A&P Peripheral Nervous System
1/120
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
121 Terms
Efferent
Motor information from brain → Periphery
Afferent
Sensory information from periphery → brain
Autonomic nervous system
Involuntary nervous system
Regulates smooth muscles, cardiac, and glands
Separated into sympathetic and parasympathetic
Neurotransmitters for the autonomic NS
Acetylcholine, epinephrine, and norepinephrine
Type of action of autonomic NS
Excitatory or inhibitory
Autonomic NS is controlled by…
Homeostatic centers in the brain (Pons, hypothalamus, medulla oblongata)
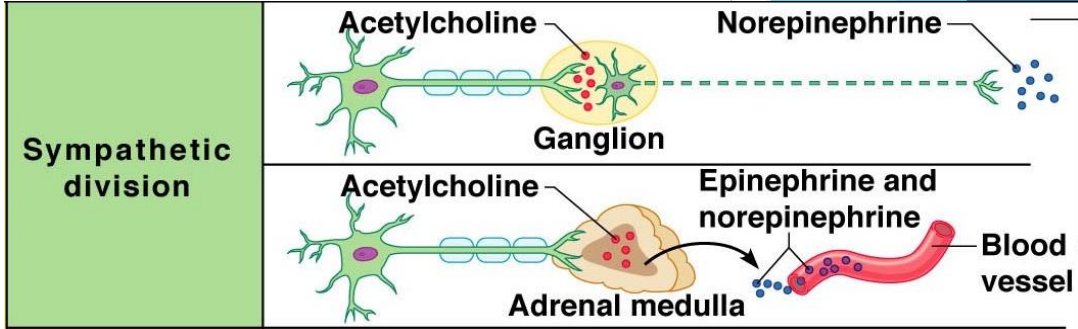
Nerves of the sympathetic NS
Short pre-ganglionic neuron and long post-ganglionic neuron
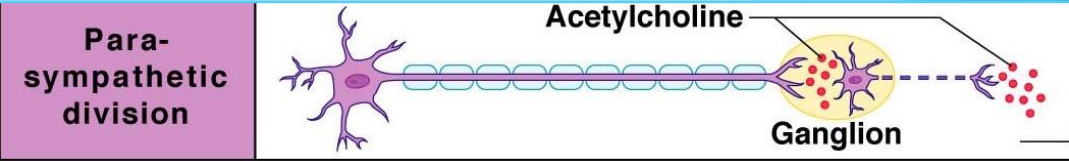
Nerves of the parasympathetic NS
Long, heavily myelinated, pre-ganglionic neuron and short post-ganglionic neuron
Neurotransmitters of somatic NS
Only acetylcholine
Action of somatic NS
Always excitatory
Somatic NS is controlled by…
The cerebrum
Sympathetic
Response to unusual stimulus
Takes over to increase activities
Exercise, Excitement, Emergency, and Embarrassment (E division)
Parasympathetic
House keeping activities
Conserves energy
Maintains body functions
Digestion, Defecation, Diuresis (D division)
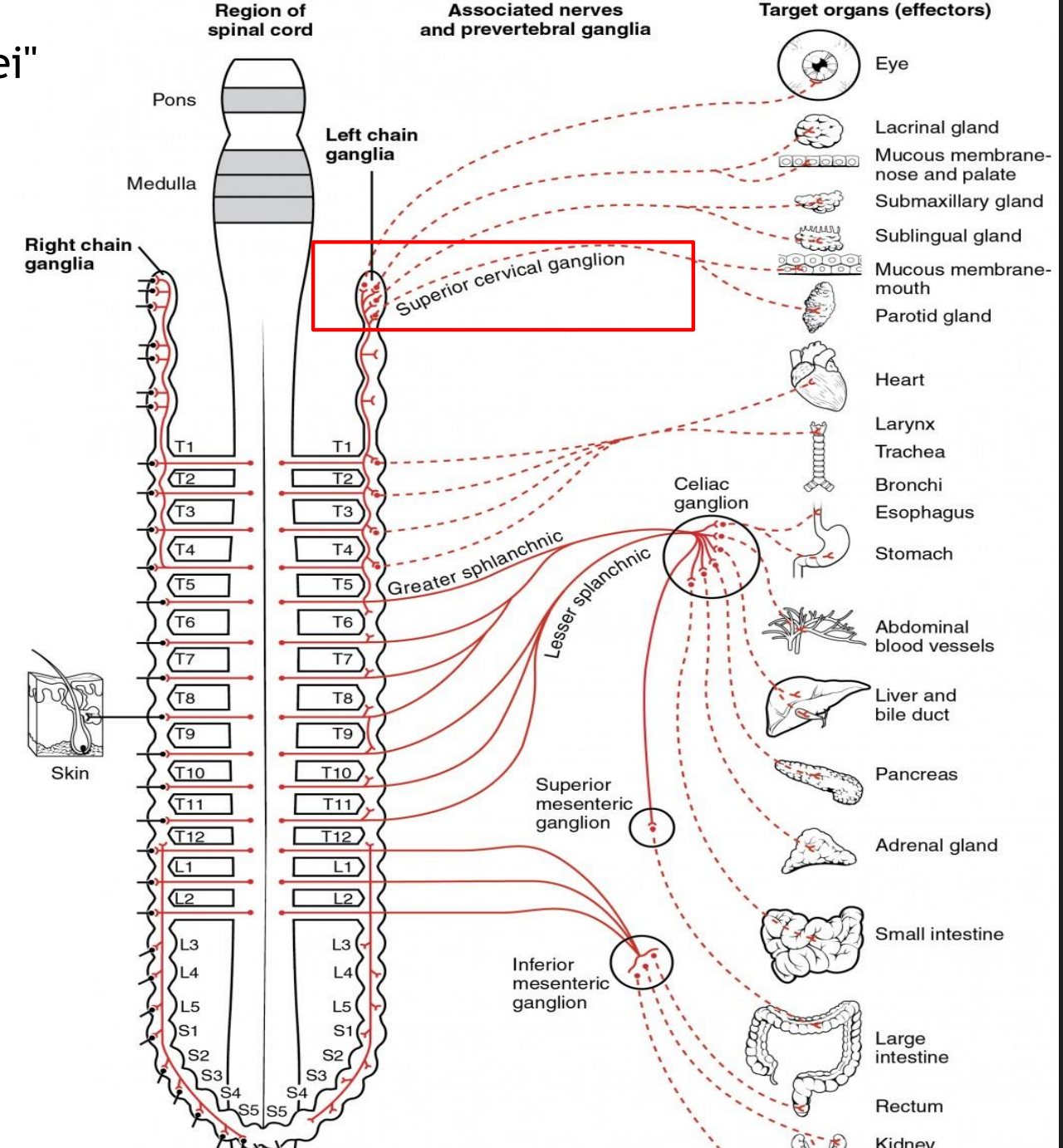
Sympathetic nerves originate from which vertebrae?
T1 through L2
The ganglia synapse located near the spinal cord
Parasympathetic nerves originate from which vertebrae?
The brainstem and S1 through S4
The ganglia synapse located near the targeted organ
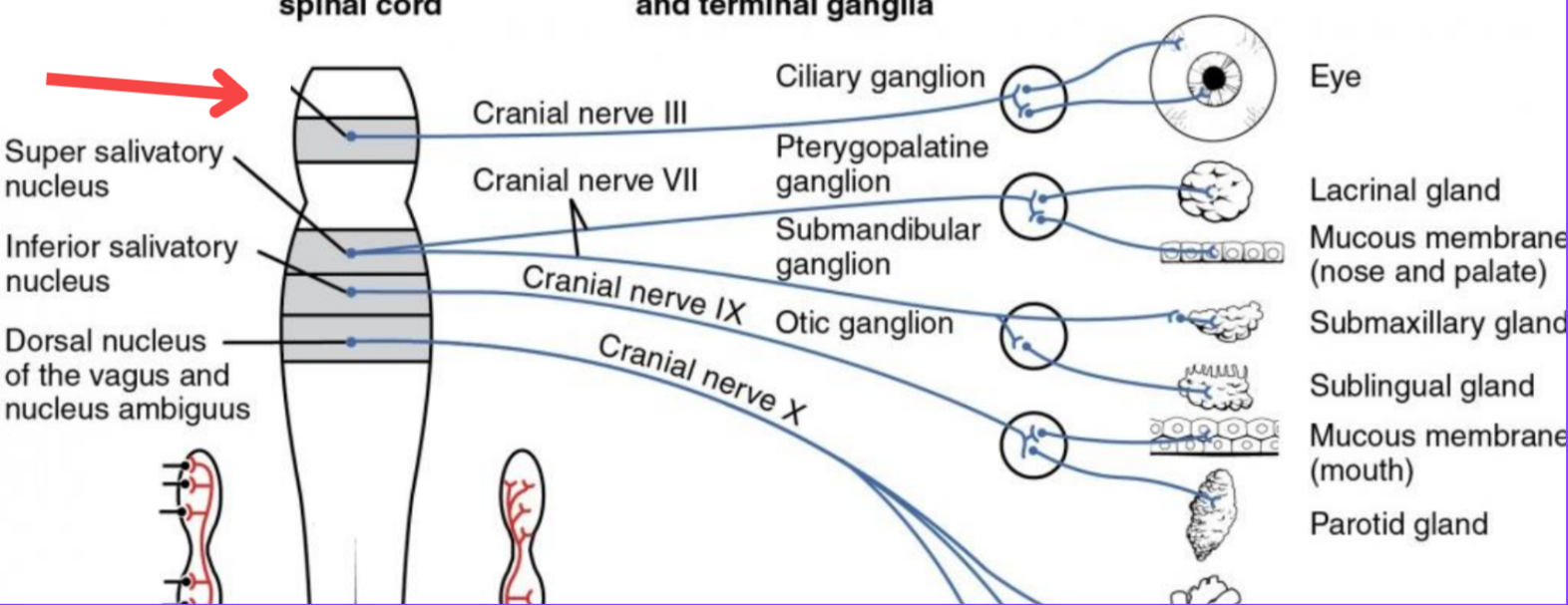
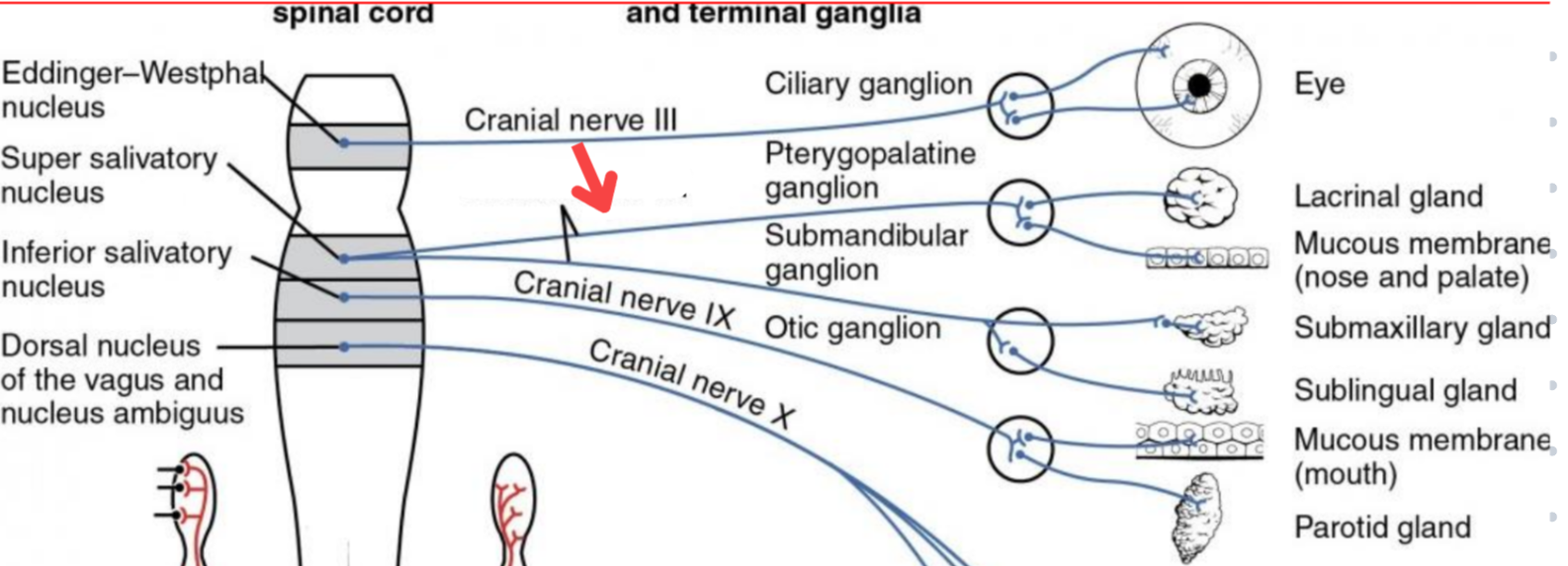
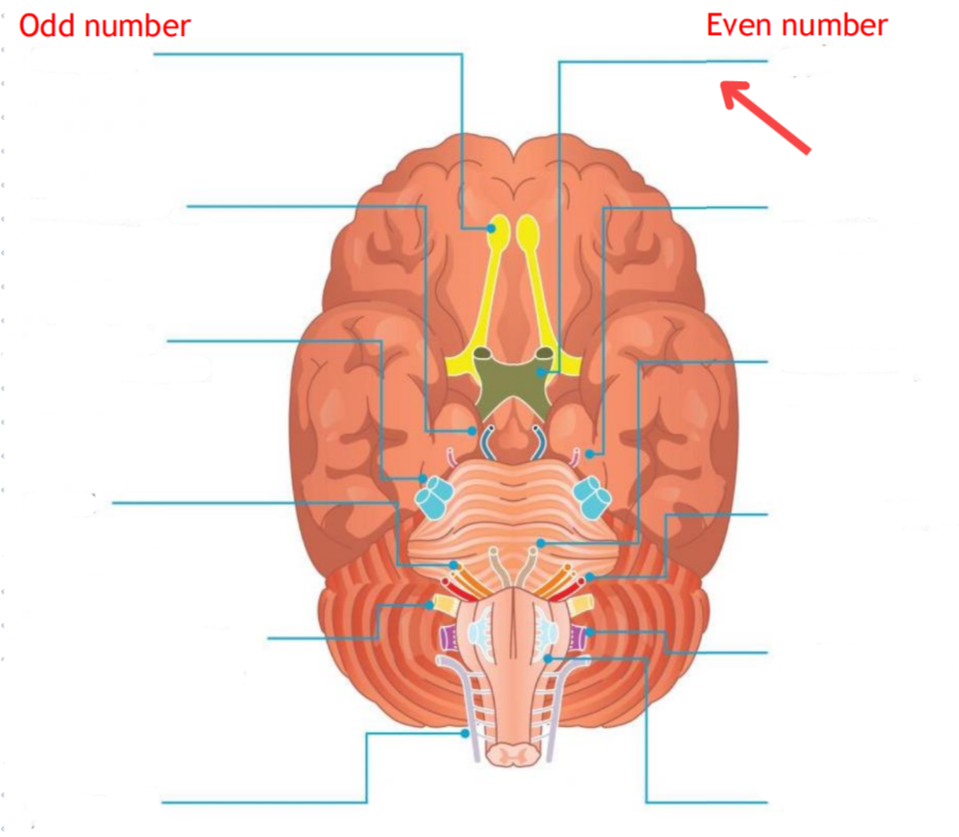
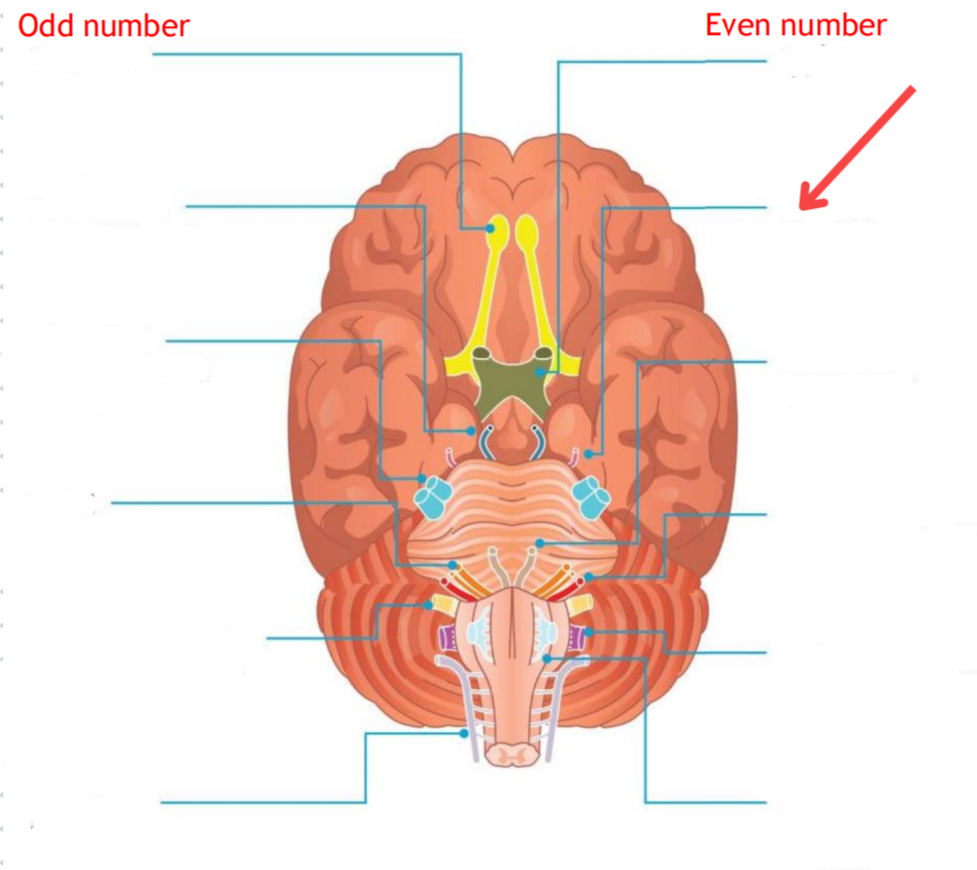
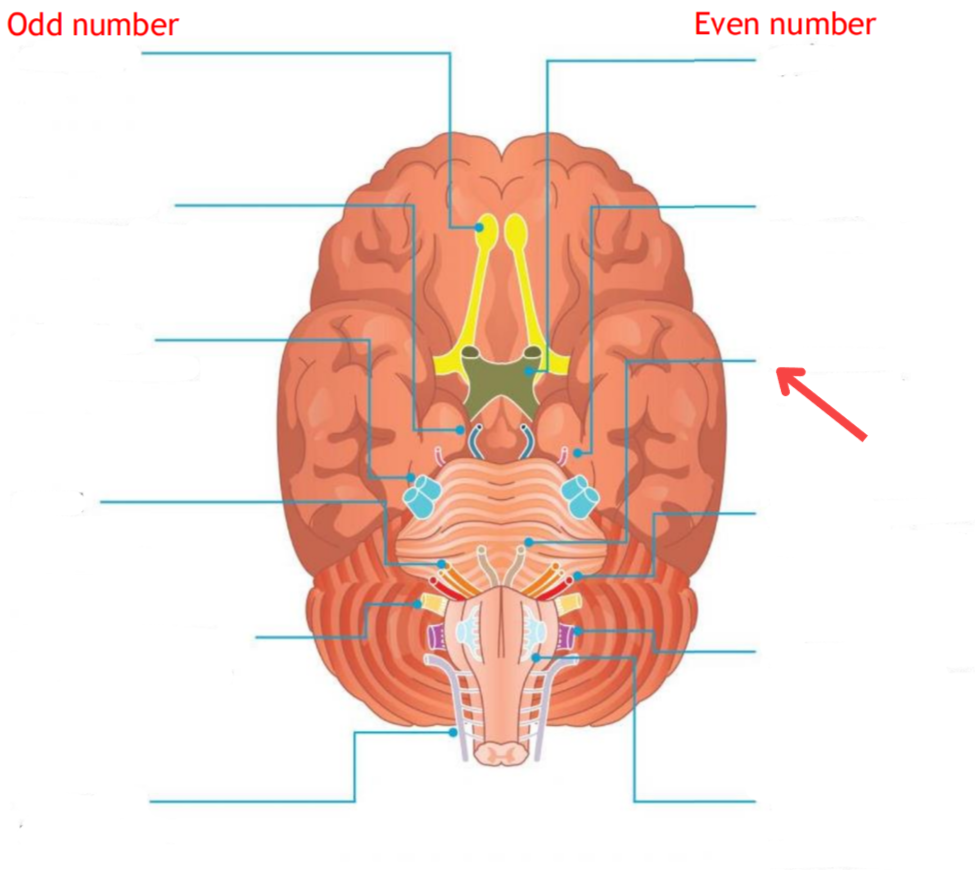
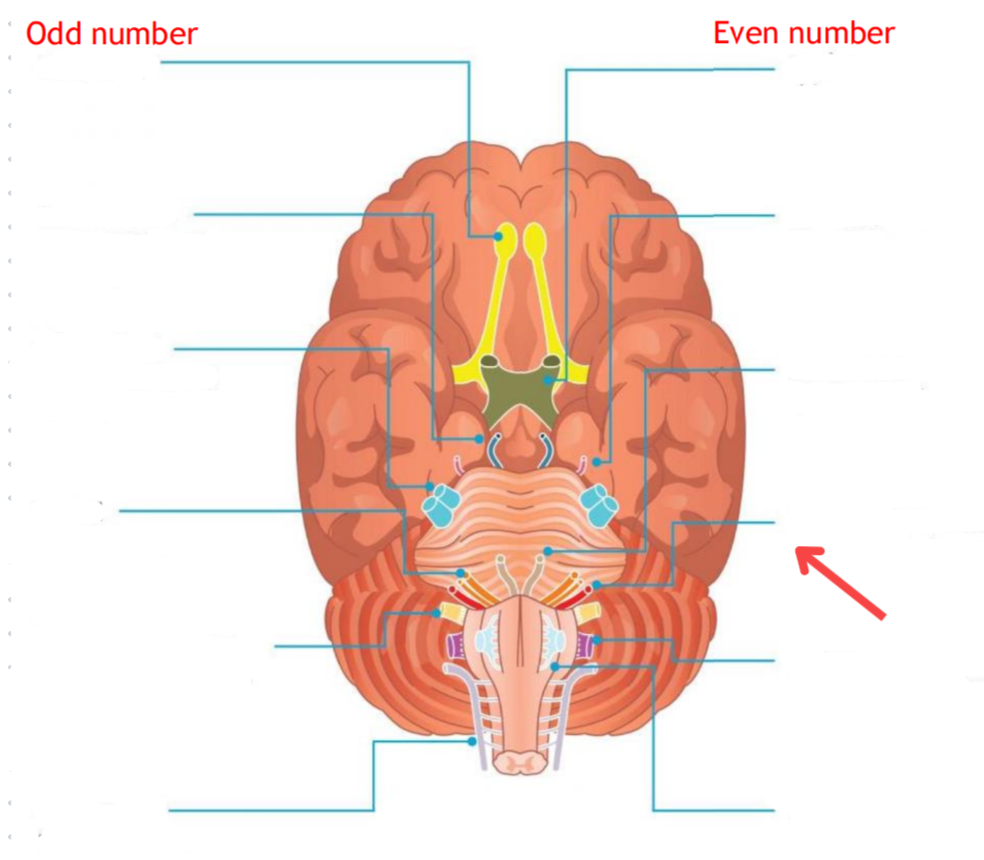
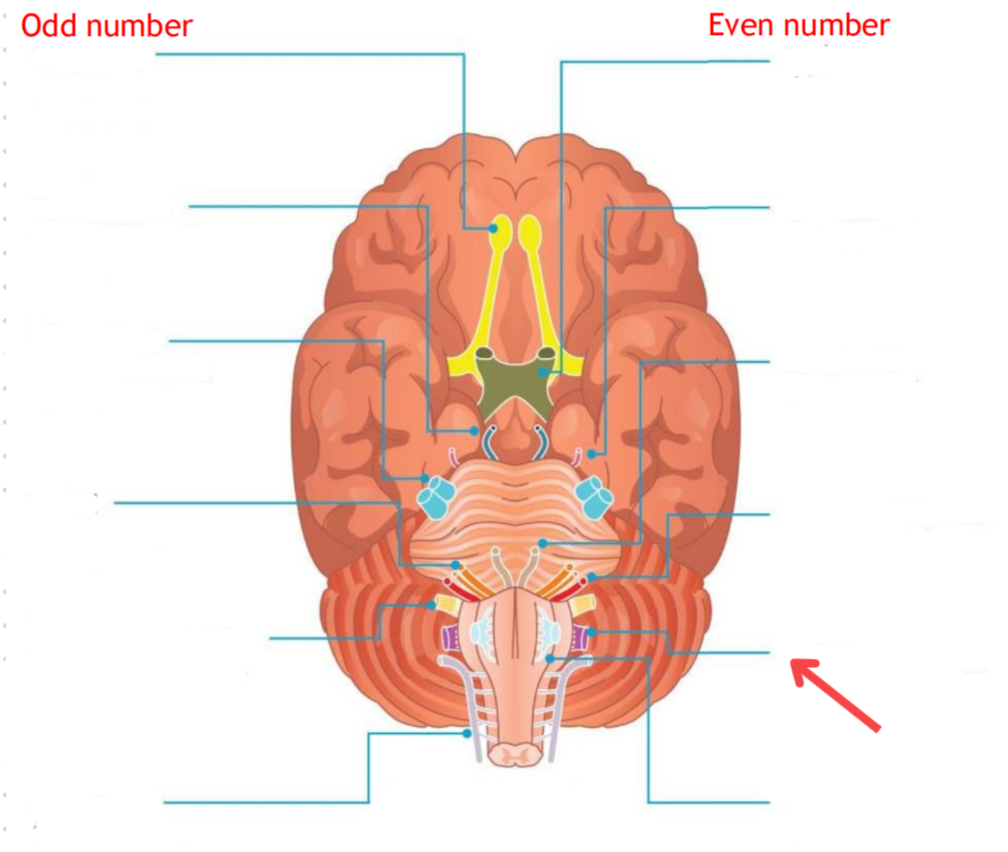
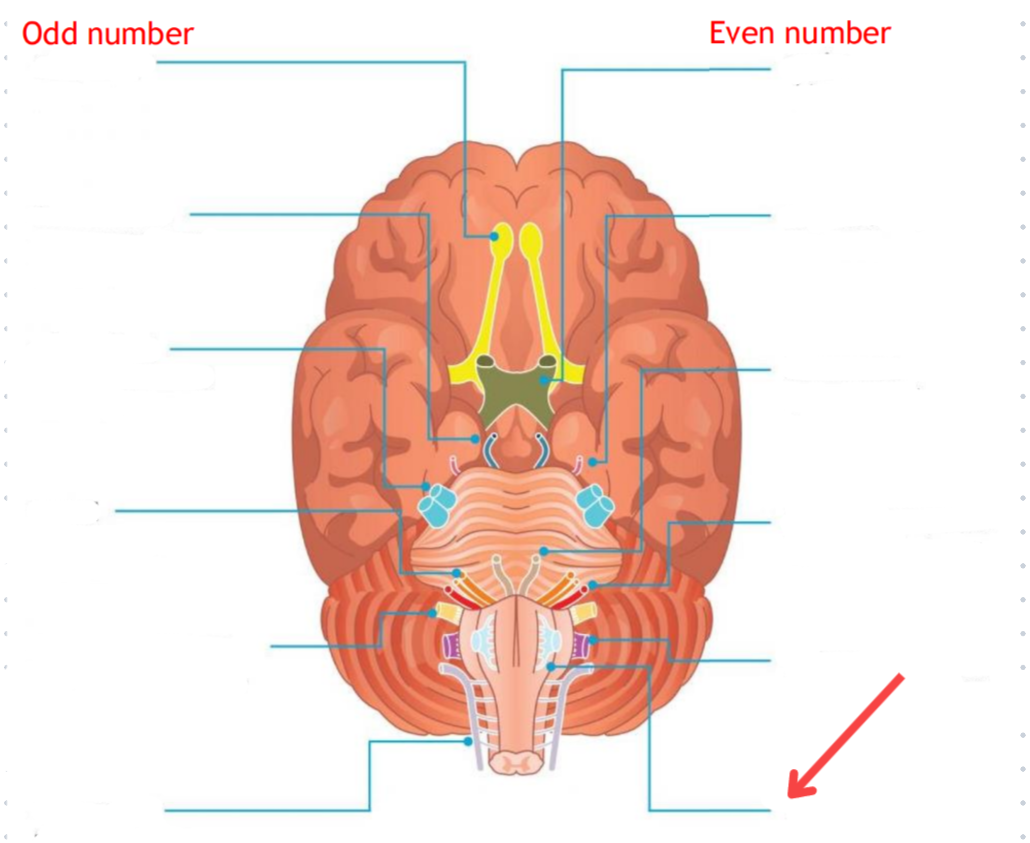
Eddinger-Westphal nucleus (Paraympathetic)
Part of the oculomotor complex
Cranial nerve III is attached, innervates the extraocular muscles
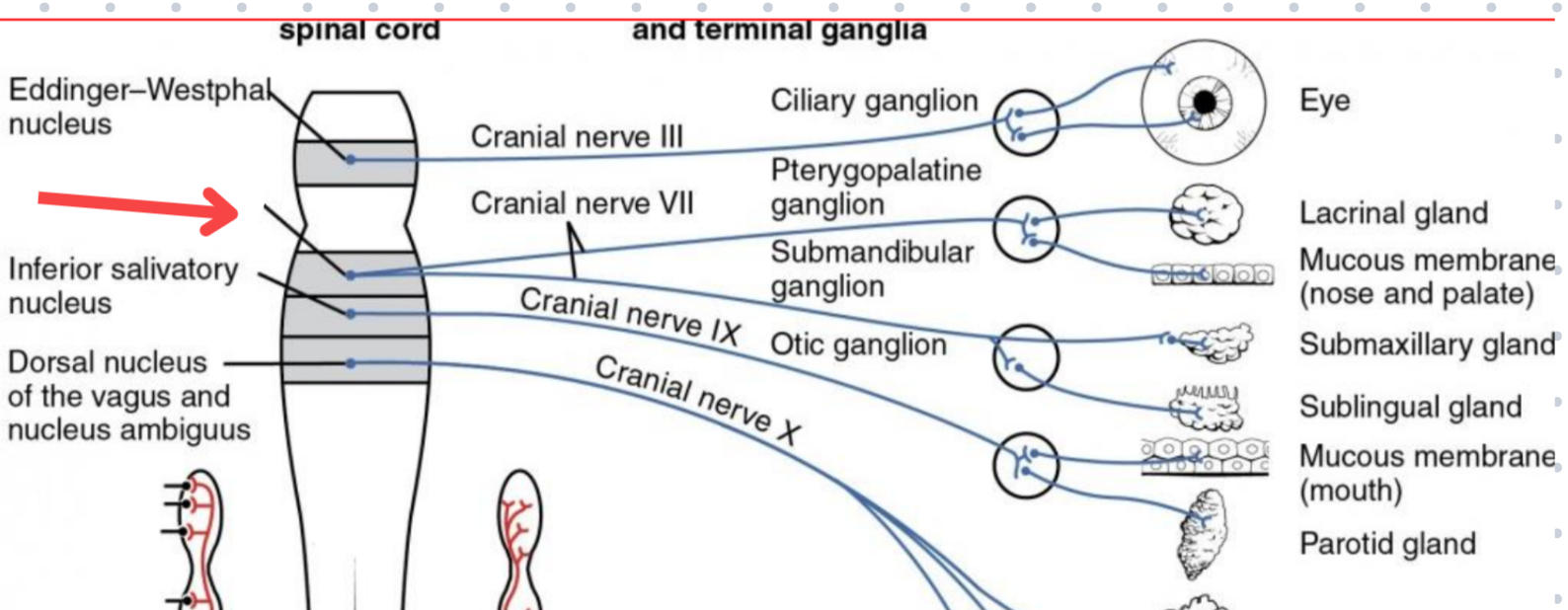
Super salivatory nucleus (Paraympathetic)
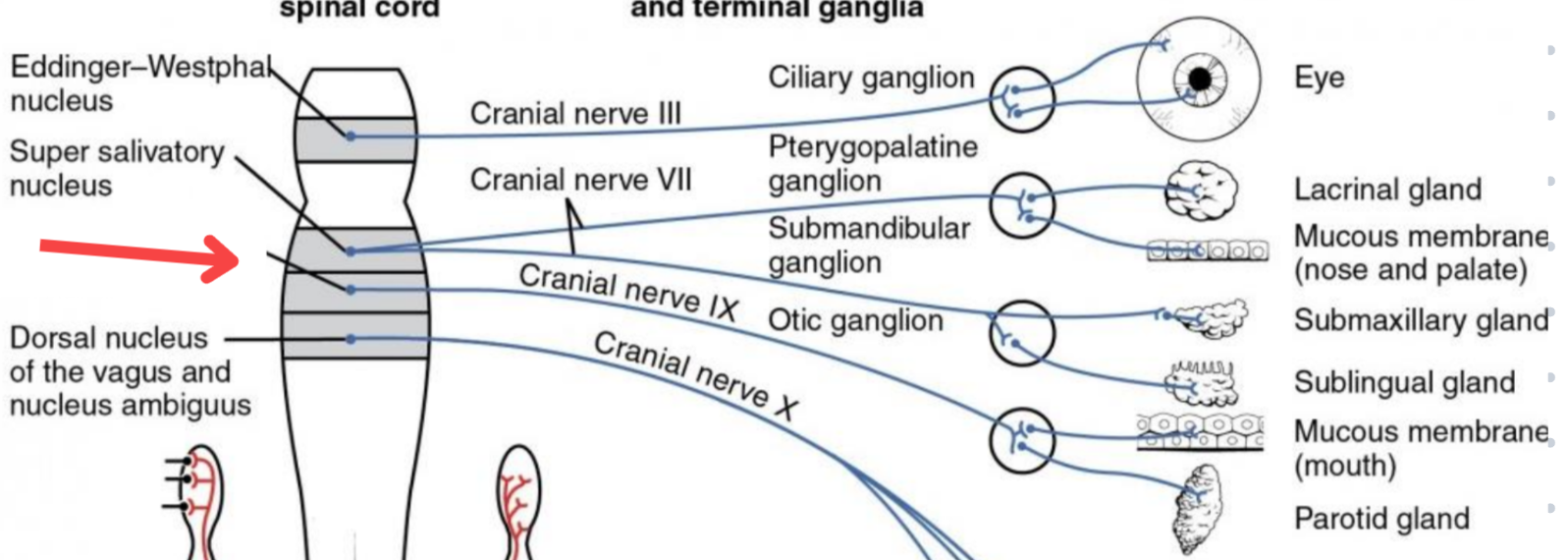
Inferior salivatory nucleus (Paraympathetic)
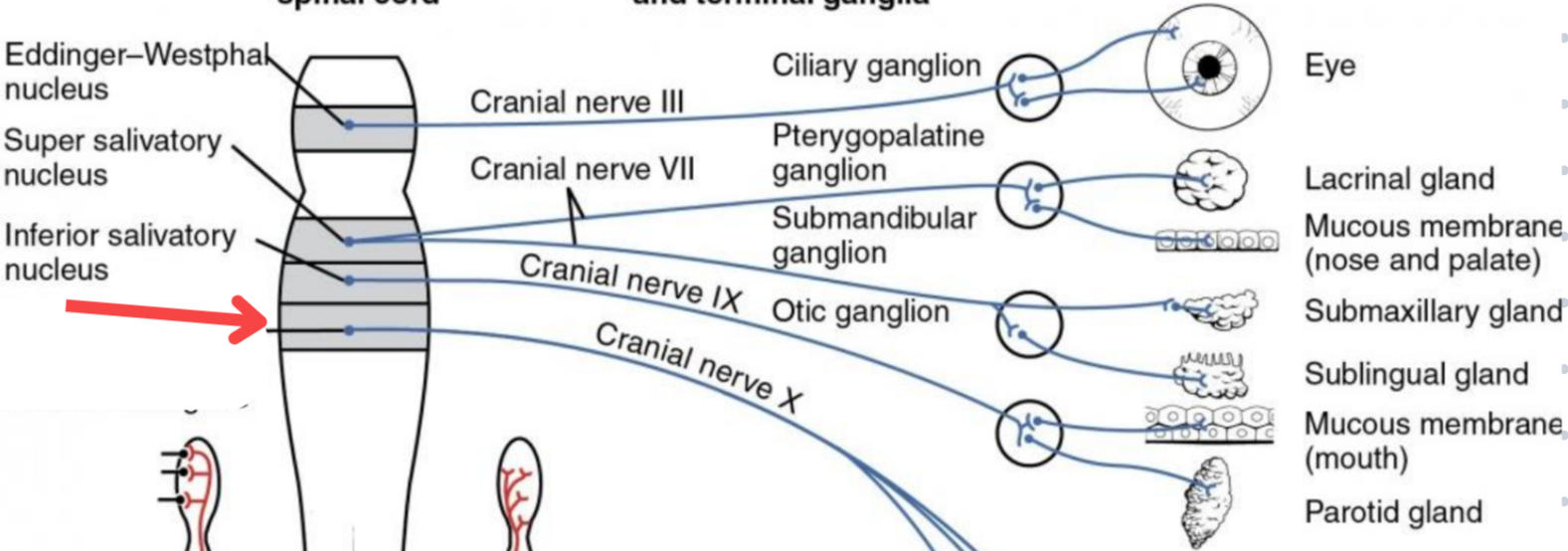
Dorsal nucleus of the vagus (Paraympathetic)
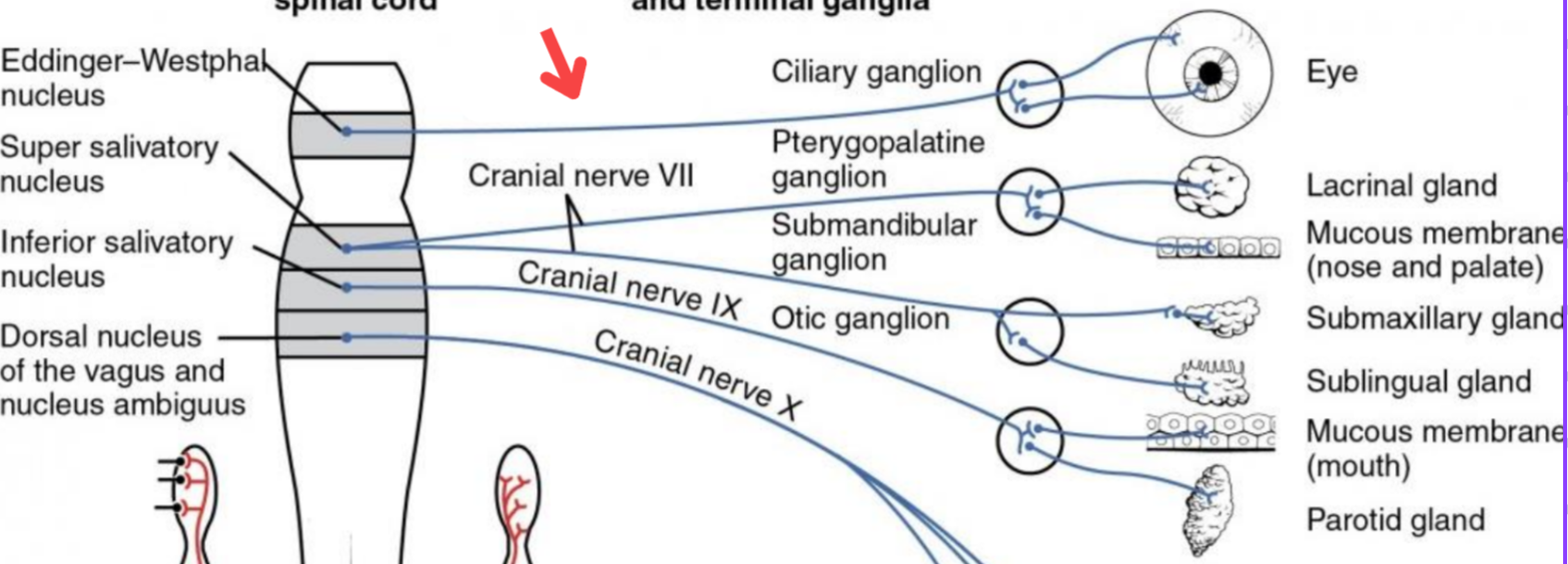
Cranial nerve III
Cranial nerve VII
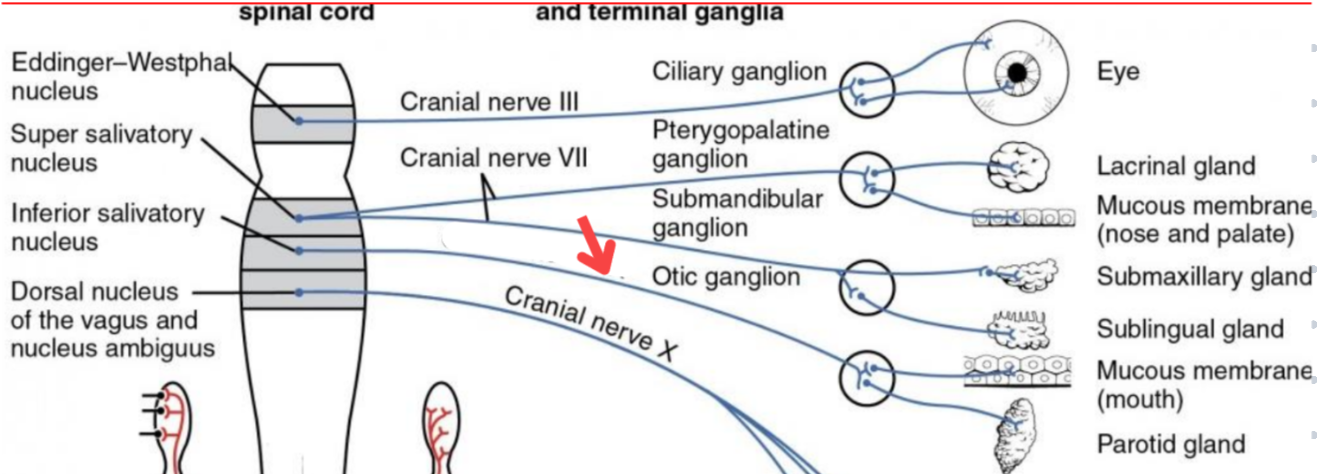
Cranial nerve XI
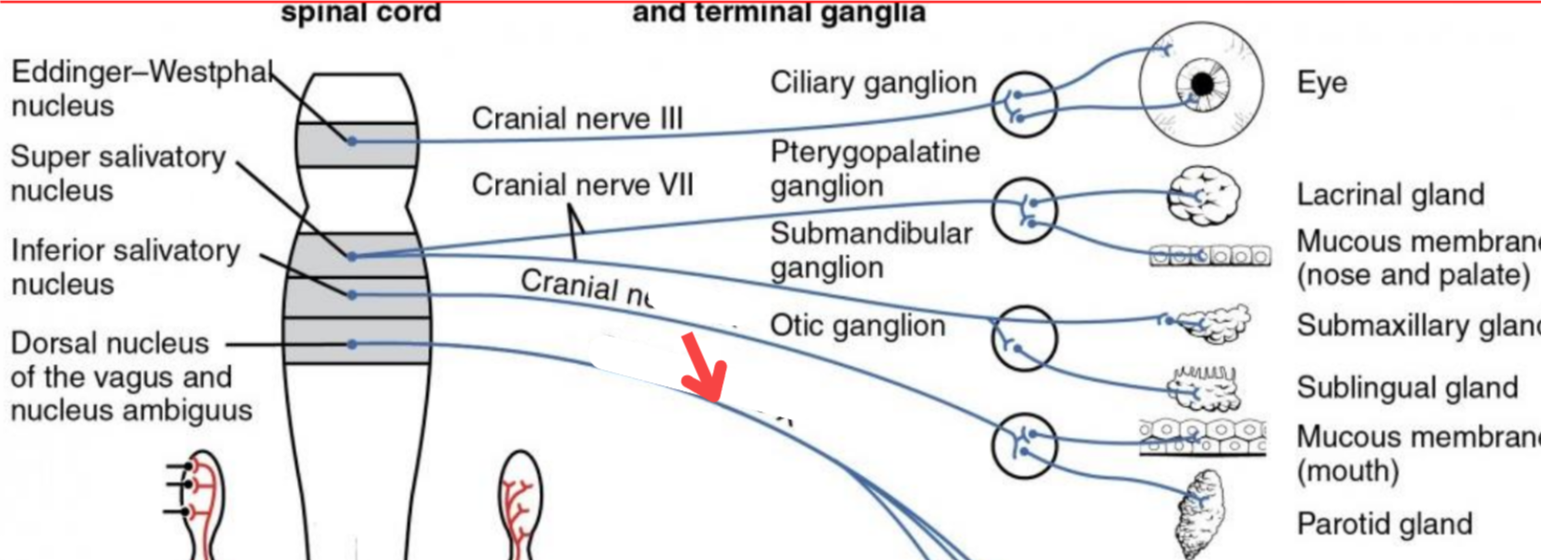
Cranial nerve X
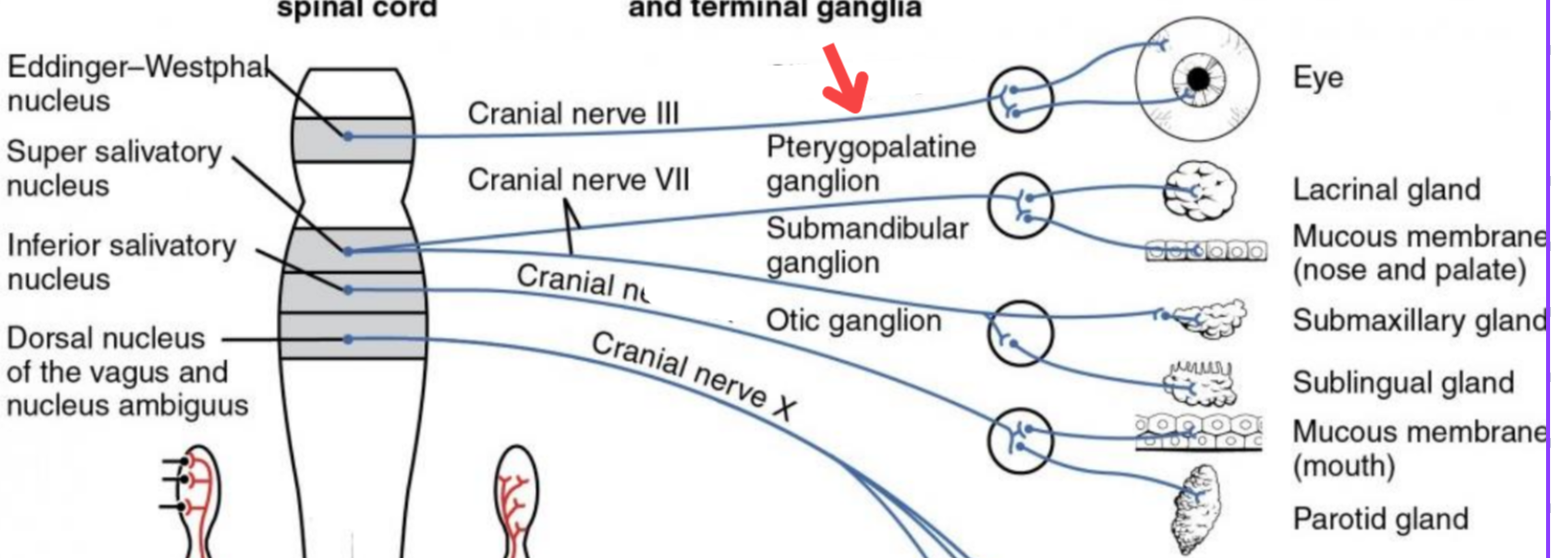
Cilliary ganglion
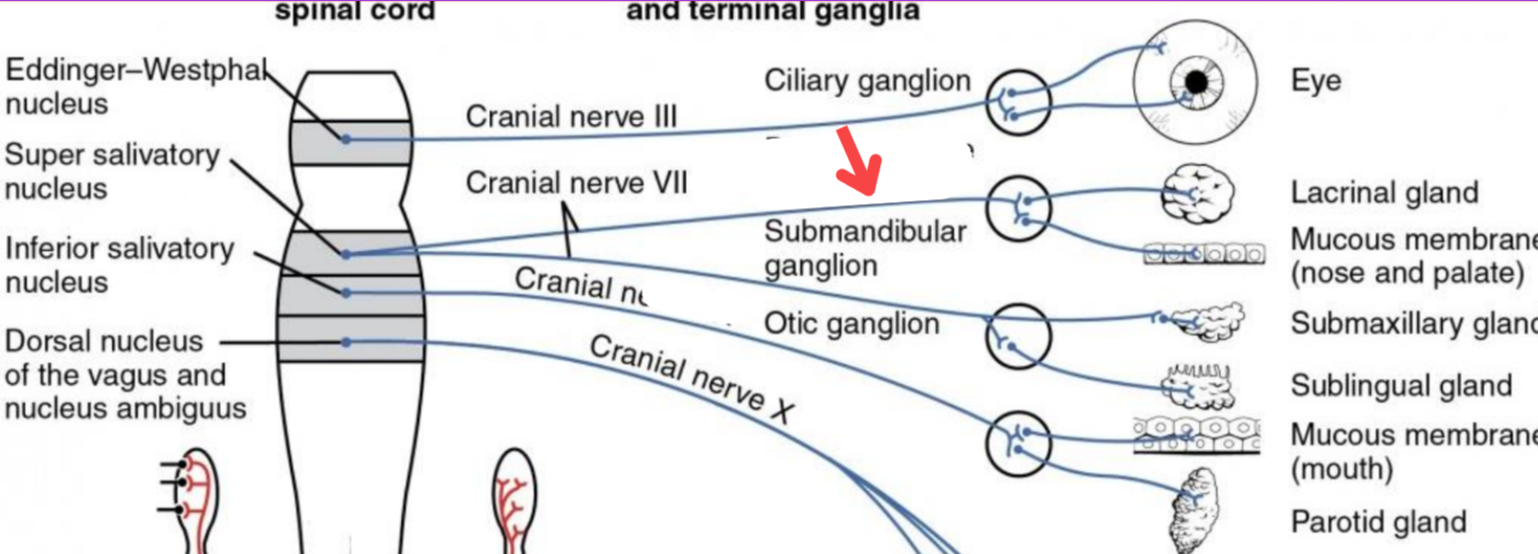
Pterogopalatine ganglion
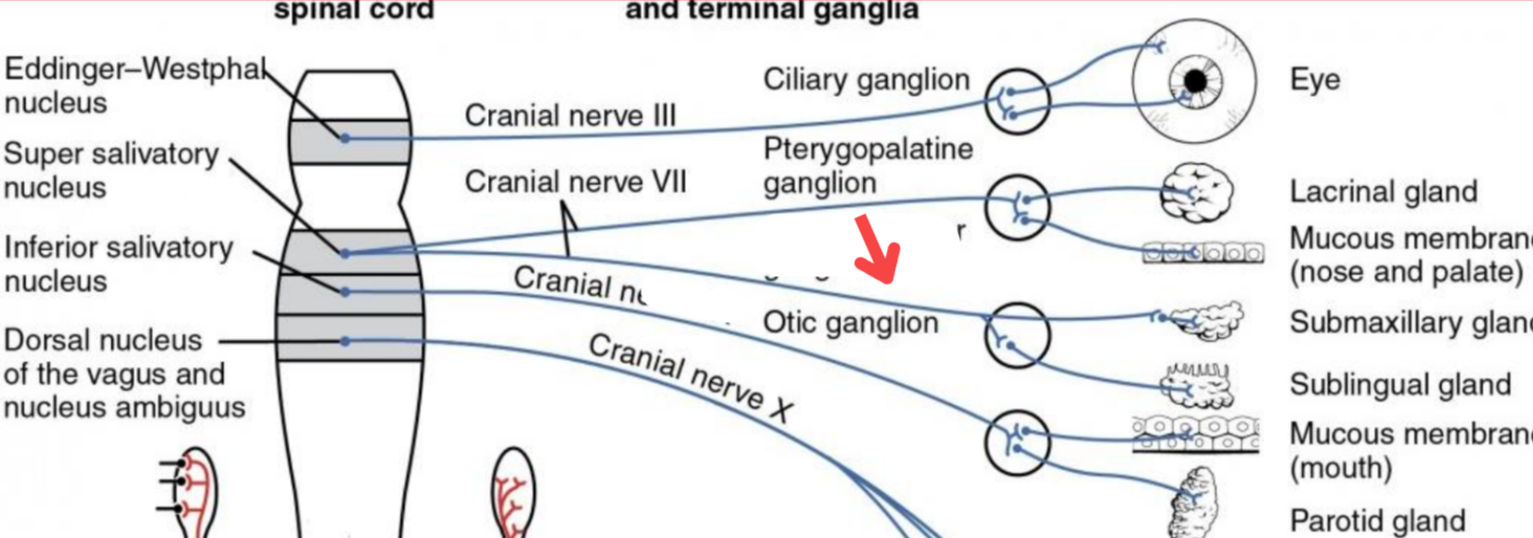
Submandibular ganglion
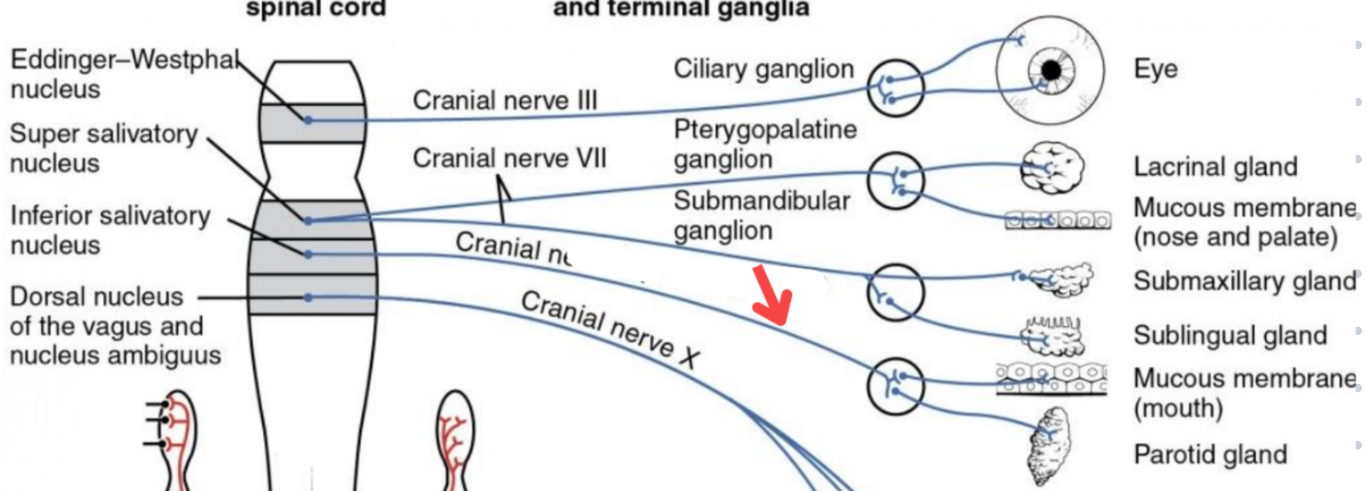
Otic ganglion
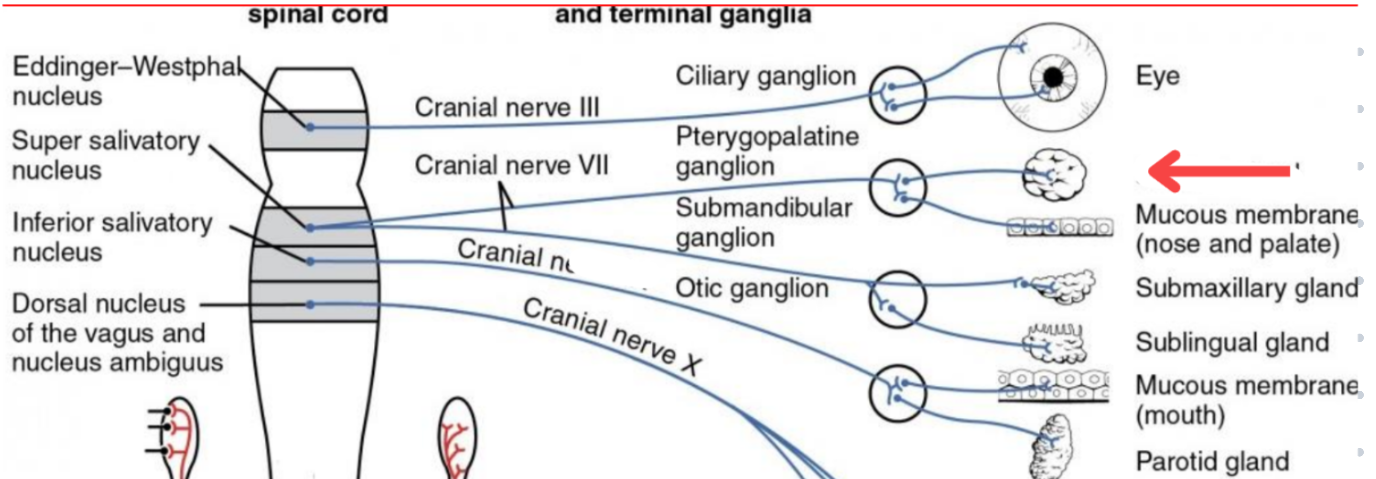
Lacrimal gland
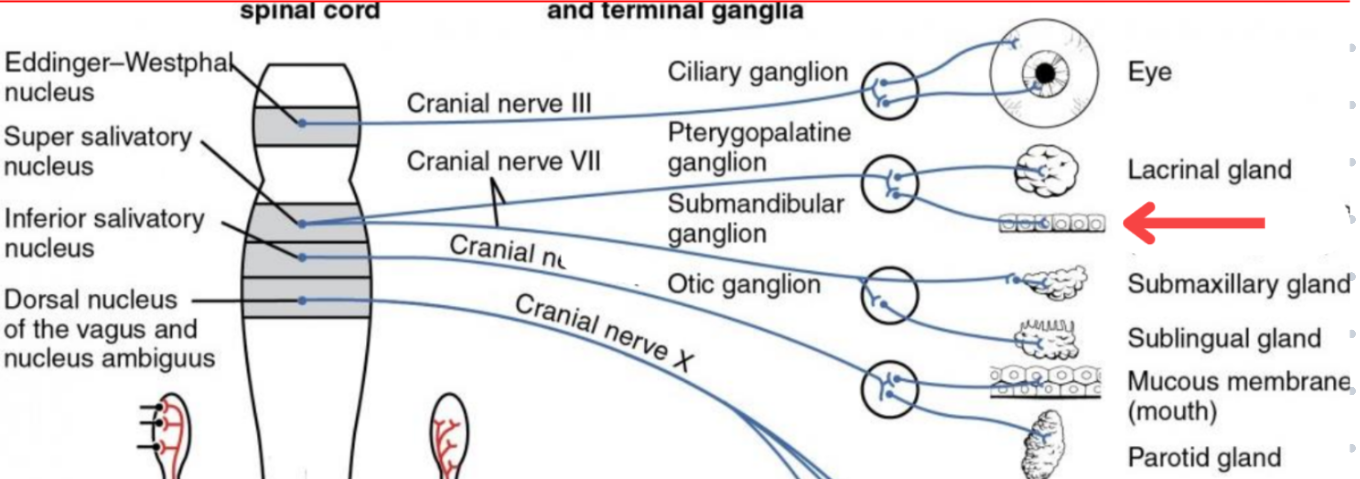
Mucous membrane (Nose and palate)
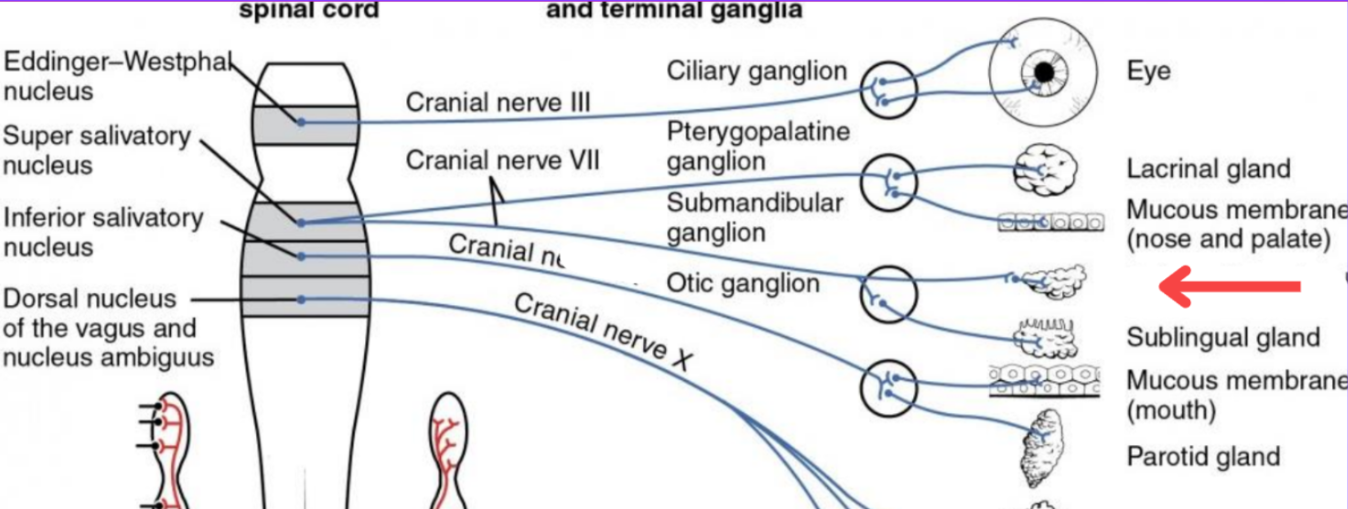
Sublmaxillary gland
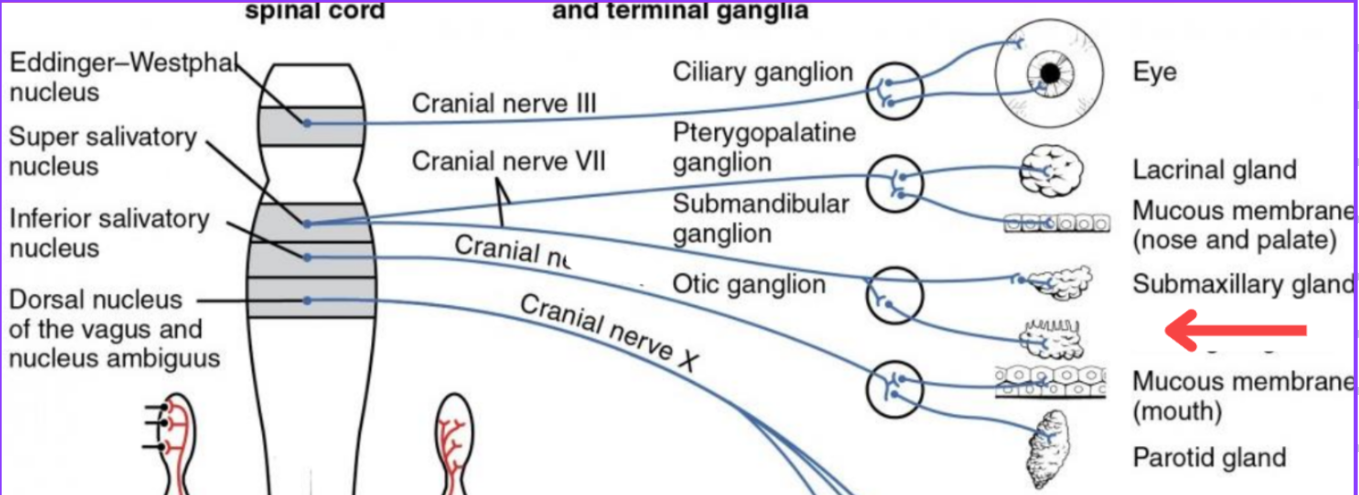
Sublingual gland
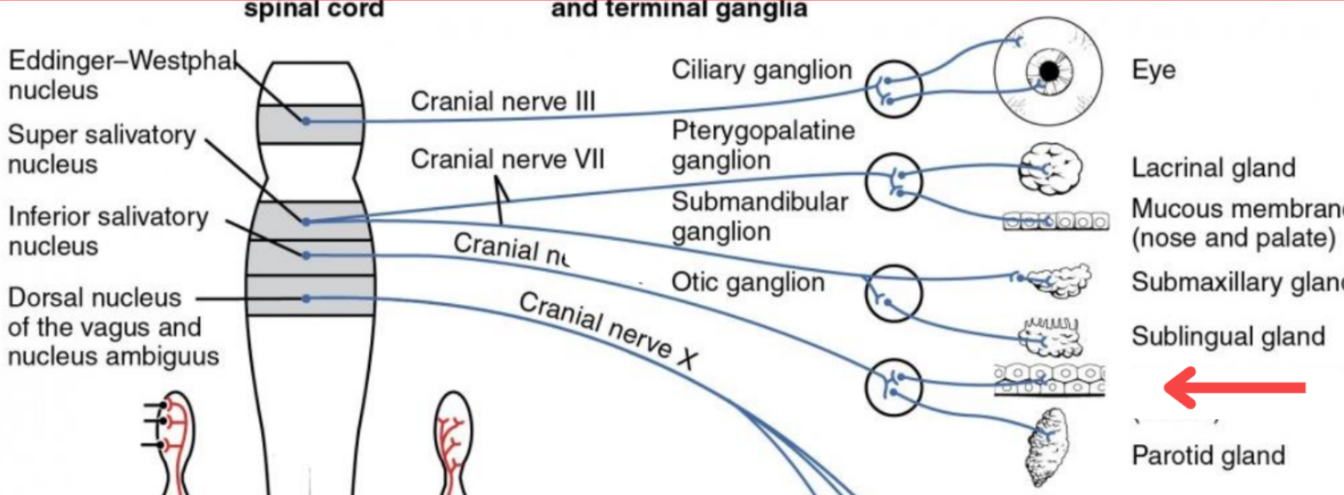
Mucous membrane (Mouth)
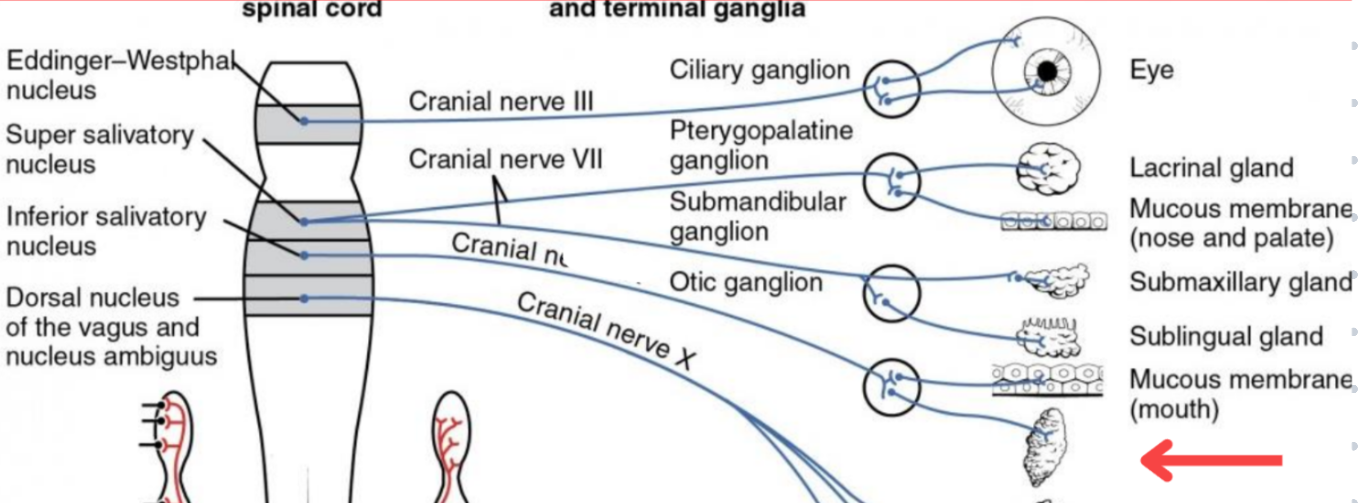
Parotid gland
Superior cervical ganglion
Main sympathetic ganglion associated with the eye
Innervates the dilator pupilae muscle
Influences blood vessels and sweat glands around the eye/forehead
Regulates vasoconstriction of the lacrimal gland
Mnemonic to remember the order of the cranial nerves
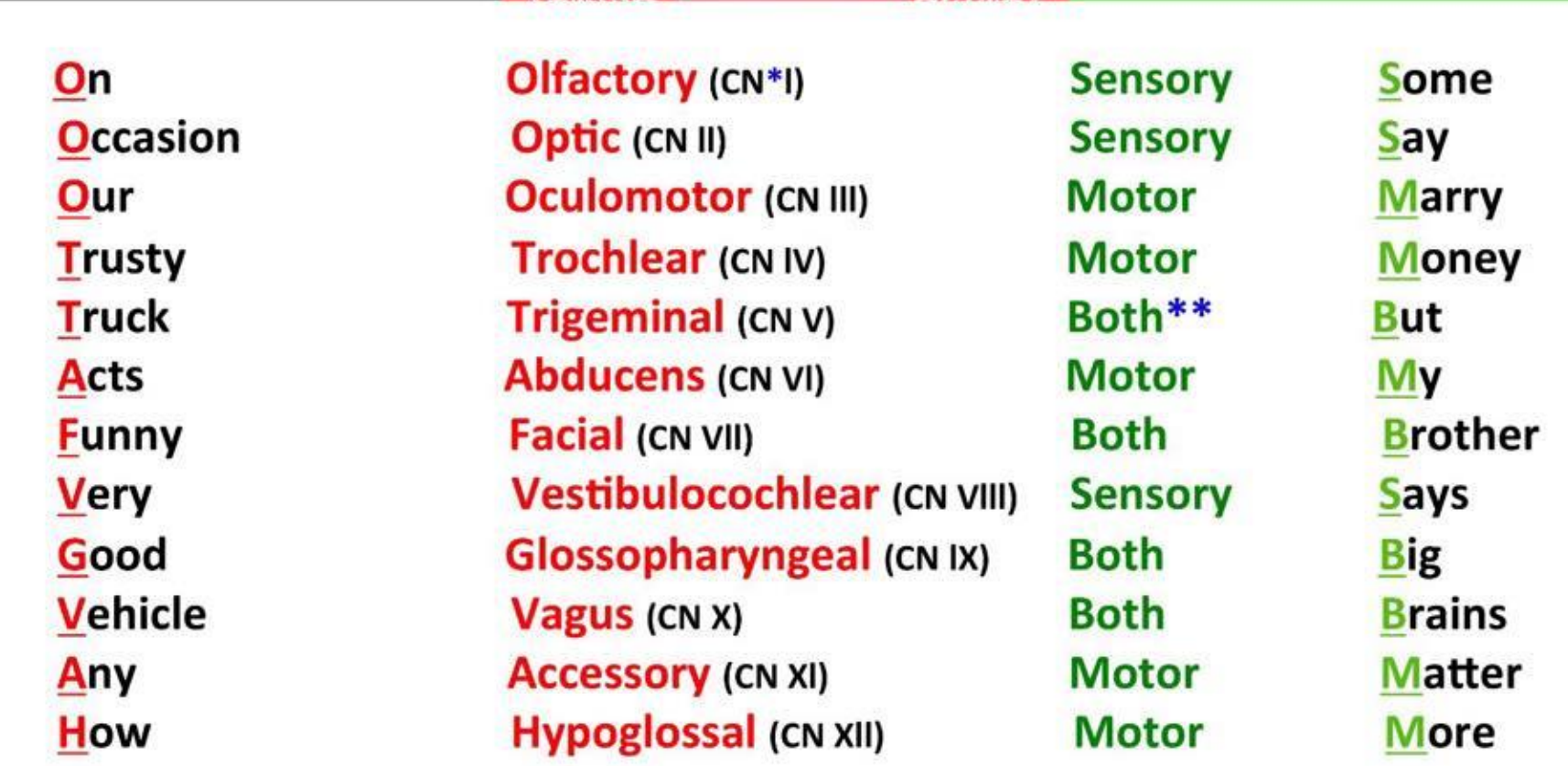
Olfactory nerve
Oculomotor nerve
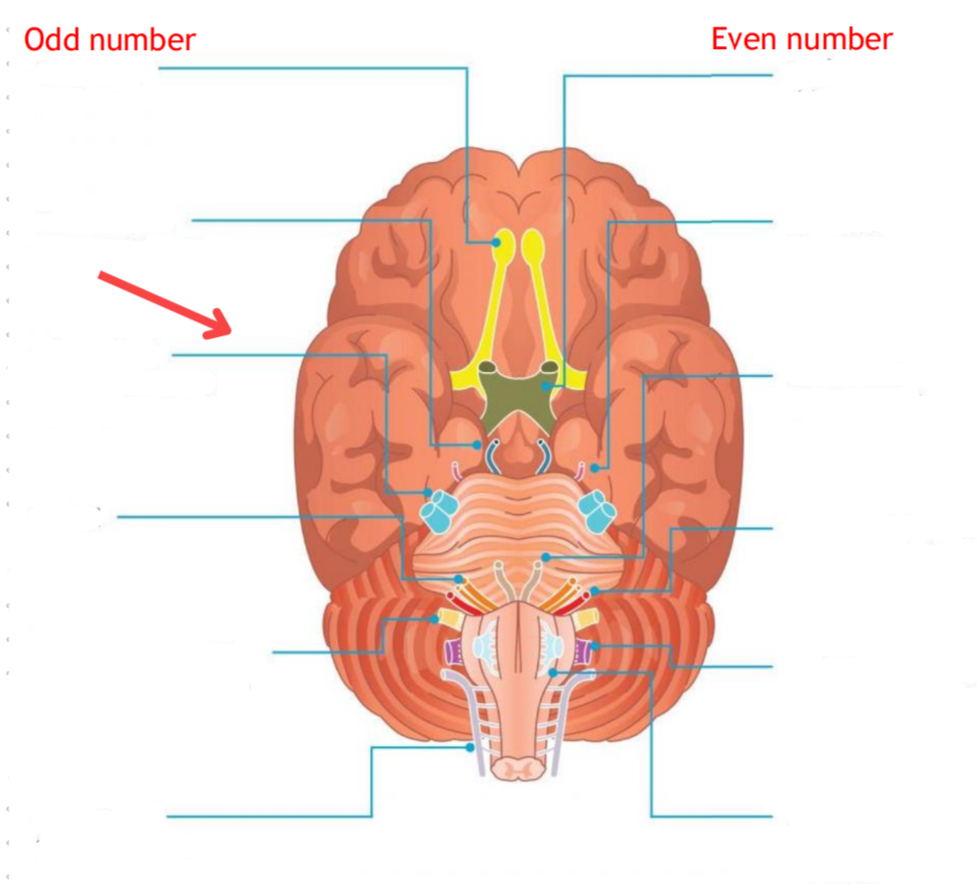
Trigeminal nerve
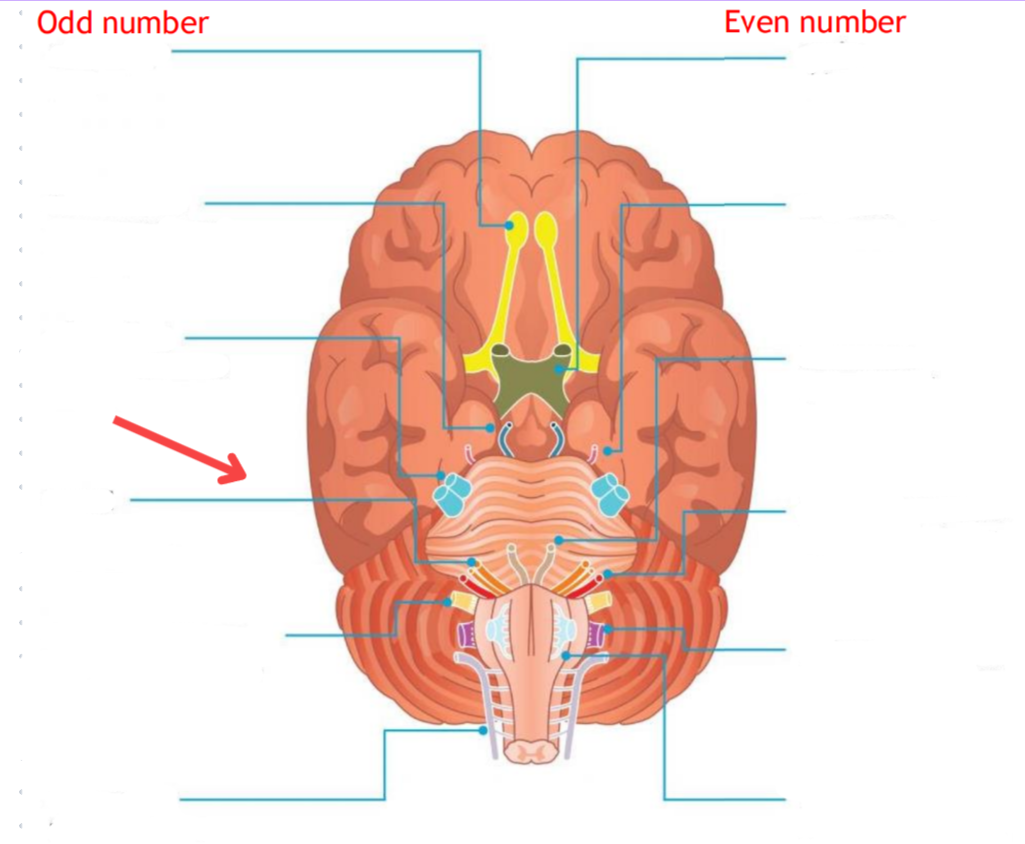
Facial nerve
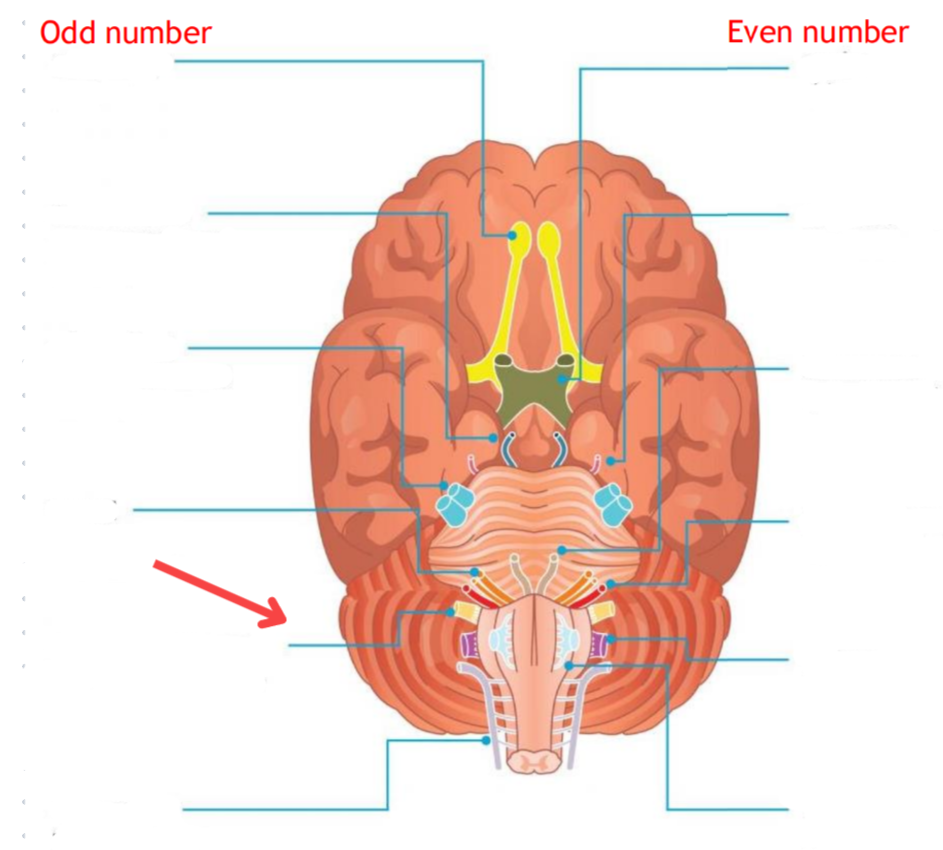
Glossopharyngeal nerve
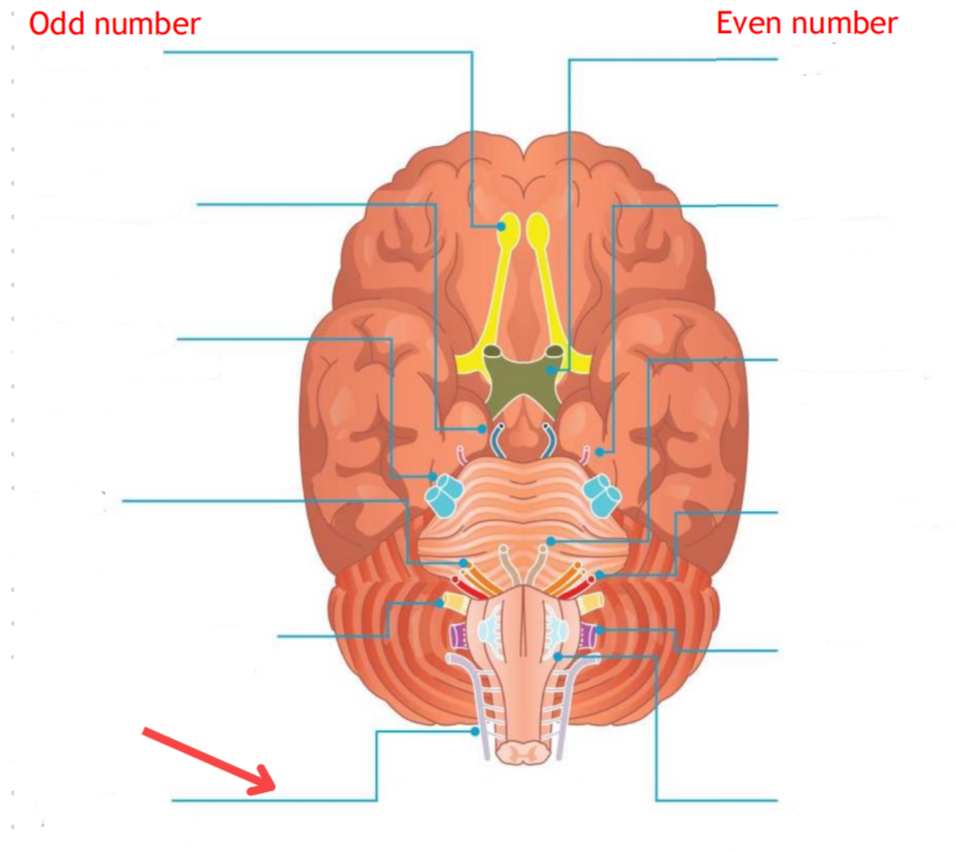
Accessory nerve
Optic nerve
Trochlear nerve
Abducens nerve
Vestibulocochlear nerve
Vagus nerve
Hypoglossal nerve
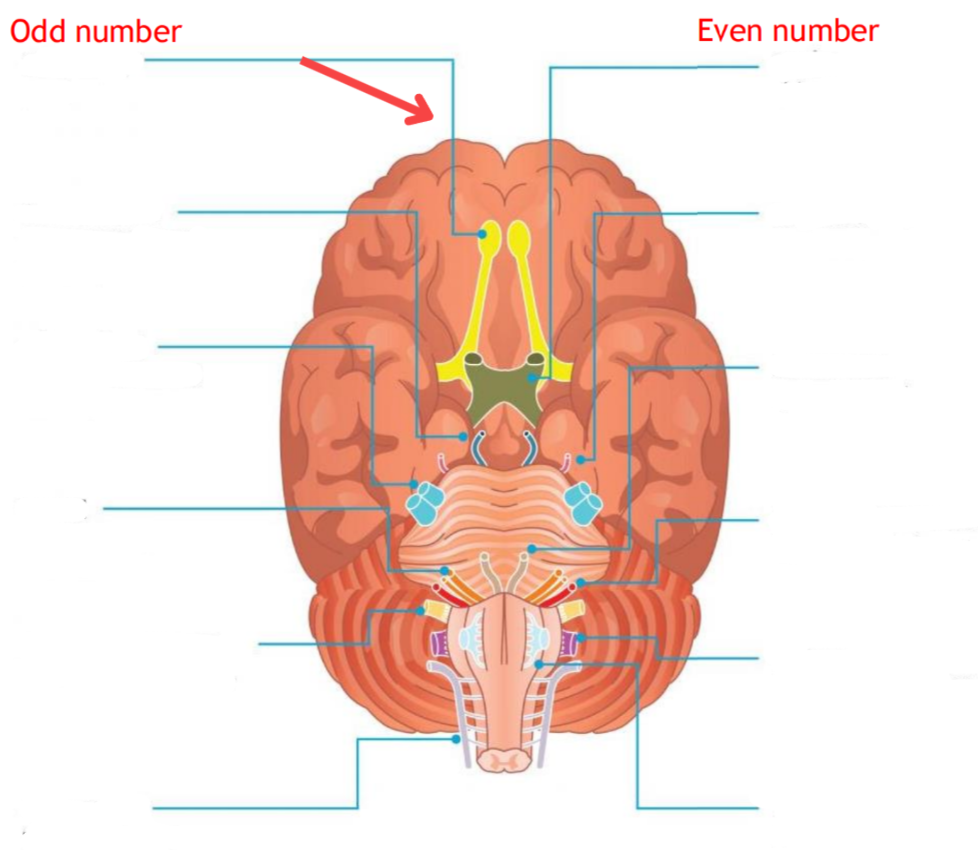
The olfactory nerve originates from…
The cortex
The optic nerve originates from…
The retina
The oculomotor nerve originates from…
The midbrain
The Trochlear nerve originates from…
The midbrain
The trigeminal nerve originates from…
The lateral pons
The Abducens nerve originates from…
The ponto-medullary
The facial nerve originates from…
The ponto-medullary
The vestibulocochlear nerve originates from…
The ponto-medullary
The glossopharyngeal nerve originates from…
The lateral medulla
The vagus nerve originates from…
The lateral medulla
The acessory nerve originates from…
Spinal cord C1-C5
The hypoglossal nerve originates from…
The ventral medulla
Nerve I exits from the…
Cribriform plate of the ethmoid bone
Nerve II exits from the…
Optic canal
Nerve III exits from the…
Superior orbital fissure
Nerve IV exits from the…
Superior orbital fissure
Nerve V1 (First branch of nerve 5) exits from the …
Superior orbital fissure
Nerve V2 (Second branch of nerve 5) exits from the…
Foramen rotundum
Nerve V3 (Third branch of nerve 5) exits from the…
Foramen ovale
Nerve VI exits from the…
Superior orbital fissure
Nerve VII exits from the…
Internal auditory meatus
Nerve VIII exits from the…
Internal auditory meatus
Nerve IX exits from the…
Jugular foramen
Nerve X exits from the…
Jugular foramen
Nerve XI exits from the…
Jugular foramen
Nerve XII exits from the…
Hypoglossal canal
CN I path of travel
Axons begin at frontal cortex and lateral olfactory striae
They extend through the cribriform plate (Ethmoid) into the olfactory bulb
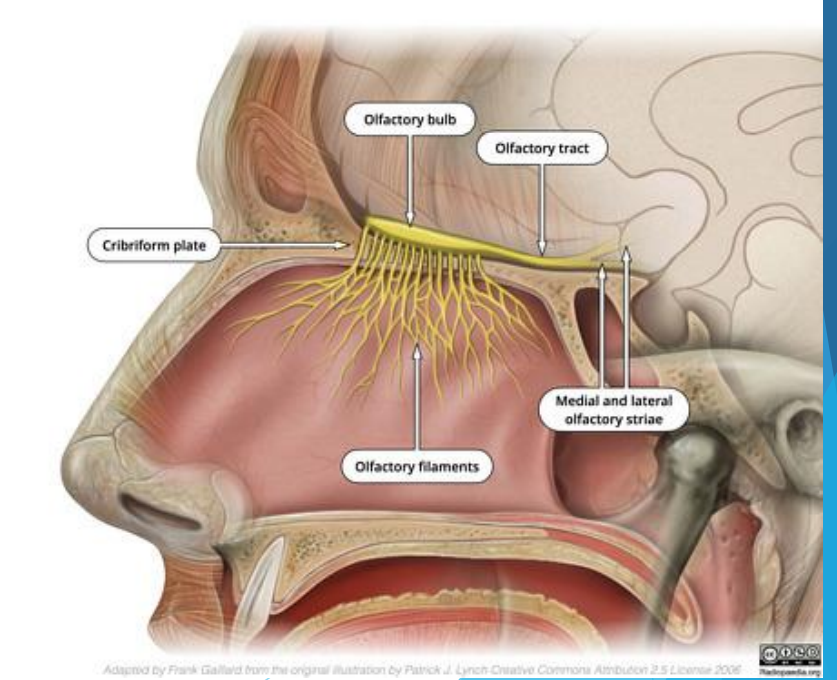
Function of CN I
Olfactory nerve
Provides sense of smell
Dysfunctions of CN1
Dysfunctions cause: Anosmia (Loss of smell)
Esthensioneuroblastoma (Cancer)
Cribriform plate fracture or anterior temporal lobe injury
Function of CN II
Optic nerve
Yeah you guessed it, visual images to the brain
Dysfunctions of CNII
Optic neuritis: Inflammation causing sudden, painful vision loss. Linked to auto immune diseases
Glaucoma: Intraocular pressure leads to loss of peripheral vision
Ischemic Optic neuropathy: Sudden, painful vision loss due to reduced blood flow
Medial rectus
Moves the eye inward (adduction)
Innervated by nerve III
Lateral Rectus
Moves the eye outward (abduction)
Innervated by nerve VI
Superior Rectus
Moves the eye upward and slightly inward
Innervated by nerve III
Inferior Rectus
Moves the eye downward and slightly inward
Innervated by nerve III
Superior Oblique
Moves the eye downward and outward
Innervated by nerve IV
Inferior Oblique
Moves the eye upward and outward (extorsion and elevation)
Innervated by nerve III
Pathway of the oculomotor nerve
Originates from the oculomotor nucleus and Edinger-Westphal nucleus
Arises from the ventral pons
Exits through the superior orbital fissure
CN III functions
Oculomotor nerve
Innervates:
Superior rectus
Levator palpabrae superioris
Inferior rectus
Medial rectus
Inferior oblique
Splits off into the superior branch and the inferior branch
Superior branch of CNIII
Smaller branch
Innervates the superior rectus and levator palpabrae superioris
Levator palpabrae superioris
Raises the upper eye lid
Inferior branch of CNIII
Larger branch
Supplies inferior rectus, medial rectus, inferior oblique
LR6(SO4)3
Mnemonic to remember which oculomotor muscles are innervated by each nerve
LR (Lateral rectus) → Nerve 6
SO (Superior Oblique) → Nerve 4
Rest are innervated by nerve 3
Parasympathetic function of CN III
Sphincter pupillae: Constricts pupil, reducing the amount of light entering the eye
Cilliary muscles: Contracts the lens to increase diopters
Dysfunctions of CNIII
Oculomotor ophthalmoplegia (Restricted eye movement)
Strabismus, ptosis (Eyelid droop), pupillary dilation
Pathway of CN IV
Originates from the dorsal aspect of the brainstem
Arises from the trochlear nucleus in the midbrain
Enters the orbit through the superior orbital fissure
Function of CN IV
The Trochlear nerve innervates the superior oblique muscle (Oculomotor)
CN IV measurements
Smallest cranial nerve But its really how you use it y’know
Longest intra-cranial course (7.5 cm)
Dysfunction of CN IV
Paralysis of the superior oblique muscle results in outward rotation
Symptoms: Double vision, weakness in downward gaze, neck pain from head tilting
CN V pathway
The trigeminal nerve
Originates from the lateral mid-pons
Travels anteriorly through the pre-pontine cistern
Splits into three branches (V1, V2, V3)
CN V1 function
Ophthalmic division
Sensory to forehead, upper eyelids, and nose
Innervates cornea, nasal cavity
CN V2 function
Maxillary division
Sensory to lower eyelids, cheeks, upper lip
Innervates upper teeth, maxillary sinuses