BIO-214 Lab #1: Plant Cells
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
7 Terms
List the Plant Cell Organelles & their functions
Nucleus
Enclosed in a double membrane
Nuclear pores: regulates communication with the surrounding cytosol
Stores DNA
Nucleolus
Structure within the nucleus
Produces ribosomes
Cytosol
Gel matrix where most of the cellular metabolism & where all the other cell organelles live
Contains water & proteins that control cell metabolism
Signal transduction pathways
Glycolysis
Intracellular receptors
Transcription factors
Cytoplasm
Collective term for the cytosol AND the organelles suspesned within the cytosol
Centrosome
Microtubule organizing center
Area where microtubules are produced
Centrosomes grow microtubules into a “spindle,” which is responsible for chromosome separation
Centriole
NOT PRESENT IN PLANT CELLS
Golgi
Stack of membrane-bound vesicles that are important for cellular transport
Lysosome
contain hydrolyic enzymes necessary for intracellular digestion
Peroxisome
Responible for protecting the cell from its own production of toxic hydrogen peroxide
Sectory Vesicle
Transport cell secretions (hormones, neurotransmitters, proteins, etc) to the cell surface for release
Cell Membrane
Phospholipid bilayer
Protective barrier against uncontrolled flow of water
Contains:
Proteins
Receptors
Pores
Cell-to-cell communication
Mitocondrion
Produce ATP
Double-membraned
Cristae: inner foldings of the mitocondrion
Increase surface area for CELLULAR RESPIRATION
Vacuole
Stores nutrients + waste products
Helps increase cell size during growth
Lyosome-like organelle for intracellular digestion
Regulates Tugor Pressure
Produces rigidity in plant cells
Cell Wall
Rigid protective cell wall made of polysacharrides (cellulose)
Function
Provides & maintains the shape of these cells
Protective barrier
Turgor pressure
Chloroplast
Contain chlorophyll pigment
Green color
Ability to absorb energy from sunlight
Photosynthesis
Double-membraned structure
Stroma: fluid inside the chloroplast
Thylakoids: coin-like structures inside the stroma
Smooth ER
Produces
Steriod hormones
Lipids
Breaks down lipid-soluble toxins in liver cells
Controls calcium release in muscle cells
Rough ER
Contains ribosomes on its surface
Protein synthesis
Ribosomes
Packets of RNA & protein
Site of protein synthesis
Consists of 2 parts
Large subnit
Small subnit
mRNA (nucleus) → ribosome → tRNA addes amino accids → protein chain is lengthened
Cytoskeleton
Function
Maintains cell shape
Cell motility
internal movement of cell organelles
Cell locomotion
Muscle fiber contractions
Made up of 2 primary protein filaments
Microtubules
Microfilaments (actin filaments)
Intermediate fibers
How are plants physically different from animal cells?
Animal
Centrosomes
Lysosomes
Plant Cells
Cell Wall
Chloroplast
Plasmodesmata
Large Central vacuole
Which structures give plant cells physical protection & support?
Cell Wall: Rigid layer found outside the cell membrane
Which plant organelle is responsible for storage?
Central vacuole
Which organelles do plant cells use to produce the sugars they need to survive?
Chloroplasts
Identify which cells the following are:

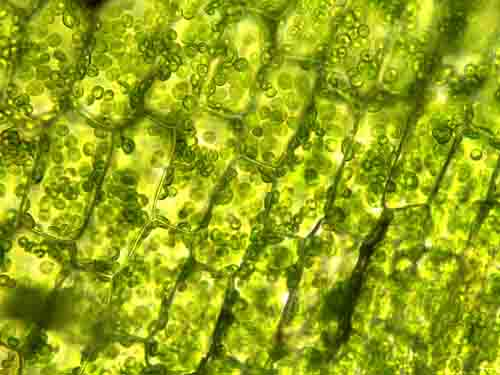
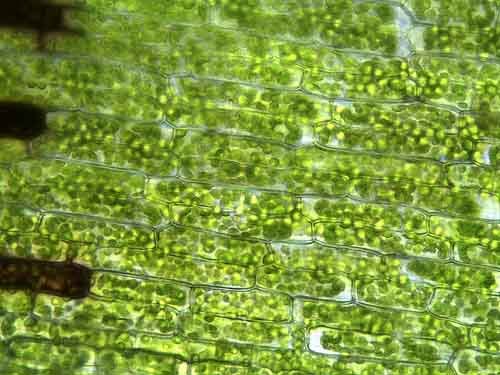
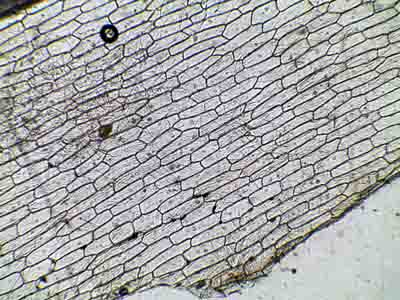
Plant Cells
Elodea cells
Rigid cell wall
Chloroplast structures
Green pigment (chlorophyll)
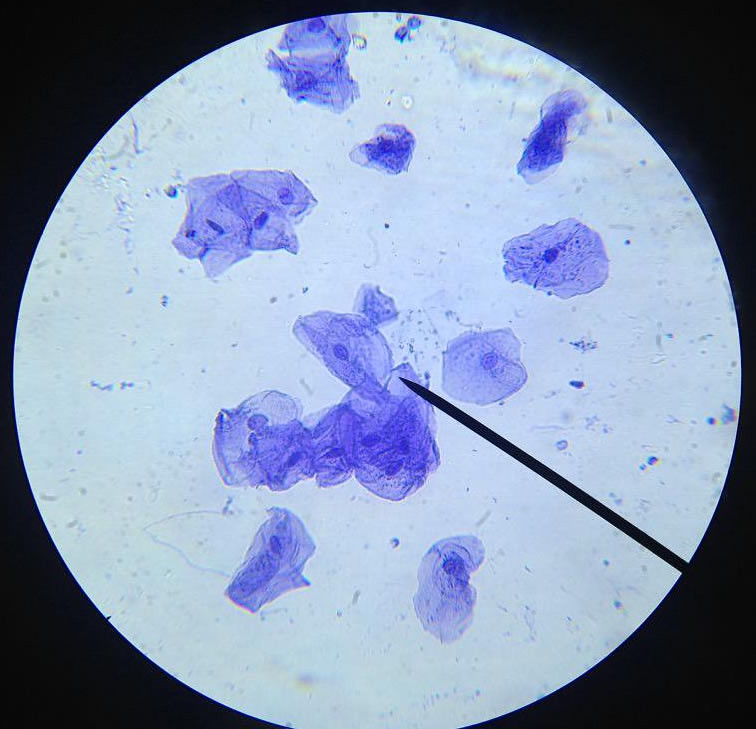
Classify the following cells:
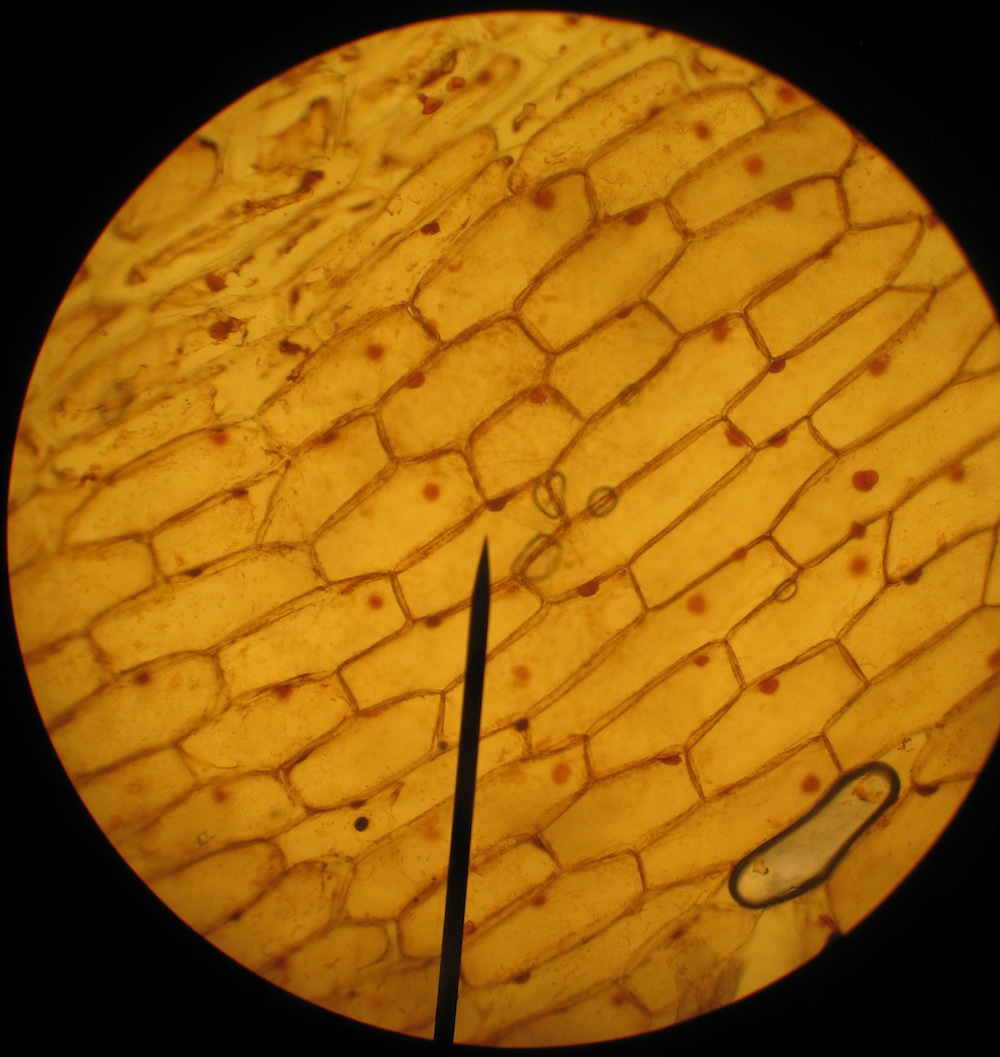
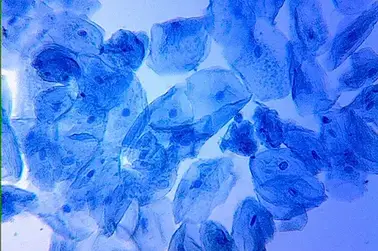

Plant Cell
Rigid Cell walls
Cells are very organized (matrix-like)
Animal Cell
No rigid cell wall (flexible cell membrane only)
Cells are scattered around