🎓BIOSCI 109 Lecture 7 Community Interactions II: Predation
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
what is the nature of the relationship between predators and prey
Prey need refuges so at least some escape predators and so that neither the predator population nor prey populations go extinct.
Explain about refuges
refuges can be strucutrally diverse (hetergenous) physcial environemnt (e.g burrows rocks) or adaptions (e.g size camouflague flight etc) or dispersal.
what impacts does predation have on populations
Have huge impacts on populations, part of poplulations (e.g juveniles), communities and prey distribution.
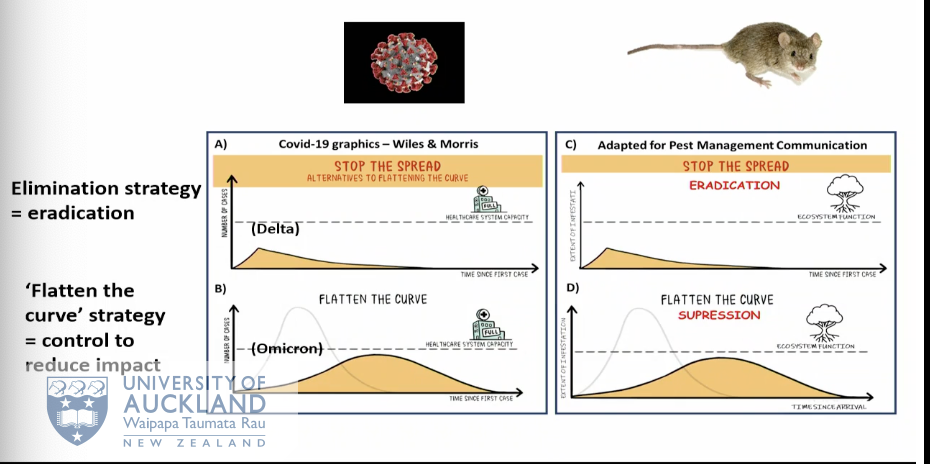
what can mammalian predator managment provide
Mammalian predator management (for conservation) can eradicate (no indiiduals remaining) or control (below a threshold) predators.
what does predator free 2050 aims.
to eradicate rats, possums & mustelids (ferrets, stoats & weasels) but comes with ecological, social & economic challenges.
How did prey evolve in Aoteroa and Pacific islands
“prey (bird & reptiles) evolved with and adapted to avian 9ususally arial) predaotrs that hunted based primarily on vision - not mammalian predators (hunt based on scent)
what type of interaction does predator have and why
The predator has an exploitive interation.
+ve= predator
-ve= prey.
predators benefit due to food consumption while prey gets eaten and is why negitive.
difference between prey and herbivory and explain about generalist and specialist.
Prey can run away while plants can’t.

Some examples of these specialist hunters.
analope having a long nose.
Huffaker's Balancing Ac
Huffaker's Balancing Act describes how species interactions and environmental factors balance to maintain stable population dynamics and biodiversity in ecosystems.It emphasizes that populations of interacting species are often influenced by both density-dependent factors (e.g., competition for resources) and external disturbances (e.g., environmental variability).
what are different type of refuges.
Burrows rocks, physical size morphological defenses, chemical defenses, colouraation and behaviour
what is the difference between avion and mammilian predators
good vision, looking for movment = avian.
use smell as primary sense = mammalian predators.
what examples of acts prey do to survive
dull - coloured birds (hard to see).
freese if sense predatrors
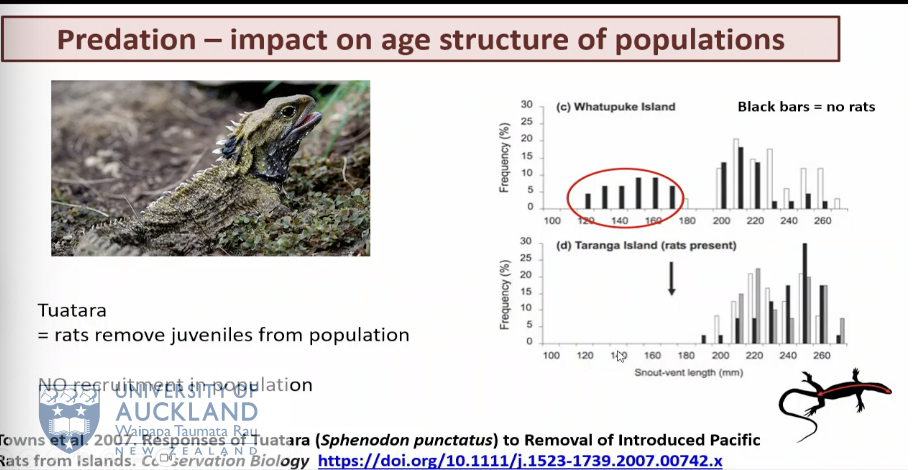
expalin the tuatara example.
rats present mean no young utuatara at all. no rats means healthy population and eaiven age distrubution.
no juvalines and will cause no recovery and recuiritment meaning no ptuatara population. so count of tuatrar doesnt matter as they will extinct due to lak of juvaniles.
explain how mammilian predators are bad
dogs kill allot of kiwi’s in most area.
possum is killing chicks of kiwi.
hedehog kill ground nesting birds, insects, reptiles.
what do cats cause
8 of our bird species are linked to cats and is why cats are bad.
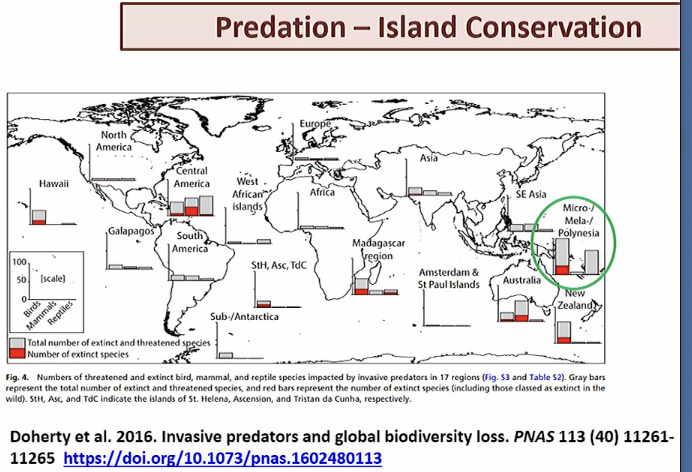
what does this mean
predators introduced impacts islands such as fiji (barred wing rail).
How does climate chagne impact islands predation.
sea level rising is wwipigng bird colonies. climate cuases stoats and rats to entre into alpine areas causing several indignous animals to die.
explain rpedator management.