ATP Synthase and ATP Yields
5.0(4)
Card Sorting
1/27
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 9:36 PM on 6/13/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
1
New cards
What is the proton motive force?
A combination of \[H+\] concentration gradient and electrical potential difference across IMS and Matrix
2
New cards
What does the F0 stalk of ATP Synthase do?
Acts as the motor by taking H+ via a subunit and sending it through the c ring
3
New cards
What AA exists on the C-ring that attaches protons to it?
Asp59
4
New cards
How many c subunits are in the c ring?
10
5
New cards
What are the subunits of the F1 portion of ATP synthase?
hexamer of α and β subunits, with γ subunit in the middle
6
New cards
What are the possible confirmations of the α and β subunits? Which way is the γ subunit turning in normal ATP synthesis?
Clockwise movement (O→L→T)
O: ADP + Pi bond (ATP released)
L: ADP + Pi locked
T: ATP formed
O: ADP + Pi bond (ATP released)
L: ADP + Pi locked
T: ATP formed
7
New cards
How much ATP does one full turn of ATP synthase form?
3 ATP
8
New cards
Which UCLA professor found the rotational ATP synthase model?
Paul Boyer
9
New cards
Do you know what the reaction coordinate diagram of ATP Synthase looks like?
This
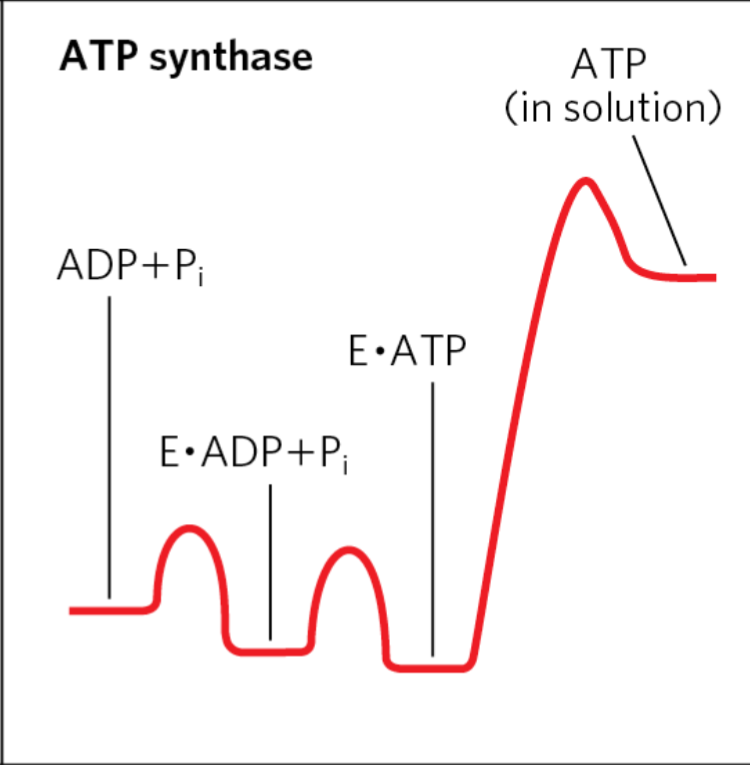
10
New cards
How does ADP get to the mitrochondrial matrix?
Adenine Nucleotide Translocase transport 1 ATP into IMS and 1 ADP into matrix at the same time
11
New cards
How does inorganic Phosphate (Pi) transported into the matrix?
Phosphate Translocase Symporter transports 1 Pi in and 1 H+ out. It can also symport 3H+ for 1 ADP.
12
New cards
What 3 compounds form the ATP-synthasome complex?
ATP synthase, Adenine nucleotide translocase, and phosphate translocase
13
New cards
The ETC and TCA are said to be _____ coupled
Obligately
14
New cards
What does adding ADP + Pi do to ATP synthesis
Nothing
15
New cards
What does adding Succinate do to ATP synthesis?
ETC activate, increasing ATP synthesis
16
New cards
What does adding CN- do to ATP Synthesis?
ETC blocked, ATP synthe halts
17
New cards
What uncouplers can uncouple ETC from ATP Synthesis?
2,4 DNP and FCCP
18
New cards
What do uncouplers do?
Move H+ without the need for e-’s; destroys proton gradient
19
New cards
What do malate and aspartate do in the malate aspartate shuttle?
Transfer e-’s
20
New cards
How does NADH get into the mitochondrial matrix from the IMS?
The Malate-Aspartate shuttle and the G3P Shuttle
21
New cards
What does glutarate and a-ketoglutarate do in the malate-aspartate shuttle?
Amino group donors/acceptors
22
New cards
How much ATP does the Malate-Aspartate shuttle yield compared to the G3P Shuttle?
2\.5 ATP compared to 1.5 ATP
23
New cards
Does the G3P shuttle need transporters?
No
24
New cards
Why does the G3P Shuttle produce less ATP than the Malate-Aspartate Shuttle?
It bypasses Complex I (misses out on proton pumping here)
25
New cards
What happens if no O2 is present?
Proton motive force collapses, stopping or reversing ATP synthase
26
New cards
If ATP Synthased is reversed (clockwise), what happens to ATP?
It is depleted by ATP Synthase
27
New cards
What genes are activated in hypoxic conditions that help with hypoxia? What do they do?
IF1 → binds ATP synthase dimers and stops reversal
HIF1 → Removes reactive Oxygen species by stopping PDH and replaced Subunit IV’s COX4-1 with COX4-2, which is better suited for low O2 concentrations
HIF1 → Removes reactive Oxygen species by stopping PDH and replaced Subunit IV’s COX4-1 with COX4-2, which is better suited for low O2 concentrations
28
New cards
What is the total ATP yield?
30-32 ATP depending on which shuttle is used to bring NADH to ETC