Ochem test 3
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
pKa of alcohol (R-OH)
16
pKa of water
15.7
pKa of carboxylic acid
3-5
pka of sp bond (Alkyne)
25
pKa of sp2 bond (alkene)
44
pKa of sp3 (alkane)
50
pKa of NH3
38
pKa of NH4+
9.2
pKa of H3O+
-1.74
what mechanism is weak base and weak nucleophile
Sn1 or E1
what mechanism is strong base and weak nucleophile
E2
what mechanism is weak base and strong nucleophile
Sn2
what mechanism is strong base and strong nucleophile
SN2(1) or E2 (2,3)
H2O: Strength of Nucleophile and base
Weak nucleophile and weak base
CH3OH: Strength of Nucleophile and base
Weak Nucleophile and weak base
R-OH: Strength of Nucleophile and base
Weak Nucleophile and weak base
Amines: Strength of Nucleophile and base
Weak Nucleophile and weak base
NaOH: Strength of Nucleophile and base
Strong Nucleophile and strong base
NaO-R: Strength of Nucleophile and base
Strong Nucleophile and strong base
CH3ONa: Strength of Nucleophile and base
Strong Nucleophile and strong base
CH3CH2ONa: Strength of Nucleophile and base
Strong Nucleophile and strong base
NaOEt: Strength of Nucleophile and base (idrk)
Strong Nucleophile and strong base
NaN3: Strength of Nucleophile and base
Strong nucleophile and weak base
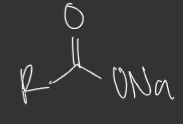
R-COONa: Strength of Nucleophile and base
Strong nucleophile and weak base
NaCN: Strength of Nucleophile and base
Strong nucleophile and weak base
CH3SNa: Strength of Nucleophile and base
Strong nucleophile and weak base
t-BuOK: Strength of Nucleophile and base
Weak nucleophile and strong base
LDA ( Lithium diisopropylamide): Strength of Nucleophile and base
Weak nucleophile and strong base
Mechanism for Strong Nucleophile and Strong base but 1°
SN2
Mechanism for Strong Nucleophile and Strong base but 2° or 3° with heat
E2
Mechanism for weak nucleophile and weak base but no heat
Sn1
Mechanism for weak nucleophile and weak base but heat
E1
E1 and E2 reactions take the hydrogen from which carbons?
From the beta or neighbor carbon of LG carbon
Protic solvents
solvents that can donate protons
Aprotic solvents
solvents that cannot donate protons
In Protic solvents, ____ halides are stronger nucleophiles
Less electronegative or larger (I>Br>Cl>F)
In Aprotic solvents, ____ halides are stronger nucleophiles
More electronegative or smaller(F>Cl>Br>I)
Acetone:Aprotic or Protic solvent
Aprotic
DMSO:Aprotic or Protic solvent
Aprotic
CH3CN:Aprotic or Protic solvent
Aprotic
DMF: Aprotic or Protic solvent
Aprotic
Hydrogen attached to N,O,F: Aprotic or Protic solvent
Protic solvents
SN1 and E1 prefer which solvent
protic
SN2 and E2 prefer which solvent
aprotic
Ethanol:Aprotic or Protic solvent
Protic
EtOH: Strength of Nucleophile and base
weak nucleophile and weak base
Mechanism EtO-
E2