AMRI 300 weeks 6-10
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
79 Terms
Why is a gradient recalled echo (GRE) sequence faster than a spin echo (SE) sequence?
Question 1Select one:
The use of a long TR
The lack of 180 degree RF pulse and lower flip angle
The use of a 90 degree RF excitation pulse
The use of inversion time
The lack of 180 degree RF pulse and lower flip angle
Due to the decreased efficiency in refocusing spins, this pulse sequence is extremely sensitive to magnetic field homogeneity:
Question 2Answer
SE
GRE
IR
3DFT
GRE
What term describes the signal that follows the application of the initial 90-degree RF pulse?
Question 3Answer
Spin echo
Gradient echo
FID
Hahn echo
FID
Which of the following is NOT an advantage when performing GRE over SE pulse sequences?
Question 4Answer
Dramatically reduced scan times (due to short TR)
Lower RF power deposition
True T2 tissue contrast acquired
Increased number of slices per unit time
True T2 tissue contrast acquired
The peak signal strength of a spin echo is less than the initial strength of the FID because of ___________.
Question 5Answer
Magnetic susceptibility
T1 relaxation
T2 relaxation
Proton concentration
T2 relaxation
Why is a Spin Echo pulse sequence able to produce true T2 weighted images?
Question 6Answer
The 90 degree excitation pulse gives full transverse magnetization
The 180 re-focusing pulse corrects T2* decay and makes it true T2
There's no double FEG application, so that makes it true T2
The long 'dead time' after the 180 allows it
The 180 re-focusing pulse corrects T2* decay and makes it true T2
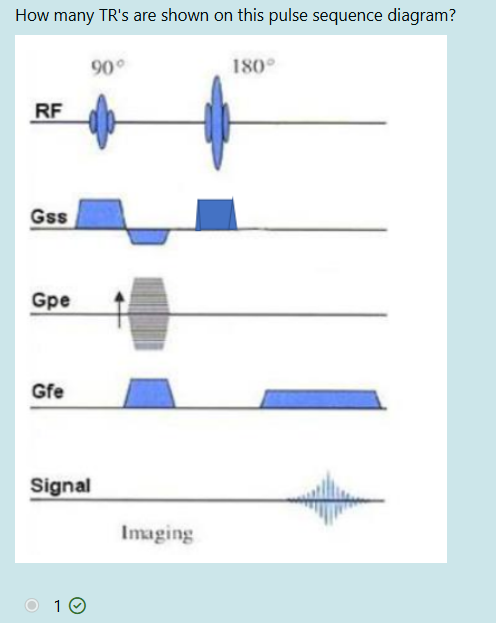
1
A pulse sequence that starts with a 90-degree RF pulse and is followed by only one 180-degree RF pulse is characterized as ___________ type of pulse sequence?
Question 8Answer
IR
GRE
CSE
Fat Saturated or Fat Suppressed
CSE
Compared to T2 weighted images, T2* looks:
Question 9Answer
More clear
Higher resolution
More crisp
Grainier (less signal rich)
Grainier (less signal rich)

A pulse sequence is repeated with similar parameters for all of K-space to make sure:
Question 2Answer
To mix T1 and T2 weighting in K-Space
To improve log function dynamic
For faster Fourier Transform
The image is diagnostic and has the same contrast all throughout
The image is diagnostic and has the same contrast all throughout
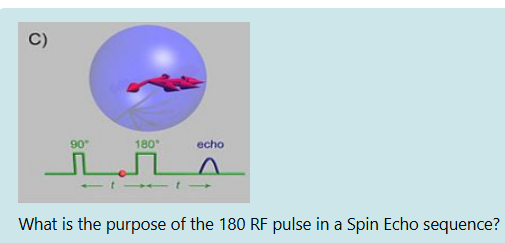
To flip the spins into the XY plane
To re-phase the spins after the FID to create an echo
To decrease the spin curve regression
To increase SAR
To re-phase the spins after the FID to create an echo
How can Spin Echo sequences create true T2 image contrast?
Question 6Answer
The 180 refocusing pulse corrects for chemical shift, susceptibility, and inhomogeneities.
Faster ADC enables this.
They are slower than GRE.
They have full transverse magnetization.
The 180 refocusing pulse corrects for chemical shift, susceptibility, and inhomogeneities.
Fast Spin Echo accelerates scan time by:
Question 7Answer
Using very short TRs
Using very short TEs
Using a low NEX value
Creating several echos every TR
Creating several echos every TR
What is Echo Train Length?
Question 8Answer
The middle sections of K-Space
The number of 180 refocusing pulses and echos created every TR
The time between echos
The time between 90's
The number of 180 refocusing pulses and echos created every TR
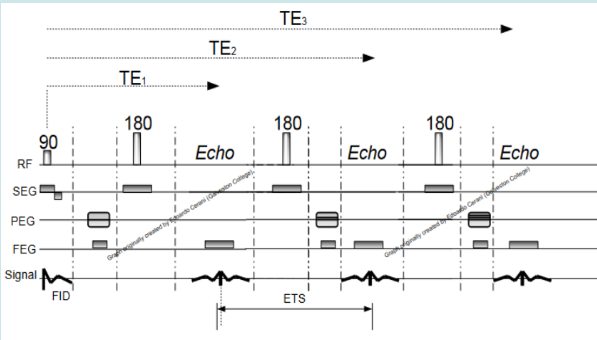
What is the ETL shown here?
Question 10Answer
1
2
3
4
5
3

FSE
GRE
CSE
STIR
GRE
Why does a larger flip angle produce more T1 weighting?
Question 15Answer
Allows for greater separation/contrast in Fat and Water spins as they return to Bo.
Makes the scan longer overall, and that always creates more T1 contrast.
Allows more time for the spins to de-phase.
Allows more turbo factor, which extends the TE
Allows for greater separation/contrast in Fat and Water spins as they return to Bo.
You should think of Ernst Angle as:
Question 16Answer
The null-point
The lowest possible flip angle
The fastest flip angle
The unrestrained flip angle
The optimal flip angle
The optimal flip angle
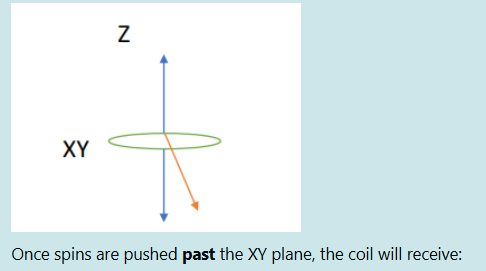
No difference in signal
Less signal
More signal
Less signal from Gadolinium
Less signal
Inversion Recovery Sequences start with:
Question 18Answer
Beta
A 180 degree inversion pulse
A 180 degree re-phasing pulse
Alpha
A 90 degree excitation pulse
A 180 degree inversion pulse
At 1.5 Tesla, a Tau of ~150 ms will be called a Short Tau Inversion Recovery Sequence, and void:
Question 19Answer
Watery tissue
Tendons and ligaments
Fatty tissue
Cancerous lesions
Fractures and Contusions
Fatty tissue
At 1.5 Tesla, a Tau of ~2000 ms will be called a Fluid Attenuation Inversion Recovery Sequence, and void:
Question 20Answer
Watery tissue
MS Lesions
Fatty tissue
Fractures and Contusions
Tendons and ligaments
Watery tissue
Gradient Recalled Echo uses:
Question 21Answer
a.
A 180 degree re-focusing pulse
b.
A turbo factor
c.
The FEG to re-phase the spins
d.
A variable flip angle
e.
An inversion pulse
C AND D
Which of these are advantages of GRE?
Question 22Answer
a.
Can be used to detect hemorrhage
b.
Short scan time (compared to SE)
c.
Lower SNR
d.
Creates more acoustic noise
e.
Less SAR
a,b,e
What is the purpose of IR?
Question 23Answer
a.
Void fluid
b.
Scan quicker
c.
Give T2* weighting
d.
Void fat
e.
Create more acoustic noise
a, d
One of the reasons we don't use the FID, is that it hasn't been spatially encoded by the PEG and FEG. This means the system doesn't know where to put it in K-Space.
Question 25Select one:
True
False
true
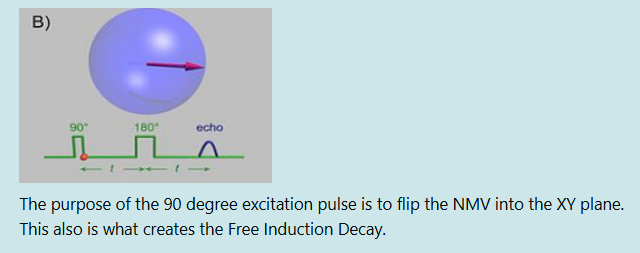
true
Any sequence with a 90 degree excitation pulse and a 180 degree re-phasing pulse is definitely SE or some variation.
Question 29Select one:
True
False
true
FSE, TSE, and RARE all mean the same thing.
Question 31Select one:
True
False
true
GRE heats the patient more than TSE.
Question 34Select one:
True
False
true
A sequence without 180 degree re-focusing pulses can still produce true T2 weighted images.
Question 35Select one:
True
False
false
Gradient applications can de-phase, but also re-phase the NMV.
Question 36Select one:
True
False
true
What mechanism rephases the dephasing hydrogen nuclei in a SE sequence?
Question 1Answer
180-degree RF pulse
90-degree RF pulse
The free induction decay signal (FID)
Gradient reversal after the 90-degree RF pulse
180-degree RF pulse
For a GRE sequence, what parameter suffers?
Question 3Select one:
Signal-to-noise ratio (SNR)
FOV
Resolution
Scan time
Signal-to-noise ratio (SNR)
In an IR pulse sequence, what is the term for the time between the initial 180-degree and the 90-degree RF pulse?
Question 4Answer
TE
TR
TI
T1
TI
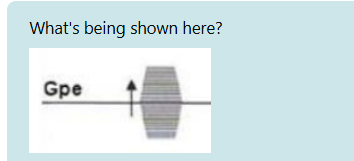
FEG being turned on during readout.
SEG turned on during the RF.
90 degree excitation pulse
PEG turned on to a different strength every TR.
PEG turned on to a different strength every TR.
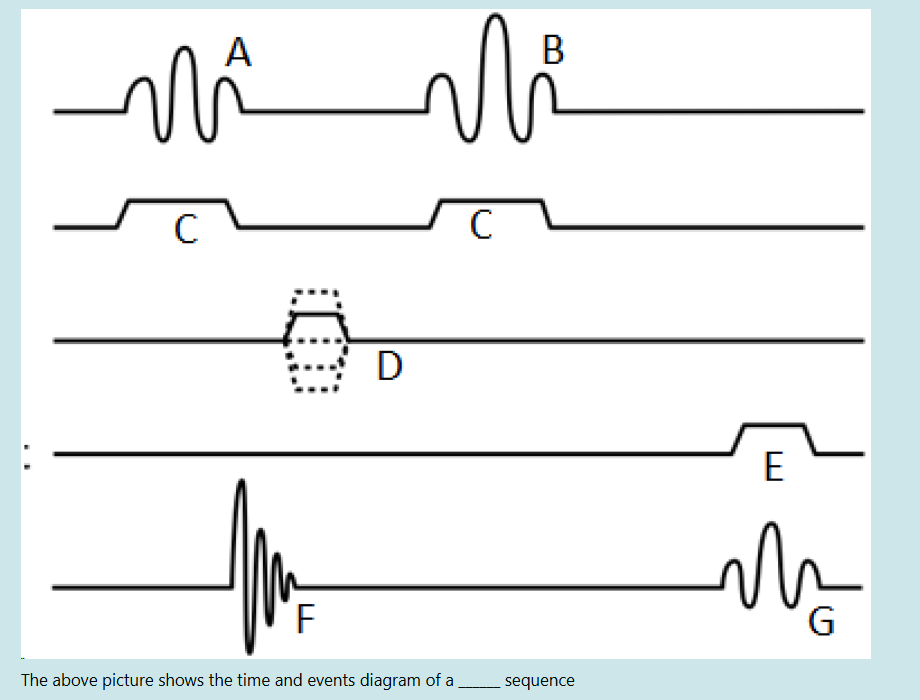
The above picture shows the time and events diagram of a ______ sequence
Question 8Select one:
SE
FSE
Double Echo SE
GRE
SE
note: 1 90 degree pulse followed by 1 180 degree pulse
A pulse sequence that starts with a 90-degree RF pulse and is followed by only one 180-degree RF pulse is characterized as ___________ type of pulse sequence?
Question 12Answer
IR
GRE
CSE
Fat Saturated or Fat Suppresse
CSE
Which parameter controls whether an IR sequence will be a STIR or a FLAIR?
Question 14Answer
TI (Tau)
ETL
TE
TR
ETS
TI (Tau)


Gfe
Gpe
Gss
Gra
Gss
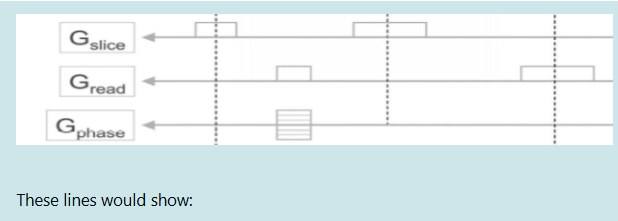
These lines would show:
Question 18Answer
RF Pulses
Analog to digital conversions
Gradient activity
Signal in the receive coil
Gradient activity
In GRE a total of _____ RF pulse/s are used in each TR
Question 19Select one:
3
2
1
4
1
In SE a total of _____ RF pulse/s are used in each TR
Question 20Select one:
1
4
2
3
2
After injection, paramagnetic contrast agents affect patient tissue in which of the following ways?
Question 1Answer
Decrease T1 relaxation time
Decrease T1 and T2 relaxation time
Increase T1 relaxation time
Increase T2 relaxation time
Decrease T1 and T2 relaxation time
For FGRE sequences, a steady state is achieved by:
Question 2Answer
TR=T1/T2
T1/TR/T2 x PEG steps
TR<T2<T1
TR = T1 squared x T2
TR<T2<T1
By repeatedly applying RF pulses with a short TR, the residual TM is refocused and contributes to the signal, leading to a steady state where the longitudinal (LM) and transverse (TM) magnetizations remain relatively constant from one TR to the next.
What is an oral agent used in MRI that is also used in CT?
Question 3Select one:
VoLumen
Radiopharmaceuticals
Iodinated contrast
Gadolinium
VoLumen
Many 0.3T open scanners ______.
Question 4Select one:
Higher net magnetism when compared to higher fields
The option for higher transverse magnetism when compared to higher fields
Do not have the capability of obtaining a T1 weighted image
Do not have a chemical fat saturation option
Do not have a chemical fat saturation option
At lower field strengths like 0.3T, the frequency difference between fat and water signals is smaller, making it difficult for the RF pulse to isolate and suppress fat effectively
Which of these pulse sequences has a mechanism to minimize the effect of slight inhomogeneities in the magnetic field?
Question 5Answer
CSE
GRE
PC-TOF
None of the above
CSE
The 180 degree refocusing pulse?
What can be run post gadolinium injection to obtain a fat saturation image?
Question 6Select one:
Chemical Fat Saturation
Standard T2
Standard T1
STIR
Chemical Fat Saturation
No, STIR (Short TI Inversion Recovery) sequences are generally not recommended after gadolinium administration in MRI. STIR is a fat suppression technique that relies on T1 relaxation times, and gadolinium shortens T1, potentially causing both fat and enhanced tissue to appear dark, obscuring the desired contrast effect.
At 1.5 T the difference between water and fat precessional frequency is about:
Question 8Answer
220 Mhz
220 Hz
3 Hz
120 Hz
440 Hz
220 Hz
The most common way GBCA's are used in clinical MRI sequences, is to take advantage of their:
Question 9Answer
Ferrous properties
Increased T2 times
Increased T1 times
Diamagnetic properties
Increased T1 times
The most important attribute of Steady State GRE sequences is their:
Question 3Answer
Extremely short TR's
Echo Train Length
T2 image weighting
Thick slices
Extremely short TR's
FGRE sequences that begin with a combination of RF pulses before the sequence begins are known as:
Question 4Answer
Prepared
Inverted
Exam Refined
Rectified
Prepared
How does flow compensation work?
Question 5Answer
Extra FEG lobes to correct for flow artifact.
Uses spoilers to reduce phase coherence between TRs.
Three PEG applications every TR.
Extra inversion pulses to correct for flow artifact.
Extra FEG lobes to correct for flow artifact.
Brain tumors are seen very well post gad because:
Question 6Answer
They have low proton density.
These tumors disrupt the blood-brain barrier and allow the gad into them.
They increase T2 times.
They stay enhanced longer than other tissues.
These tumors disrupt the blood-brain barrier and allow the gad into them.
Why do MS lesions show up as T2 hyperintensities?
Question 8Answer
That area has hemorrhage.
MS is an infection.
Inflammatory processes are generally T2 hyperintense.
MS are malignant tumors.
Inflammatory processes are generally T2 hyperintense.
Why do protocols include post contrast T1 Fat/Sat sequences?
Question 9Answer
Because fatty tissue is abnormal.
Because abnormal areas are T2 hyperintense.
To help differentiate abnormal enhancement from regular fatty tissue.
To reduce scan time.
To help differentiate abnormal enhancement from regular fatty tissue.
Why couldn't you just have the patient drink a lot of water as PO contrast for an MR of the abdomen?
Question 10Answer
The peristalsis would create too much motion.
It would be too T2 hyperintense to be diagnostic.
The SAR levels would increase rapidly.
The patient would need to urinate and be unable to finish the exam.
The water would be quickly absorbed by the jejunum.
The water would be quickly absorbed by the jejunum.
Fat Saturation sequences saturate the fatty tissue with what?
Question 13Answer
Signal
RF energy
Gradients
Contrast
RF energy
The number of slices that can be scanned in one concatenation/acquisition depends on:
Question 18Answer
Bo
Resolution
TE
FOV
TR
TR
Max number of slices is 12 with the TR you've selected. You prescribe 40 slices. Without changing TR, how many concatenations are required for this sequence?
Question 19Answer
1
2
3
4
5
4
The purpose of a gap in between slices is:
Question 20Answer
Increase in-plane resolution
Reduce partial-voluming
Eliminate or reduce cross-talk
Decrease gradient load
Eliminate or reduce cross-talk
If slice order was 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8, it would be called:
Question 22Answer
Interleaved
Extricated
Interpolated
Contiguous
Extrapolated
Contiguous
If slice order was 1,3,5,7,2,4,6,8 it would be called:
Question 23Answer
Extrapolated
Interleaved
Extricated
Interpolated
Contiguous
Interleaved
SSFSE is used for:
Question 25Answer
a.
Cardiac MRI
b.
Spine MRI
c.
Ankle MRI
d.
Abdomen MRI
e.
Fetal MRI
A,D,E
Which pulse sequences combine Spin Echo and Gradient Recalled Echo components?
Question 26Answer
a.
EPI
b.
SPGRE
c.
SE DWI EPI
d.
GRASE
e.
SSFSE
c,d
Which types of contrast are no longer approved or no longer produced?
Question 28Answer
a.
Gadolinium Chelate Injections
b.
Iron Oxide Injections
c.
PO contrast made of Gadolinium, Manganese, or Iron
d.
Manganese Injections
b,c,d
Which are names for Fat Saturation?
Question 29Answer
a.
F/S
b.
CHESS
c.
Chemical Fat Suppression
d.
IR Prep
e.
DWI
a,c
What are the drawbacks of increasing slice thickness?
Question 30Answer
a.
Lower T1 and T2 contrast
b.
Lower in-plane resolution
c.
Lower matrix size
d.
Possible partial-voluming of small pathology
b,d
Which are advantages of increasing slice thickness?
Question 31Answer
a.
Less slices are required to cover a volume of anatomy
b.
Less cross-talk
c.
More slices can be obtained in every concatenation
d.
Better signal to noise
a,d
All MRI pulse sequences are built on a variation of either SE or GRE.
Question 32Select one:
True
False
true
Double Echo Spin Echo acquires a line of K-Space for a T1 weighted image and a T2 weighted image during each TR.
Question 34Select one:
True
False
flase
it acquires a PD and a T2 at the same time NOT T1
Fractional NEX and Partial Fourier mean the same thing.
Question 35Select one:
True
False
true
Areas with faster T1 relaxation are brighter on T1 weighted images.
Question 36Select one:
True
False
true
Eovist liver protocols should include a 20 minute delayed 'hepatobiliary' phase after the injection.
Question 37Select one:
True
False
true
STIR sequences can be used to see IV gad enhancement.
Question 39Select one:
True
False
false
bc the contrast shortens the t1 and t2 times to the point that the frequencies of water and fat become too unpredictable. if we don’t know the exact processional rates and inversion time required to null one of them (oversaturate), we cant do a proper STIR