2.1 - Geographically-Discriminatory Trade Policies
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
8 Terms
RTA no. over time
Since 1992 the no. of RTAs has exploded
RTAs easier to agree on than multilateral agreements
Not all between geographically close nations
Post 2015 no. new RTAs has fallen
Countries running out of plausible new partners
Lower incentives to deepen integration
Spike in 2021 from disintegration - Brexit & its new deals
GATT / WTO and RTAs
GATT / WTO based on multilateral approach
Regionalism is the most significant exception to the non-discriminatory rules
3 sets of rules:
Article 24 of GATT
Enabling clause
Article 5 of GATS
Article 24 of GATT
FTAs & CUs allowed if trade barriers post integration don’t rise on average
tariffs or NTB barrier not raised
Enabling clause
Allows preferential treatment towards developing countries + Permits RTAs between developing countries for trade in goods.
Theory is that RTAs increase growth
This is the basis for GSP
Developed nations offer non-reciprocal preferential treatment to goods from developing
Sometimes GSP used for political reasons BAD
GATS article 5
Establishes conditions that permit trade liberalisation in services among regional partners
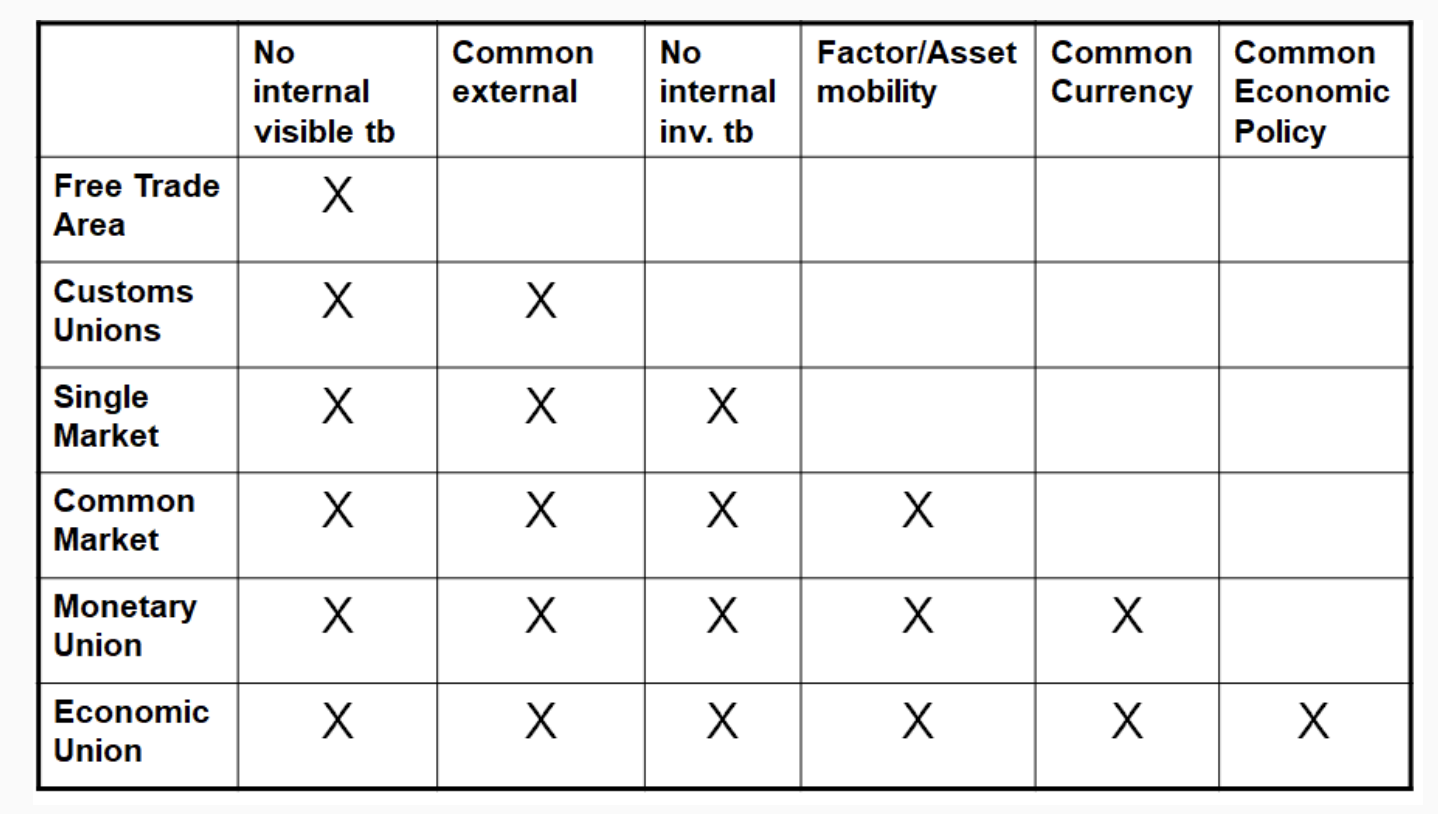
Structures of RTAs
Split of RTAs notified to WTO
FTAs - 60%
CUs - 10%
Other - 30%