ESRM 201 Plant ID MT 1
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
55 Terms
angiosperm
seed enclosed in fruit
gymnosperm
seed enclosed in cones (i.e. conifers)
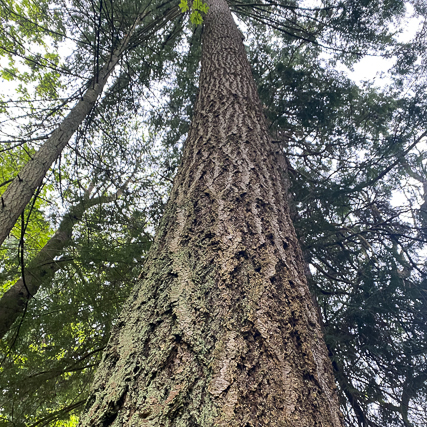
douglas fir
pseudotsuga menziesii
Characteristics: mouse tail bracts on cone, rough thick bark, little apex buds at top of branches, plastic needle arrangement

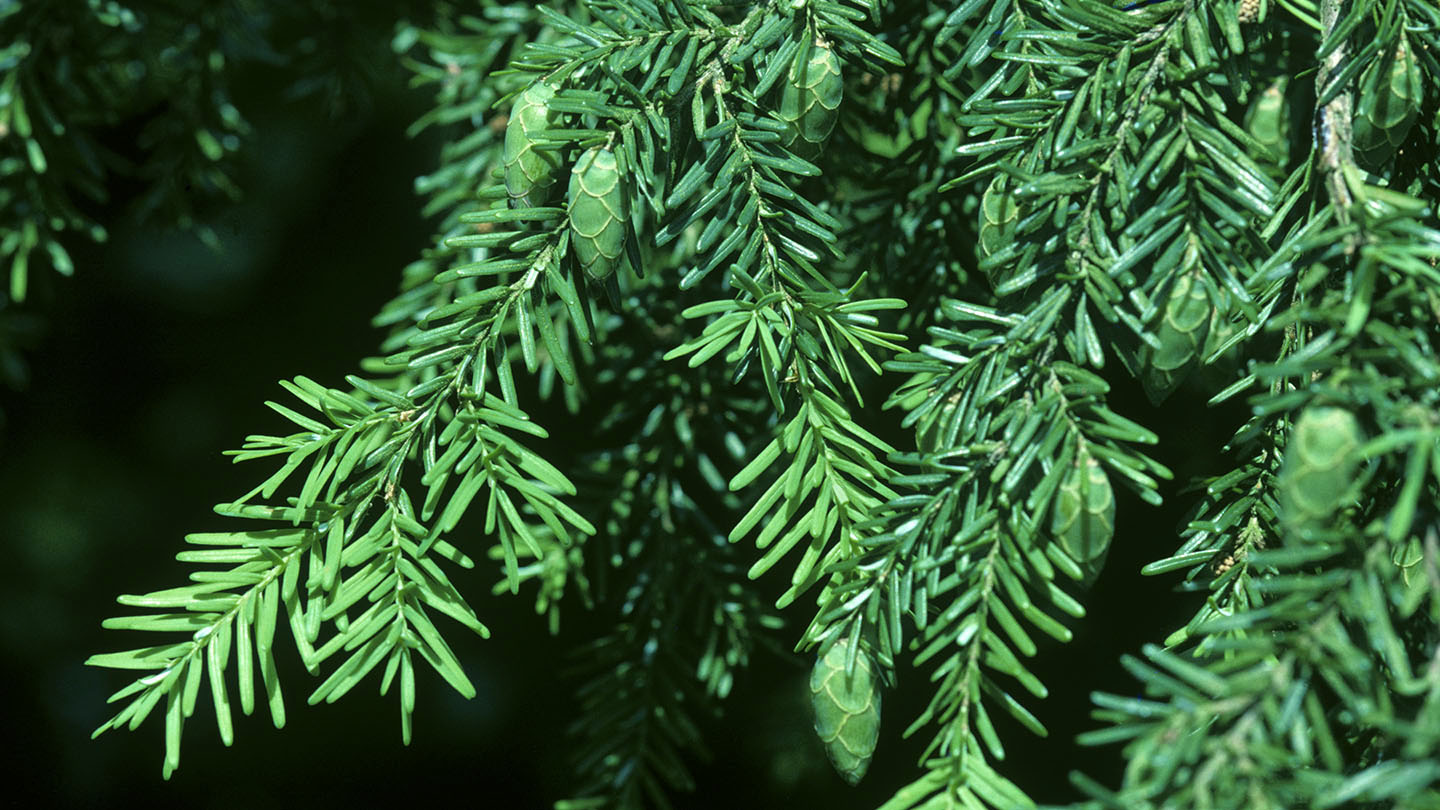
western hemlock
tsuga heterophylla
characteristics: “bad hair day” needle arrangement, small scaly cones, droopy branches, flad rounded needles

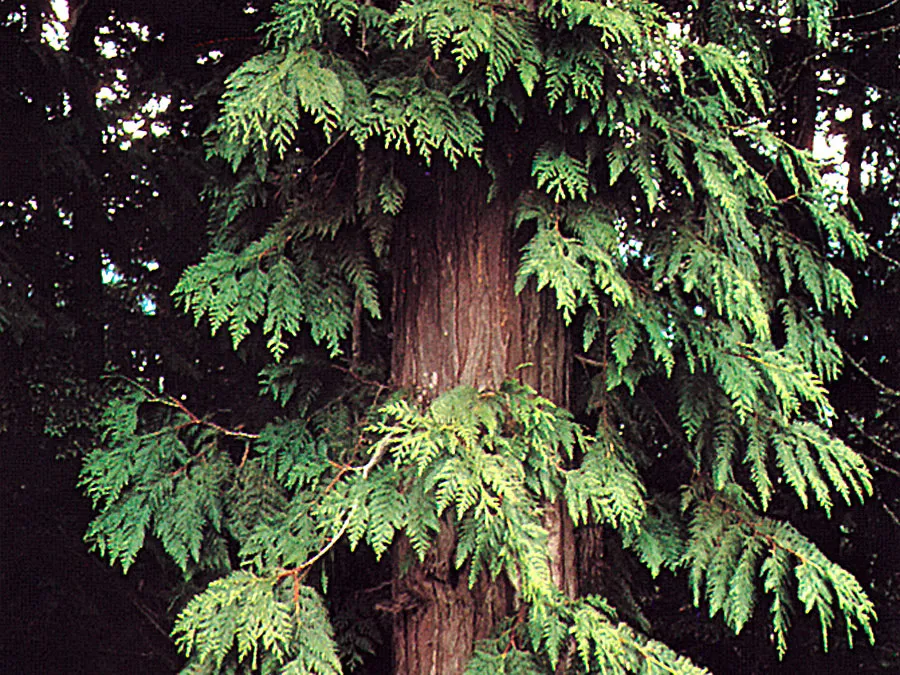
western red cedar
thuja plicata
characteristics: plicated=pleated in latin —> pleated, stripy bark, small rosette shaped cones, flat arranged scaly needles

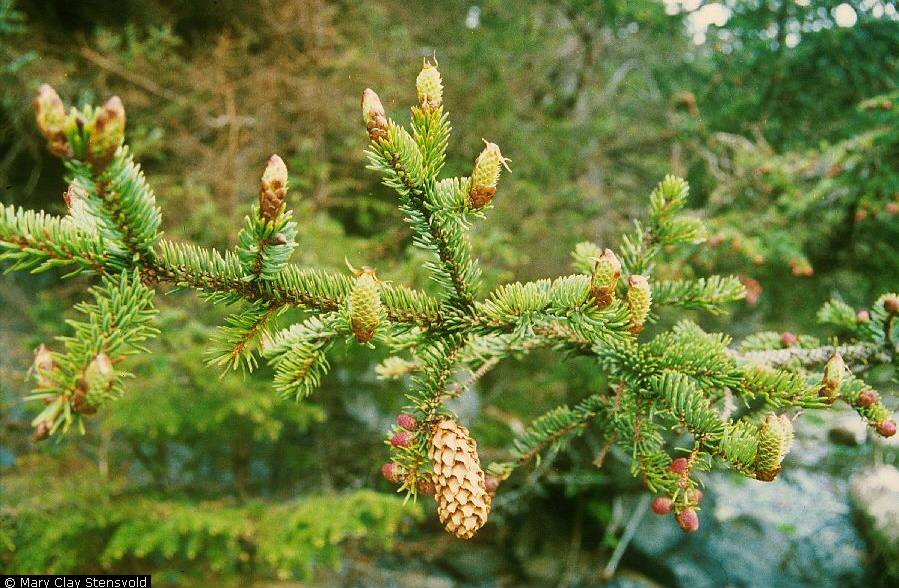
sitka spruce
picea sitchensis
characteristics: spiky needles, bottle brush arrangement, sterigmata pegs left behind when needles fall, plate-like scaly bark

Engelmann spruce
picea engelmannii
chracteristics: blu-ish tint from wax, strong sturdy upward branches, bottle brush arrangement
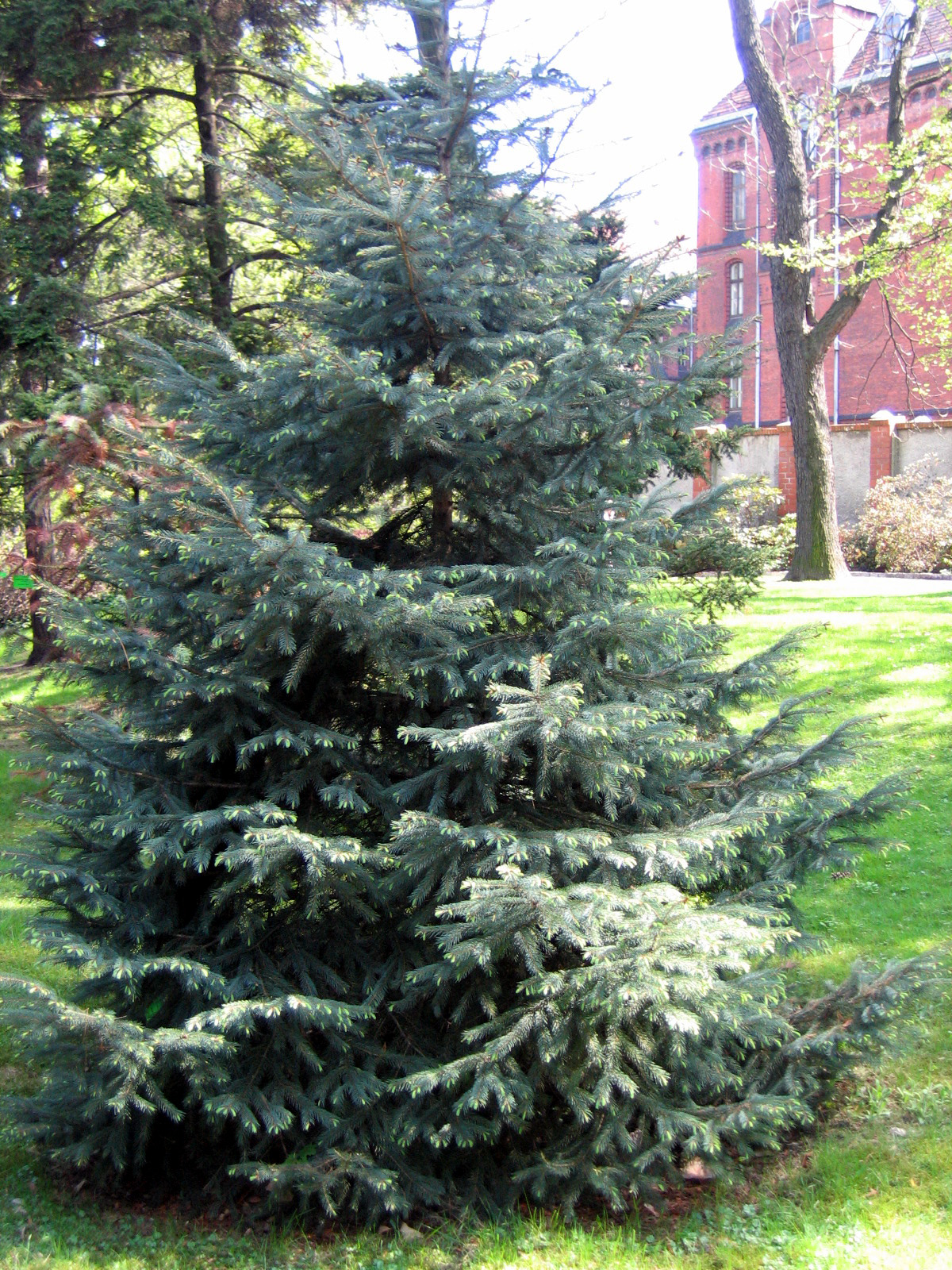

grand fir
abies grandis
characteristics: cruciform branching with flat needle arrangement, citrusy pine scent, few needles on main branch, trunk scars that give eyeball, rounded needle with small notch
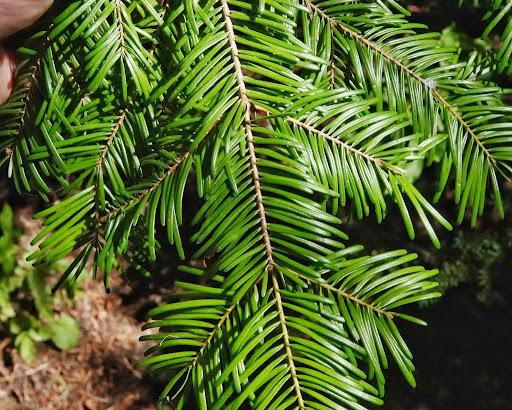

sub-alpine fir
abies lasiocarpa
characteristics: sparse spindly tree, stomatal banding on both sides, terpentine smell
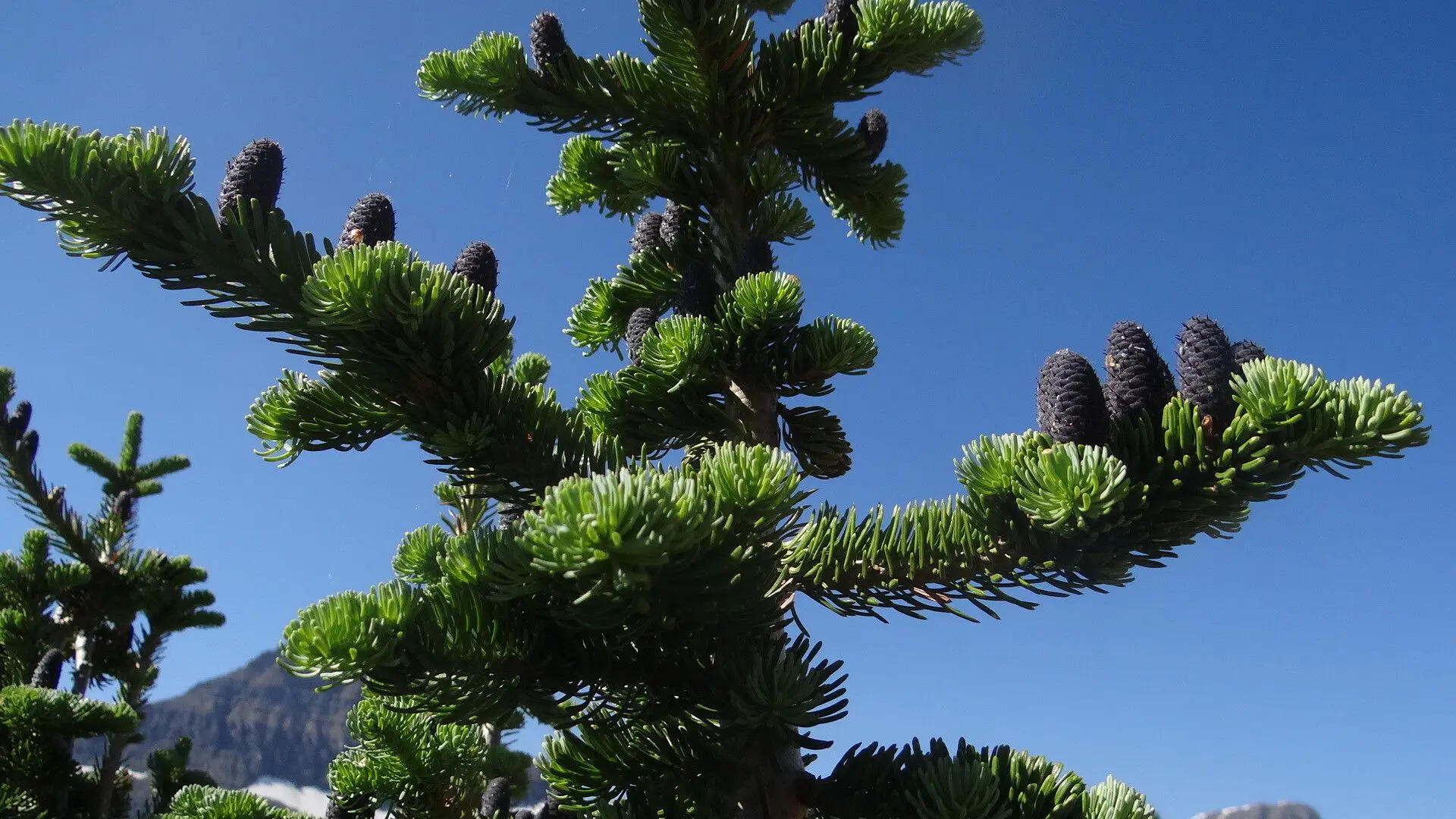

pacific silver fir
abies amabilis
characteristics: rib along top of needle, cruciform and ski jumpers, scars on skinny light brown trunk, 2 bright white stomatal bands
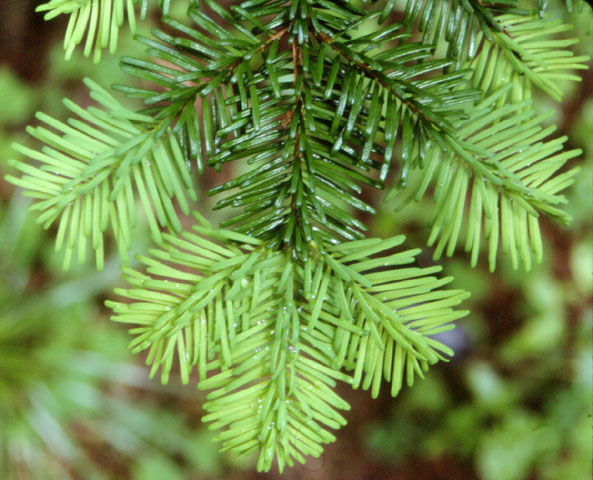

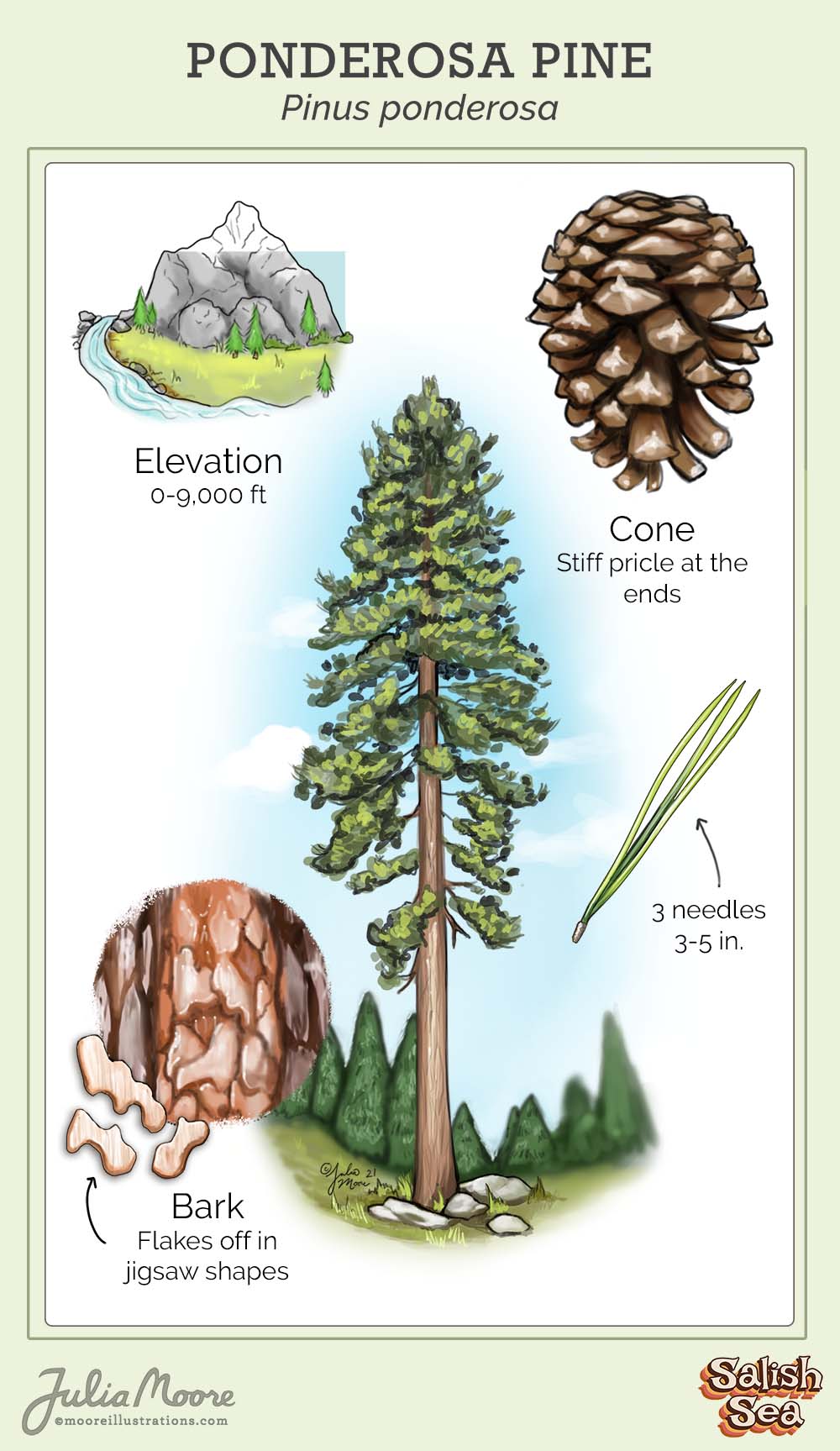
ponderosa pine
pinus ponderosa
characteristics: long 3 fasicle needles, thick bark, sparse tree, low surface area of leaves
pacific madrone
arbutus menziesii
characteristics: evergreen, scaly bark that peels off to reveal cinnamon , ovular leaves, low apical control, berries
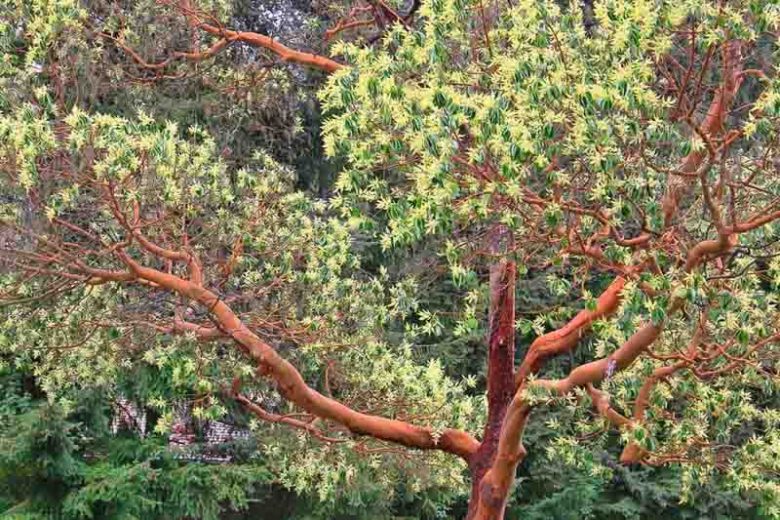

big leaf maple
acer macrophyllum
characteristics: huge dinner plate sized heavily lobed leaves, low apical control, ridged, moisture-rich bark is ideal for epiphytes
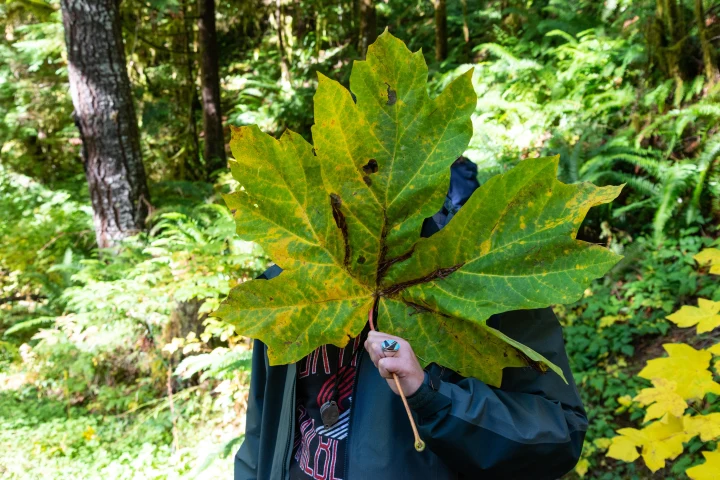

osoberry
oemeleria cerasiformis
characteristics: desiduous, leafs out during early spring before canopy cover inhibits PS, smells like cucumber or snap peas
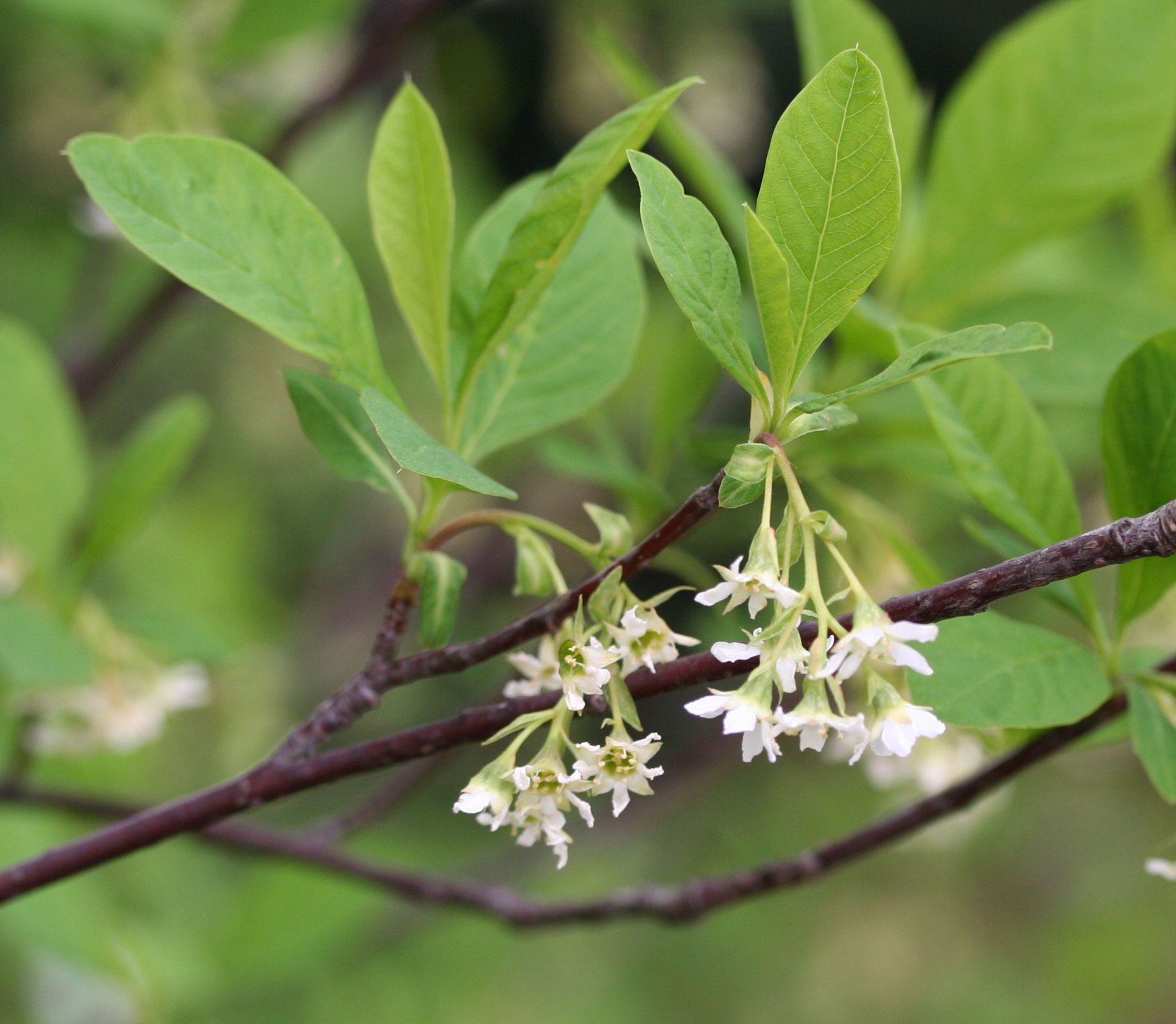

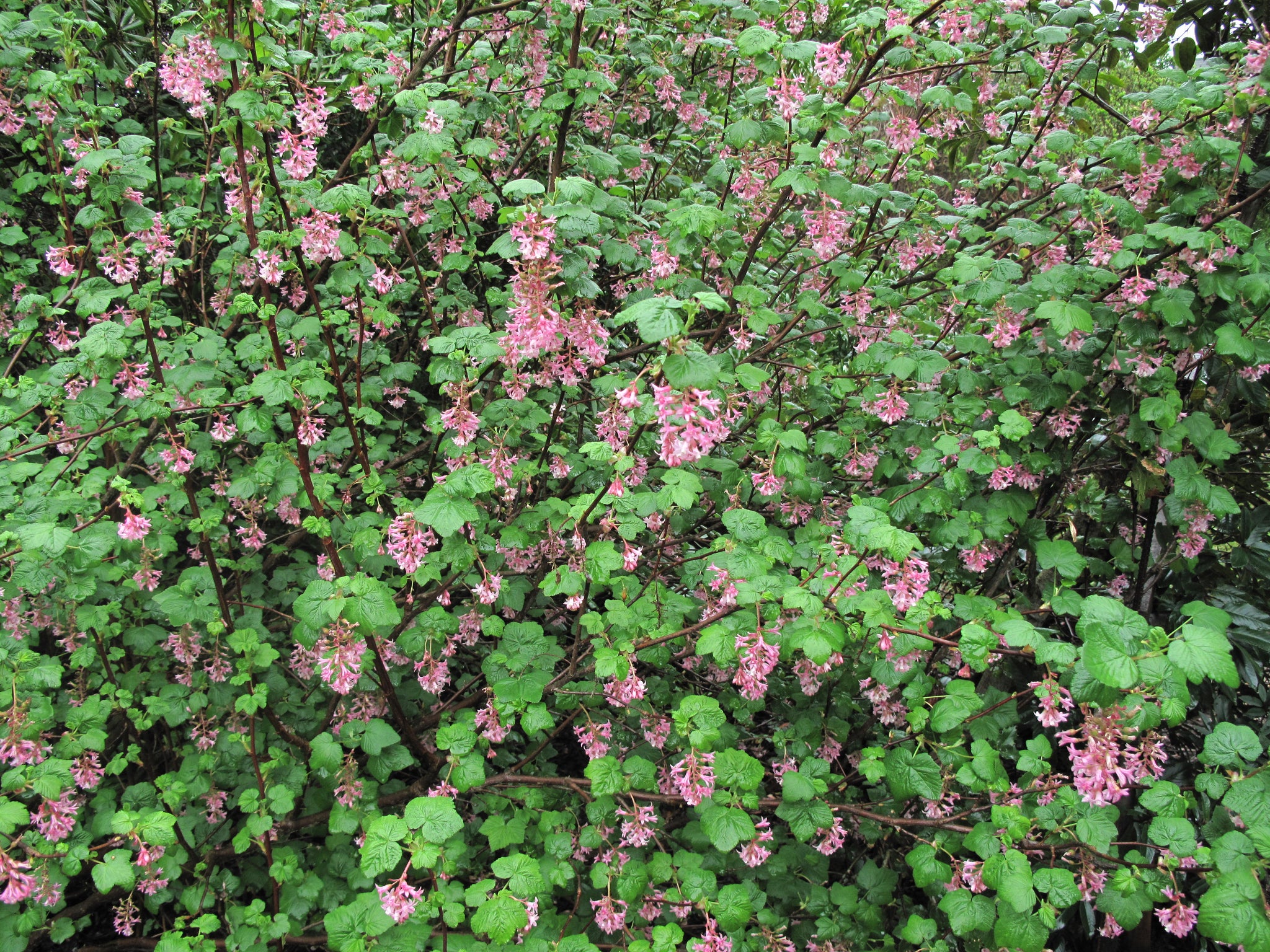
red flowering currant
ribes sanguineum
Characteristics: lobed leaves, small bottle brush arranged five petal flowers, leafs out early—important pollinator, 2nd WPBR host

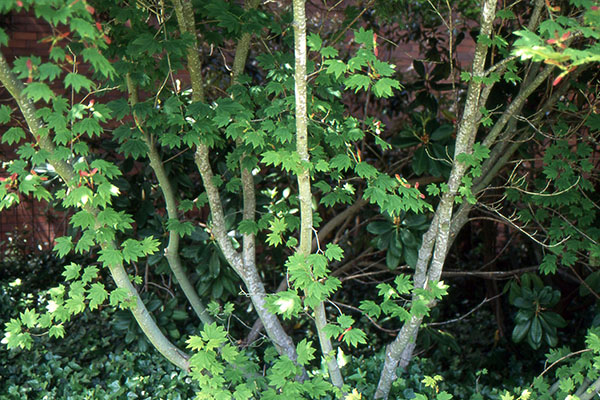
vine maple
acer circinatum
characteristics: branchy/shrubby, smooth greyeenish bark, low apical control, highly lobed rounder relatively medium sized leaves

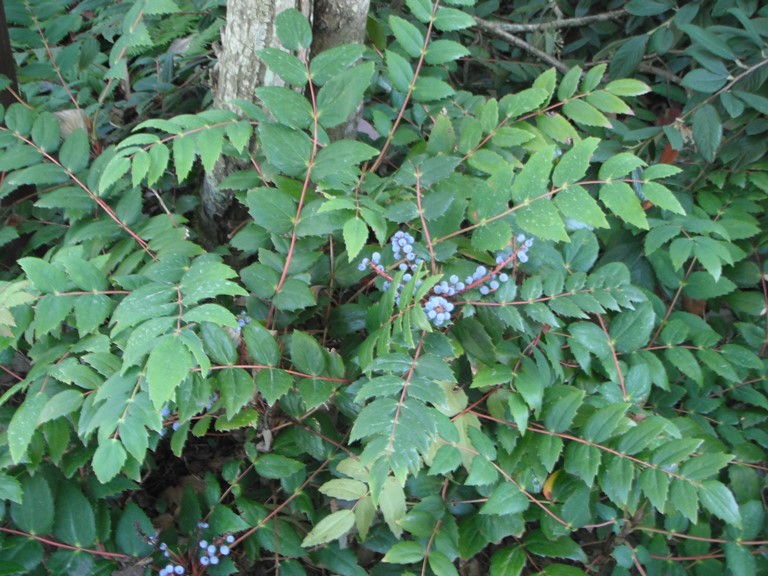
dull oregon grape
mahonia nervosa
characteristics: woody petiole goes all the way down, lighter, duller leaflets, serrated leaf edges, >9 leaflets because nervous so puts on more, yellow flowers that produce berries,

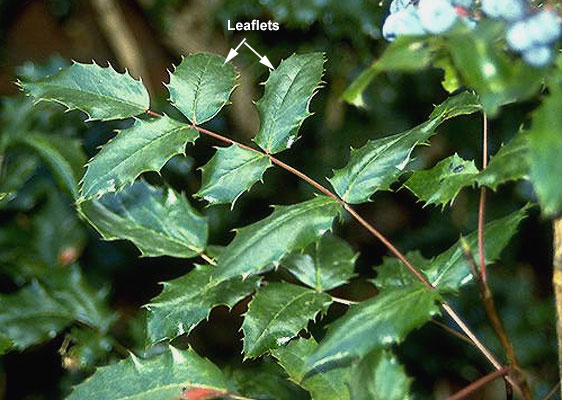
shiny oregon grape
mahonia aquafolim
characteristics: waxy darker coating (shiny like water), <11 leaflets, taller

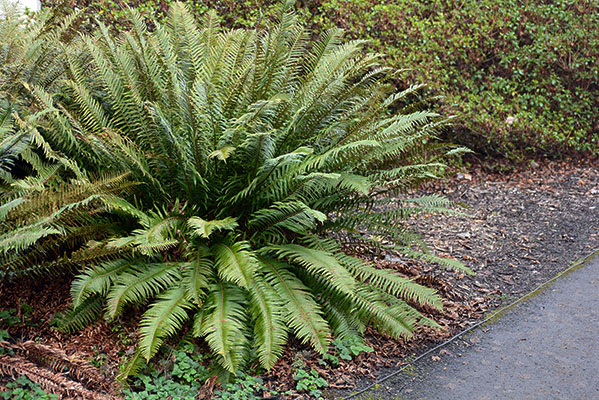
western sword fern
polystichum munitum
characteristics: polySTICH—stitching pattern on underside of fern, leaves look like swords with a hilt, seed packets

salal
gaultheria shallon
characteristics: thick egg shaped leaves, creeps along understory, evergreen, withstand many conditions, low apical dominance

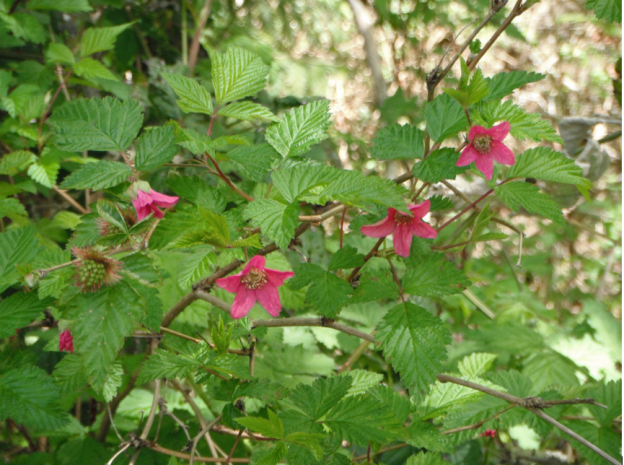
salmon berry
rubus spectabalis
characteristics: 3 leaflet compound leaf, fold over top leaflet—> looks like a butterfly, serrated edges, thin, desiduous, thriny stem…early successional: nutrient poor soil, reproduces quickly because rhizomes allow for resprouting, berries (animal dispersal), not shade tolerant

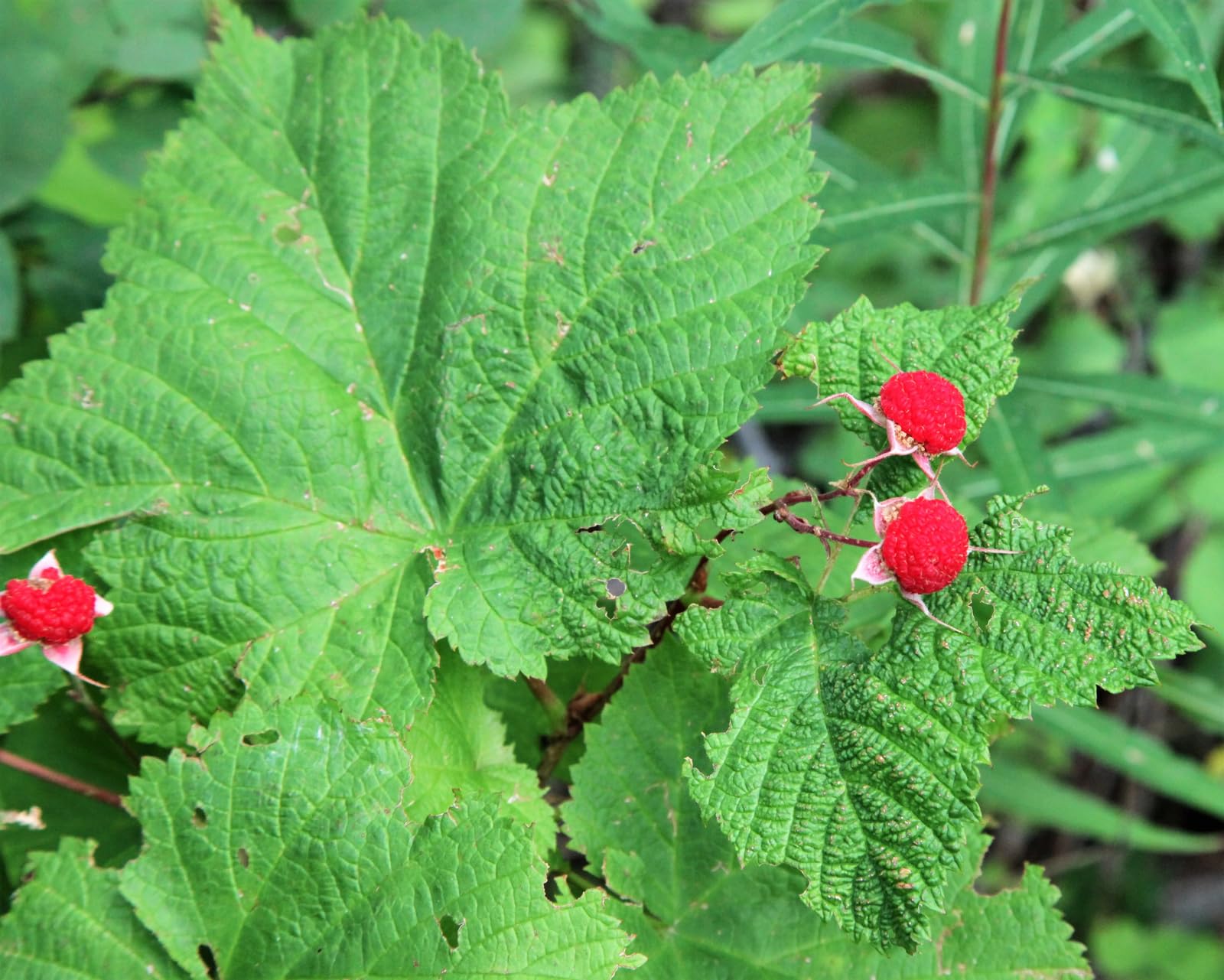
thimble berry
rubus parviflorus
simple leaf, hairs—>soft, large five lobed serrated palmated leaves, no thorns, white flowers…early succession: hairs reflect light instead of comp leaves, rhizomes

Red alder
alnus rubra
characteristics: pretty smooth bark with blisters (lenticells) that act as snorkels for tree in highly saturated soil, root nodule that fix nitrogen in nutrient poor soil (early succession), orange/red pigment, white patches (lichen), simple leaves that are inruled (bowly), serrated, catkins—coney seed ones, long pollen ones
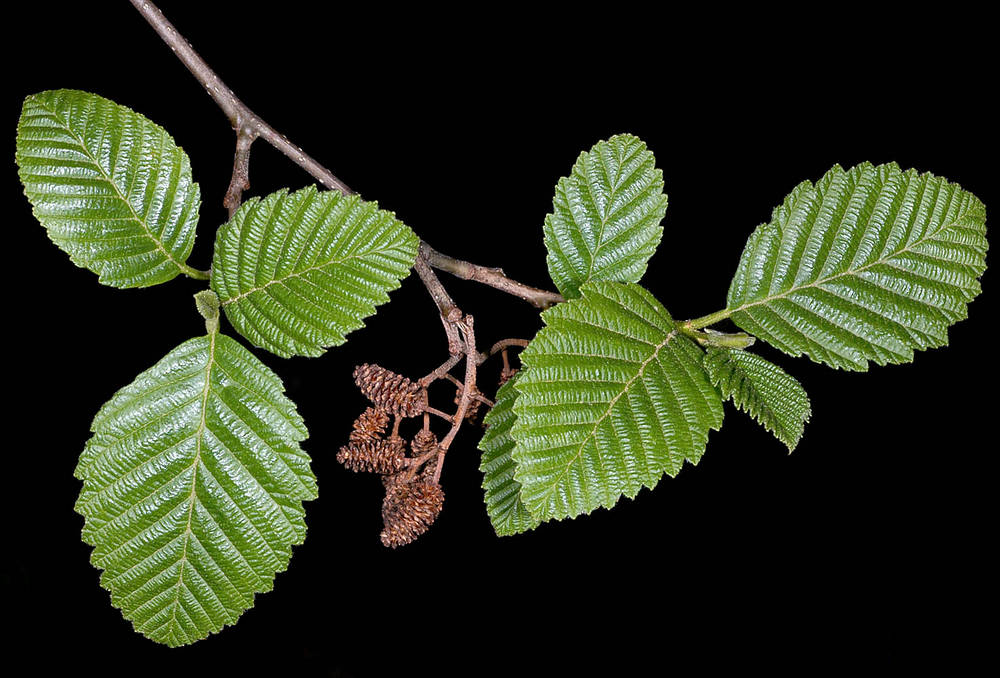

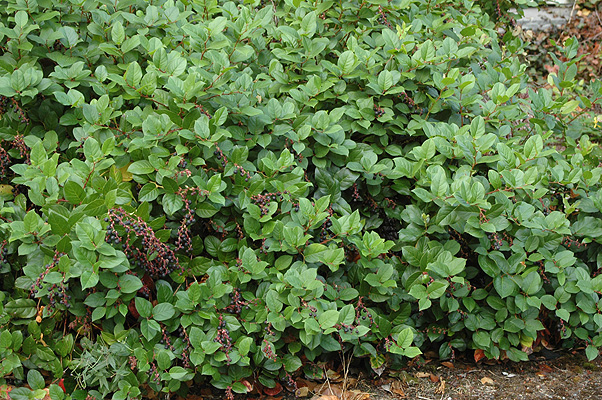
Red elderberry
sambucus racemosa
characteristics: serrated edge leaflets, 5-7 leaflets, sometimes top one is split, edible flowers, berries (animal dispersal), rhizome resprout (early succession), sunny
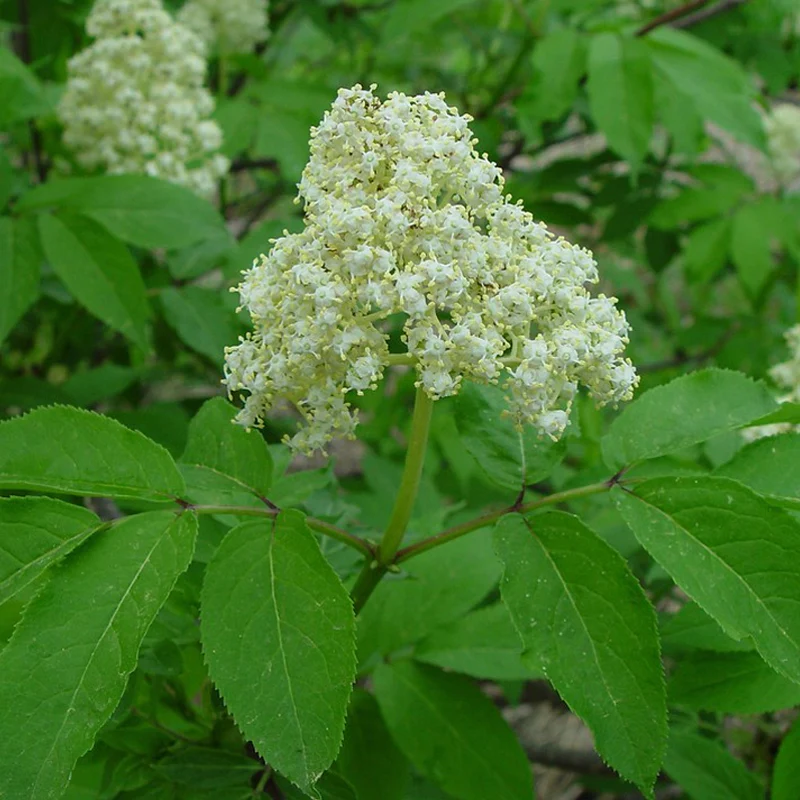

pacific yew
taxus brevifolia
characteristics: taxol harvested for chemo, flat needles with no stomatal banding, bright green underside, not cruciform, red berries, fleshy cones
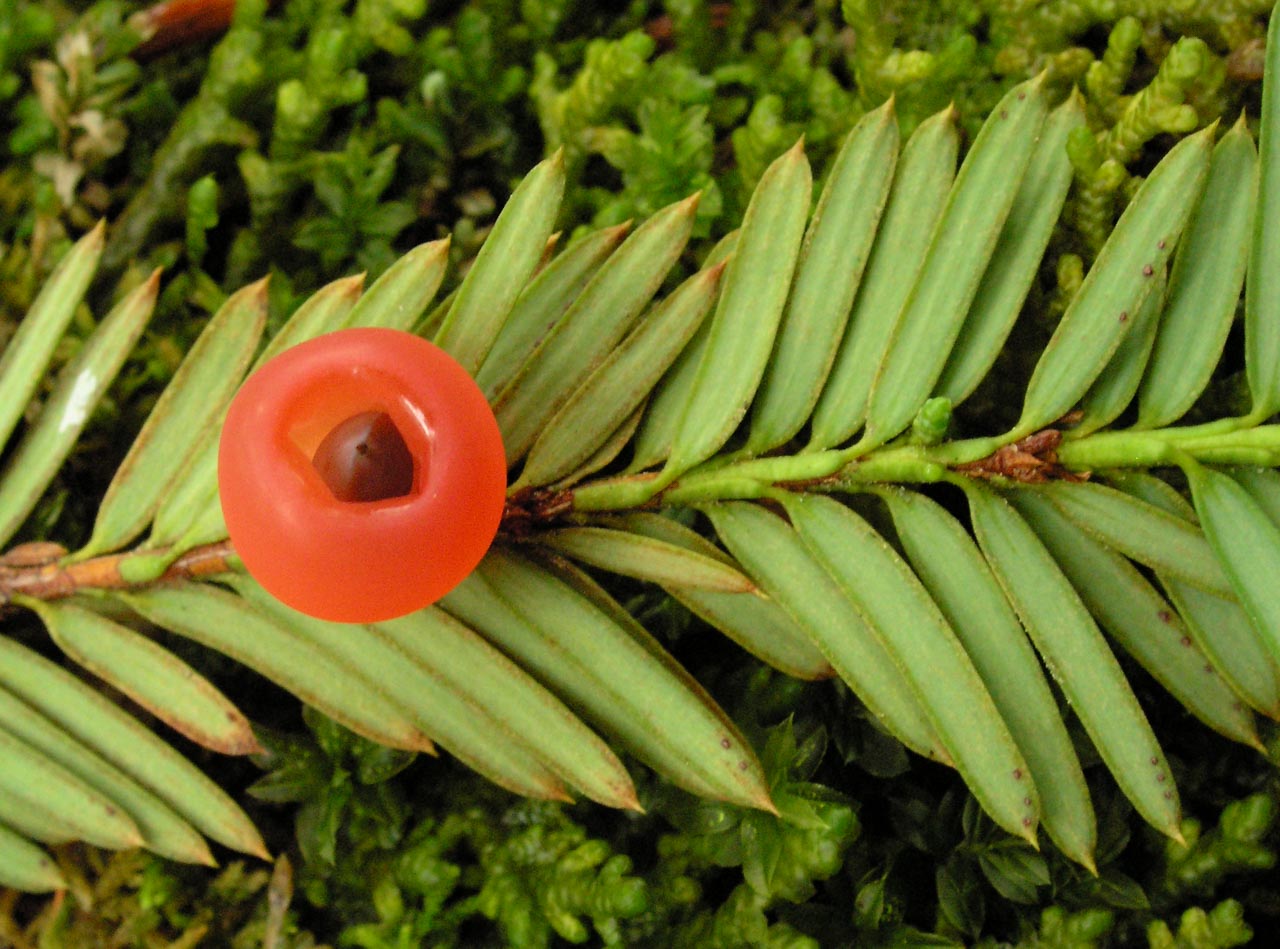

garry oak
quercus garryana
characteristics: lobed longevity leaves—take in as much nutrients as possible, high anti-fungal investment (tannins), acorns
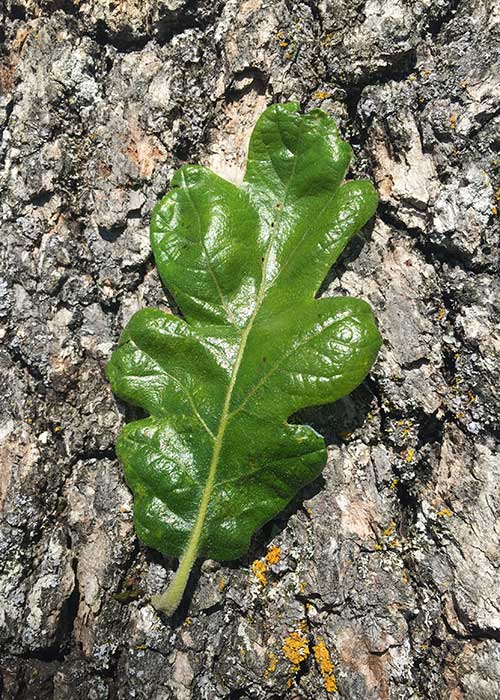

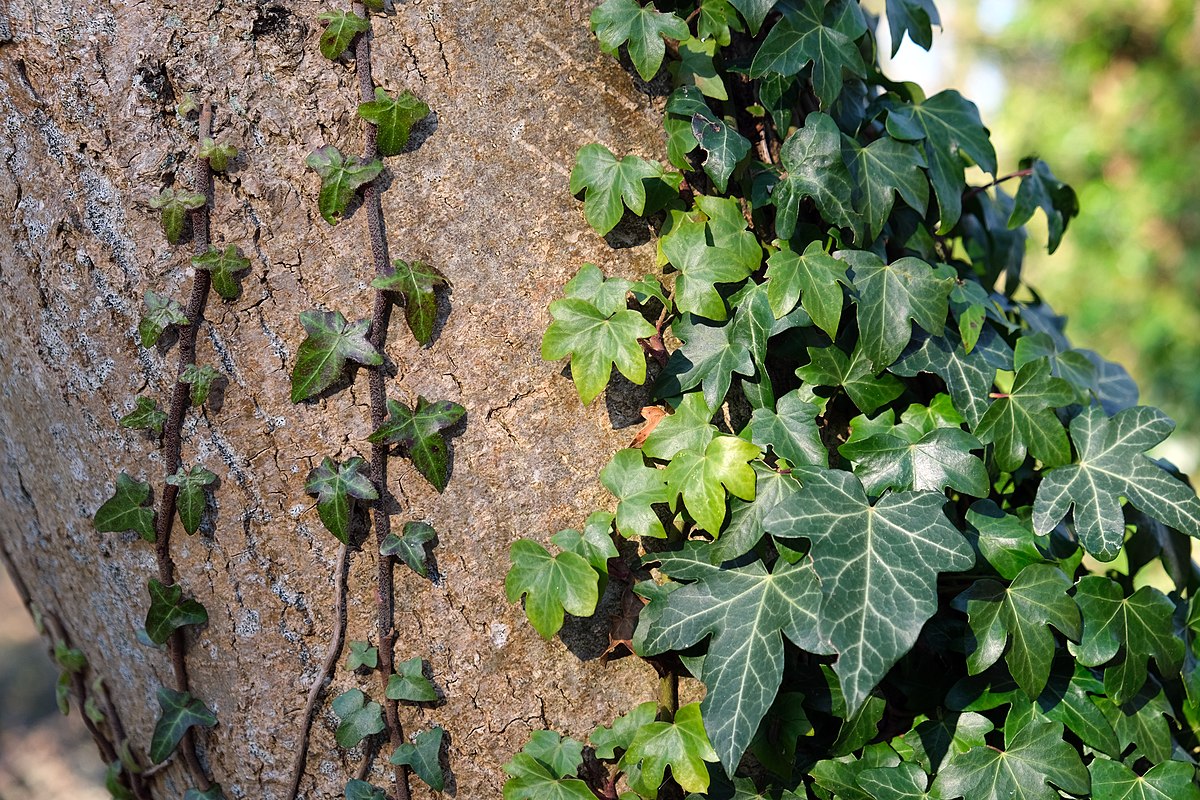
english ivy
hedera helix
characteristics: tri/pent-lobed, vine, invasive

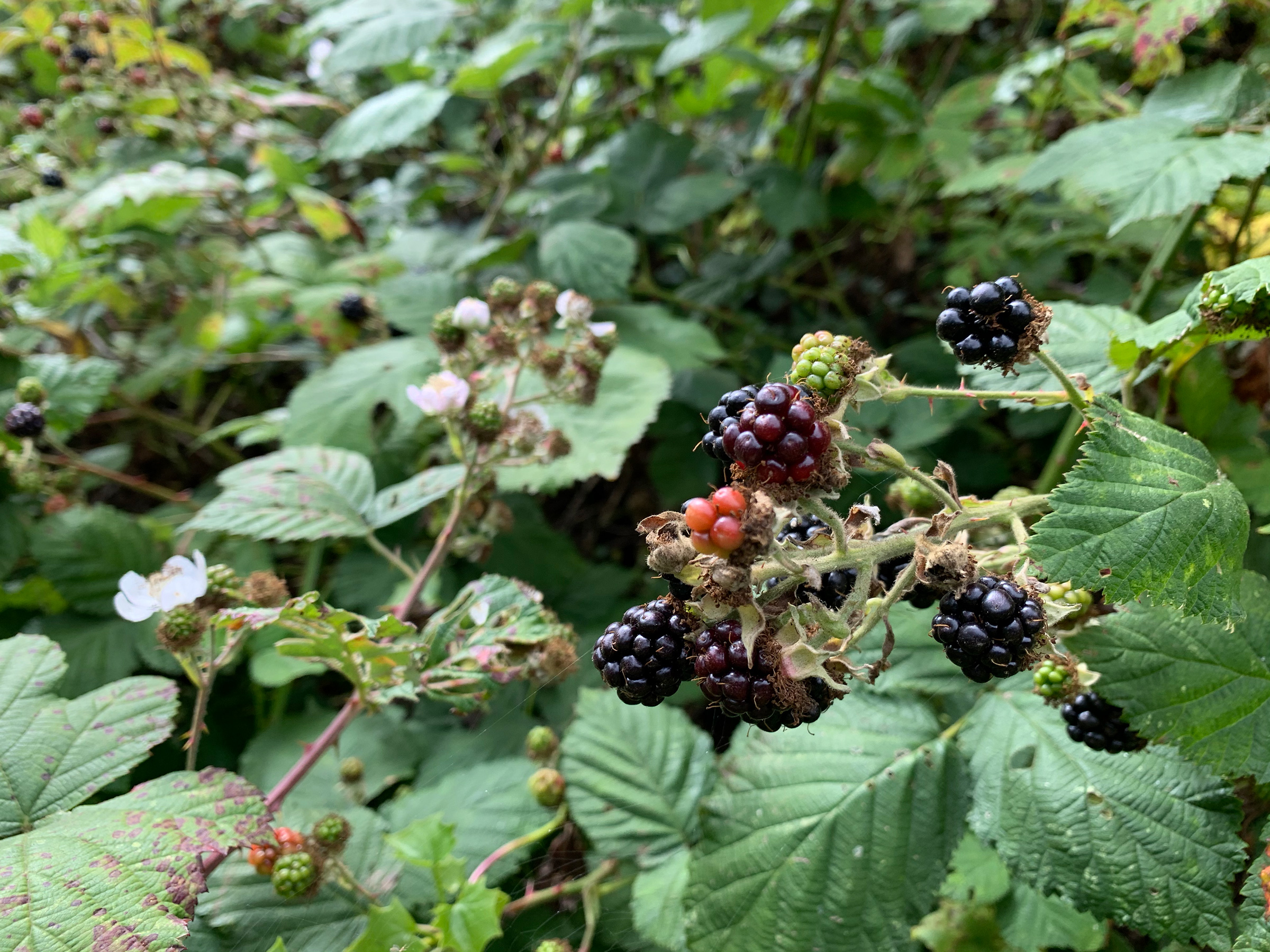
himilayan blackberry
rubus armeniacus
characteristics: looks like salmonberry leaves but thorns on petiole rather than stem, leaf hairs, 3 OR 5 leaflets,

serotinous cones
sealed until high intensity fires occur and reeseeding is needed i.e. pinus contorda
early vs intermediate vs late succession
early: high sun exposure, rhizomes/regrowth techniques, plants include rubus parvifolium and spectabalis, alnus rubra
intermediate: shade tolerance increasing, leaf surface area inc
late: high canopy cover, shade tolerant af, i.e. douglas fir
soil textures
clay: thick due to compactness of small particles, more moisture=higher respiration rate
silt: inbetween
sand: grainy, large particles, good drainage—>deep rooted plants, higher rate of decomposition (higher O2 circ)
respectively 20, 40, 40 = loam
carkeek park
secondary succession zone due to mill and fishery
UBNA
restoration site form past as waste dump
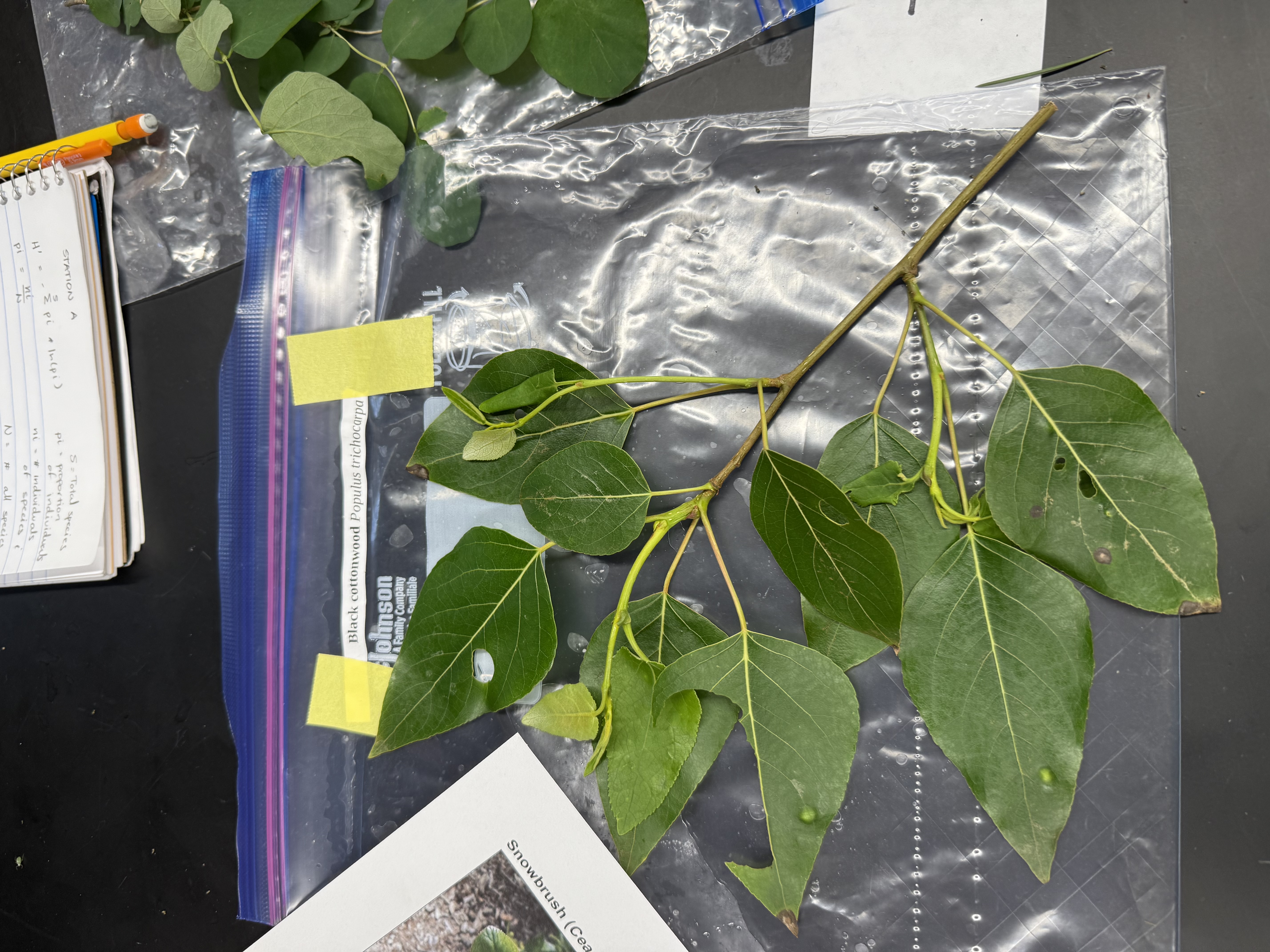
Black cottonwood
Populus trichocarpa
characteristics: long petiole, longer lancelot/heart shaped leaves with serrated edges, fluffy fruit/seed poofs

sitka willow
Salix sitchensis
characteristics: bottom tapered leaves with soft, plush silvery hairs on the underside
snowberry
Symphoricarpos albus
Characteristics: opposite heterogeneous leaves, poisonous; used by tribes to knock out fish
scotch broom
Cytisus scoparius
Characteristics: non-native shrubby plant with yellow flowers, quickly repopulates after a disturbance
rhizobium
bacteria that forms nodules along roots
frankia
bacteria that forms nodule clusters on roots of non-legume plants
ecto mycorrhizal fungi
fungus that forms (protective) sheath around root tips, more specific to woody plants so high dominance in PNW
arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi
fungus that penetrates root cells with arbuscules, more generalized; found on 85% of plants, ancestral state—helped with plants’ aquatic to terrestrial transition
symbiosis
living together of unlike organisms, encompasses + and - interactions including: mutualism (++), neutralism(=), competition(- -), parasitism(+-), commensalism(0+), ammensalism(-0)
benefits of microbial symbiosis
improved mineral nutrition (P,N) by extending root systems, water relations (assisting transport), disease protection i.e. endophytes, extends niche and tolerance of various enviro conditions
wetlands
anywhere saturated with water either permanently or seasonally supporting species adapted to wet conditions
types: marine/coastal—rocky←better for biodiversity; estuarine—enclosed body where fresh and salt water mix, critical for salmon i.e. puget sound; riverine—paths shift overtime, lacustrine—PNW lakes due to glacial retreat, poor fed←oligotrophic low nutrients, high clarity, well fed←eutrophic nutrient rich, natural or human influence i.e. fertilizer runoff; palustrine—wetlands categorized by their vegetation types (marsh, swamp, bog, fen)
water cycle
cyclical process of water
hydrographs
display how water runs through systems i.e. storm surge ones are very important because helps to predict floods, lag time: difference between peak rainfall and peak discharge, base flow: what a river can normally hold (direct relationship with [vegetation], more veg=higher base flow
snoqualmie river
flood plain zone, plants are adapted to quick influxes of water i.e. flexible stems, seasonal surges post snow melt and storm run off
abiotic disturbances
involves non-living forces like fires, floods, droughts, etc acting on biota
biotic disturbances
caused by living organisms i.e. disease, herbivory, invasive species, etc
Disturbance regimes (categories)
intensity: strength and magnitude
severity: impact/extent of damage i.e. mortality
frequency: hoe often disturbance occurs
duration: how long a disturbance happens
spatial scale: geographic area extent of disturbance
pulse & press
pulse: like - fb, disturbance only briefly passes through system and og conditions can be returned to i.e. drought
press: like + fb, disturbance does not allow for easy return to og conditions i.e. rising global temperatures → like ice-albedo feedback
fire (common in PNW abiotic disturbance)
how does it move through system? creeping, active surface, crown
what kind of fuel? continuous along understory, ladder
how is behavior measured? by flame height and length→ability of fire to reach canopy and how much fuel is available
affected by topography, weather, and fuel
W vs E side: less frequent but higher intensity and higher fuel load, resilience; higher frequency but lower severity and fuel load because more accustomed or resistant i.e. thick bark—respectively
biotic disturbances
root, canker, foliage, twig and foliage, vascular wilts, rusts
perspectives on introductions
trad W vs indigenous: invasive=threat, more -, narrow perspective; survivors of disruption telling stories of resilience, not all outsiders are invaders—respectively
disruptions
key drivers of ecological change