5.2 Resistance & Resistivity
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
8 Terms
How does materials have _________ to the flow of charge?
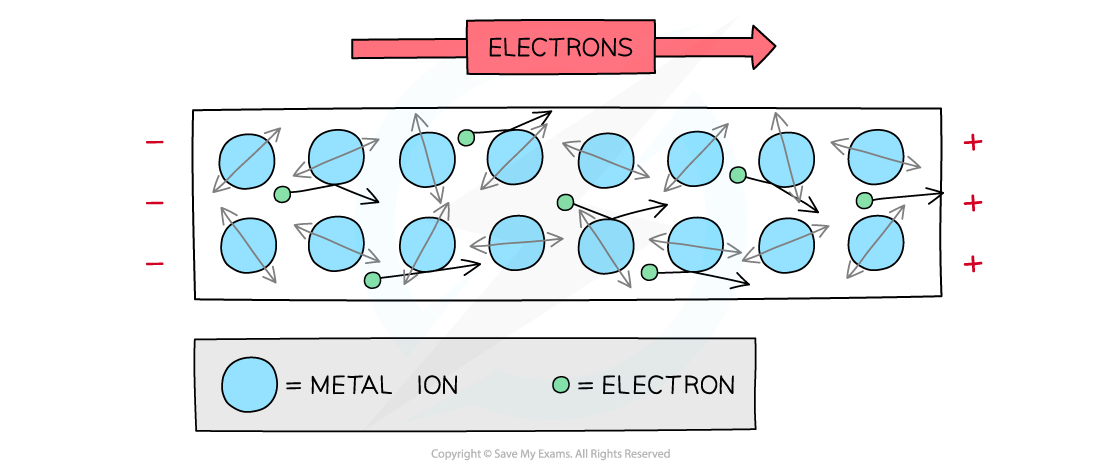
What is the relationship between free electrons as they move through the wire and ions?
Materials have resistance to the flow of charge: Current flow of charge, ions resisting flow causes resistance
Free electrons move through metal wire, collides with ions in the way so transfer some/all of their kinetic energy on collision causing electrical heating
What does resistance depend on?
Equation of Resistance and units =
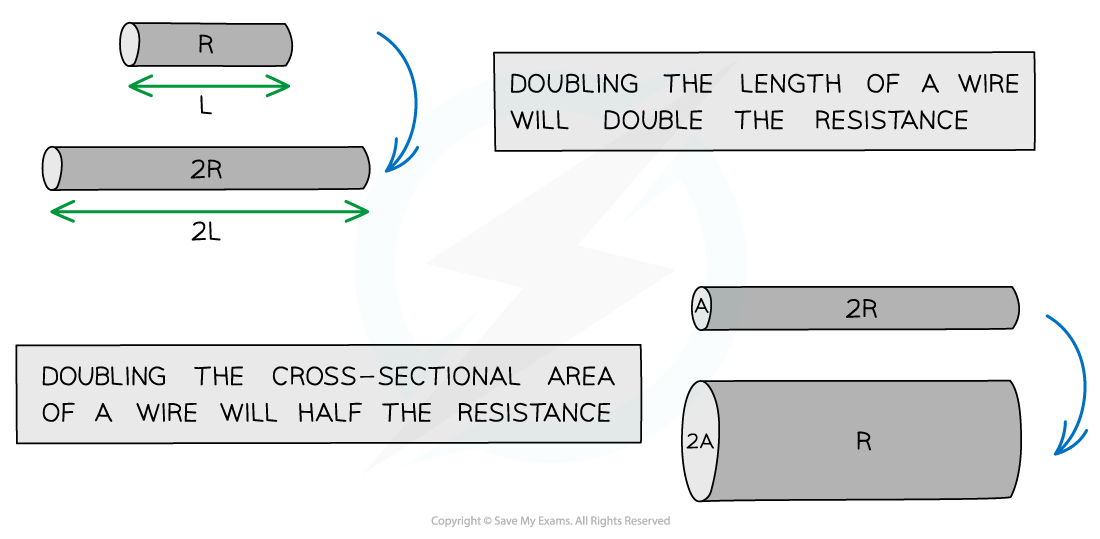
Resistivity equation: The longer the wire = ,The thicker the wire (cross-sectional area) =
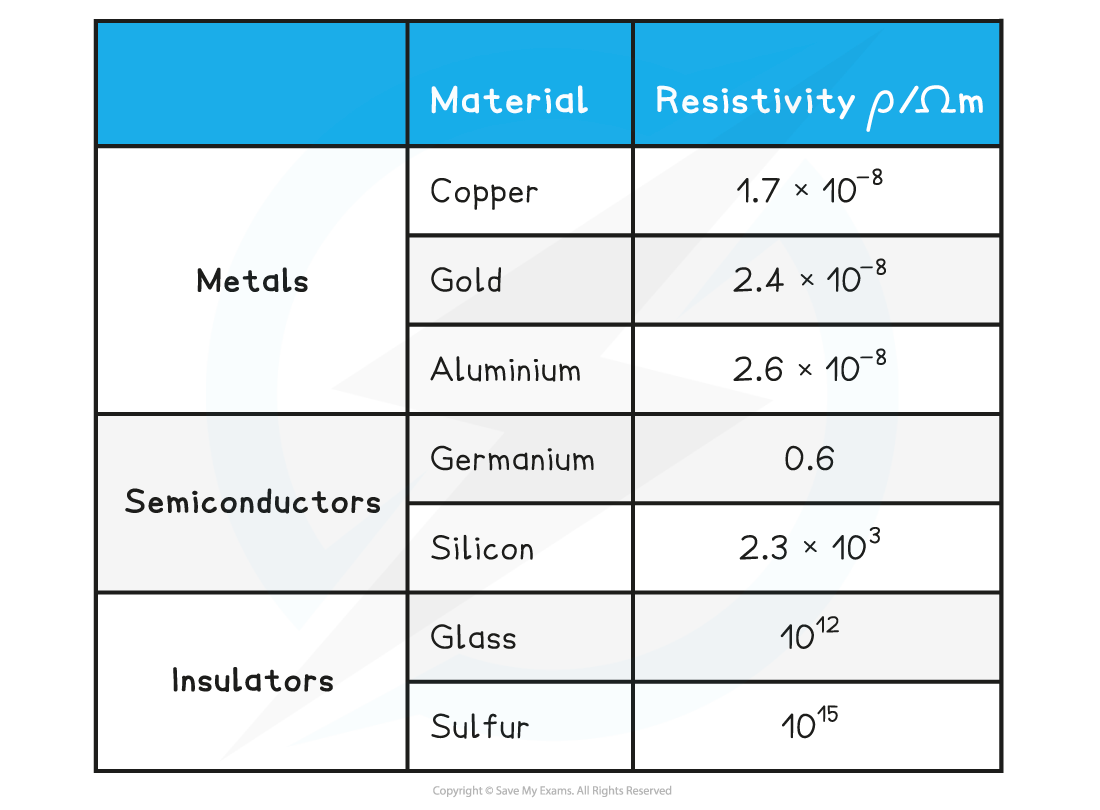
Resistivity (Ω m) is property describes….
Resistance depends on length of wire, cross-sectional area through which current passing, resistivity of the material
Equation of Resistance = R=ρL/A. A = Area = π × r/d2,
R = resistance ( Ω), ρ = Resistivity (Ωm) , L = length (m), Cross-sectional area (m2)
Resistivity equation: The longer the wire, the greater its resistance, The thicker the wire, the smaller its resistance
Resistivity (Ω m) is property describes extent a material opposes flow of electric current through it
Property of material, dependent on ______
Higher resistivity of material so it has…
Copper, relatively ______resistivity room temperature, used for electrical wires — ________ flows through very ______
Insulators have _____ resistivity, ______ current will flow through them
Cross-sectional area of a wire is proportional to the diameter ______ so if diameter doubles, area ______ causing resistance to ______ by a ________.
Property of material, dependent on temperature
Higher resistivity of material, higher its resistance
Copper, relatively low resistivity room temperature, used for electrical wires — current flows through very easily
Insulators have high resistivity, no current will flow through them
Cross-sectional area of a wire is proportional to the diameter squared so if diameter doubles, area quadruples causing resistance to drop by a quarter.
Solids: vibrating atoms
Higher the temperature =
What happens when electric current flows of free electrons in a material?
Current decreases, resistance will ________ (from _ = _ _)
What does metallic conductors obey and if temperature increases or decreases what does this cause?
In a thermistor what happens when increases in temeperature?
Solids: vibrating atoms
Higher the temperature, the faster these atoms vibrate
Electric current flow of free electrons in a material so electrons collide with vibrating atoms which impede their flow, so current decreases
Current decreases, resistance will increase (from V = IR)
Metallic conductor obeys Ohm's law: Increase in temperature causes increase in resistance, Decrease in temperature causes decrease in resistance
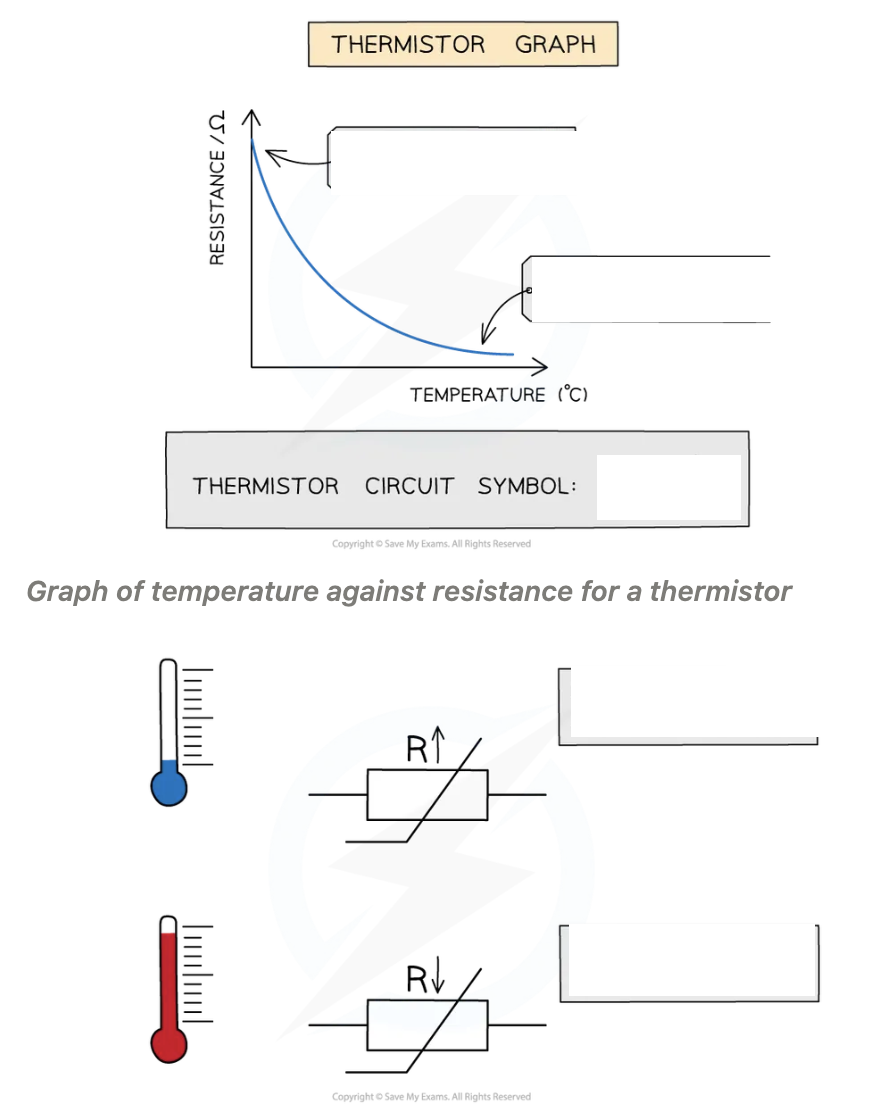
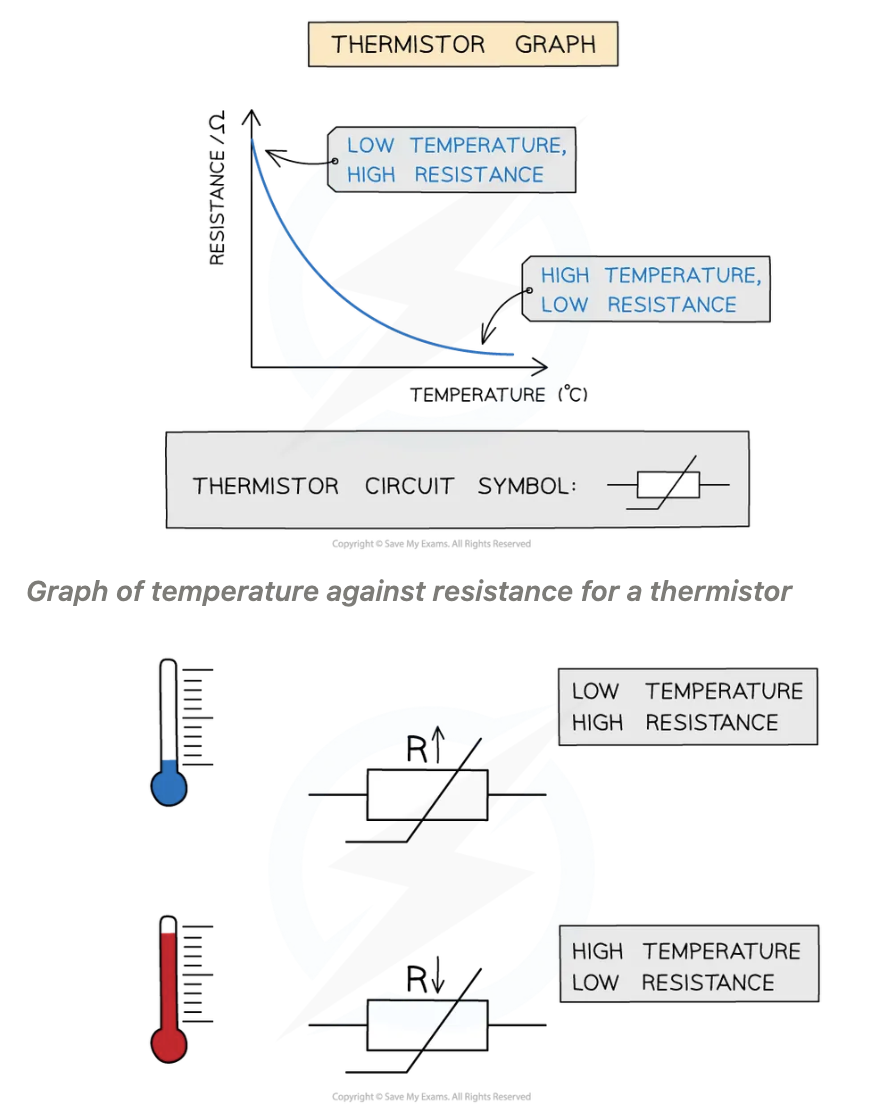
Thermistor, increase in temperature causes decrease in resistance
What is a thermistor?
What is ntc?
Thermistors temperature sensors uses:
Thermistor hotter, resistance _______
Thermistor cooler, resistance ______
Thermistor non-ohmic conductor, sensory resistor resistance varies with temperature
Most thermistor negative temperature coefficient (ntc) components so if temperature increases, resistance of thermistor decreases
Thermistors temperature sensors uses: circuits in ovens, fire alarms and digital thermometers
Thermistor hotter, resistance decreases
Thermistor cooler, resistance increases
Do all material have resistivity?
Resistance: ________ flows through material, ______ up and electrical energy _______ as _______ energy
How is resistivity of material lowered?
All materials have some resistivity - even good electrical conductors e.g. copper and silver
Resistance: electricity flows through material, heats up and electrical energy wasted as thermal energy
Resistivity of material lowered by lowering its temperature
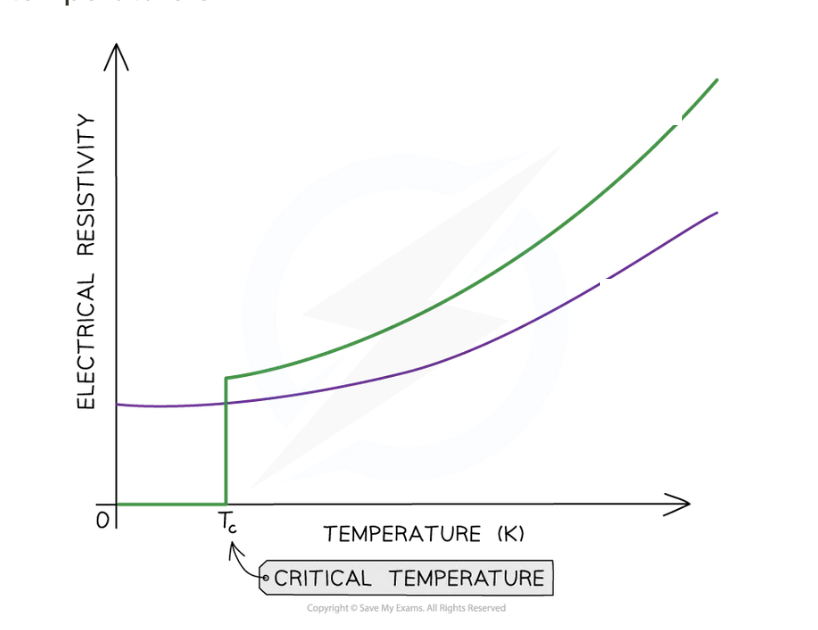
Superconductor:
Critical temperature/temperature threshold/transition temperature:
Common superconducting material:
Are all materials superconductors?
Superconductor: A material with no resistance below a critical temperature.
Critical temperature: The temperature at which a material becomes superconducting
Common superconducting material mercury has a critical temperature of 4.2 K
Superconductivity is property only certain materials have the characteristics above

Disadvantages of superconductors:
What are superconductors useful for?
Why is superconductors used in strong magnetic fields:
Applications:
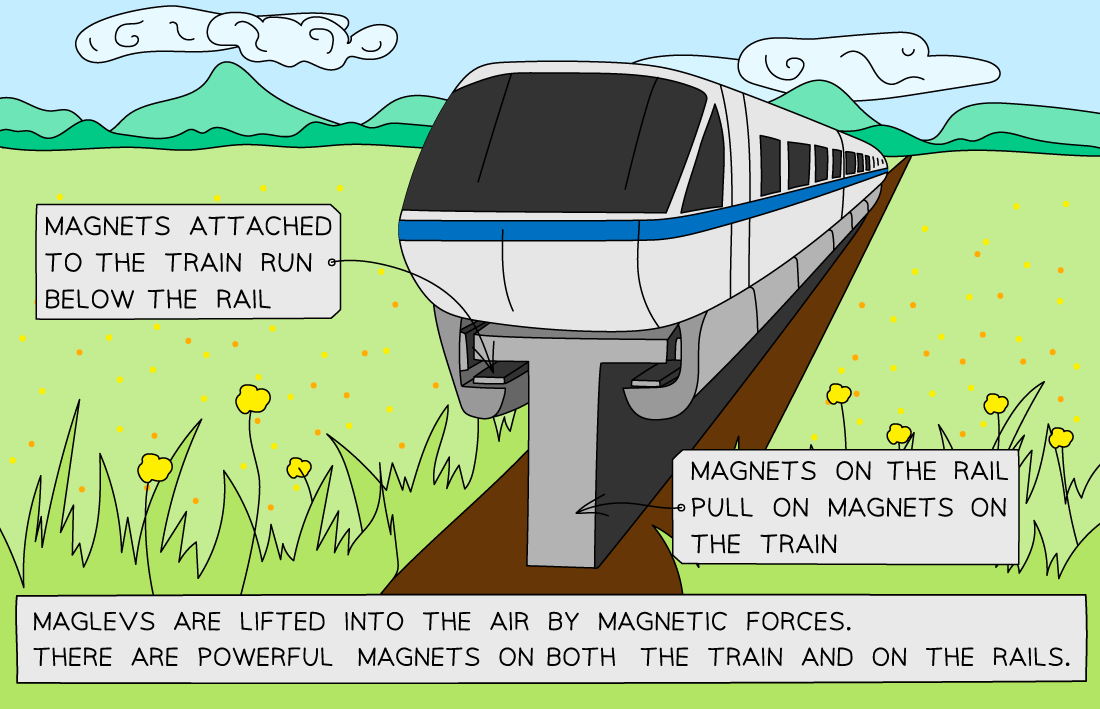
What and where are maglev trains?
Getting it having a low temperature cold is difficult and expensive - uses lots of power
Superconductors useful for applications that require large electric currents
Useful for production of strong magnetic fields, reduction of energy loss / dissipation in the transmission of electric power
Applications: MRI scanners, Transformers & generators - for fewer fire risks, Motors, Monorail trains, Maglev (magnetic levitation) trains, Particle accelerators - need large magnetic fields to accelerate particles, Fusion reactors, Electromagnets, Power / electrical cables, Microchips,
Maglev trains require extremely strong electromagnets to levitate the train due to such a large mass so cna travel at extremely high speeds up to 603 km / h
Maglev train systems currently only exist in Japan, South Korea and China