Plant and Animal Cells
1/32
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards based on lecture notes about cell structure and function.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
About Cells
Cells are the basic structural and functional units of life.
There are many different types of specialized cells.
In animals there are muscle cells, bone cells, brain cells, and skin cells to name a few.
In plant cells there are root cells, green cells to name a few.
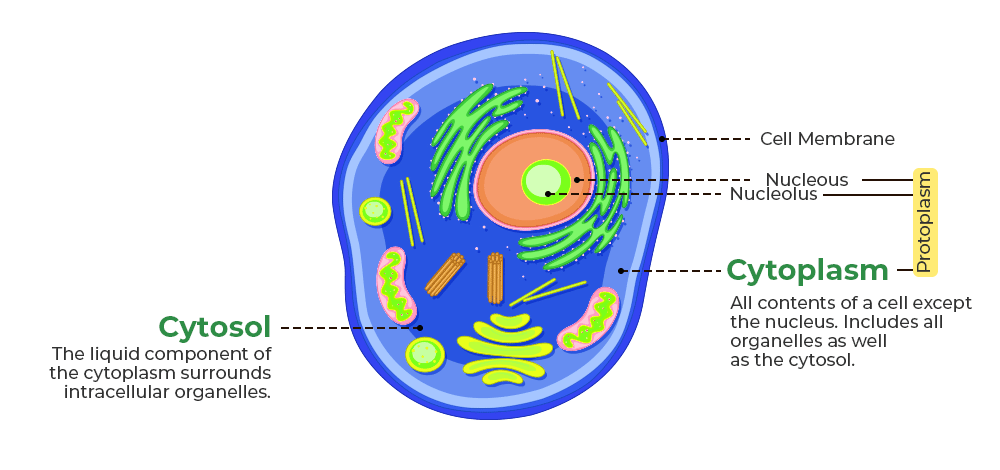
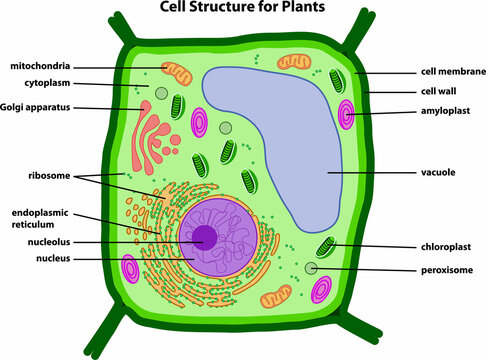
Cytoplasm
The jelly-like fluid that is found in a cell.
It is made up of mostly water and salt.
It is present within the cell membrane of all cell types and contains all organelles and cell parts.
It helps to fill out the cell and keeps organelles in their place.
Extracellular Fluid
The aqueous solution found outside the cytosol.
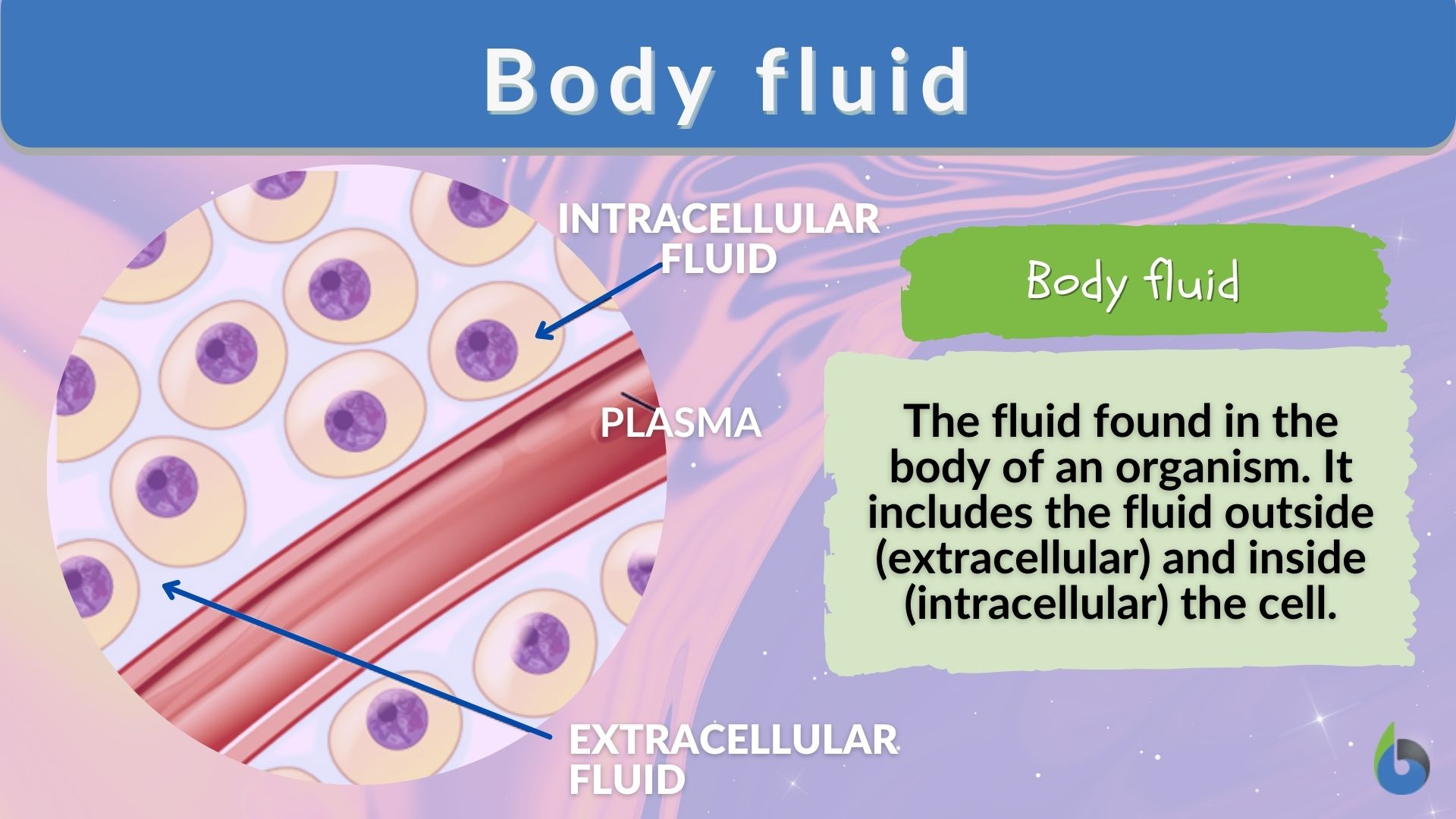
Cytosol
The liquid portion of the cytoplasm where many chemical reactions occur.
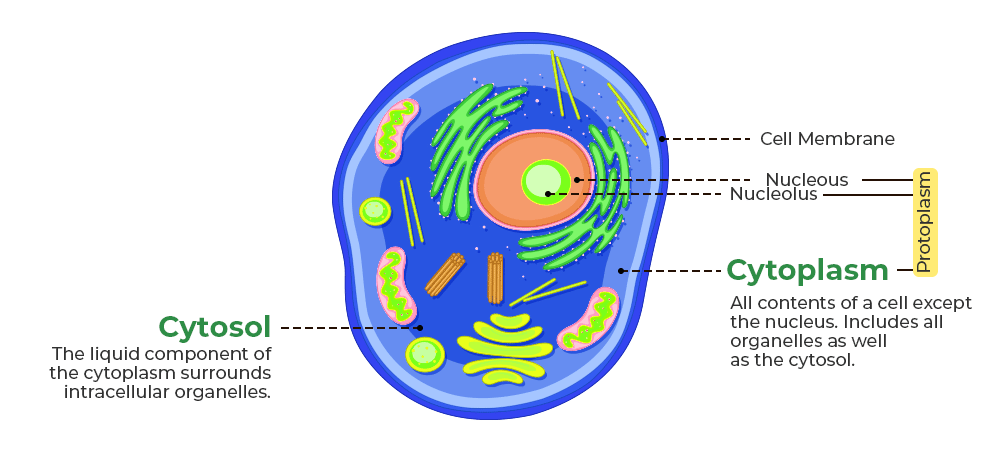
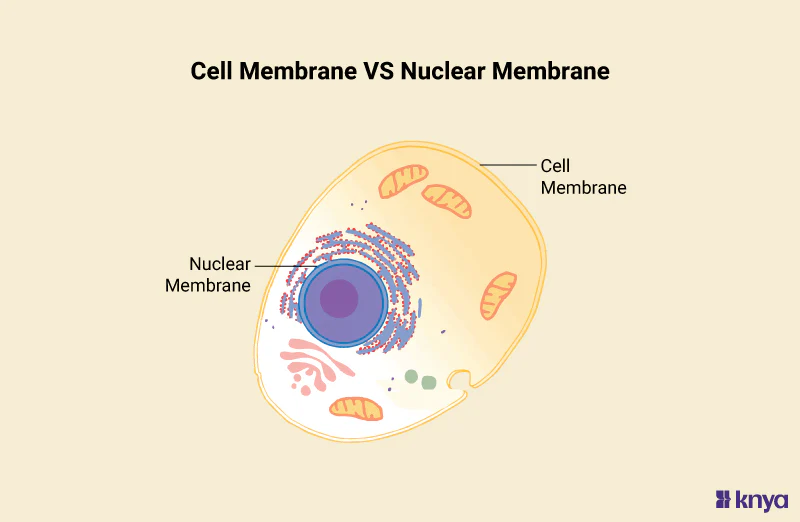
Cell Membrane
The thin flexible film that separates the cytosol and cell organelles from the extracellular fluid.
Holds the contents of the cell together.
Controls the movement of materials into and out of the cell.
Membranes
Plant and animal cells have a number of organelles that are surrounded by membranes.
A membrane is composed of a bilayer (double layer) of fat (lipid) molecules called phospholipids and other compounds called proteins, and carbohydrates.
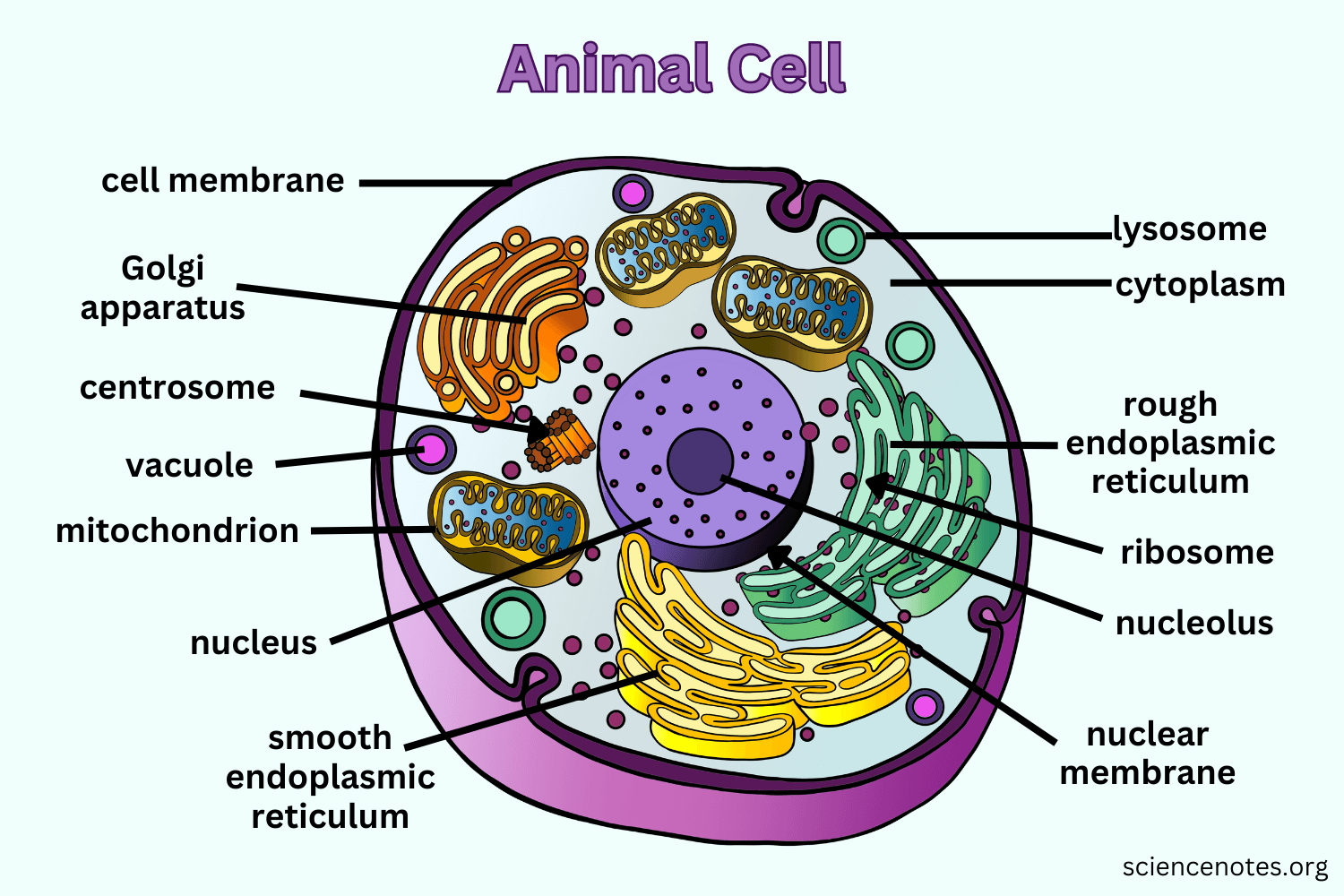
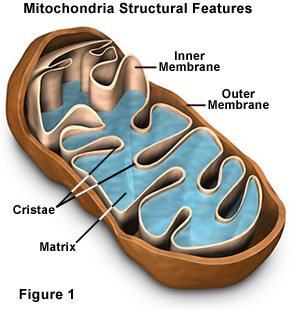
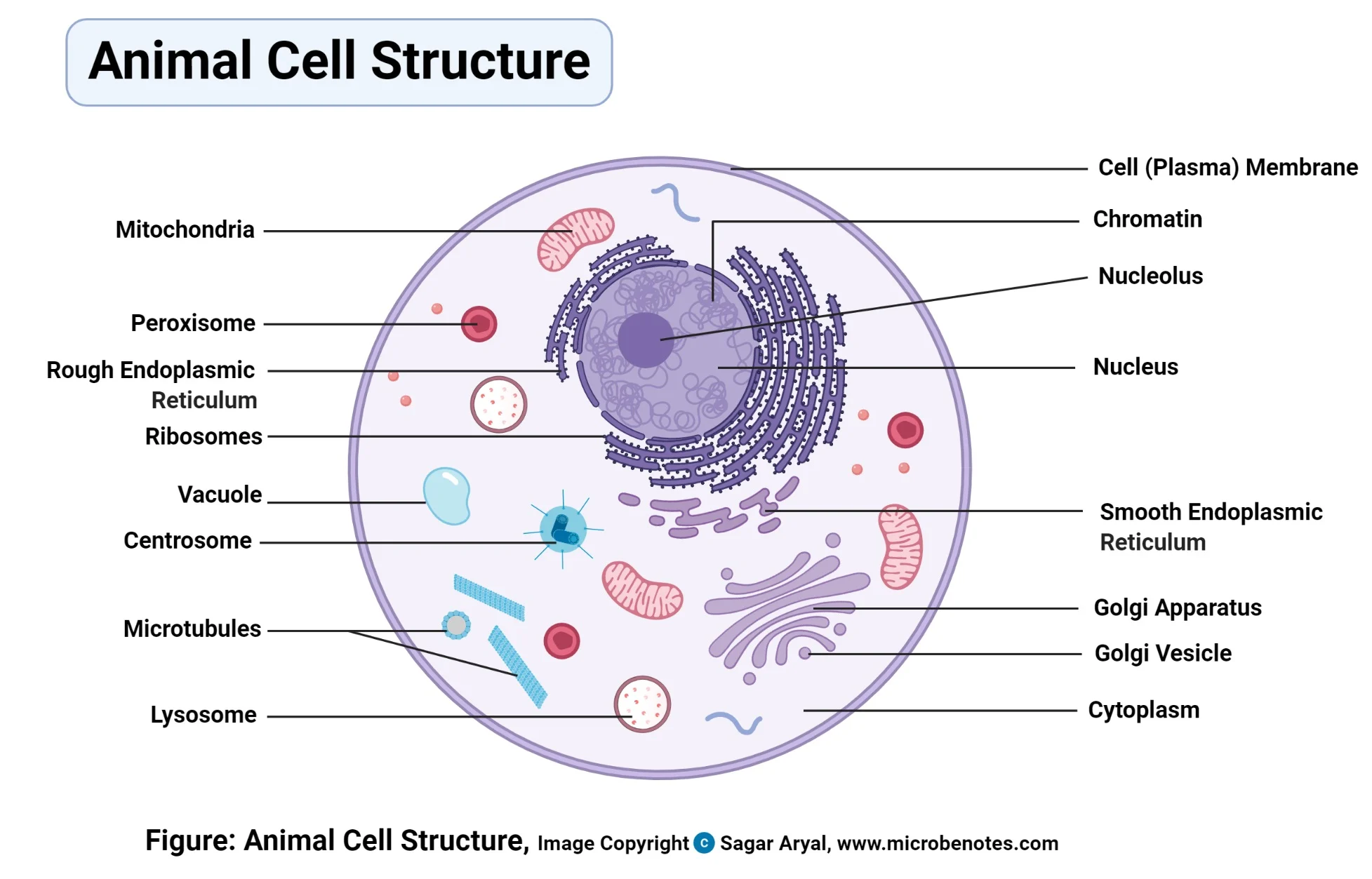
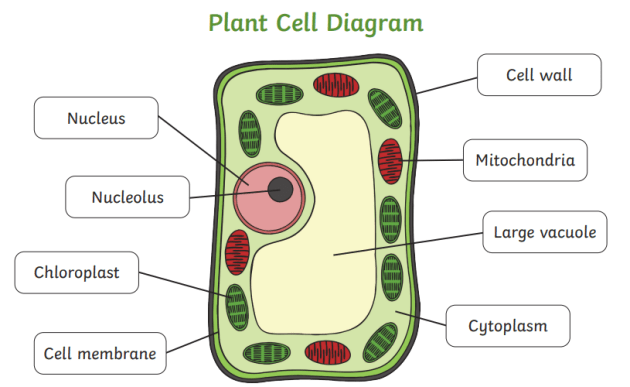
Mitochondria
Circular or rod-shaped membranous organelles that float freely in the cytosol.
Cellular respiration (a series of chemical changes that produce compounds that cells use as a source of energy) takes place in the mitochondria.
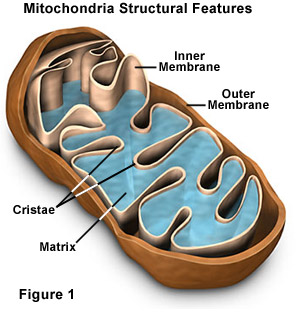
Mitochondria Membranes
The smooth outer layer.
A highly folded inner membrane called cristae (singular crista). Cristae contains compounds that help carry out the reactions of cellular respiration and provides a large surface area on which these reactions occur.
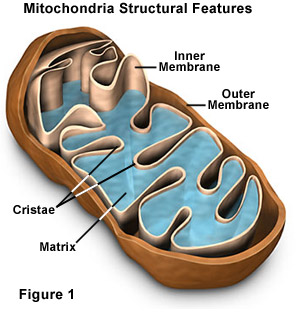
Cristae
Highly folded inner membrane of mitochondria containing compounds for cellular respiration.
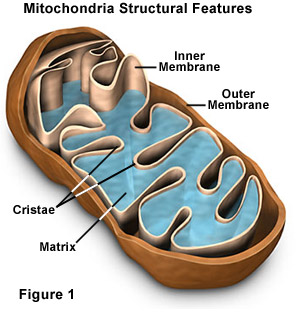
Matrix
Interior space of a mitochondrion filled with protein-rich fluid where many chemical reactions occur.
Nucleus
The control center of the cell that directs all of its activities.
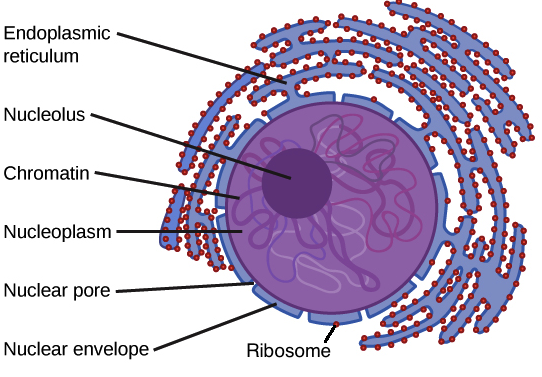
Nuclear Envelope
Porous double membrane separating the nucleus from the cytoplasm.
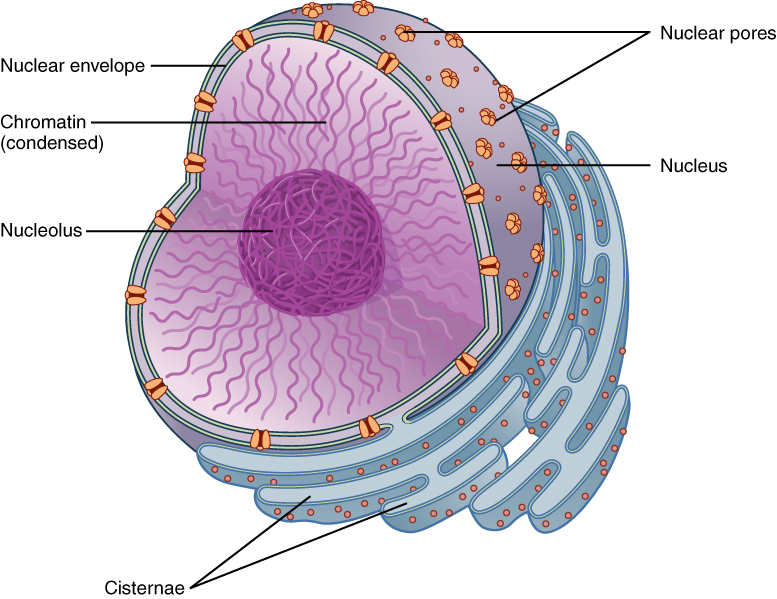
Nucleoplasm
Mixture of chemicals that store information used by other cell organelles in carrying out their functions.
Rich in compounds called nucleic acids including ribonucleic acid (RNA) and deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA).
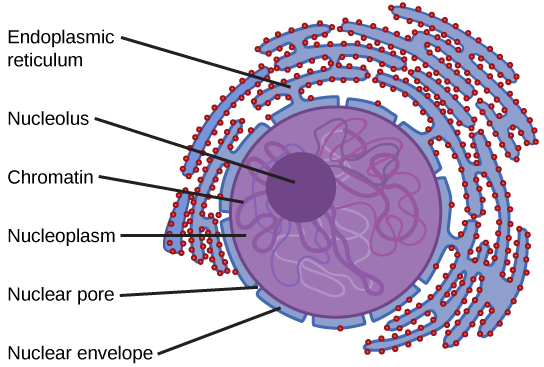
Ribosomes
Organelles used by the cell to produce proteins (protein synthesis)
Either float in the cytoplasm or attach to the membranes.
Usually, free floating ribosomes manufacture proteins for use outside the cell.
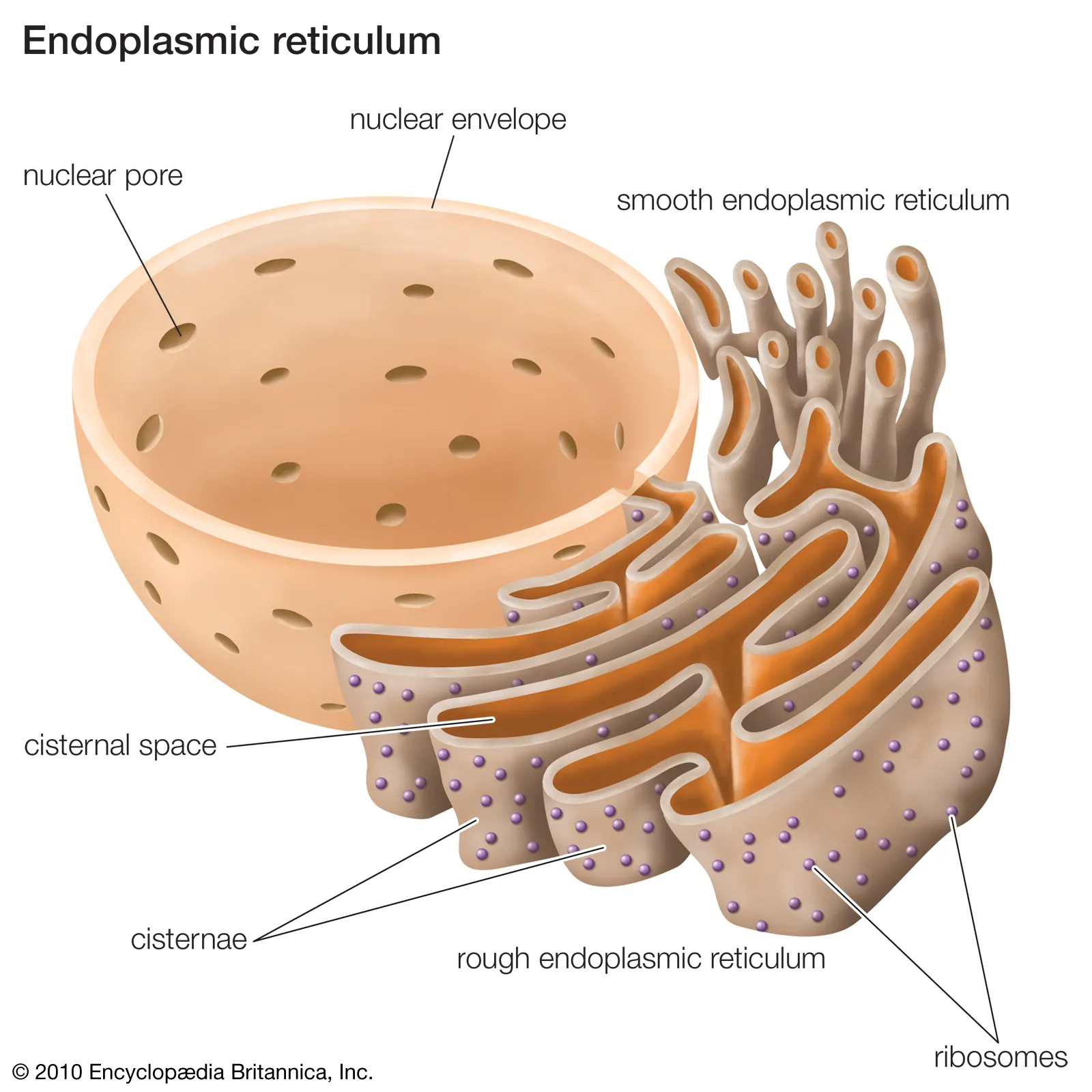
Endoplasmic Reticulum
Complicated system of membranous tubes and canals that connect the nuclear envelope.
Think of the endoplasmic reticulum as a complex subway system with crisscrossing tunnels and stations. Serving as a transportation system in the cell.
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER)
Endoplasmic reticulum containing attached ribosomes where many proteins are manufactured.
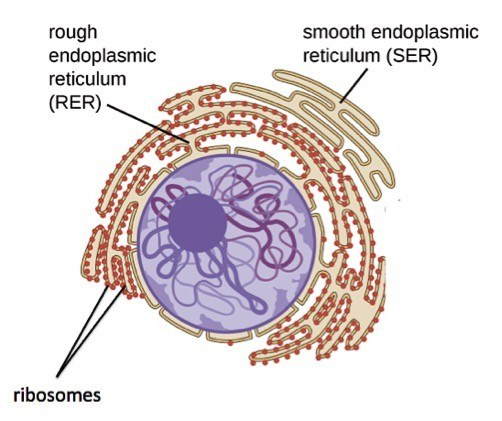
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (SER)
Endoplasmic reticulum with no ribosomes where fat is produced.
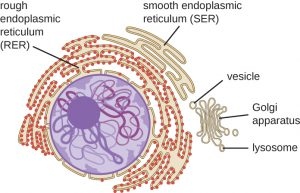
Vesicles
Packages that pinch off from the endoplasmic reticulum and travel to the Golgi apparatus.
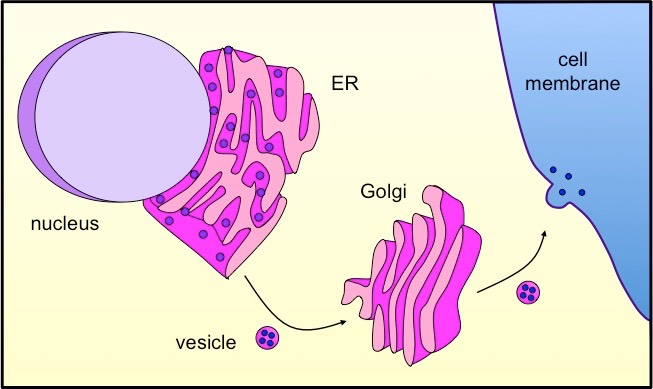
Golgi Apparatus
Made of several membranous tubes that look like a stack of flattened balloons.
Chemically changes the fats and proteins produced into the endoplasmic reticulum and then packages the in vesicles. The vesicles move through the cytoplasm, attach to the cell membrane and release their contents into the extracellular fluid.
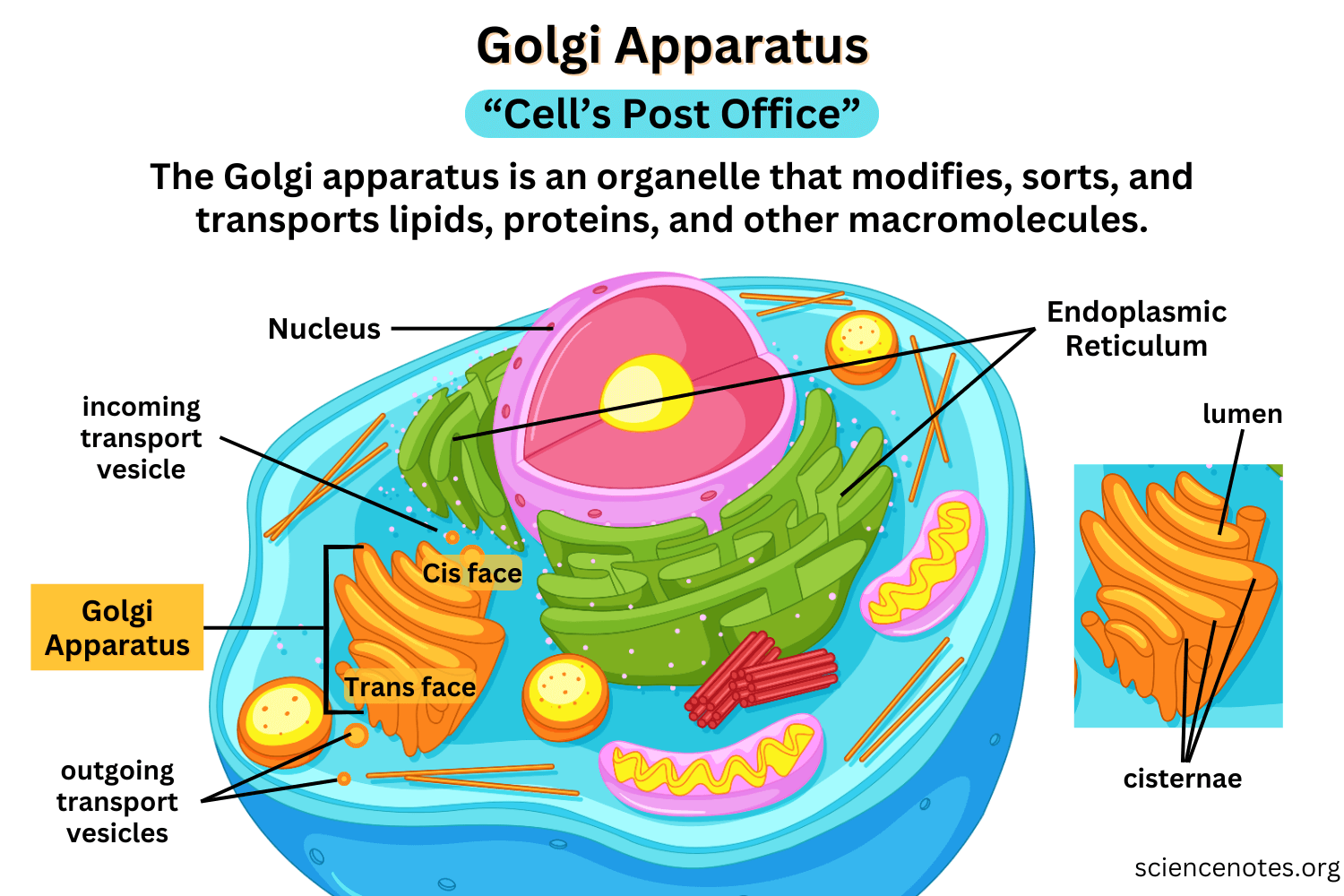
Lysosomes
Some of the vesicles formed by the Golgi apparatus are called lysosomes.
Are cell organelles containing proteins that break down the molecules that cells are made of into their individual chemical components. They may help to digest food particles.
Also are used to destroy potentially dangerous microorganisms such as bacteria and viruses.
When animal cells get old, the lysosomes break open and decompose the entire cell. This is called apoptosis, seen as the cell committing suicide.
Apoptosis
Process where lysosomes break open and decompose an entire cell, also known as cell suicide.
Cell Wall
An additional outer covering found only in plant cells.
Cell walls are firm yet porous.
Cell walls give plants their rigidity while allowing water in the soft materials to pass through.
Plastids
Free-floating membranous organelles found in the cytosol of plant cells.
Plastids are small structures inside plant cells (and some algae) that make and store important compounds like food and pigments.
There are different types of plastids, including:
Chloroplasts – for photosynthesis (contain green pigment chlorophyll)
Chromoplasts – for storing pigments like red, orange, yellow (in fruits and flowers)
Leucoplasts – for storing starch, oil, or proteins (in roots or seeds)
Chloroplast
A plastid containing chemicals necessary to perform photosynthesis.
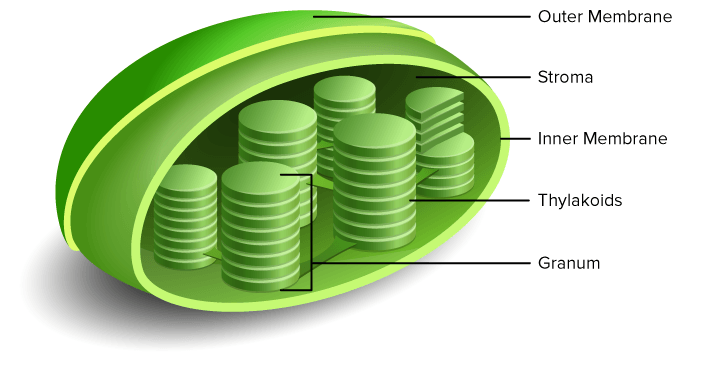
Thylakoid
A system of interconnected compartments inside the chloroplast.
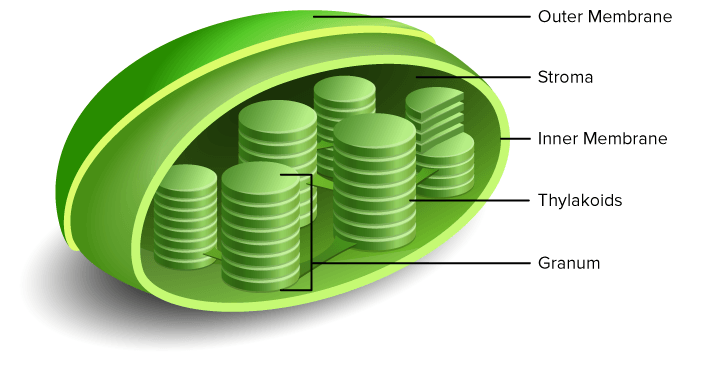
Grana
Thylakoids are usually stacked on top oof one another forming the structure called the grana
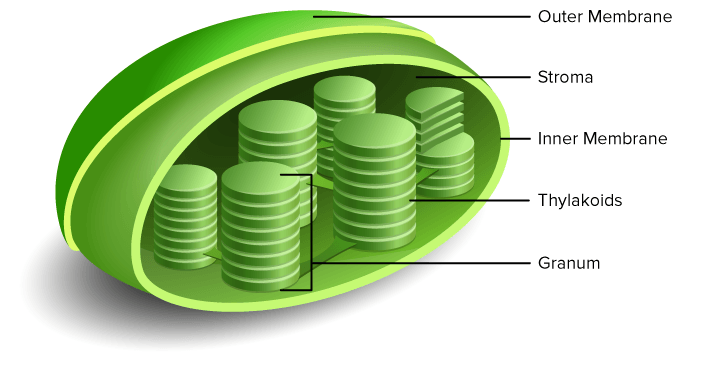
Chlorophyll
Green pigments found in the membranes of thylakoids responsible for the start of photosynthesis.
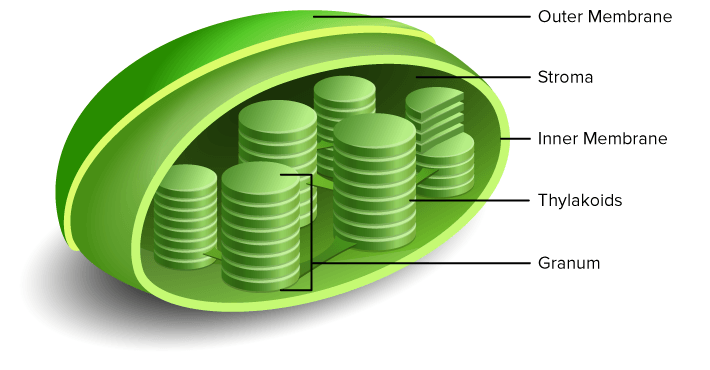
Stroma
The protein-rich fluid found in the space between the thylakoid membranes. Compounds needed for photosynthesis and DNA that allow chloroplast to reproduce are found here.
Plastid - Amyloplasts
White or colorless plastids that store the energy-rich products of photosynthesis in the form of starch.
Plastid - Chromoplasts
Colorful plastids containing red, orange, and yellow pigments.
Vacuoles
Large, membrane-bound sacs filled with a watery solution containing dissolved sugars, minerals, and proteins.
One or two large vacuoles help keep the cell membrane pressed firmly against the cell wall.
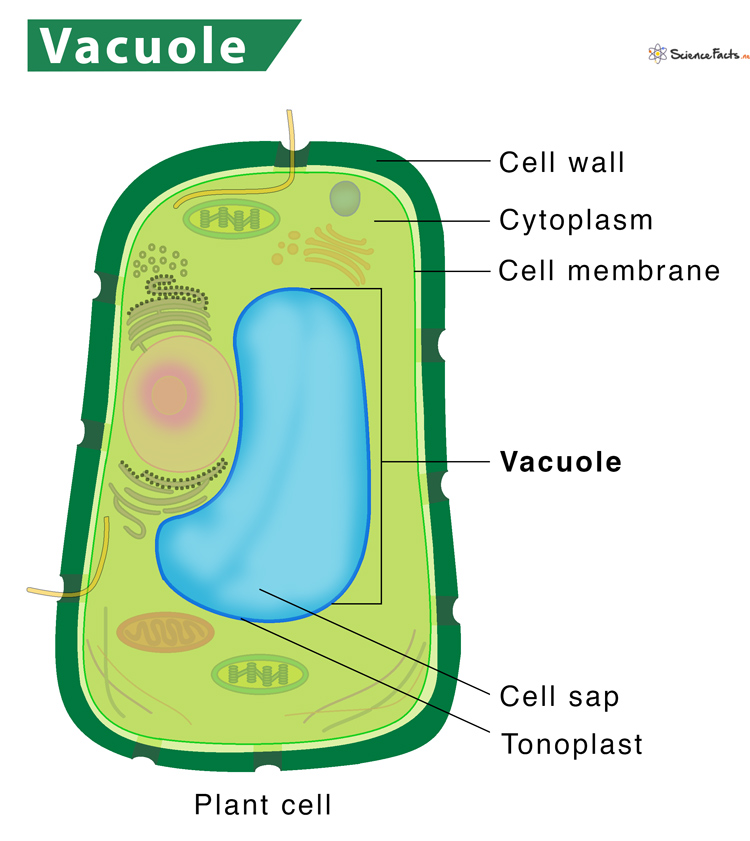
Turgor Pressure
Pressure that helps keep the cell membrane pressed firmly against the cell wall.
Putting Stem Cells to Work
Many medical experts believe that stem cells can be used to treat a variety of illnesses and injuries, including wound healing, bone regeneration, and disease such as cancer, heart disease, and Parkinson's disease.