relationship to BOS
- think: orient myself within my cone of stability
- COM usually L1 of vertebral body
- body will instinctively do something to prevent a fall
COM vs COP
- COM: point at center of TOTAL body mass
- COP: center of distribution of total support force applied to supporting surface (ground rxn force acting on body)
- COP MOVES continuously arounf COM to keep it within BOS
center of gravity (COG)
vertical projection of COM
BOS
area of body in contact w/ support surface
COM and COP together gives a better insight into___
stability than either COP or COM alone
postural demands
change based on different tasks and environments
- each indiv solves postural demands with unique movement ability
- ex: task: maintain sitting posture; indiv: constraints on strength; environ: chair on wheels
how do stability requirements vary with tasks?
COG can be projected within or outside BOS (walking)
- all tasks req postural control
- stability and orientaton demands change with overy task
- task and environ influence porientation and stability demands of task (sitting vs walking)
Balance/postural control emerges from the
- indiv
- postural task
- environment
(venn diagram)
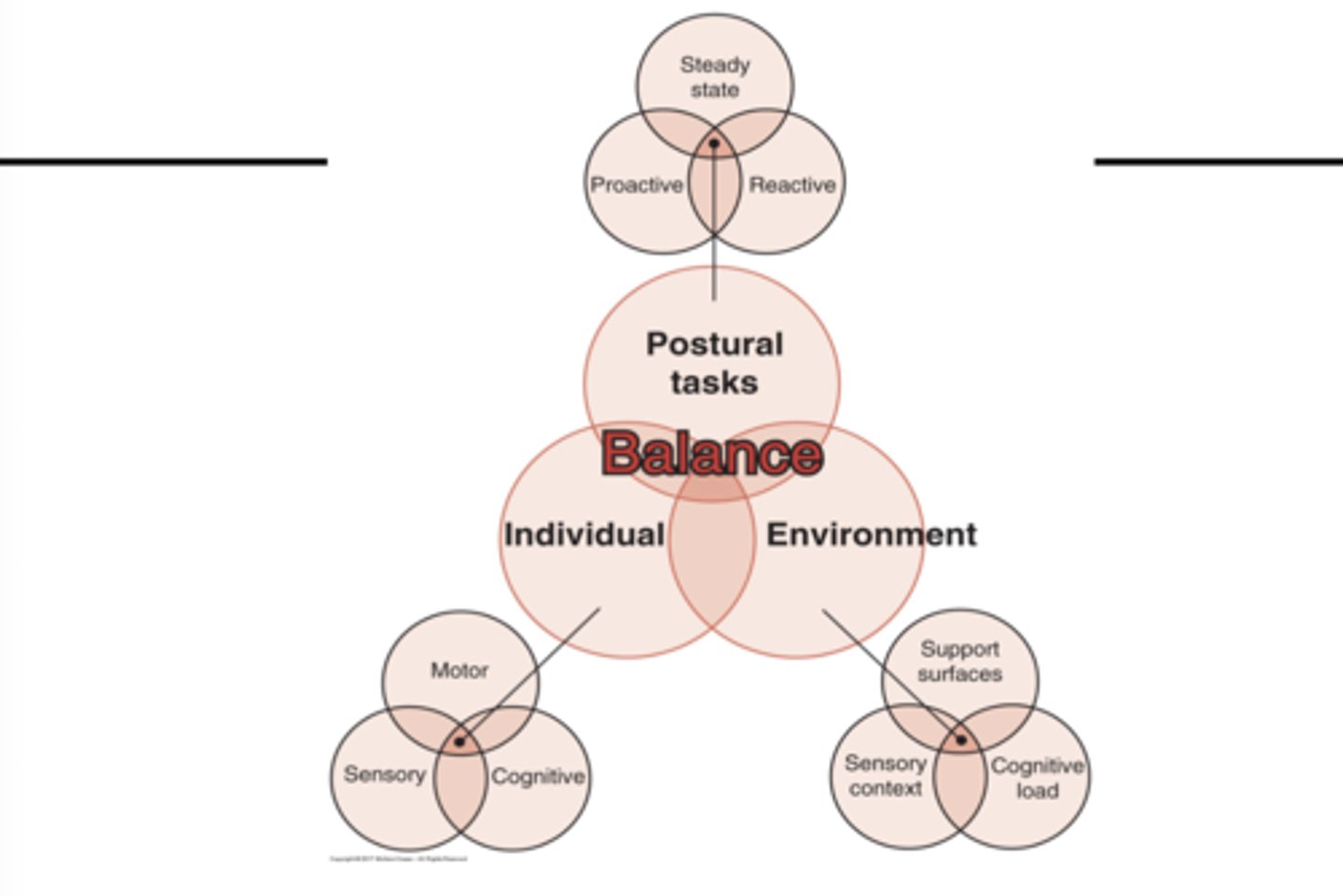
Types of postural tasks
- steady state
- proactive
- reactive
Postural task (constraints): steady state balance
ability to control COM relative to BOS in fairly predictable and nonchanging conditions.
- Sitting, standing quietly, and walking at a constant velocity
- maintaining your position
- mod plantigrade
Postural task (constraints): Reactive balance
ability to recover a stable position following unexpected perturbation by an external force
- older pt have poor rxn
- inability to rapidly generate and apply appropriate corrective muscle forces to recover balance = fall
reactive balance - mechanism (movement strategy)
feedback - postural control that occurs in response to sensory feedback (visual, vestibular, or somatosensory) from an external perturbation
anticipatory balance: mechanism (movement strategy)
feedforward = anticipatory postural adjustments made in anticipation of a voluntary movement that is destabilizing to maintain stability during mvmt
Postural task (constraints): anticipatory balance
ability to activate muscles in legs and trunk for balance controlin advance of potentially destabilizing voluntary movements
- Ex: lifting heavy object from the ground or stepping onto curb
- assuming posutre in state of readiness
- delayed in Parkinson's
Movement strategies come ____ concious movement in postural control
before
Individual Systems for Postural Control
- motor
- sensory
- cognitive
Individual systems: motor (4)
- joint ROM
- spinal flexibility
- muscle properties
- biomech relationships among linked body segments
Individual systems: cognitive
- unconcious, not effected by environment
- basis of adaptive and anticipatory effects
- modifying sensory and motor systems in response to changing task and environ
- dual taksing, attention
- aging effects this
Individual systems: sensory
individual sensory systems
- visual, vestibular, and somatosensory systems
- process of sensory organization
- ex: neuropathy and sensory feild deficits
Types of environmental constraints (3)
- support surface
- sensory context
- cognitive load
Environmental constraint: supporting surface
- Thick foam, carpet, grass vs solid floor
- Pebbles, stone walkways
Environmental constraint: Sensory context
way sensory information is used for balance control
- how we are getting info trom the environment
- Dim, laser, disco lights
- Loudness, roller coasters (vestibular)
- Bay bridge: shadows in peripheral vision that causes distraction
- Foreground and background
Environmental constraint: Cognitive load
environment increases mental load (crowds)
- pt is hard of hearing --> may focus on hearing instead of balance
- multi-tasking --> affects cog systems used for balance
Individual Systems for Postural Control require 7 things:
- Musckuloskeletal components
- internal representations
- adaptive mechanisms
- anticipatory mechanisms
- sensory strategies
- individual sensory systems
- neuro-muscular synergies
internal representation
how the indiv has an idea of the environment
adaptive mechanisms
with pathology or habit
sensory strategies
- using railing while walking down stairs (hapatic touch)
- looking down while walking
- parkinson's: rhythmic auditory for stepping
Indiv systems: higher level planning (2)
- frontal cortex
- motor corext
Indiv systems: Coordination (2)
- brainstem
- spinal networks coordinating muscle response synergies
Indiv systems: force generation (2)
- motor neurons
- muscles
Indiv systems: Sensory/perceptual processes (3)
- visual
- vestibular
- somatosensory
Motor control of quiet stance (3)
- alignment
- muscle tone
- postural tone
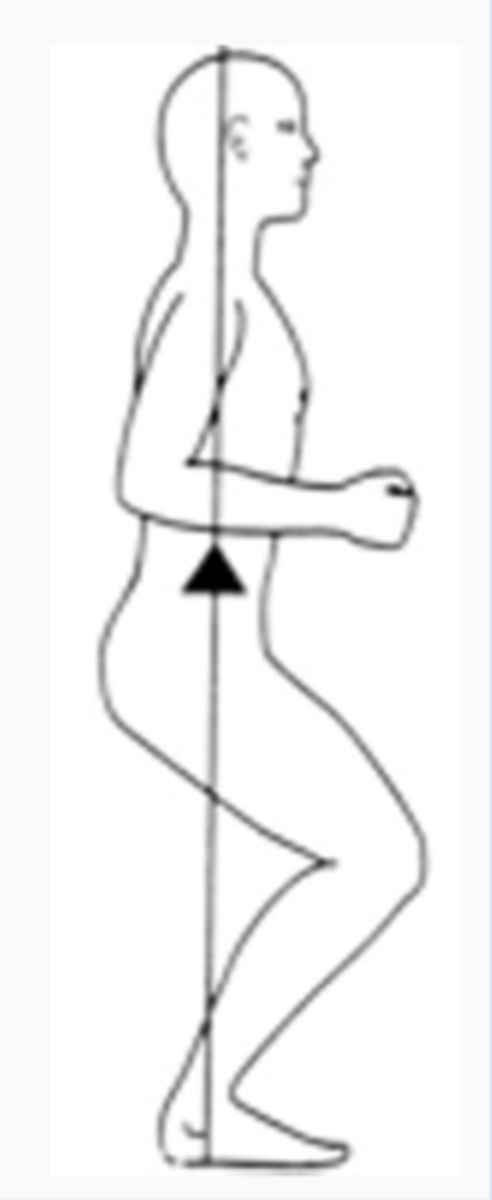
Quiet stance: Alignment
like stacking blocks
- vertical line between mastoids, front of SH, hip, just infront knee, and infront of ankle (posture assessment)
- minimizes effects of gravity
- tonic muscle activity
- body maintained with least amount of energy expenditure
Quiet stance: Muscle tone
intrinsic stiffness
- there is no muscle tone in a relaxed state (dead weight)
- tone is attributed to low-level conciousness of recycling cross bridges (stiffness, being awake)
- tone = state of readiness
Quiet stance: Postural tone
activation of anti-grav muscles to counteract force of gravity
- Back ect, abdominals, glute med, neck ext, PF, DF, iliopsoas
- lesion in dorsal roots = dec postural tone
- somatosensory inputs to neck influence trunk and limbs - tonic neck reflex
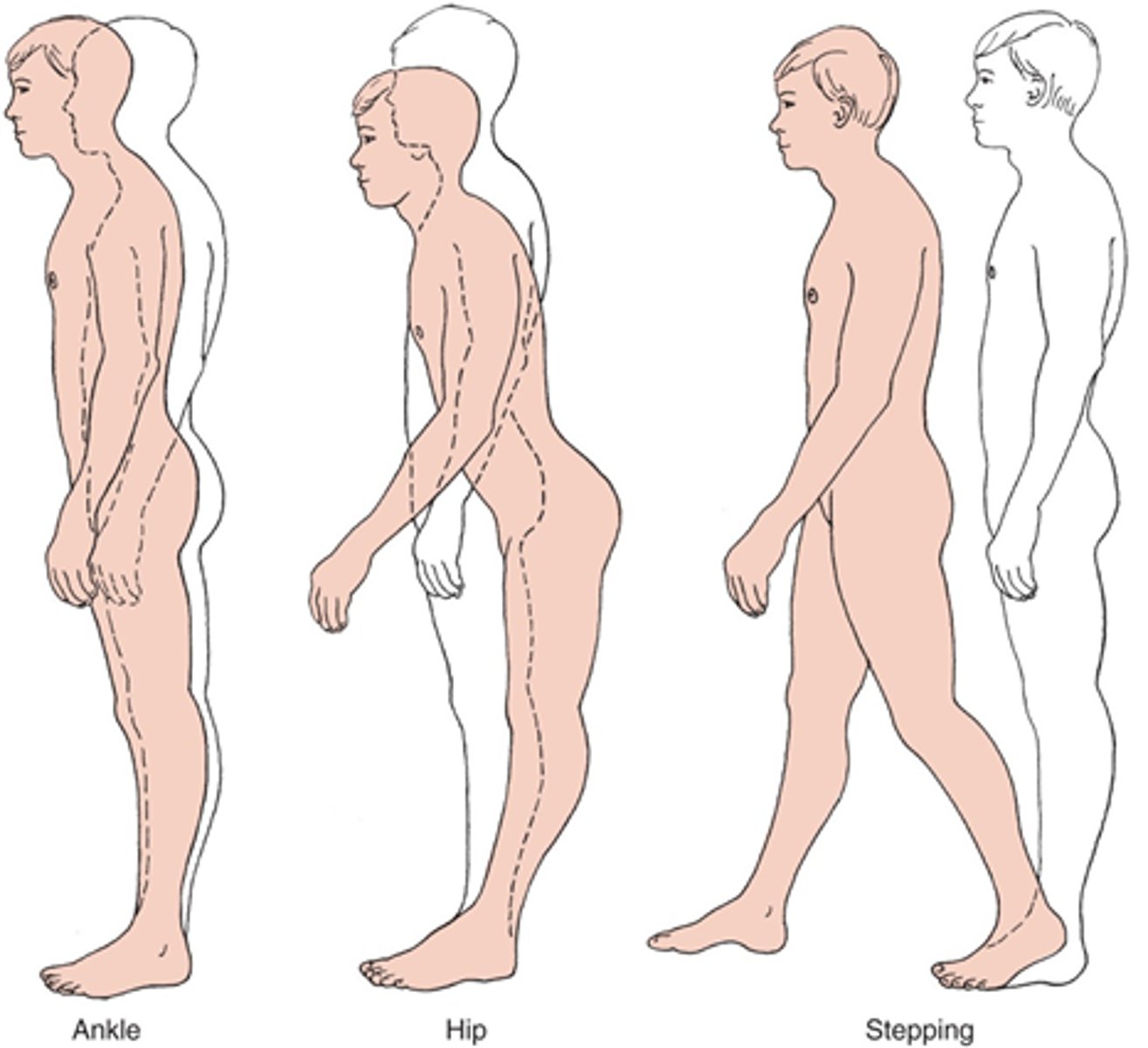
Antero-posterior stability (3) strategies
- ankle
- hip
- stepping
- most sway occurs in AP direction
AP strategies occur in which direction?
distal --> proximal
- Ankle strategy: distal
- Hip strategy: intermediate
- Stepping strategy: proximal
Alternate strategies:
- Reach-and-grasp
- Parachute response
- Suspensory strategy
Ankle strategy
- postural sway control from the ankles and feet
- head and hips move in same direction at same time as a unit
- response to small, slow, midline displacement
- surface broad and stable enough to allow pressure against it - nonmoving surface
Ankle strategy with FORWARD sway (plate moving back)
Order of muscle activation:
1. gastrocnemius
2. hamstrings
3. paraspinals
think: MA in direction of plate
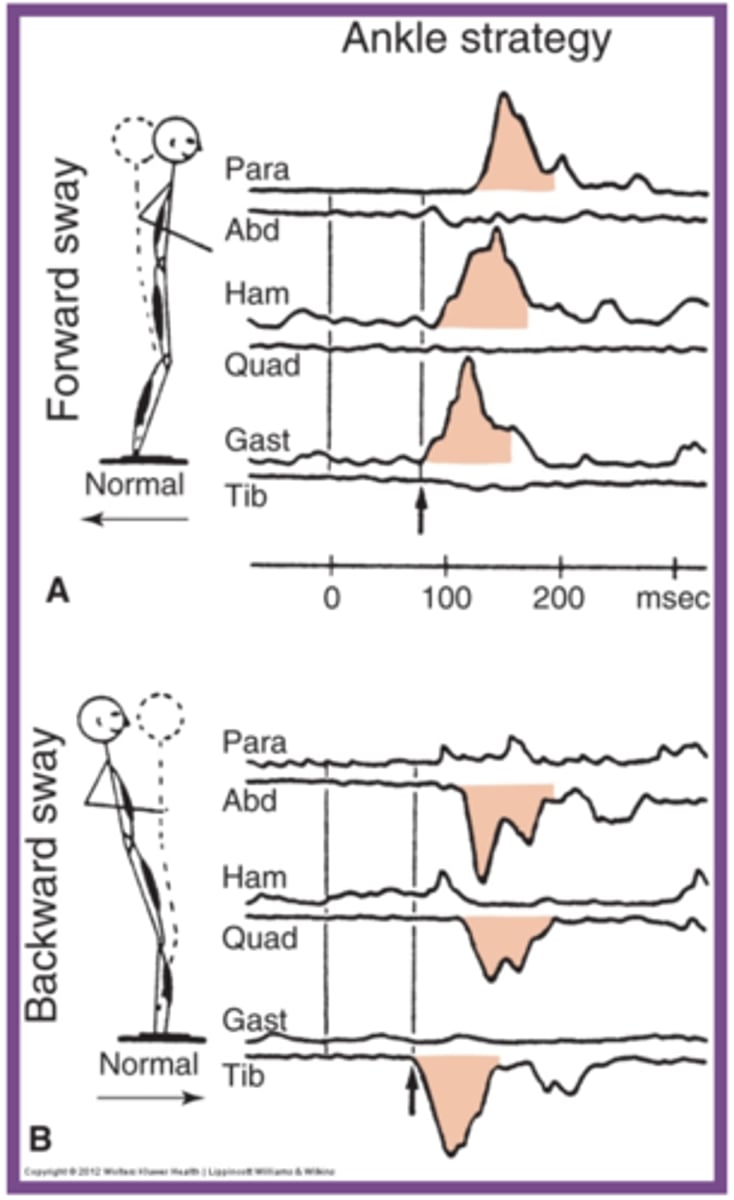
Ankle strategy with BACKWARD sway (plate moving forward)
Order of MA:
1. anterior tibialis
2. quadriceps
3. abdominals
- ant muscles activated
ankle - distal to proximal MA for both directions
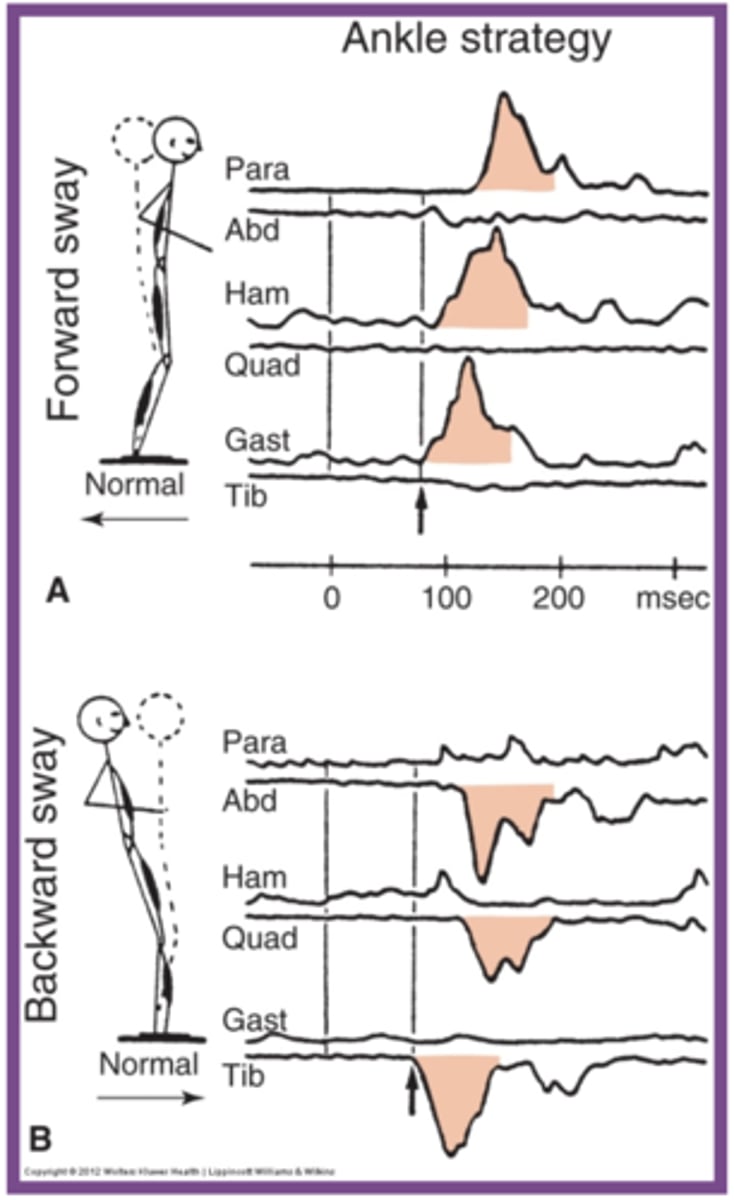
Hip strategy
- Postural sway control from hip, pelvis, trunk
- Head and hips travel in opposite directions (Counterbalance)
- Used when movement is large, fast, nearing limit of stability
- Surface is too narrow or unstable to allow counter pressure
- NO ANKLE STRAT
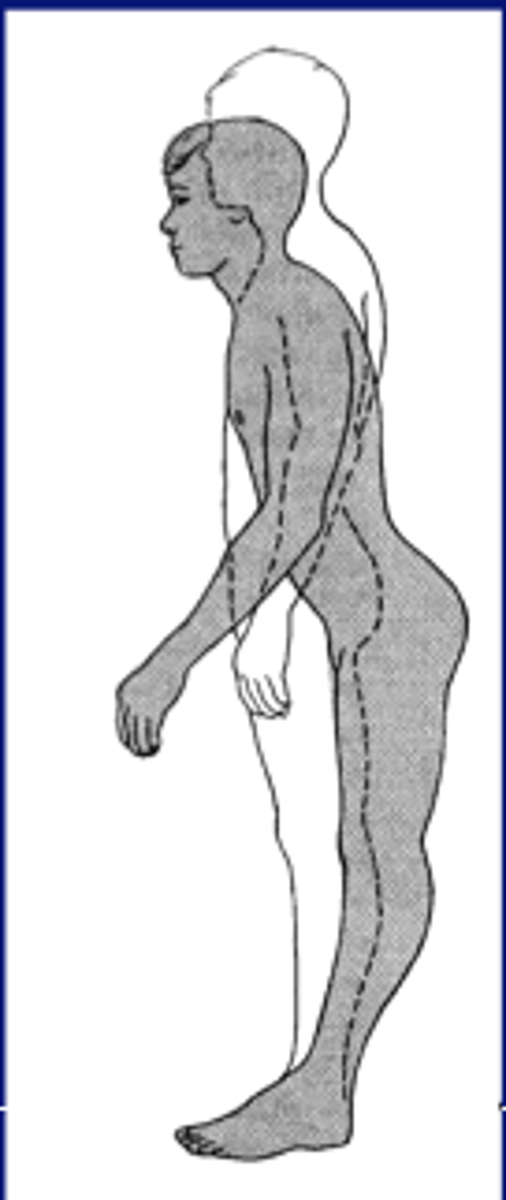
Hip strategy with FORWARD sway (plate moving back)
Order of MA (but kinda at same time)
1. abdominals muscles
2. quadriceps
Think: MA in direction of sway
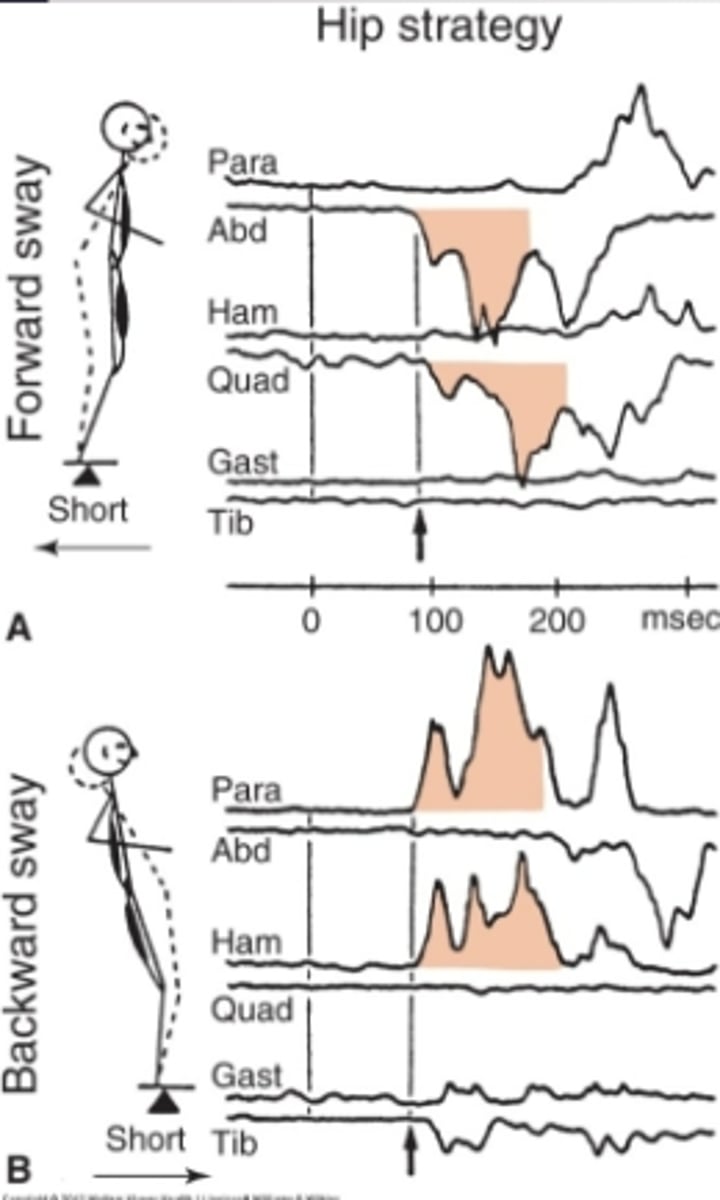
Hip strategy with BACKWARD sway
MA
1. Paraspinals
2. hamstrings
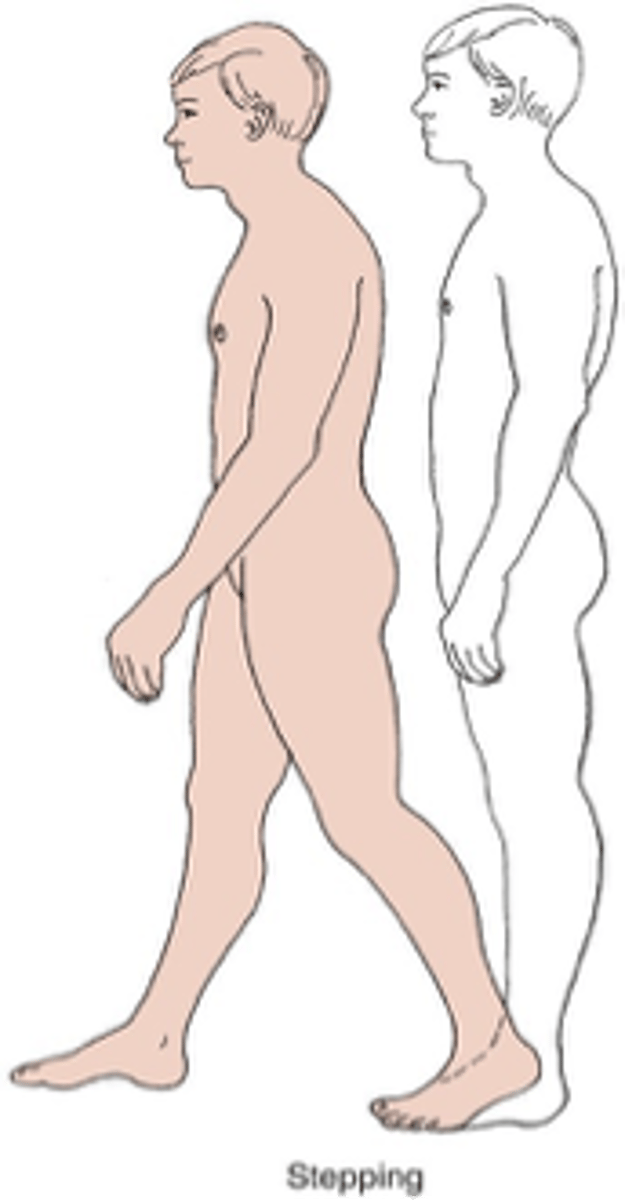
Stepping strategy
used when Ankle and Hip fails
- attempt to re-establish new BOS with active limb when COG has exceeded original BOS
Suspensory strategy
Lowering the COG toward BOS
- Used when a combination of mobility and stability is required
- used when Ankle and Hip fails
Reach-and-Grasp (RG) strategy
Complex: multi-limb coordination
- takes loss of balance & environmental factors (available/NA) into account
- used when Ankle and Hip fails
How much time does it take to perform the RG compared to a similar voluntary movement?
takes half the time (is 2x faster)
- No pre-planning. Timing, direction, amplitude, speed are spontaneous (most likely pre-programed)
Parachute response
protective responses that body from injury during a fall
- in response to a tilting surface
- used when Ankle and Hip fails
Medio-lateral strategy
- Abduction-Adduction at the hip
- Muscle patterns in proximal-to-distal direction
- NO ANKLE
Multi-directional strategies
- No unique muscle activation pattern for each direction
- No clear synergy organization
- Complex CNS process modulated by continuous feedback signals that are context specific
strategies adapt to the environment by...
modifying behavior in response to new tasks
- ex: firm surface vs foam; narrow beam vs firm surface
--> narrow beam = hip strat
Newer concepts of postural control strategies: strategy order
Ankle>hip>step in this order
- step strategy doesnt have to be last
- based on BOS and speed (new research)
- pertubation too fast --> step
Newer concepts of postural control strategies: order with increasing speed
Ankle>hip>step in this order with increasing speed
- Strategies dont need to change with speed
- Based on critical point (new research) - 1st increased muscle work at lower strategy till critical point.
Newer concepts of postural control strategies: clinical applications
train for all strategies, in all environments, for all postural demands
- Individual factors determine use of postural control
strategies
proactive balance control
Anticipatory postural muscle activity seen before voluntary arm and leg movement
phases
- prepatory balance
- Compensatory balance
Proactive/anticipatory control: Prepatory phase
50 ms before voluntary movement
- Compensate for destabilizing forces
- activating core muscles, taking wide base, etc
Proactive/anticipatory control: Compensatory phase
Reactivation after voluntary movement
- Stabilize body with feedback
Sensory Systems in postural control (3)
postural control is not just the ability to generate and apply forces to control body position
- sensory
- vestibular
- vision
Visual system
Provide info on postion and motion of head with respect to surrounding objects
- not always accurate source of orientation info about self motion
Sensory system
kinesthetic and proprioceptive, skin sensation, DTR, joint capsule (position and motion about body with refrence to supporting surface)
- includes haptic touch
- Cruising, using hand for sensation to balance)
- Light touch dec sway that happens
Vestibular system
- used in steady state and postion of head with movement
- cannot work alone to provide how body is moving in space
EXAMPLE
- Moving room closer to baby --> child sways back to keep same distance from TV (anterior muscles activated)
- Sensory field changed (no perturbation)
- Labyrinthine reflex
sensory organization test (SOT)
objectively identifies abnormalities in the patient's use of the three sensory systems that contribute to postural control: somatosensory, visual and vestibular
SOT: Condition 1 (Stable surface, EO)
- Accurate: Vest, Vision, Somato
- Inaccurate: NA
SOT: Condition 2 (Stable Surface, EC)
- Accurate: Vest, Somato
- Inaccurate: Vision
SOT: Condition 3 (Stable Surface, Unstable Vision)
- Accurate: Vest, Somato
- Inaccurate: Vision
SOT: Condition 4 (Untable Surface, EO)
- Accurate: Vest, Vision
- Inaccurate: Somato
SOT: Condition 5 (Untable Surface, EC)
- Accurate: Vest
- Inaccurate: Vision, Somato
SOT: Condition 6 (Untable Surface, Unstable Vision)
- Accurate: Vest
- Inaccurate: Vision, Somato
SOT: which condition is the most difficult?
situation 6