(CIE A2 Biology) Genetic engineering specifics - enzymes/vectors/promoters/markers (based on SaveMyExams revision notes)
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
Genetic Engineering
The deliberate modification of characteristics of an organism by manipulating its genetic material.
Restriction Endonucleases
Enzymes that cut DNA strands at specific sequences to isolate desired genes.
Reverse Transcriptase
An enzyme that synthesizes complementary DNA (cDNA) from an mRNA template.
DNA Polymerase
An enzyme that converts single-stranded cDNA into double-stranded DNA.
DNA Ligase
An enzyme that catalyzes the formation of phosphodiester bonds to splice DNA fragments.
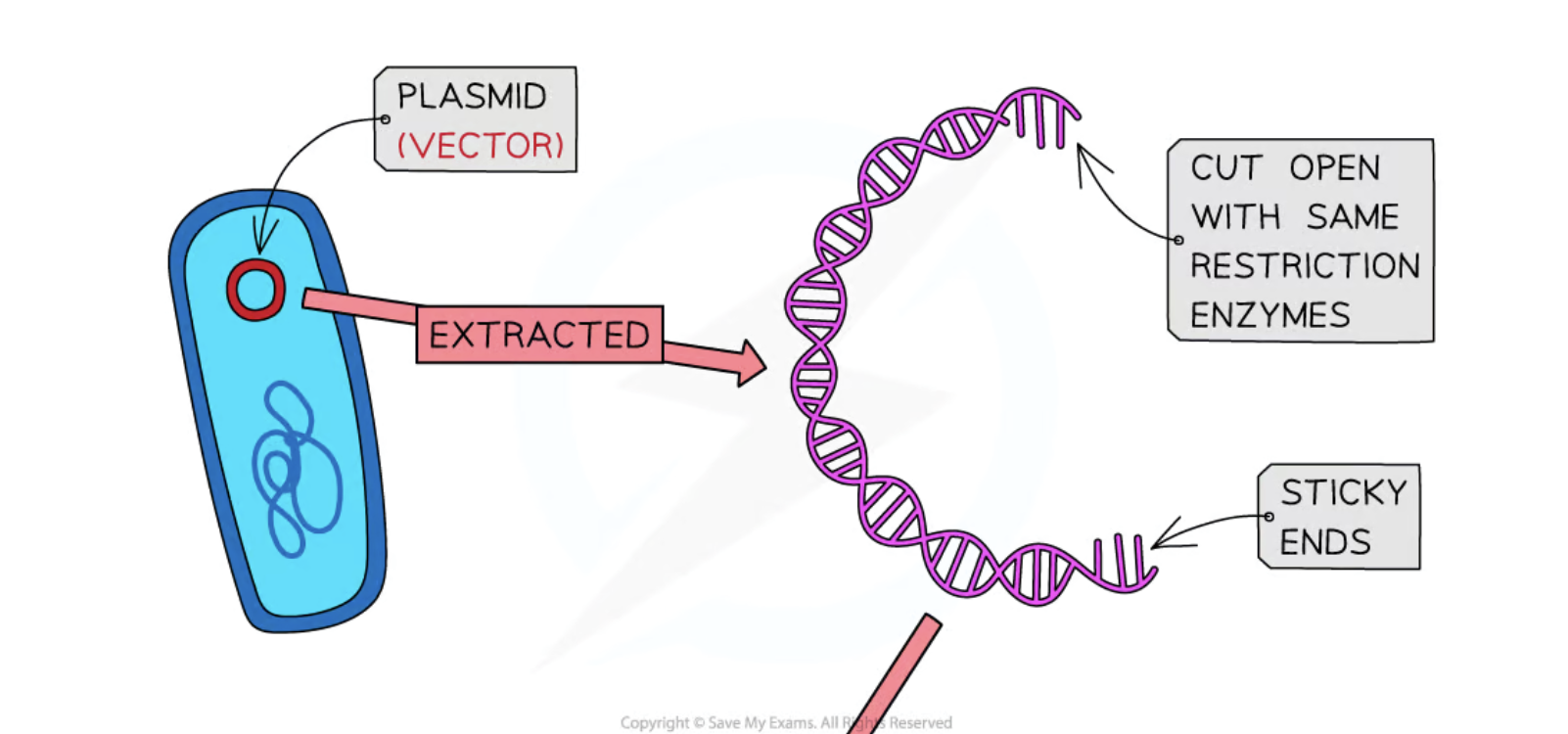
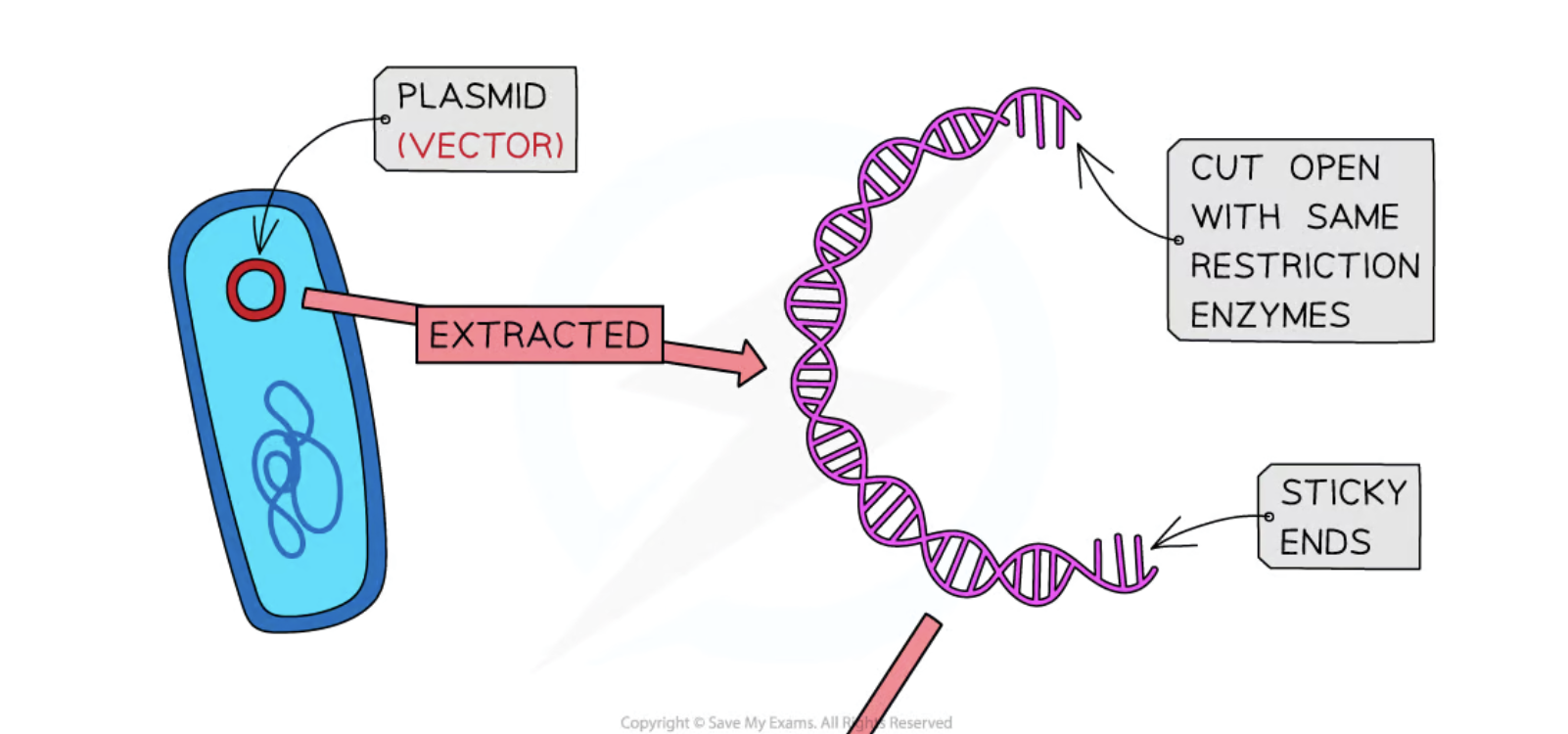
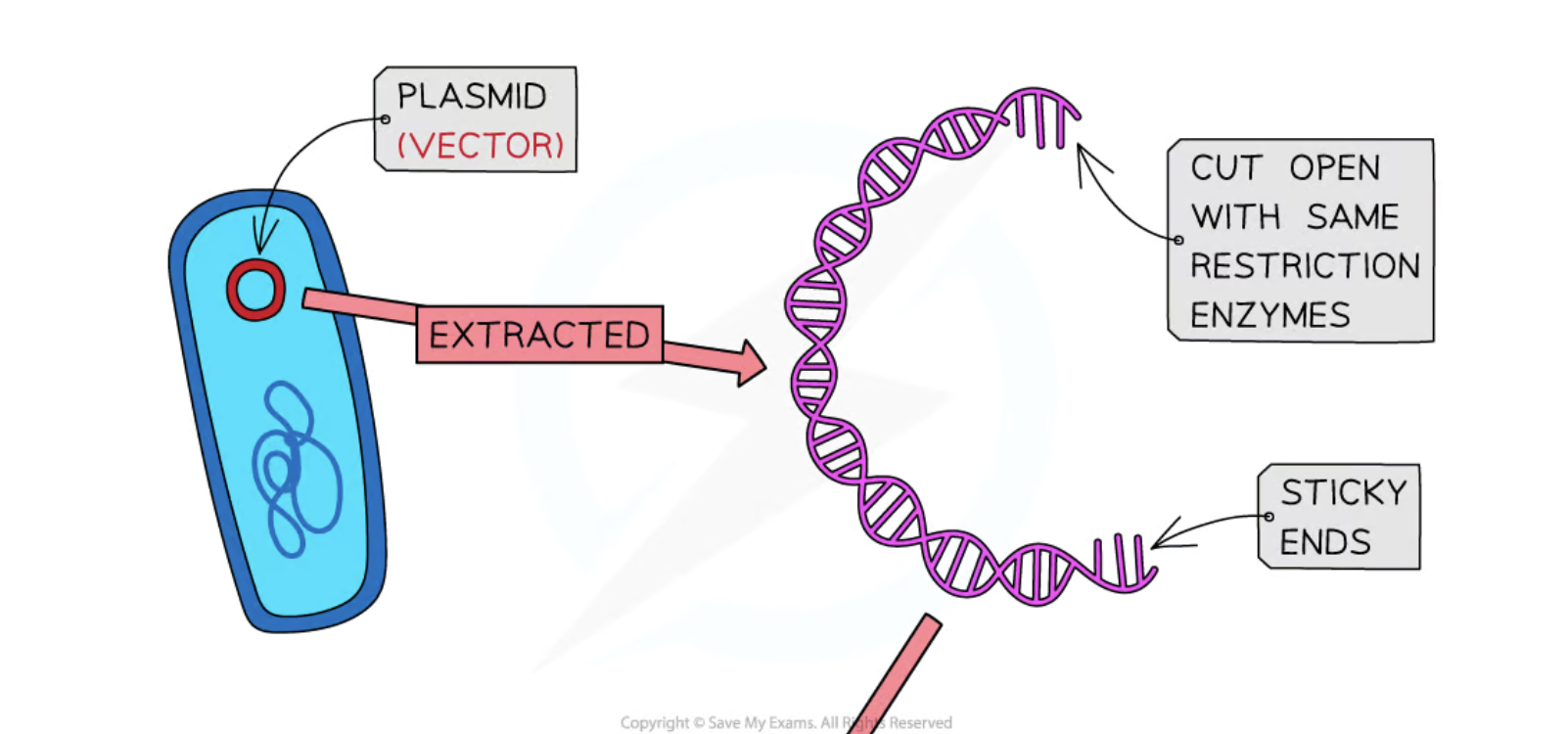
Sticky Ends
Uneven ends of DNA fragments created by restriction enzymes that facilitate the joining of DNA pieces.
Blunt Ends
Even ends of DNA fragments created by cutting straight across the DNA.
Plasmids
Small, circular rings of double-stranded DNA that can replicate independently in bacterial cells.
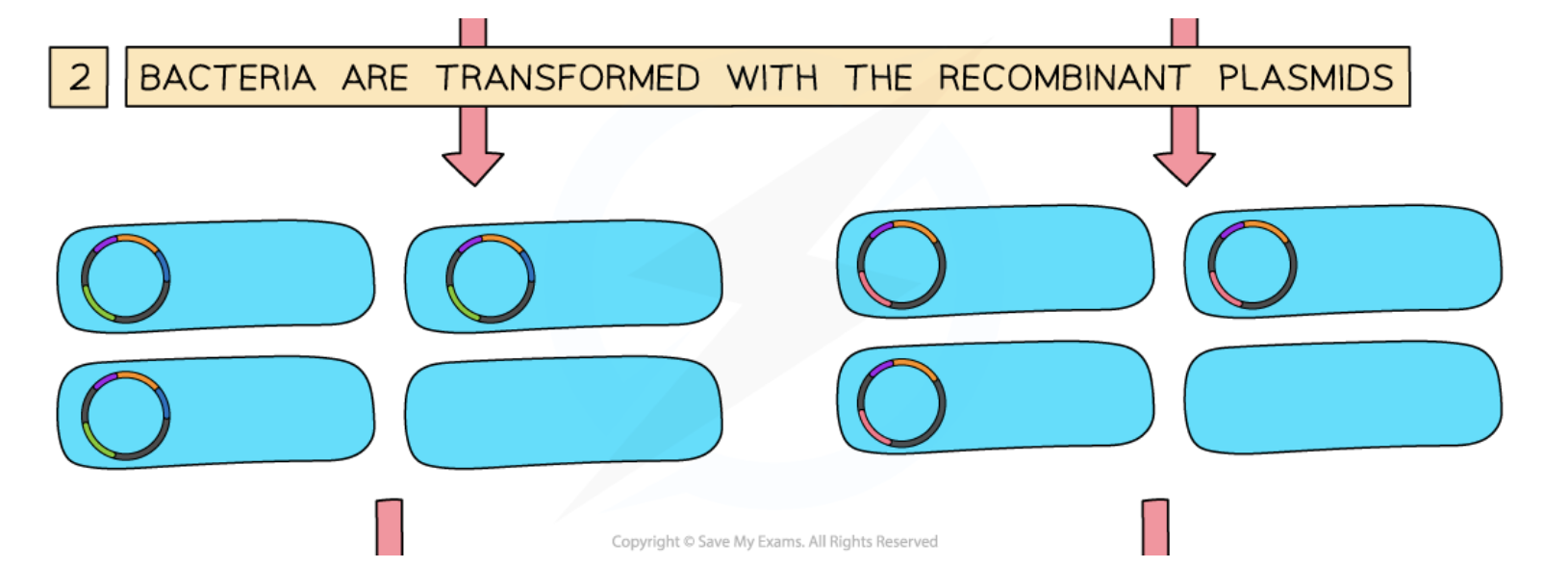
Transformation
The process by which plasmids are introduced into bacteria.
Adenovirus
A type of virus used as a vector in gene therapy.
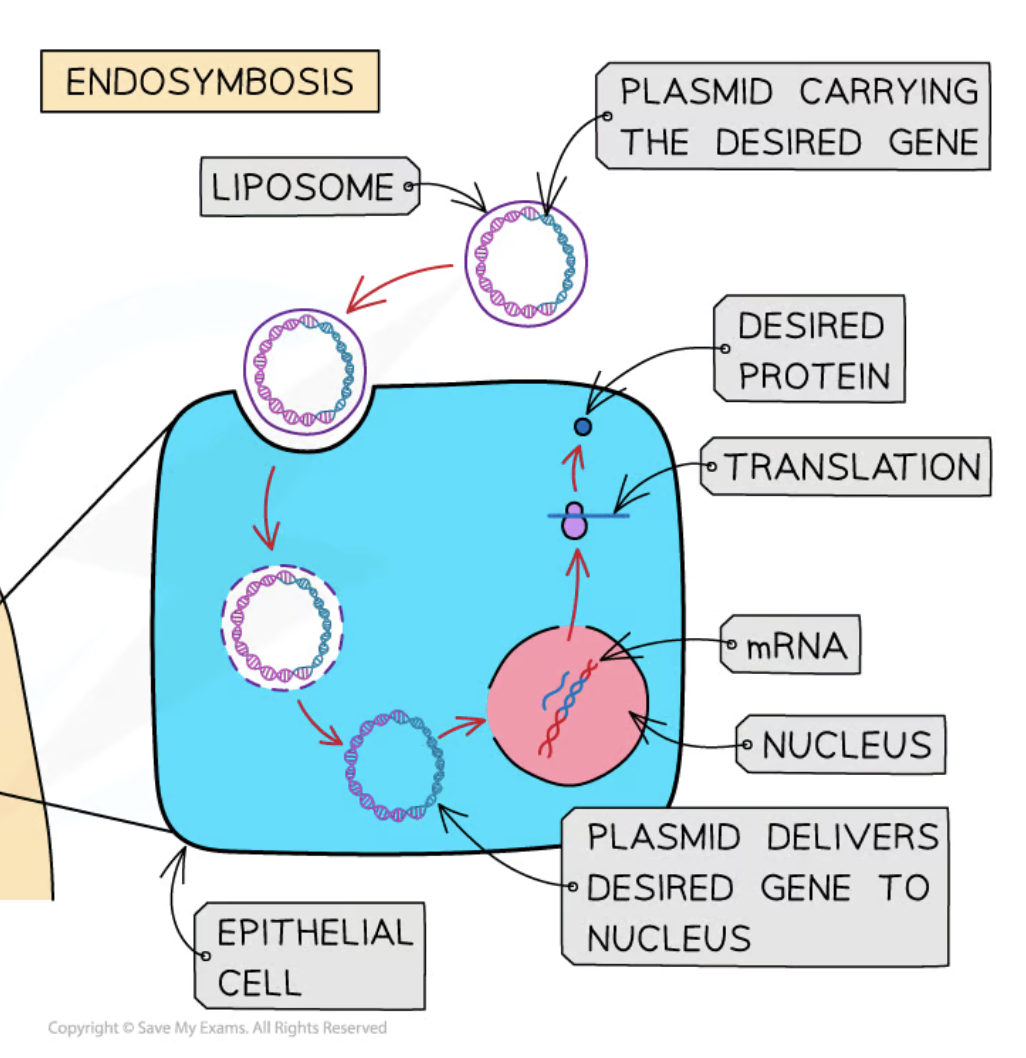
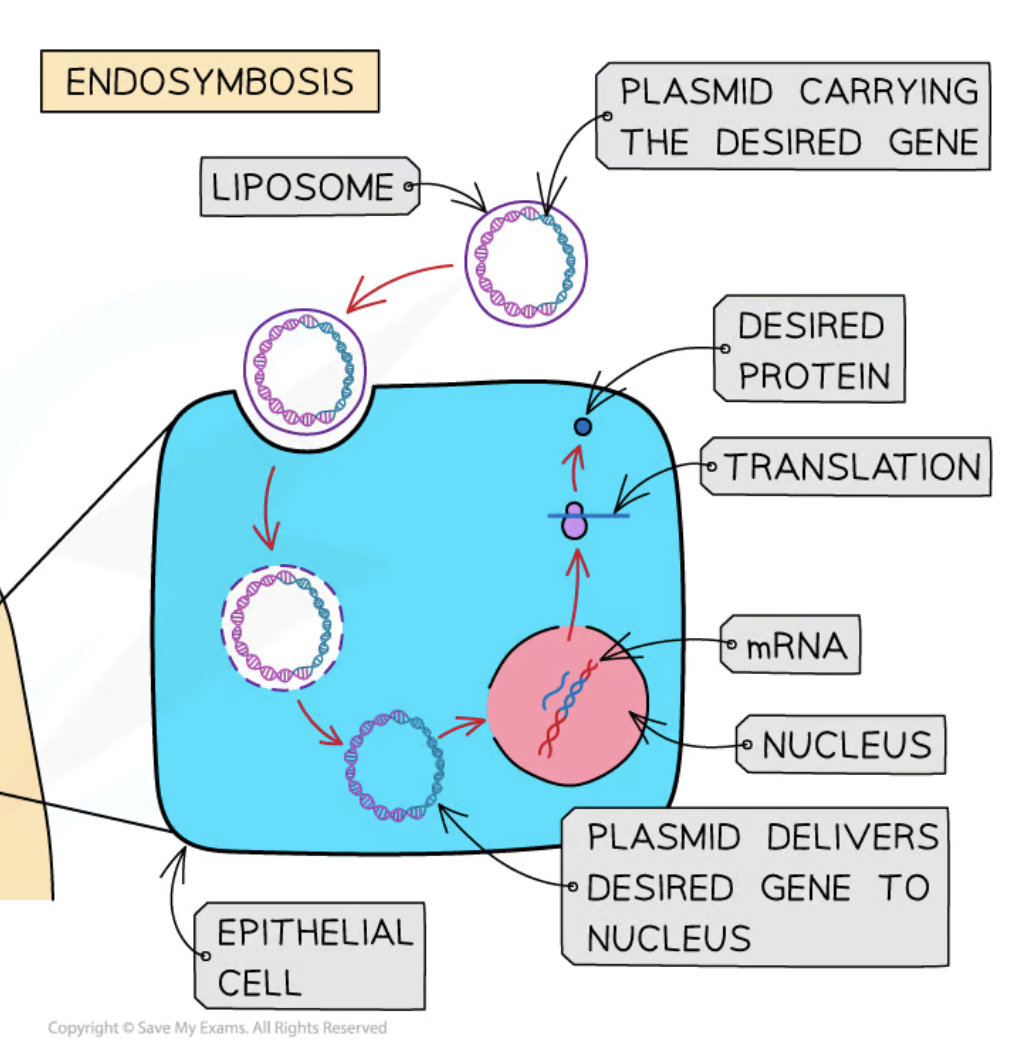
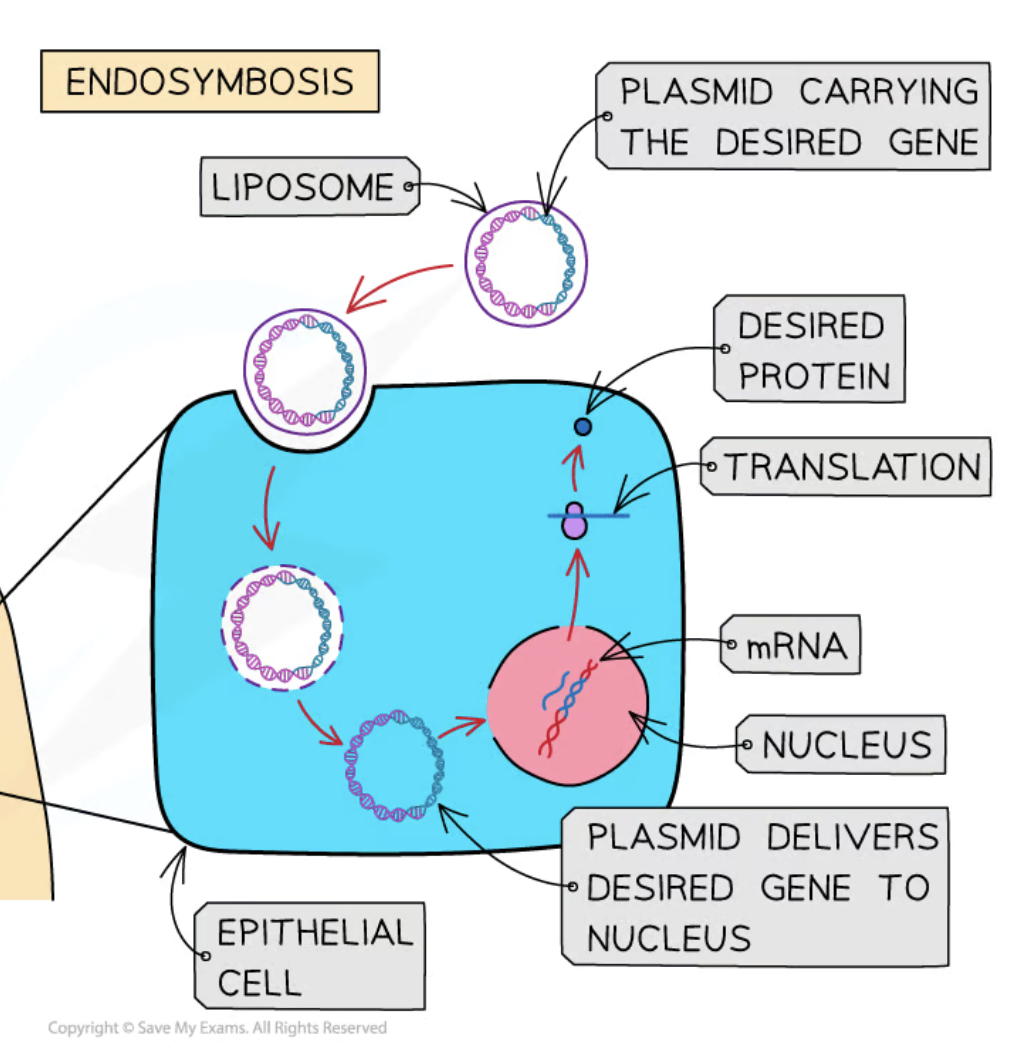
Liposomes
Small spherical vesicles with a phospholipid layer used to deliver genes.
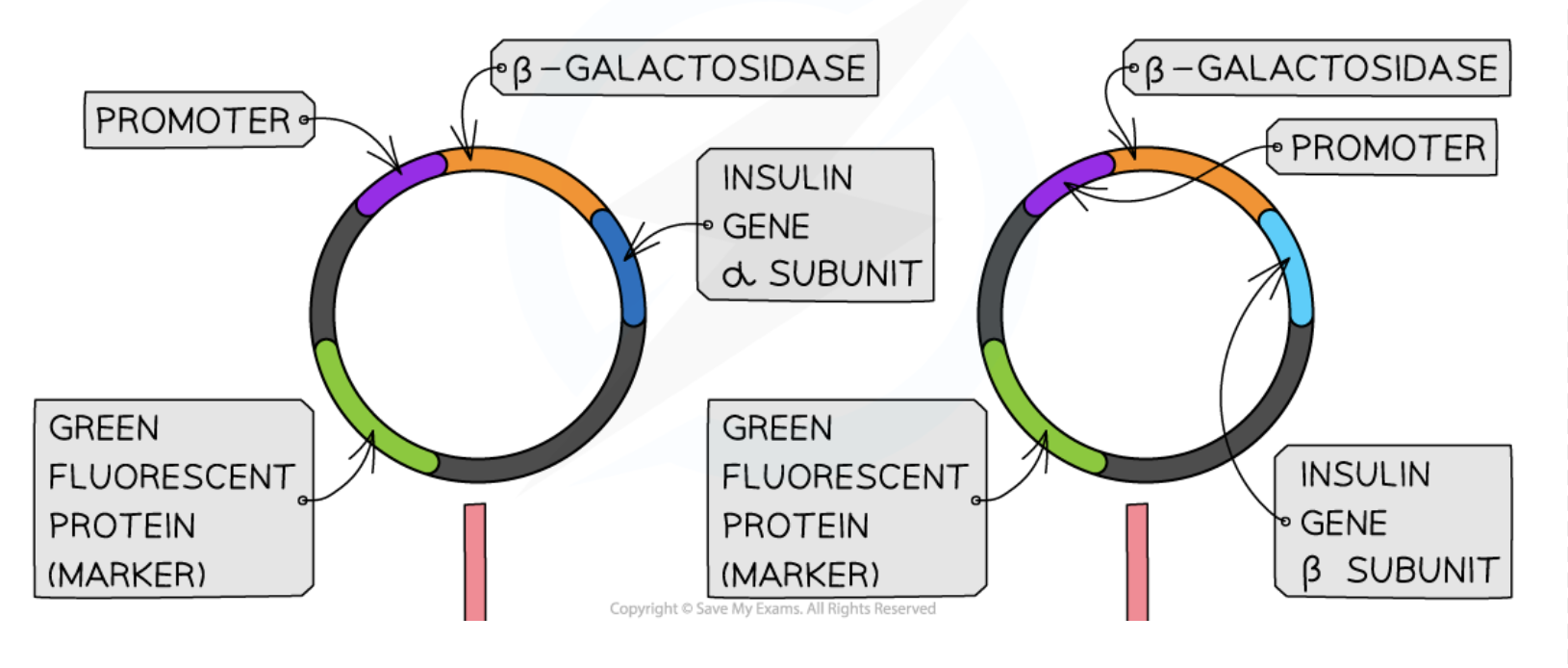
Promoter
A region of DNA that initiates transcription and determines gene expression.
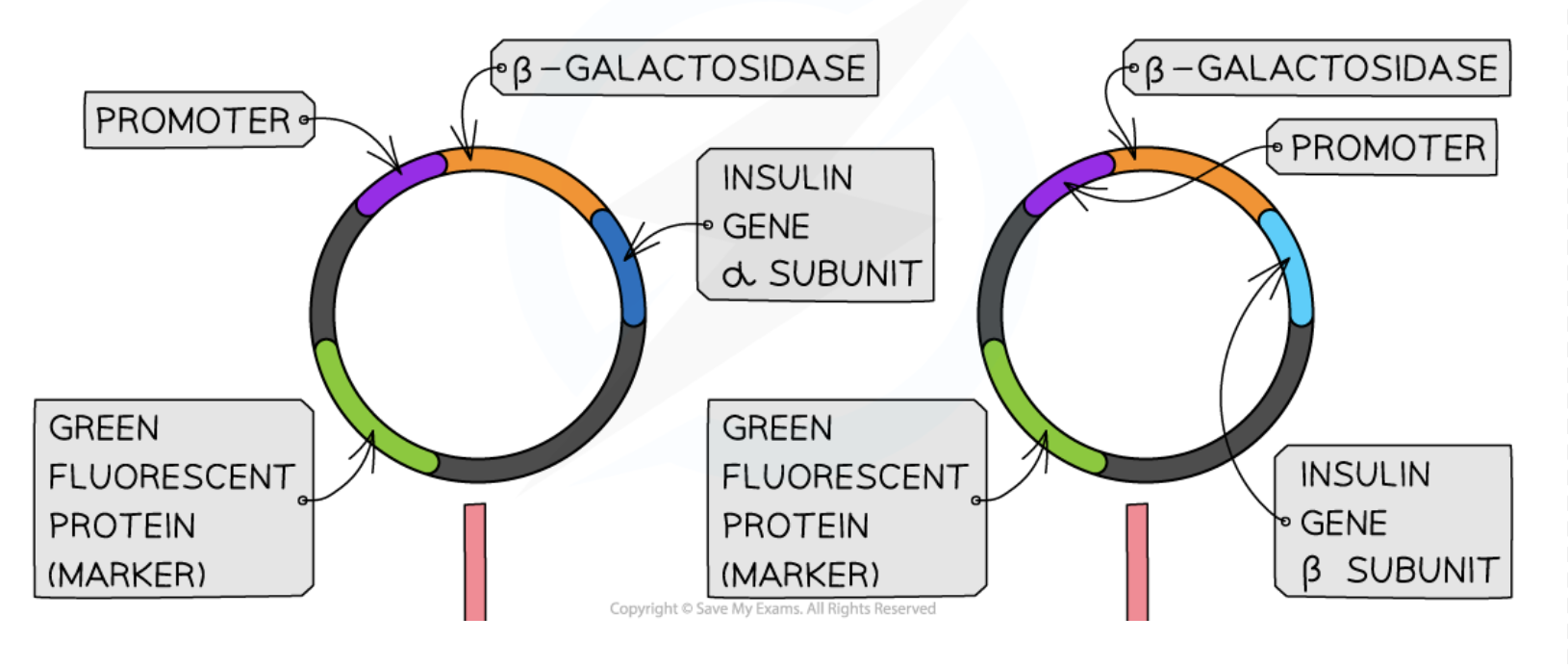
Marker Genes
Genes used to identify which cells have been successfully transformed with recombinant DNA.
Antibiotic Resistance Genes
Genes that confer resistance to antibiotics, often used as markers in genetic engineering.
Green Fluorescent Protein (GFP)
A protein that emits green fluorescence when exposed to ultraviolet light, used as a marker.
cDNA (Complementary DNA)
DNA synthesized from an mRNA template using reverse transcriptase.
Transcription
The process of copying a segment of DNA into RNA.
RNA Polymerase
An enzyme that synthesizes RNA from a DNA template during transcription.
mRNA
Messenger RNA, which carries the genetic information from DNA for protein synthesis.
Introns
Non-coding sequences in a gene that are removed during RNA processing.
Eukaryotic Cells
Cells that contain a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles.
Scientific Modification
The process of altering organisms through genetic engineering techniques.
Vector
A vehicle, such as a plasmid or virus, used to transfer genetic material into another cell.
Calcium Chloride Solution
A chemical solution used to facilitate the uptake of plasmids by bacterial cells.
Electroporation
A technique that uses an electrical field to increase cell permeability to DNA.
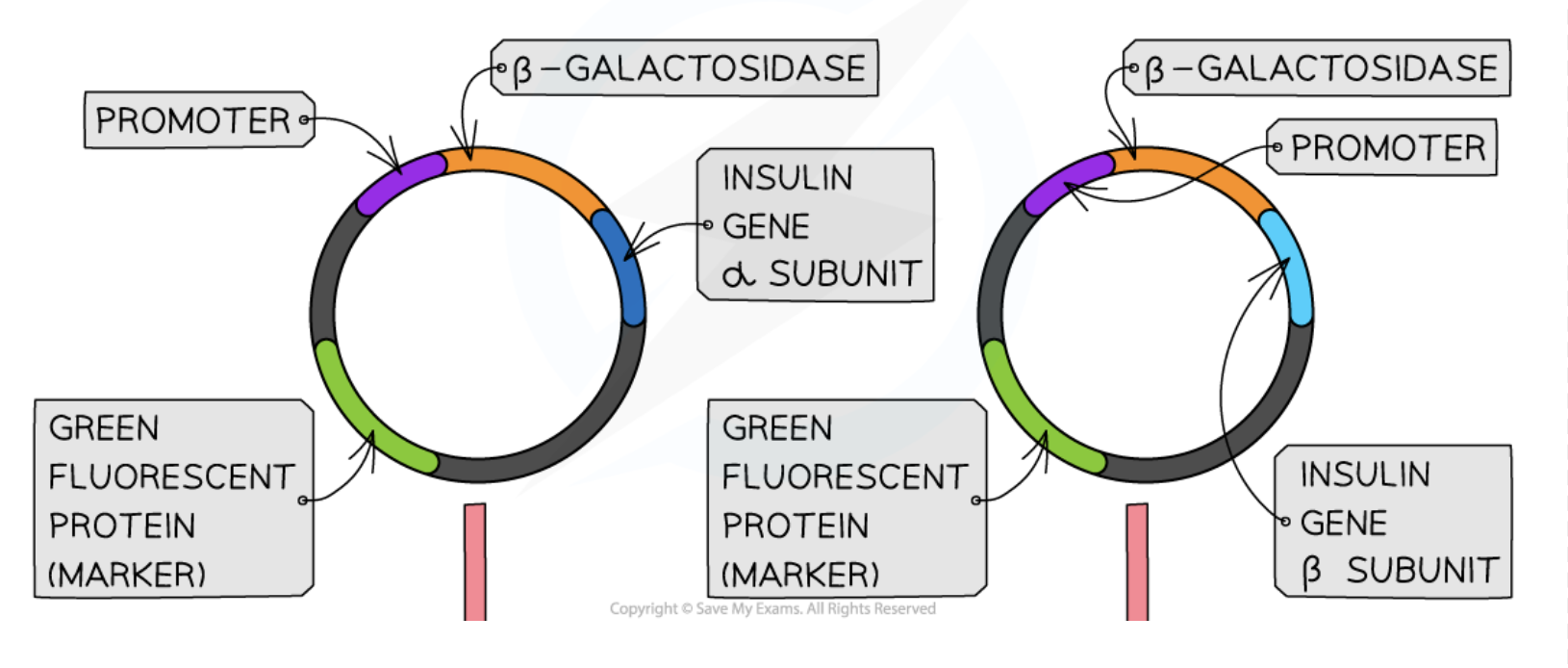
Recombinant Plasmid
A plasmid that contains a fragment of DNA from another organism.
Transformation Efficiency
The percentage of cells that successfully take up the plasmid during transformation.
Bacterial Plasmids
Plasmids that are found naturally in bacteria and can carry genes for various traits.
Gene Therapy
A medical technique that modifies a person's genes to treat or prevent disease.
Retroviruses
A type of virus that can integrate its RNA into the host genome.
Gene Expression Regulation
Control of the timing and rate of gene expression.
Gene Isolation
The process of separating a specific gene from the rest of the DNA.
Phosphodiester Bonds
Covalent bonds that form the backbone of DNA and RNA.
Bacterial Transformation Process
The introduction of foreign DNA into bacteria using methods like heat shock or electroporation.
Lentiviruses
A subclass of retroviruses used in gene therapy to deliver genetic material.
Non-coding DNA
DNA sequences that do not encode for proteins but can have regulatory functions.
β-galactosidase
An enzyme produced by bacteria that is involved in lactose metabolism.
Gene Modifications
Alterations made to the genetic material of an organism.
Expression of Insulin Gene
The transcription and translation process resulting in the production of insulin.
Marker Identification
The method of detecting transformed cells in genetic engineering.
Gene Cloning
The process of creating copies of a specific gene.
Nucleotide Pairing
The interaction between complementary bases in DNA during replication.
Viral Vectors
Genetically modified viruses used to deliver genes into host cells.
Phospholipid Layer
A double layer of phospholipids that makes up the cell membrane and liposomes.
Ultraviolet Light Detection
A technique used to identify transformed bacteria by fluorescence.
Safety Concerns in Genetic Engineering
Risks associated with gene transfer, including antibiotic resistance spread.
Fluorescent Markers
Genes that code for fluorescent proteins, allowing for easier identification of modified cells.
Cystic Fibrosis Treatment
Gene therapy approaches aimed at introducing functional genes into patients with cystic fibrosis.