Pathology Final
1/42
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
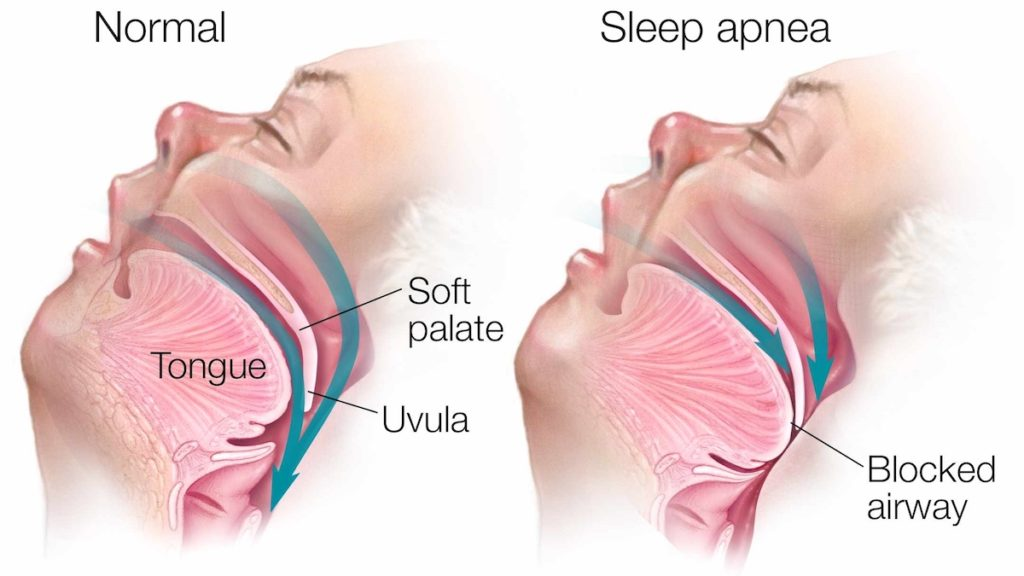
What is Sleep Apnea?
A condition in which breathing is stopped or becomes shallow while sleeping. It can be caused by
Causes of sleep apnea
The relaxation of the muscles at the back of your throat to the point where it denies proper breathing.
Presentation of Patient with Sleep Apnea
A patient with sleep apnea would show high amount of daytime sleepiness, morning headaches, gasping or choking for air when laying down. The doctor may recommend a sleep study and a physical examination for patients showing these characteristics.
Treatments of Sleep Apnea
Sleep apnea would best be treated with lifestyle changes, avoiding alcoholic beverages, along with a CPAP (continuous Positive Airway Pressure) Machine.
Pulmonary Embolism
A condition which occurs when a clump of material, most often a blood clot, gets stuck in an artery in the lungs, blocking the flow of blood. The portions of lung served by each blocked artery can't get blood and may die. Causing a pulmonary infarction.
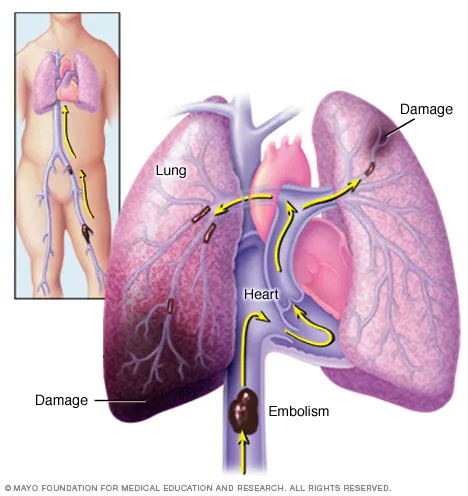
Causes of pulmonary embolism
A blood clot. These blood clots almost always are caused by a clot in the deep vein in the leg.
Diagnosis of pulmonary embolism
Chest X-RAY
Blood Tests
Ultrasound
CT Scan
Pulmonary Angiogram
MRI
Symptoms of Pulmonary embolism
Sudden shortness of breath (most common)
Chest pain (usually worse with breathing)
A feeling of anxiety.
A feeling of dizziness, lightheadedness, or fainting.
Irregular heartbeat.
Palpitations (heart racing)
Coughing and/or coughing up blood.
Sweating.
(John Hopkins Medicine)
Lung Cancer
Cancer that forms in the lungs, usually found in the cells that line the air passages.
Causes of Lung Cancer
The main cause of this condition is the smoking of tobacco products. Secondhand smoking is also another cause of this condition.
Diagnosis of Lung Cancer
Chest X-RAY, MRI, CT
Sputum Cytology, when the mucus you coughed up is studied under a microscope to search for lung cancer cells.
Biopsy
Treatments of Lung Cancer
Radiation such as Chemo
Surgeries that remove the tumor from the lung.
Treatments for Pulmonary Embolism
Medicines such as blood thinners and clot dissolvers.
Surgical procedures like clot removal may also be employed
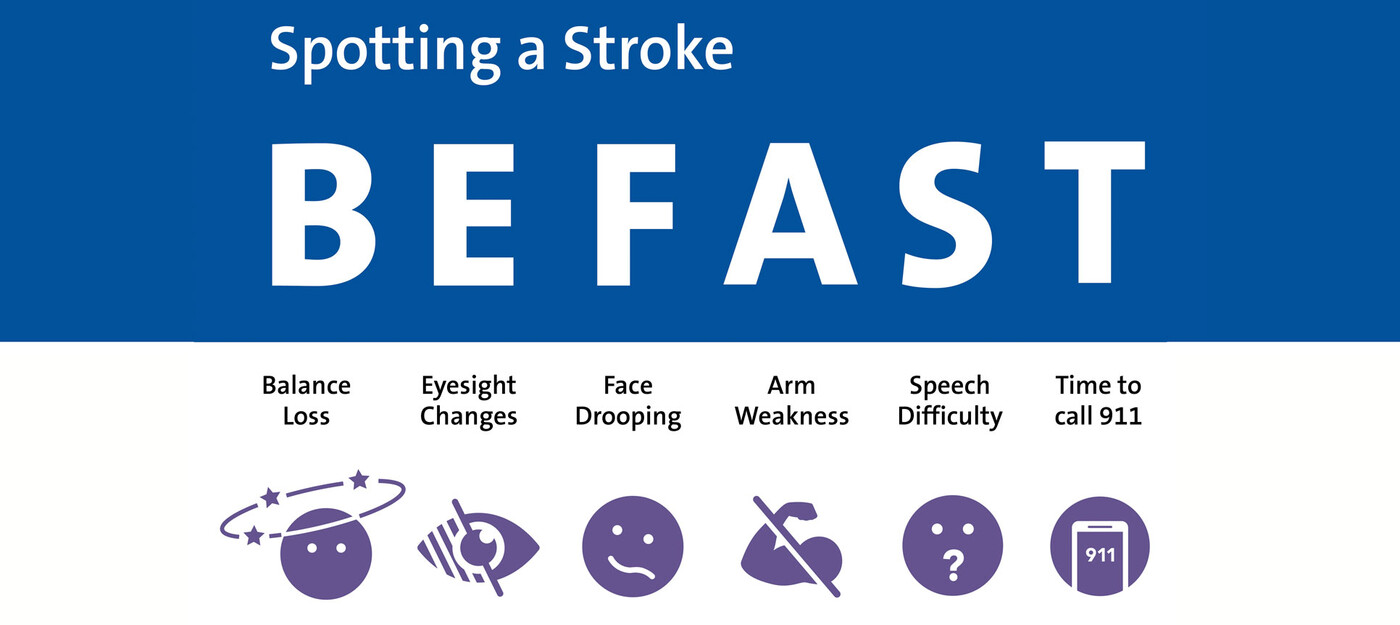
Stroke: BE FAST Acronym?
B: Balance Changes
E: Eyesight Loss
F: Face Drooping
A: Arm Weakness
S: Speech Difficulty
T: Time to call 911.
8 D’s of Stroke
Detection: Detection involves rapid recognition of stroke symptoms.
Dispatch: Dispatch involves early activation of emergency medical services.
Delivery: Delivery is the prompt transport of the patient to a hospital, preferably a stroke center.
Door: Door refers to the arrival of the patient at the ED. Ideally, the stroke team should be in place at the receiving facility prior to the patient’s arrival to ensure prompt assessment and diagnosis.
Data: Data collection is a vital component of the chain of survival. A CT scan is an essential tool needed for an accurate diagnosis.
Decision: A decision regarding the type of treatment needed is the next step in caring for a patient with a stroke.
Drug/Device: Drug administration, if appropriate, is the next link in the chain of survival.
Disposition: This step in stroke care focuses on the continuing care of the stroke patient.
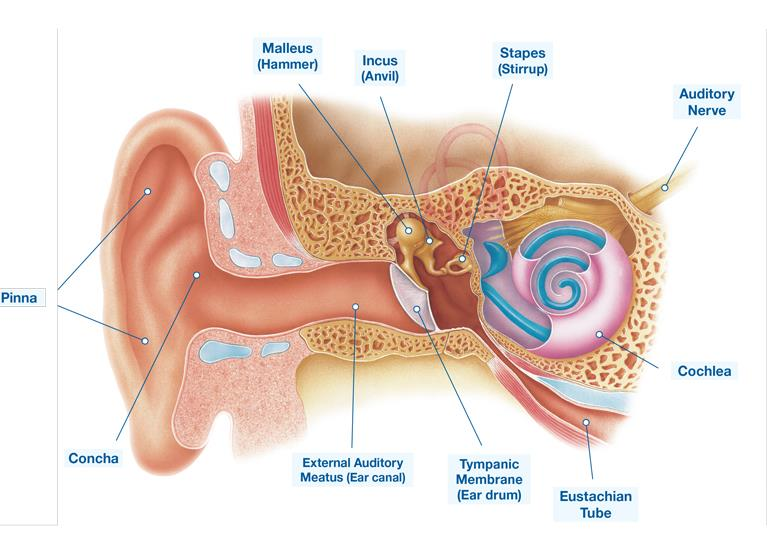
Ear Anatomy
Myringotomy
A surgical procedure that involves making an incision in the eardrum to relieve pressure and drain fluid from the middle ear.
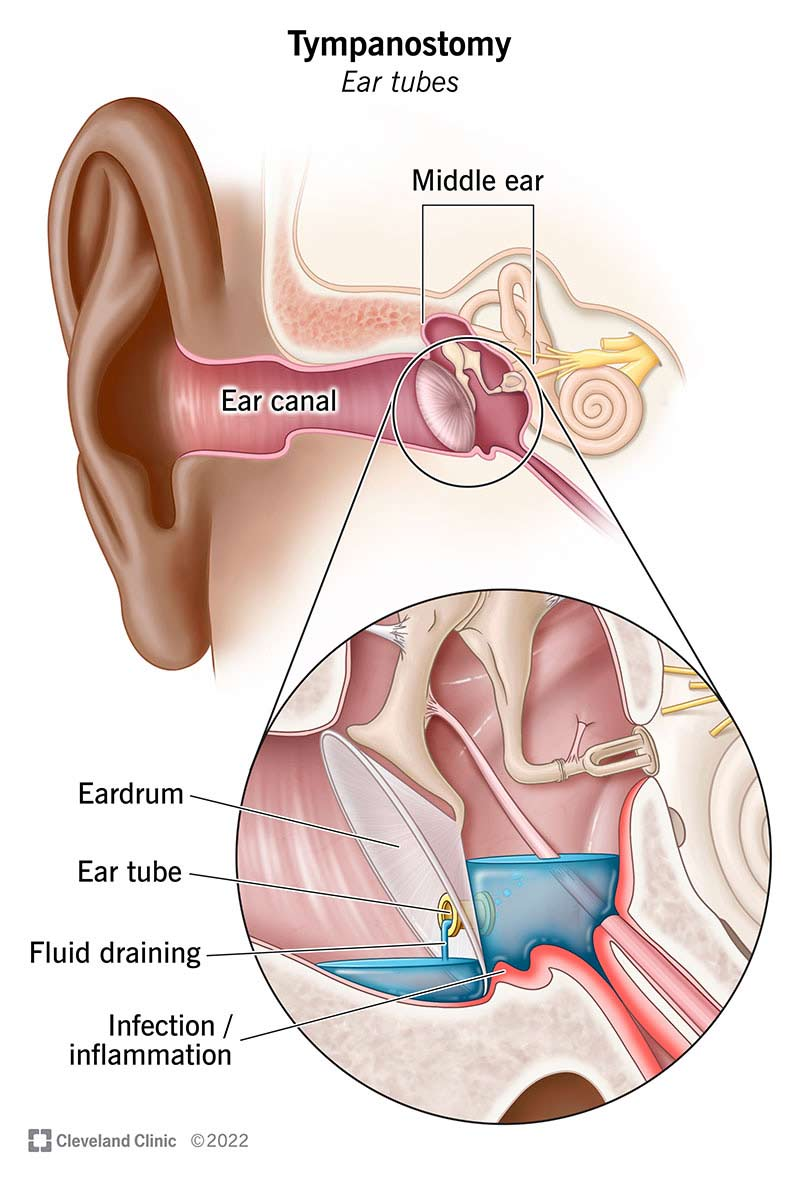
When should someone qualify for a myringotomy?
When the patient has frequent ear infections, barotrauma or other conditions caused by fluid in your ear.
Cerumen Impaction
When too much earwax builds up and blocks the ear canal.
How to get rid of Cerumen Impaction?
It is removed by a healthcare provider.
What does an otoscope allow the medical provider to inspect?
The Otoscope exam helps assess the condition of the external auditory canal, tympanic membrane and the middle ear.
What does an ophthalmoscope allow the medical provider to inspect?
It allows the provider to look at the back of your eye.
Cardiomyopathy
a chronic disease that affects the heart muscle, making it harder for the heart to pump blood.
Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy occurs when the muscle of the left ventricle thickens. This can block blood flow to the rest of the body.
Heart is TOO STRONG
Dilated Cardiomyopathy
The cavity of the heart is enlarged and stretched, compromising the heart's ability to pump normally and relax appropriately.
Heart is TOO WEAK
Restrictive Cardiomyopathy
Restrictive cardiomyopathy occurs when the heart muscle becomes stiff and not able to fill with blood properly.
Heart is TOO STIFF
Cardiac Conduction System
Sinoatrial Node (SA Node): 60-100 BPM
AV (Atrioventricular Node): 40-60 BPM
Left and Right Bundle Branch: 20-40 BPM
Purkinje Fibers: 15 BPM
Cranial Nerves
1: Olfactory: Sensory, smell
2: Optic: Sensory, vision
3: Oculomotor: Motor, eye movements
4: Trochlear: Motor, eye movements
5: trigeminal, Mixed, Sensation from face, muscles of mastication
6: Abducens, Motor: Innervates the lateral rectus, abducts the eyes
7: Facial, Mixed: Facial expression, anterior 2/3 of tounge
8: Vestibulochochlear: Sensory, Sense of sound and balance
9: Glosopharyngeal, Mixed, posterior 1/3 of the tongue
10: Vagus, Mixed, Laryngeal and Pharyngeal muscles, sensory from organs.
11: Accessory: Motor, Controls muscles near spine
12: Hypoglossal: Motor, Muscles of tongue.
Clinical Cranial Nerve Exam
CN 2: Take a look over the shoulder where the wall meets the ceiling.
CN 2 and 3: Take a look right at the eyes, pupillary Responces.
CN 3,4,6: Follow finger without moving the head.
CN 5: Trigeminal, clench Jaw
CN 7: Smile, puff cheeks
CN 11: Tongue straight out
CN 9 and 3: Say AHHHH, voice quality, palatal movement, uvula midline
CN 11: Shrug your shoulders,
CN 8: Following all directions
Range of Motion of Shoulder
180 degrees
Which muscles and tendons comprise the shoulder?
The supraspinatus, infraspinatus, teres minor, and subscapularis muscles, deltoids
What tendons comprise the shoulder
Long head of the biceps tendon
Supraspinatus tendon
Infraspinatus tendon
Teres minor tendon
Subscapularis tendon
Pectoralis minor tendon
Coracobrachialis tendon
Short head of the biceps tendon
Which fossa does the supraspinatus muscle reside in?
Supraspinous fossa
Which fossa does the infraspinatus muscle reside in?
Infraspinous fossa
Which fossa does the subscapularis muscle reside in?
Subscapular fossa
What are the attachments for the deltoid?
Deltoid tuberosity, upper part of scapula (shoulder blade) and the side of your clavicle.
What are the 2 major landmarks protruding from the proximal humerus?
Greater and Lesser Tubercle
Describe the positioning of the greater and lesser tubercle.
Greater Tubercle: Located on the lateral (outer) side of the proximal humerus, near the head of the bone.
Lesser Tubercle: Located on the anterior (front) aspect of the proximal humerus, just below the head of the bone.
What attaches to the greater and lesser tubercle
Greater: supraspinatus, infraspinatus, and teres minor muscles
Lesser: The subscapularis muscle
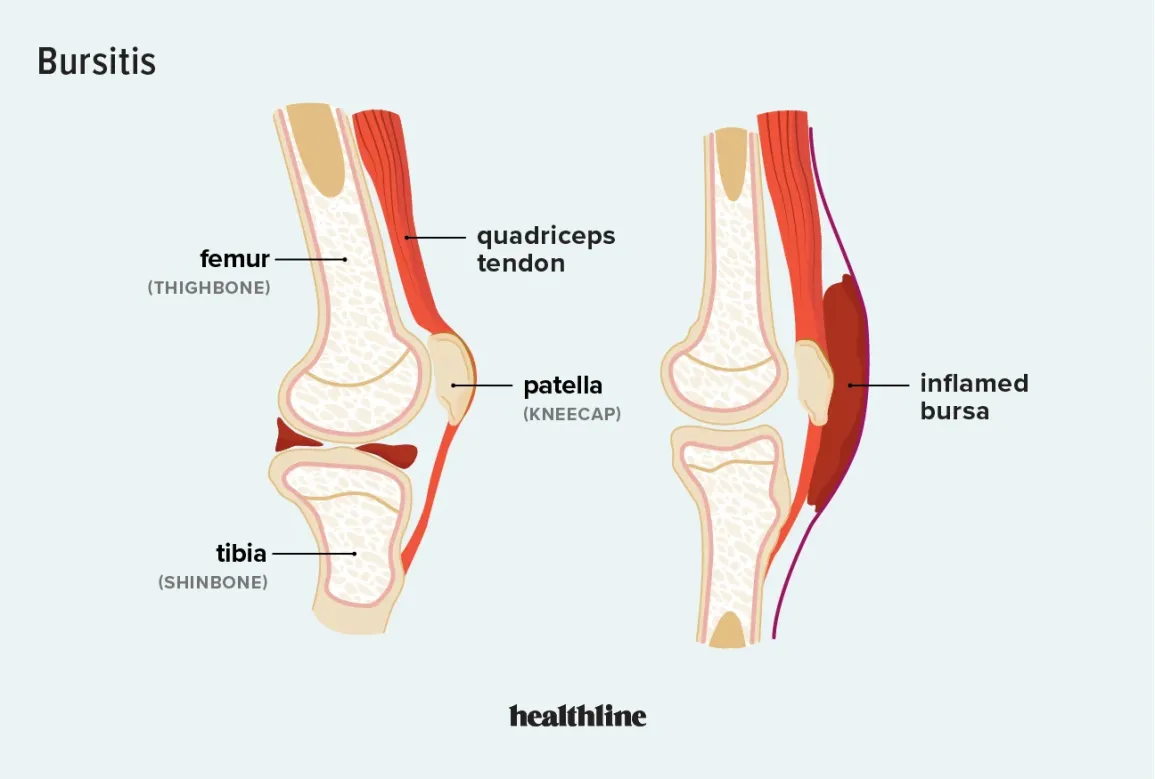
What do we call the condition of a bursa when it is irritated, swollen and likely traumatized?
Bursitis, when the bursa is irritated, Bursitis can cause pain, swelling, redness, stiffness, and a loss of motion
Bursa: Fluid filled sacs that reduce friction and facilitate movement.