BISC 202 prokaryotes (W6-9)
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
what is the most unique thing about sexual reproduction compared to asexual reproduction?
sexual reproduction produces individuals with new genetic combinations, as the alleles from two sources mix and produce a genetically-distinct offspring
sex and reproduction in eukaryotes
sex, which is making new genetic combinations, and reproduction, which is making new cells, are separate events
reproduction in prokaryotes
in prokaryotes, there is no meiosis and cells divide by binary fission
prokaryotes only have one circular chromosome, and sometimes some small circular plasmids, they are not diploid
sex in prokaryotes

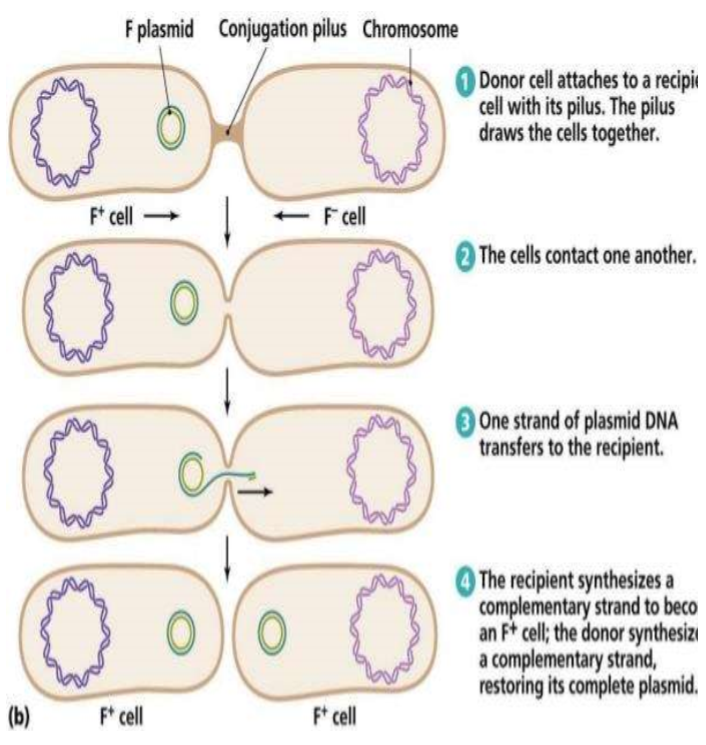
conjugation
a “donor” cell forms a pilus that can attach it to a “recipient” cell
it can then transfer a copy of a plasmid (or even parts of the chromosome) to the recipient cell
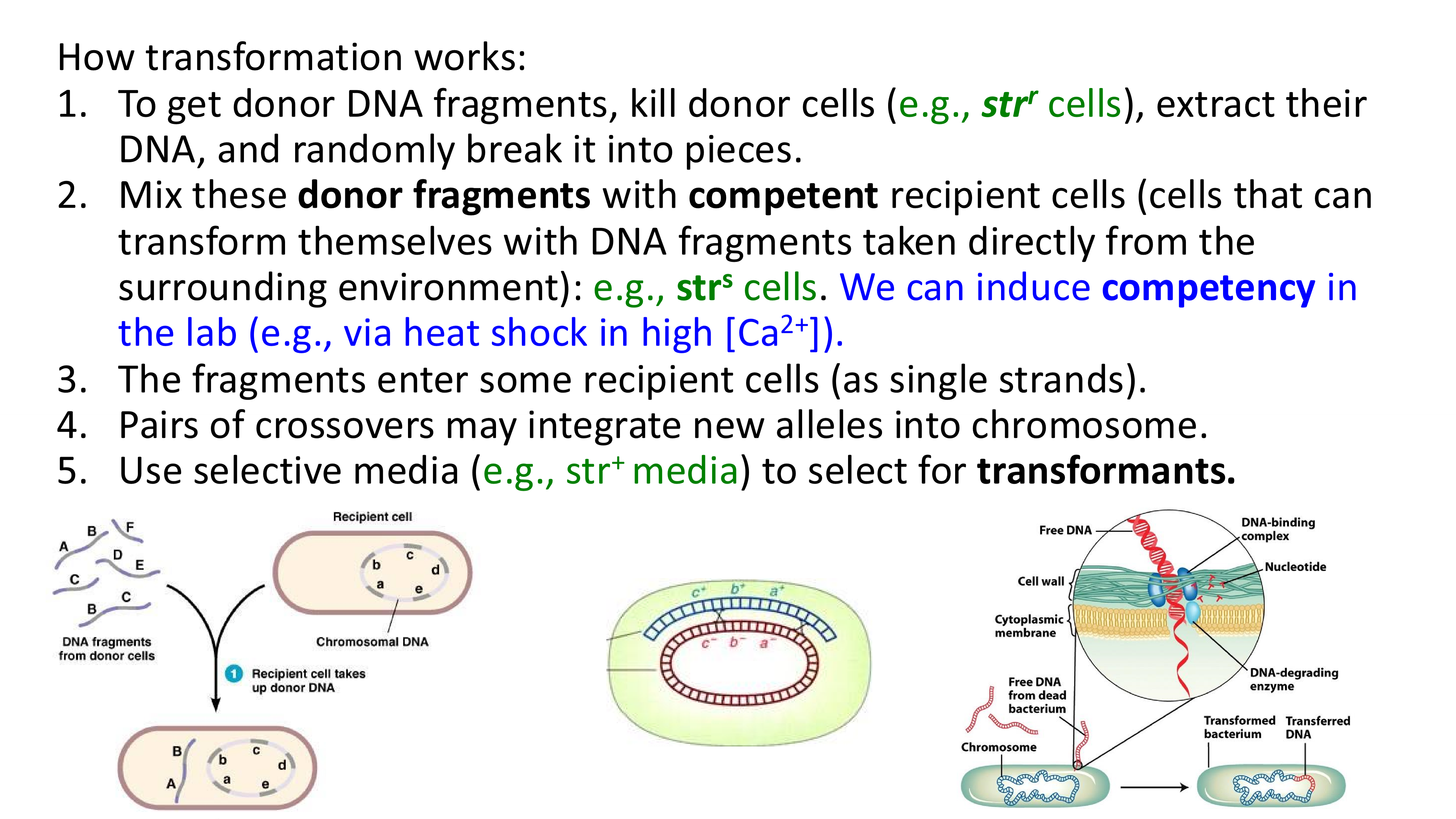
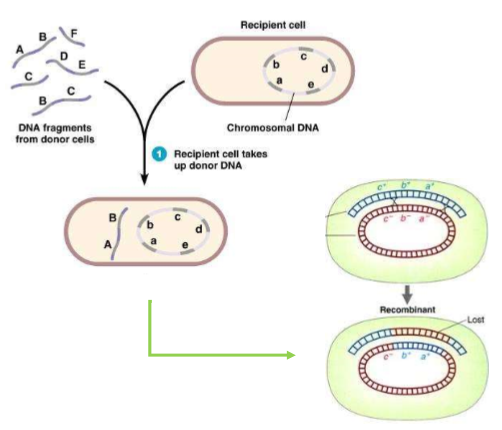
transformation
a recipient cell can pick up DNA fragments from the surrounding environment and incorporate pieces of it into its genome through pairs of crossover events
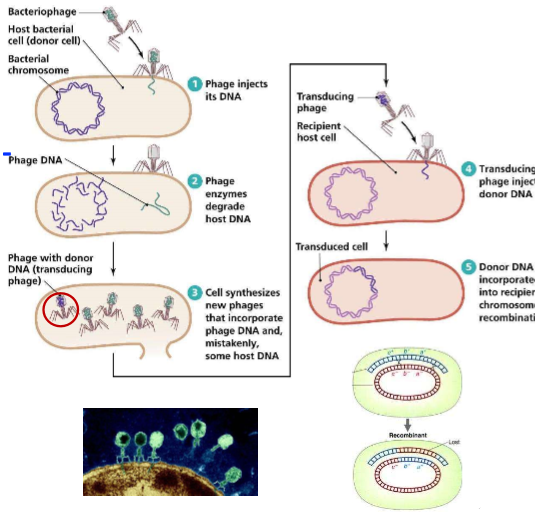
transduction
a bacteriophage (a bacteria infecting virus) can transfer some DNA from its previous host into the recipient host cell
normally, phages only hold phage DNA, but sometimes the new phage protein coat accidentally carries some bacterial DNA, instead
advantages of working with bacteria

selection systems
kill or prevent growth of cells that don’t have the trait we want, so that we can pick out one or a few cells with the desired trait form among billions of cells
ex. antibiotic resistance, metabolic requirements
antibiotic resistance
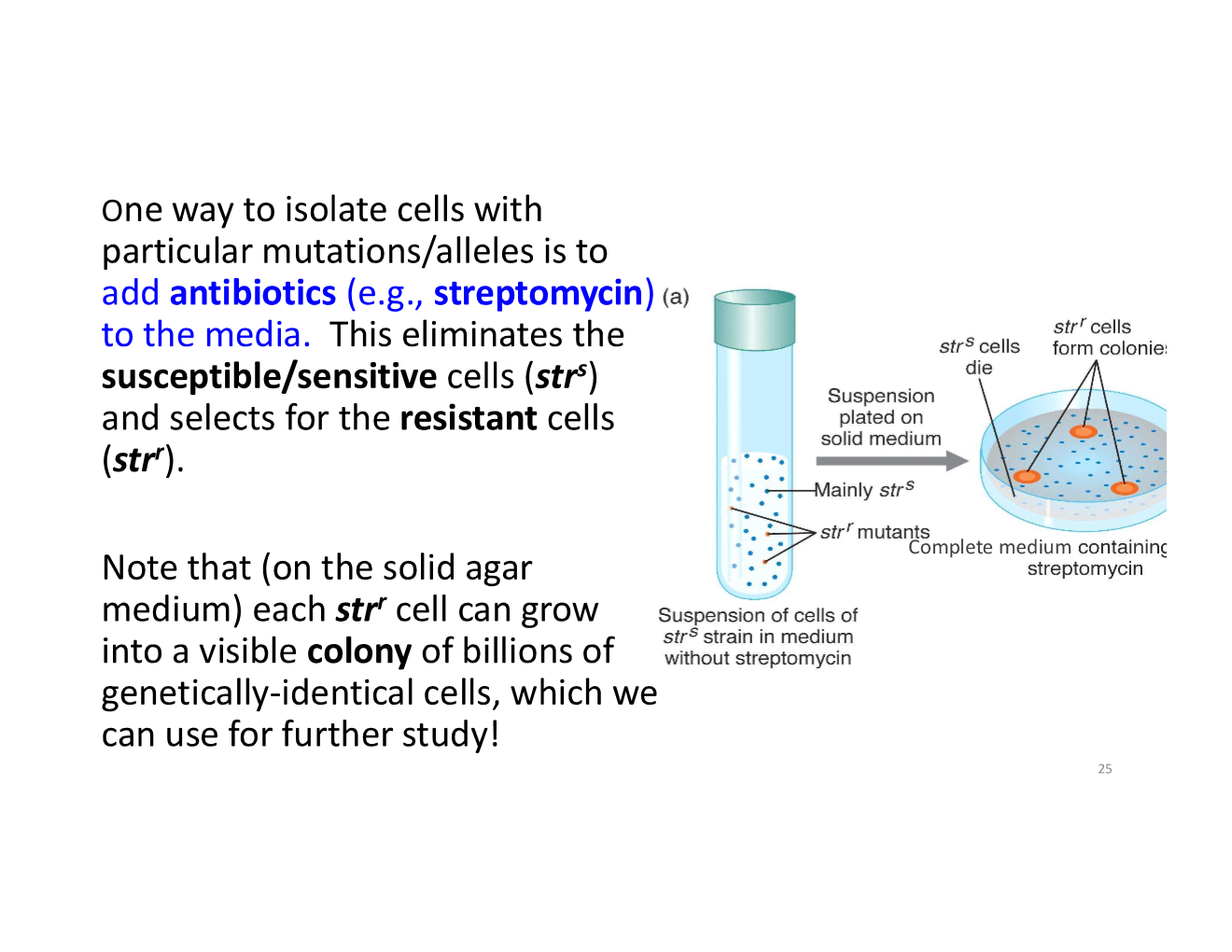
grow cells in large numbers in liquid culture lacking the antibiotic - then “plate” large numbers of cells onto solid medium containing the antibiotic; the few cells that grow have gained resistance and their descendants form colonies

metabolic requirements
grow cells in liquid culture containing particular nutrients, and then plate large numbers of cells onto solid medium lacking these nutrients; only cells that can produce the missing substances will survive
what is one way to isolate cells with particular mutations/alleles?
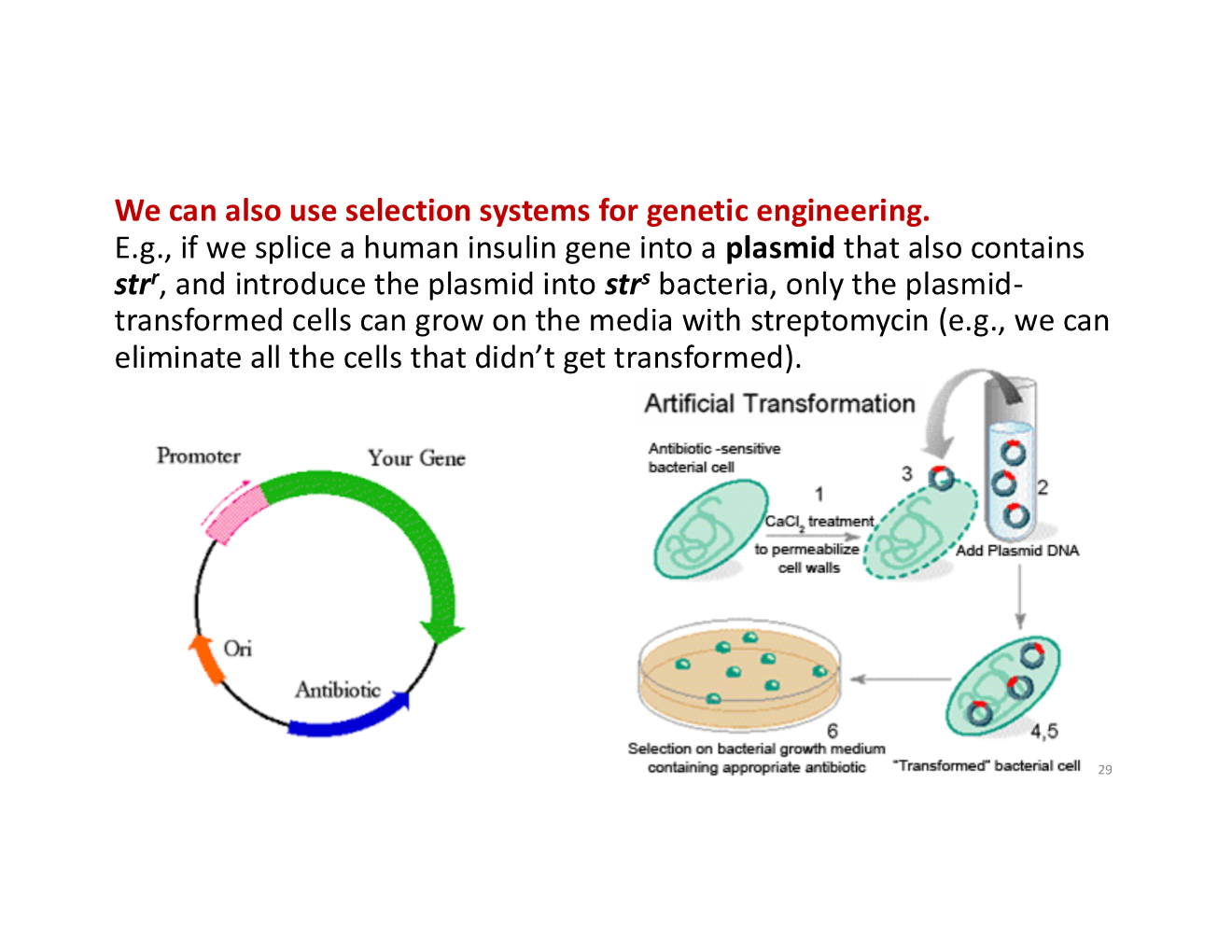
how can we use selection systems for genetic engineering?
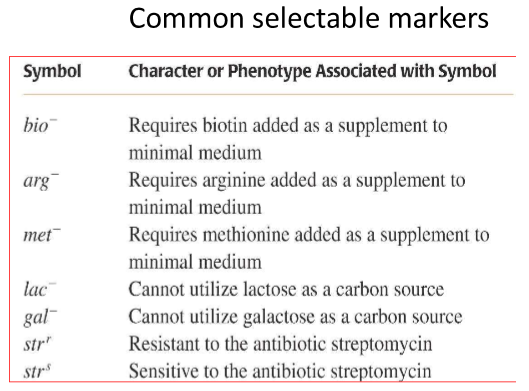
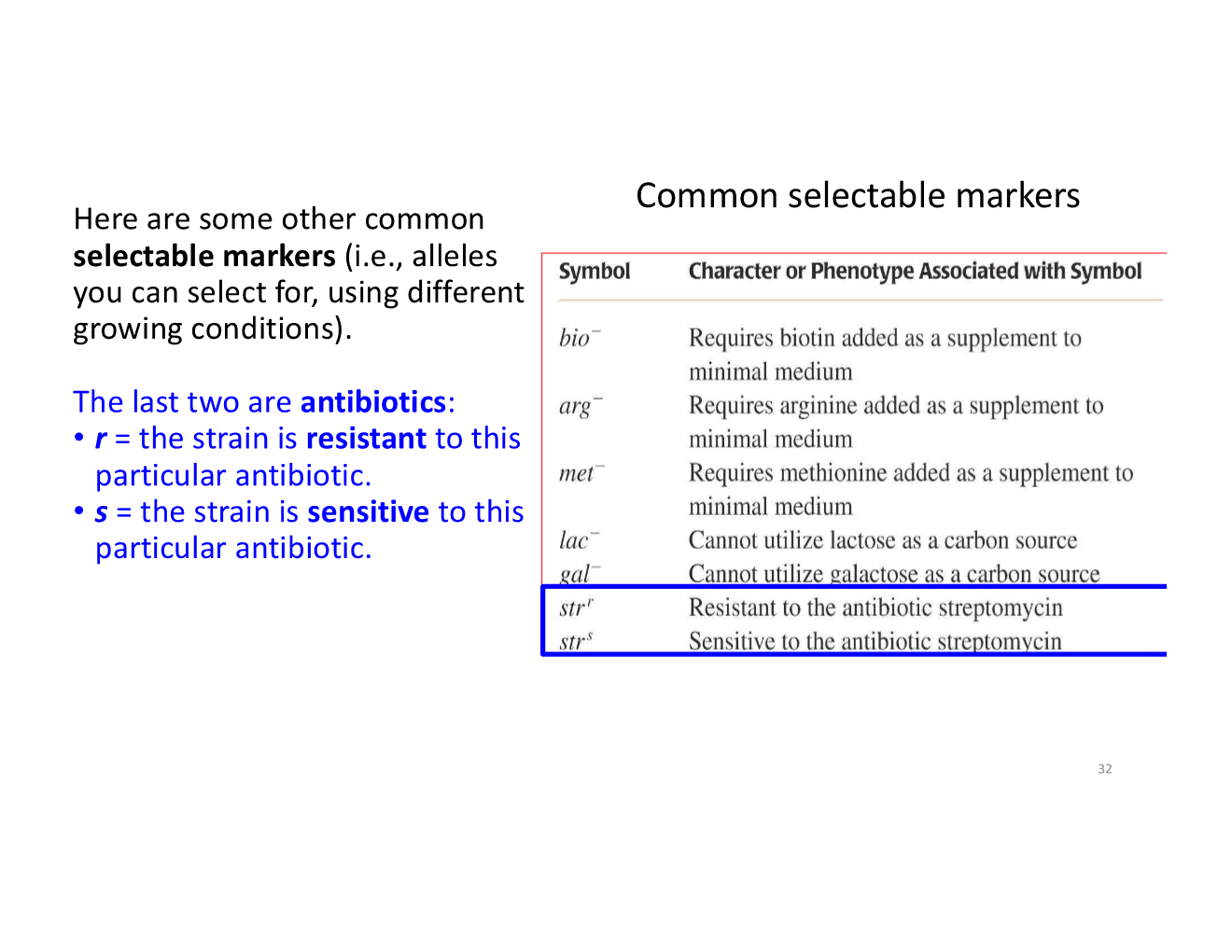
selectable markers
alleles you can select for, using different conditions
common selectable markers
bio-, arg-, and met-
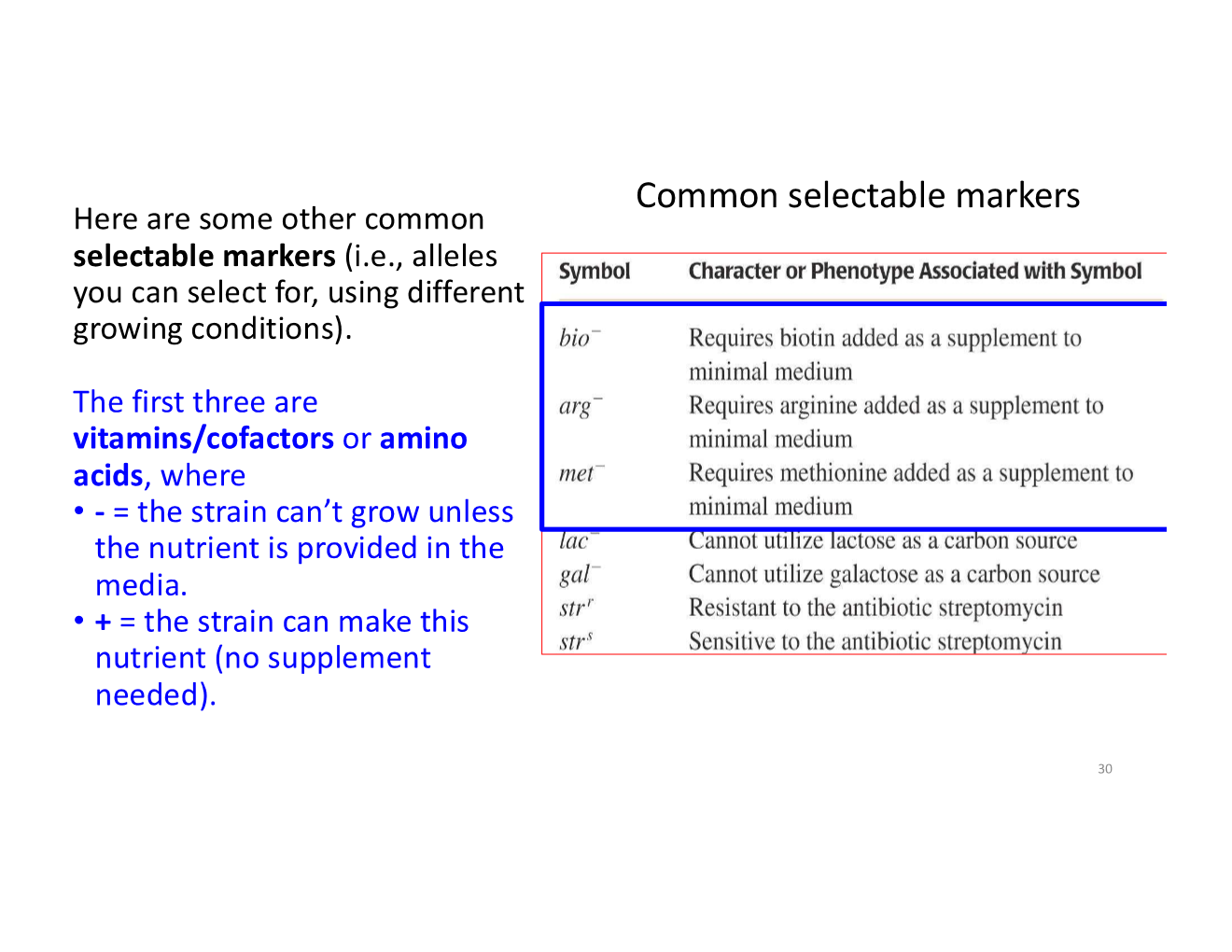
lac- and gal-
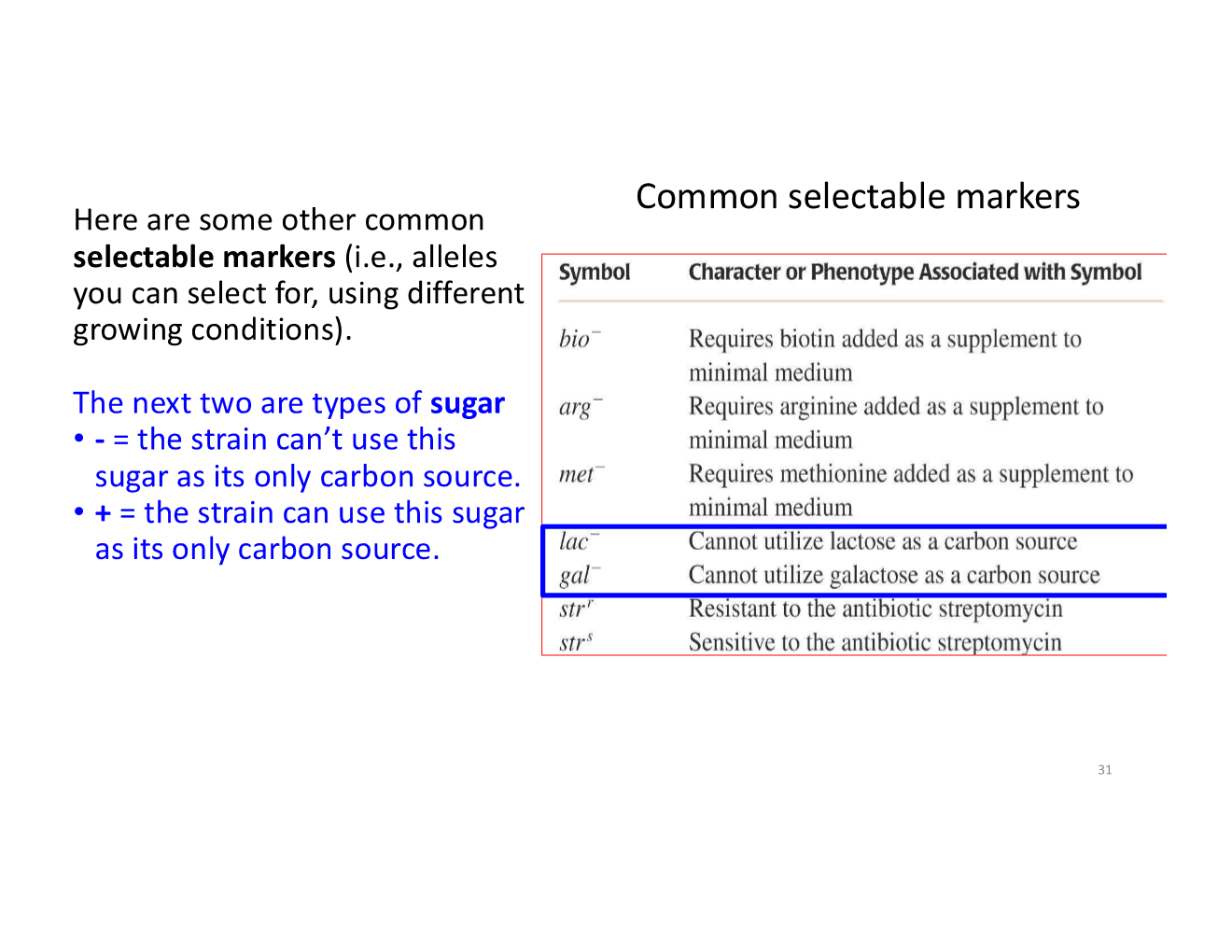
strr and strs
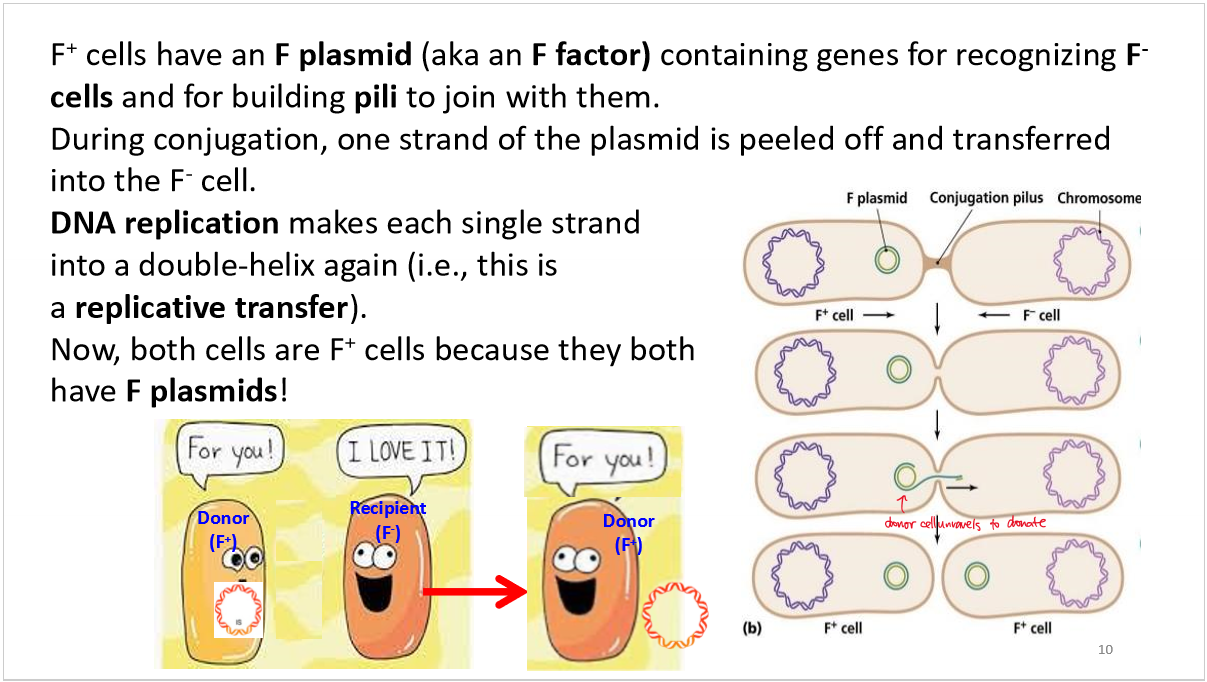
nature of conjugation

if the donor cell is not labelled F+ :
it cannot recognize the other cell
it cannot create a pilus
it cannot give away their genetic material
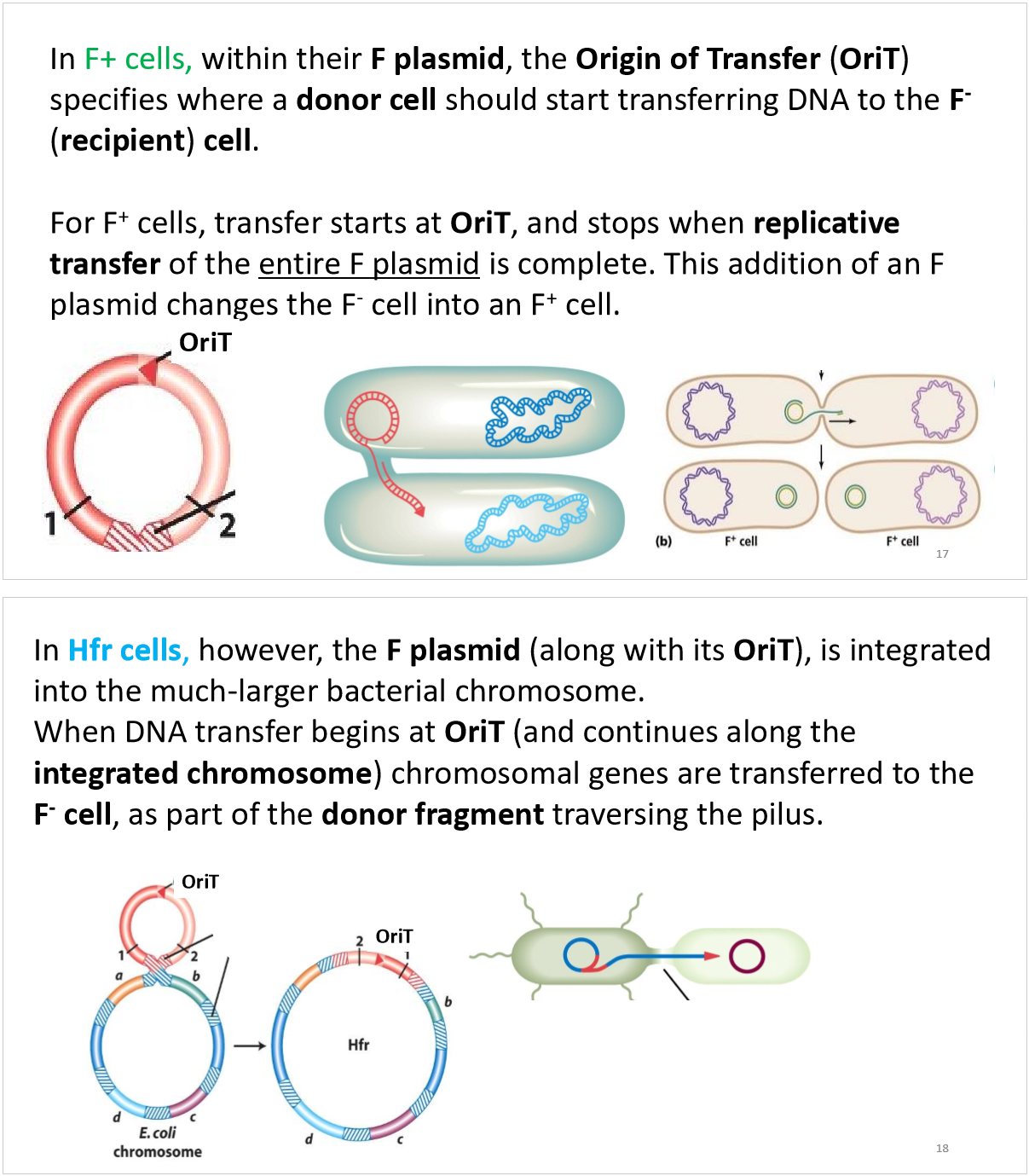
F plasmid
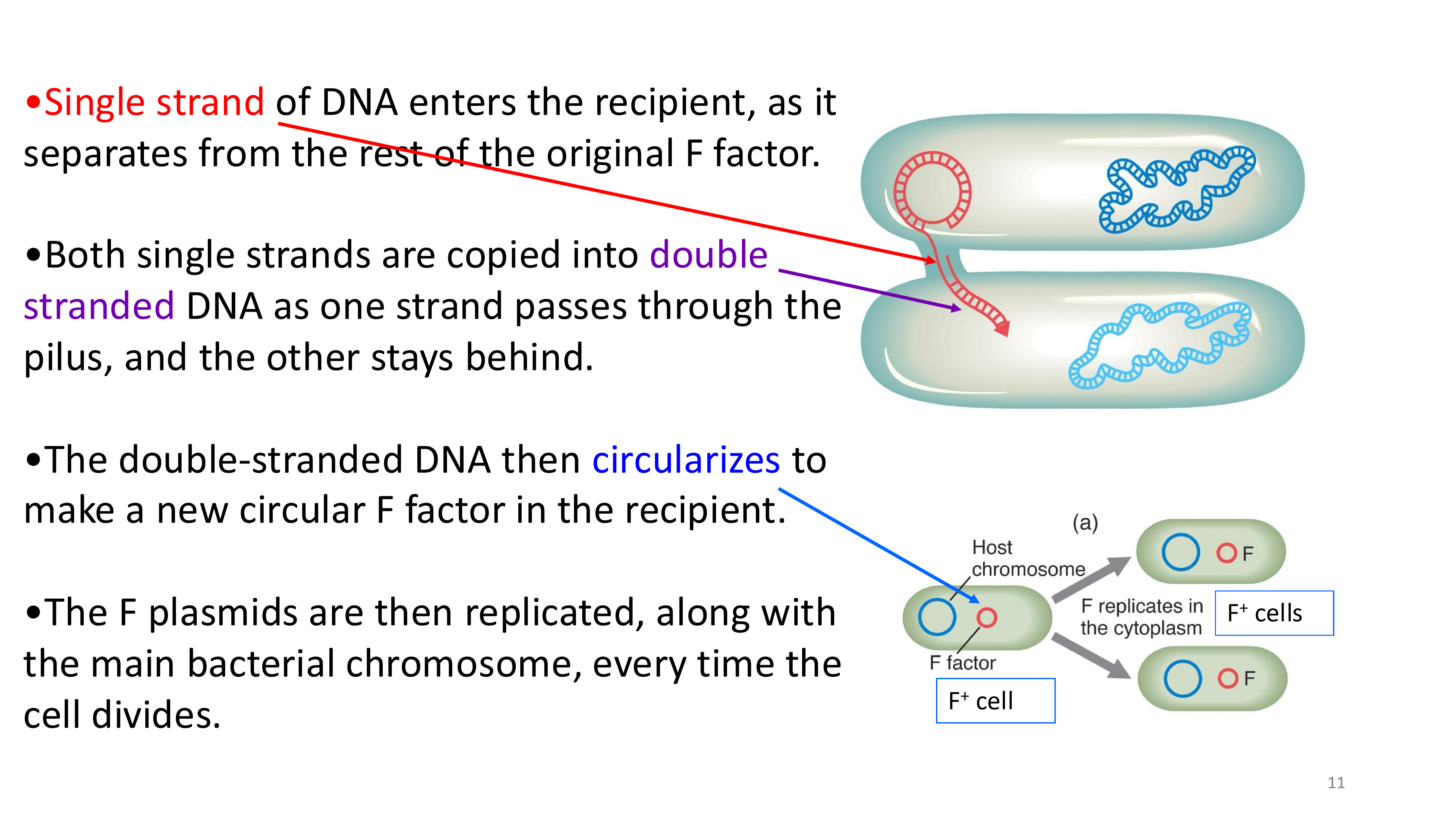
how is the F plasmid transferred and replicated during bacterial conjugation?
what happens when the F factors is integrated into the bacterial chromosome?
the F+ cell becomes an Hfr (high frequency recombination) cell
can Hfr cells still donate DNA to F-/recipient cells?
yes, because Hfr cells still have the F plasmid’s genes for forming pili and donating genes (e.g., same genes, just different arrangement)
are Hfr cells more or less likely to donate chromosomal genes to recipient cells, when compared to F+ cells?
1000x more likely
OriT
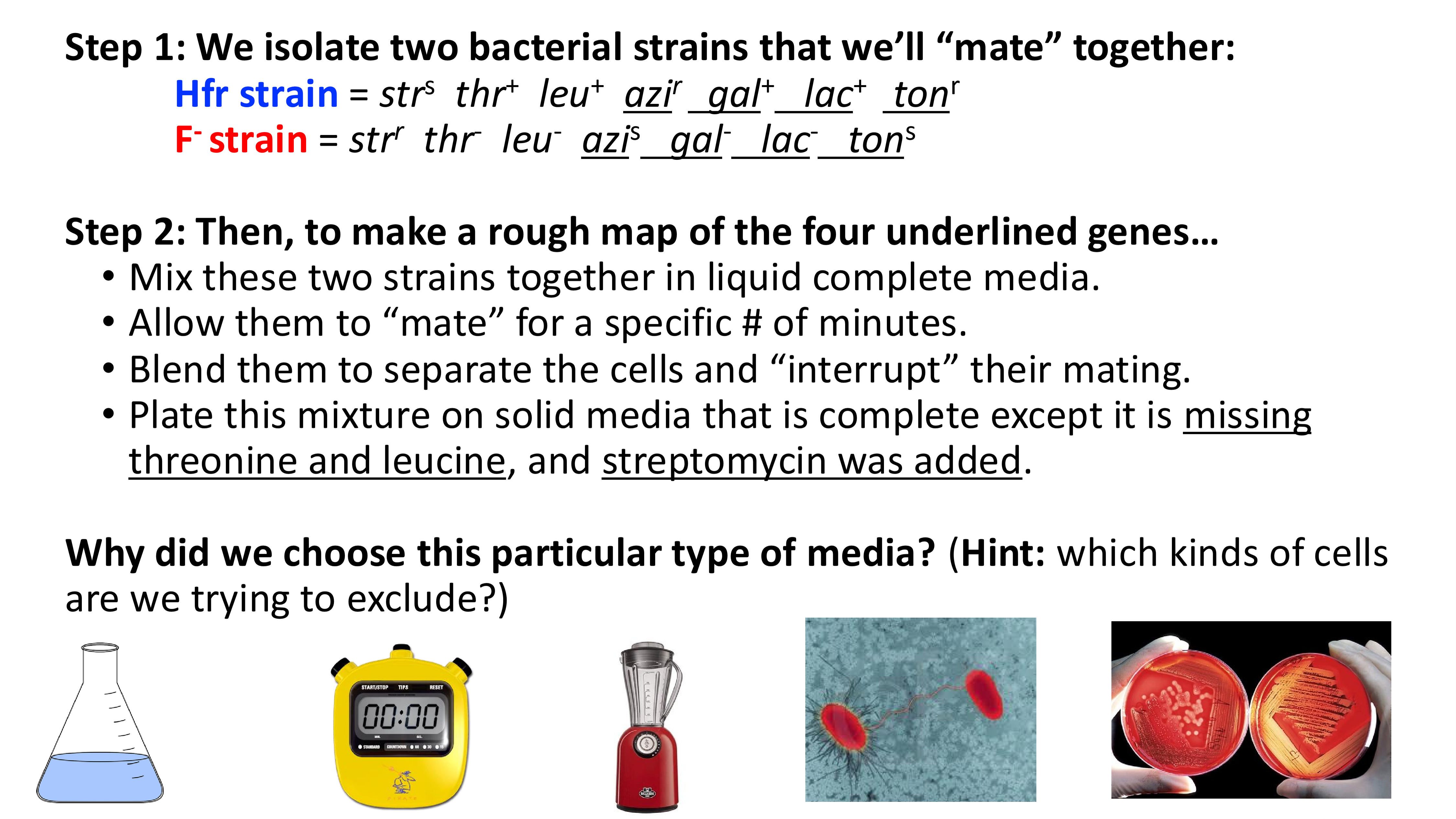
crude mapping using interrupted conjugation
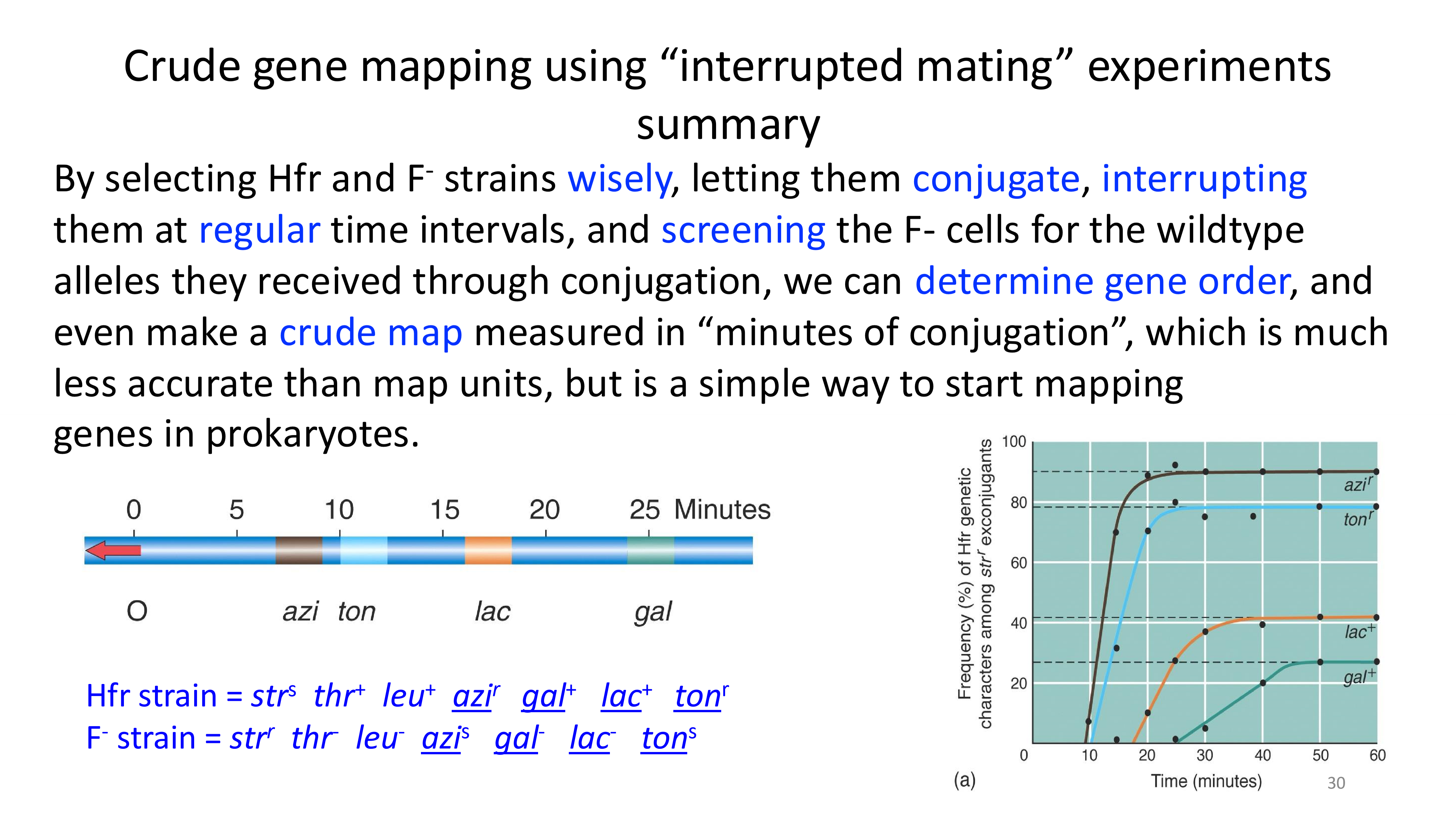
crude gene mapping using “interrupted mating” experiments summary
what is the problem with mapping a prokaryote’s genome
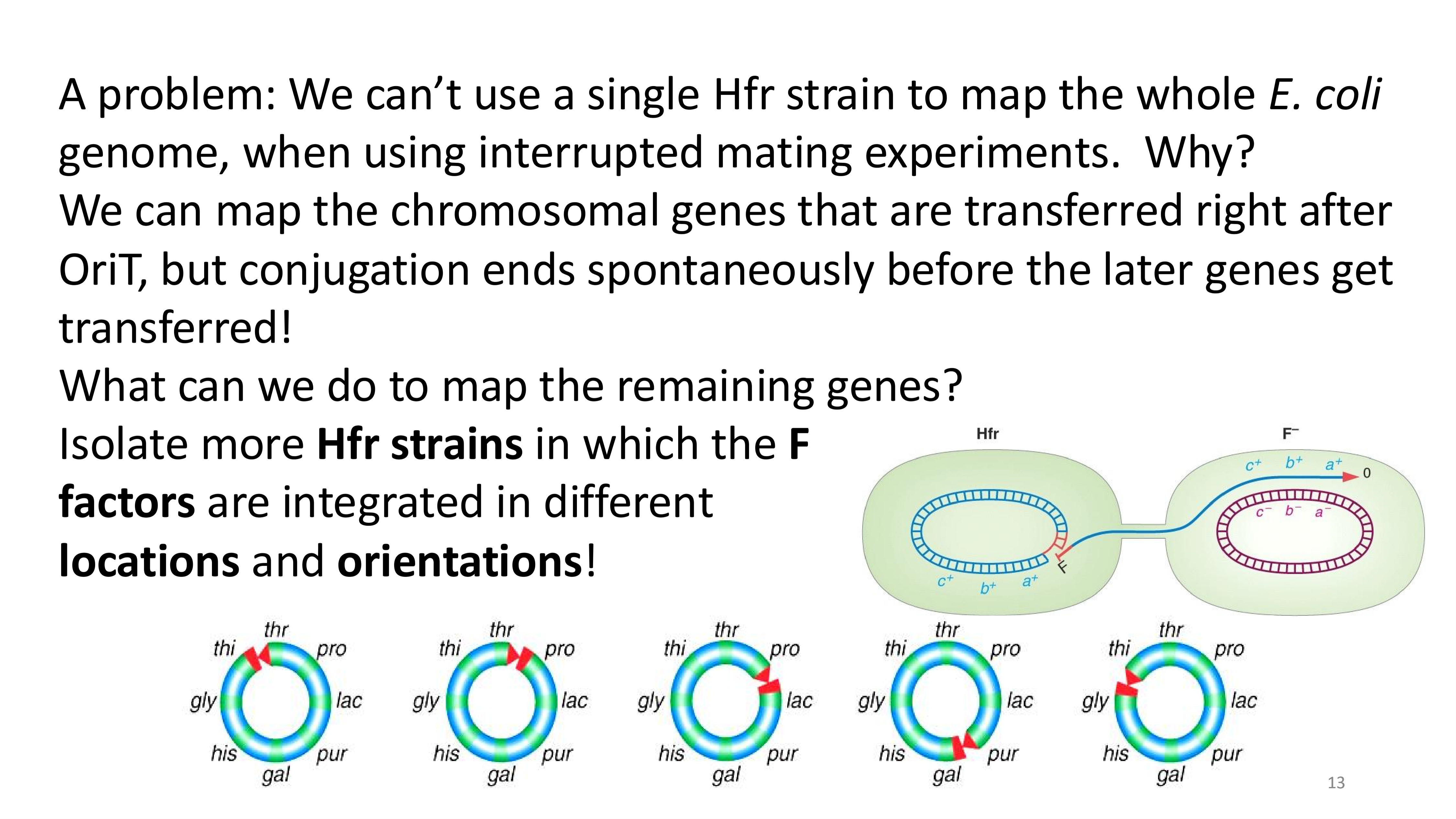
integration when mapping genes
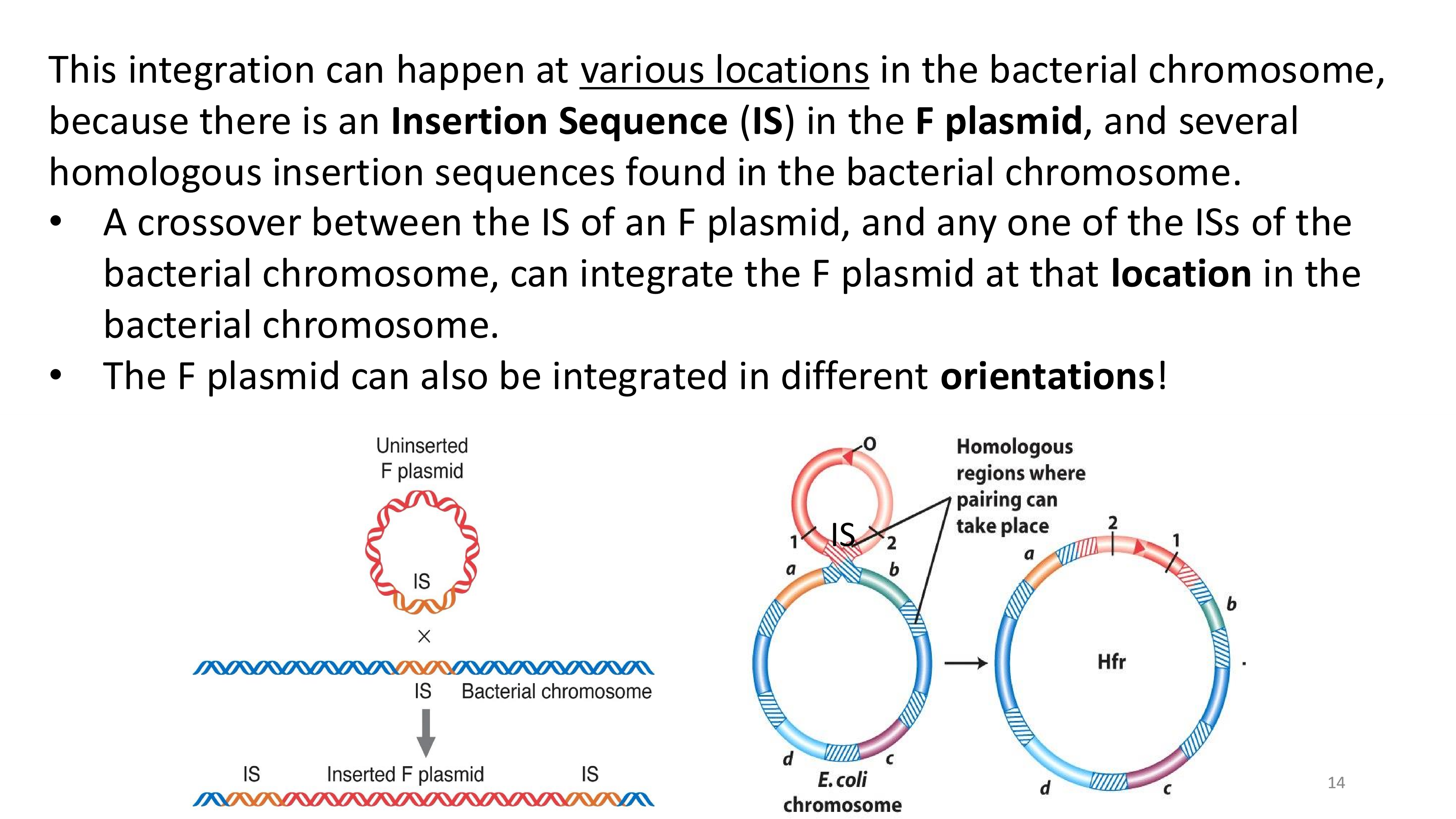
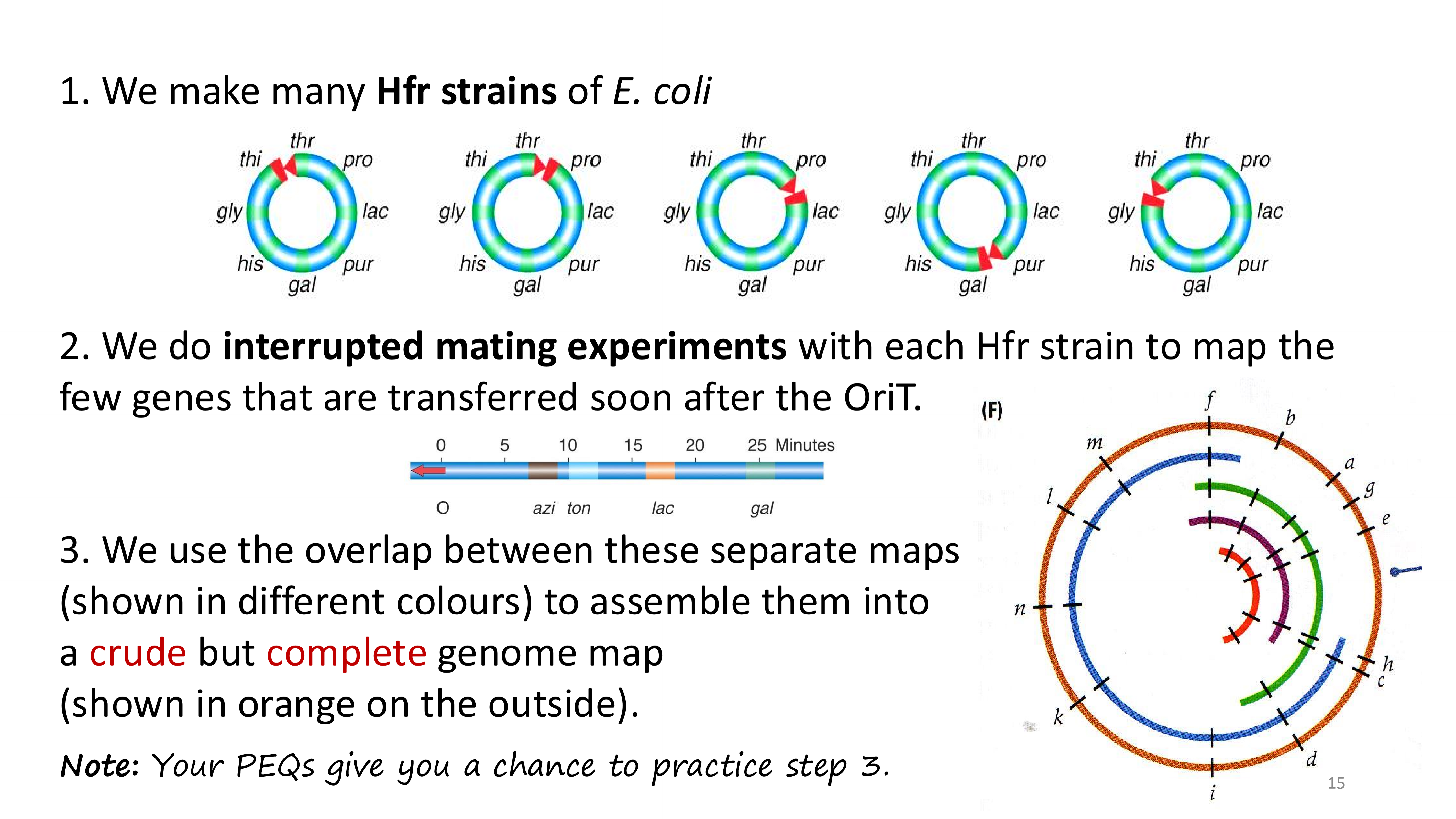
how would we make a complete crude genome map?
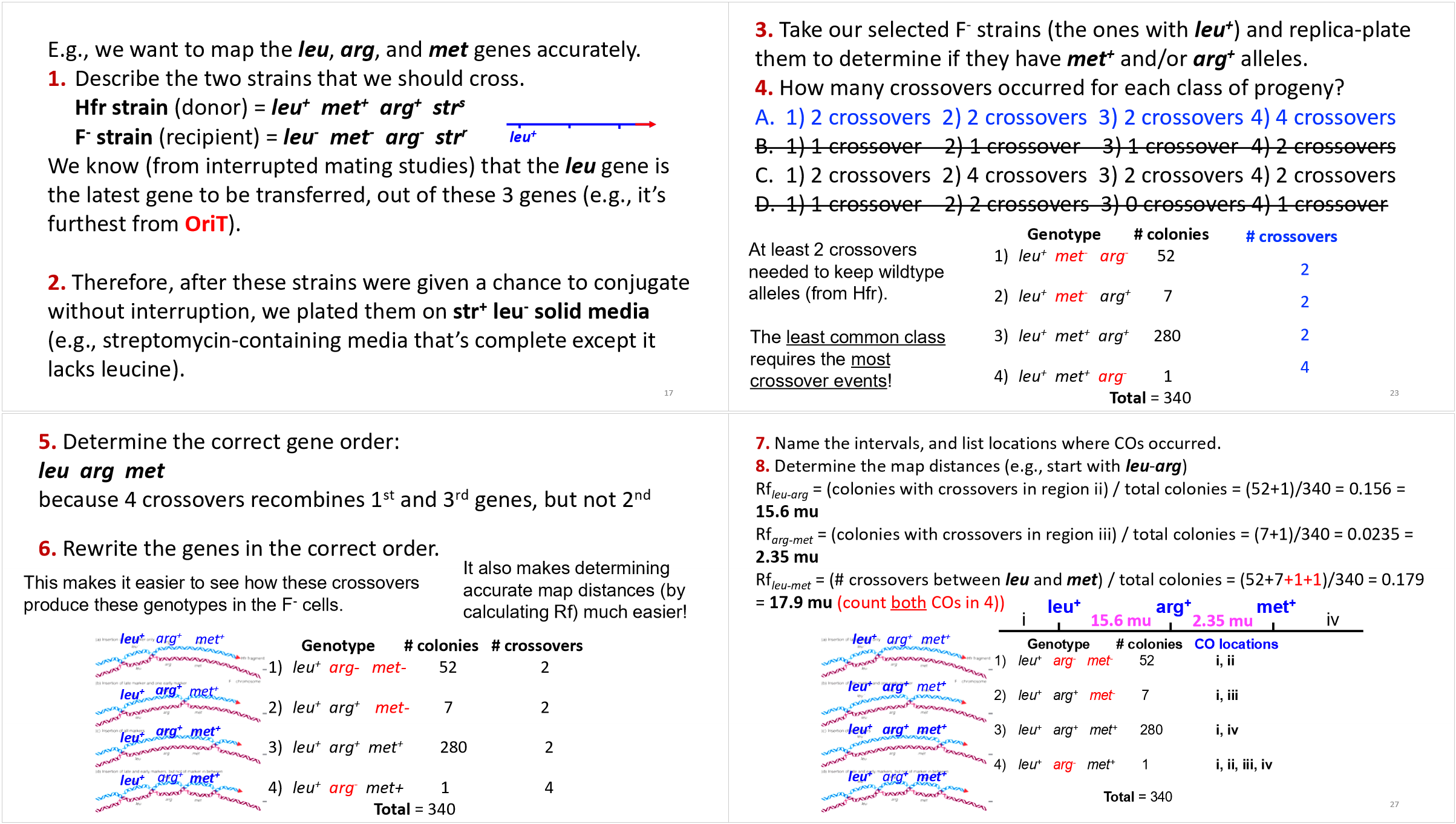
high-resolution mapping with conjugation and recombination frequencies
mapping with conjugation vs transformation
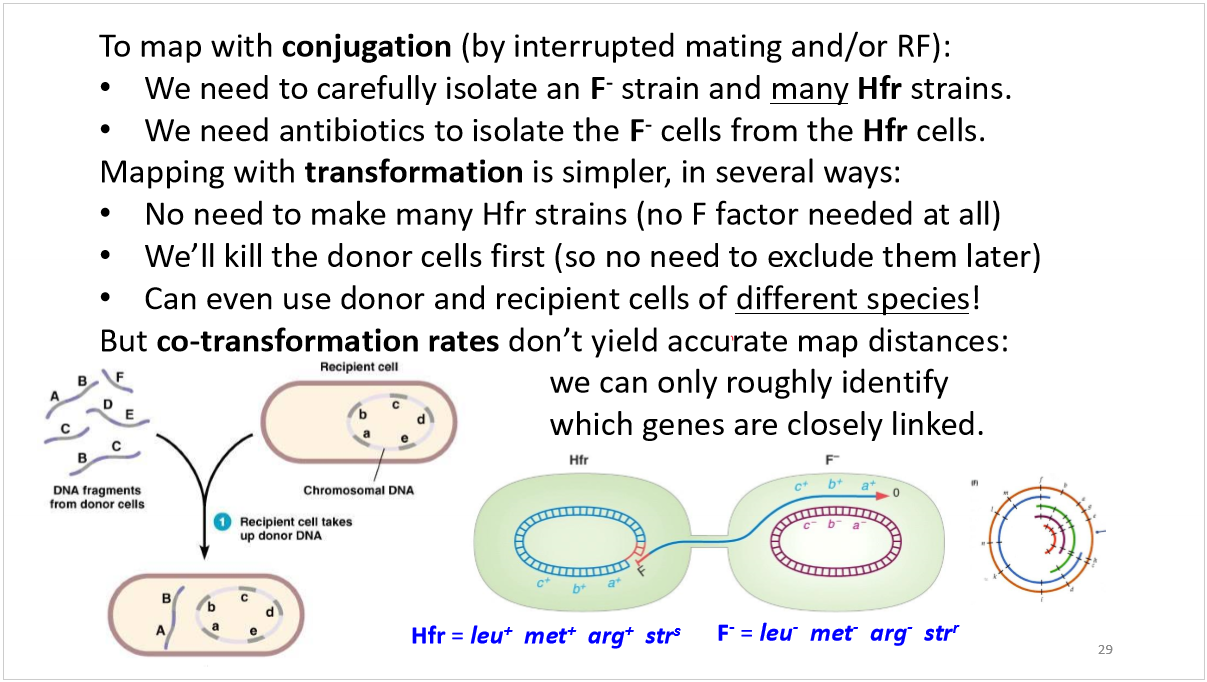
how does transformation work?