Ch. 14 Quiz- Monopoly
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
How did DeBeers keep the price of diamonds so high for so long?
DeBeers restricted the number of diamonds available for sale
A monopoly…
a. is a price taker
b. faces competition from other firms producing close substitutes
c. restricts its output
d. sets a low price by controlling the level of output
c. restricts its output
Which of the following is a potential barrier to entry into a monopoly market?
a. fixed costs are large relative to variable costs
b. diseconomies of scale exist
c. the required infrastructure for an industry is low cost
d. consumers prefer to buy from monopoly producers
a. fixed costs are large relative to variable costs
The government protects intellectual property rights because they…
encourage research and development
When the monopolist chooses its quantity supplied, it will set the price…
equal to the amount consumers are willing to pay for that quantity
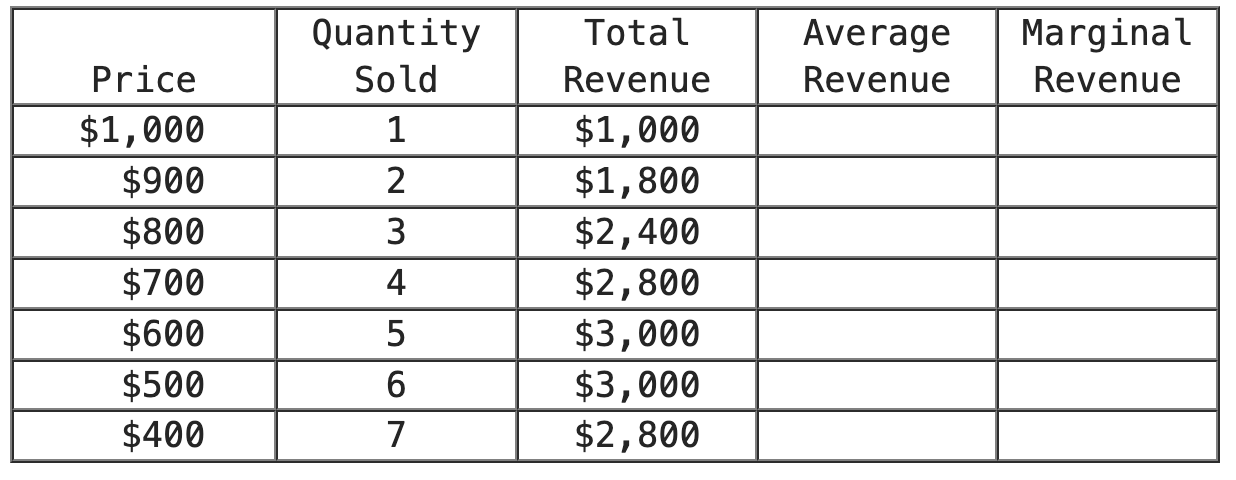
The table represents the revenues earned by a monopolist. Graphing the first two columns of the table will yield which curve?
market demand
For a monopolist, the quantity effect…
is the increase in revenue from selling a greater quantity at a lower price
For a monopoly producing at any output level greater than one, the average revenue curve…
is the same as the demand curve
The profit-maximizing decision for the monopolist
is to produce at the quantity where marginal cost equals marginal revenue
The monopolist is able to enjoy profits in the long run for all of the following reasons EXCEPT…
a. its price is set above its marginal costs
b. there is no threat of competition
c. it can charge a price that is higher than its average total costs
d. its marginal cost equals its average revenue
its marginal cost equals its average revenue
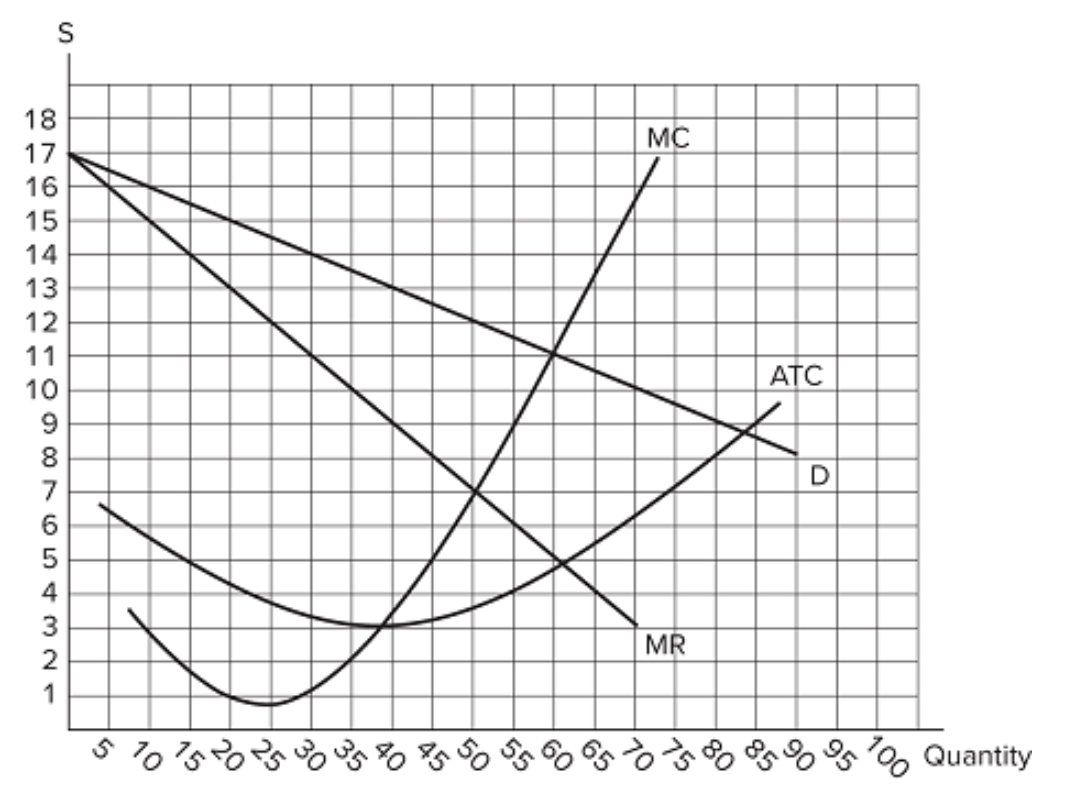
This graph shows the cost and revenue curves faced by a monopoly. The profit-maximizing price is…
$12
Which one of the following is NOT a reason a firm may lose some of its monopoly power?
a. antitrust laws
b. vertical or horizontal splits
c. pressure from consumers
d. economies of scale
economies of scale
The presence of a privately owned monopoly is beneficial to…
the monopolist
With regard to monopolies, economists believe…
a. the government should never intervene in a natural monopoly market
b. the reduction in efficiency can be offset by increases in equity
c. the gains from maintaining a monopoly never outweigh the total welfare costs due to lost surplus
d. whether or not to maintain a monopoly is a normative argument that has no right answer
d. whether or not to maintain a monopoly is a normative argument that has no right answer
Some economists argue the best response to a monopoly is to
do nothing at all
Natural monopolies
can capture the lowest production costs possible for the industry
A consequence of a publicly owned natural monopoly is…
the loss of the profit motive
Some argue that the best government response to monopolies is no response at all, because…
the creation of effective regulation may be too difficult
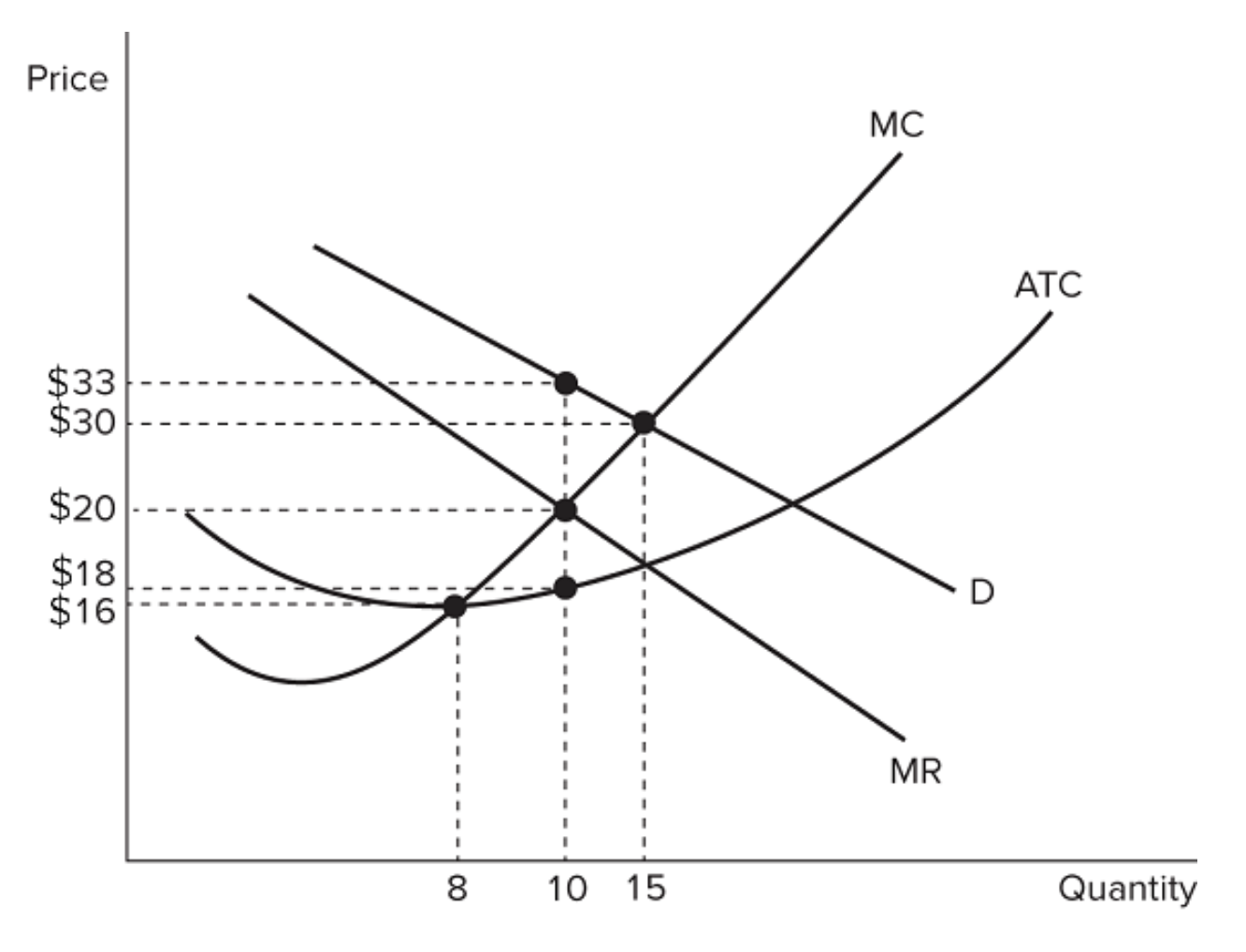
The graph shown represents the cost and revenue curves faced by a monopoly. What profit is earned by the monopolist in the short run?
$150
Which of the following goods has no close substitutes?
a. water
b. a Hershey’s chocolate bar
c. an IBM PC
d. Forever Amber, a romance novel by Kathleen Winsor
a. water