INTB Exam , INTB Exam 1, INTB Exam 2
1/104
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
105 Terms
True or False
The Globalization of Markets (demand side) occurred because the merging of historically distinct and separate national markets into one huge global marketplace. In many markets, the tastes and preferences of consumers in different nations are converging on some global norm, creating a global market. Examples are Coca-Cola, McDonald's, IKEA, Starbucks, and Apple
True
True or False
Specific tariffs are the ones levied as a proportion of the value of an important good, while Ad valorem tariffs are the ones levied as a fixed charge for each unit of an imported good.
False
True or False
One characteristic of High-Income countries is that households have high ownership levels of basic products and the service sector accounts for a high proportion (more than 50%) of the Gross National Income (GNI)
True
True or False
Collectivism is the system that stresses the primacy of collective goals over individual goals
True
True or False
One of the advantages of franchising is the low development cost
True
True or False
The eclectic paradigm for OLI framework explains the internationalization process through ownership of specific advantages (O), location-specific advantages (L), and Internalization advantages (I)
True
True or False
A Local Content Requirement (LCR) is a demand that some specific fractions of a good be produced domestically, LCR can be in physical terms or value terms
True
True or False
The Nordic theory or Uppsala model advocates that the internationalization of firms occurs due to the technological cycle of the products
False
True or False
The "Customs Union" increases trade barriers between member countries and adopts a common external trade policy
False
True or False
Innovation cycles are becoming shorter the the ones in the past
True
True or False
The gravity equation in international trade is one of the most robust empirical findings in economics: bilateral trade between two countries is proportional to their respective economic size, measure by their GDP, and directly proportional to their geographic distance
False
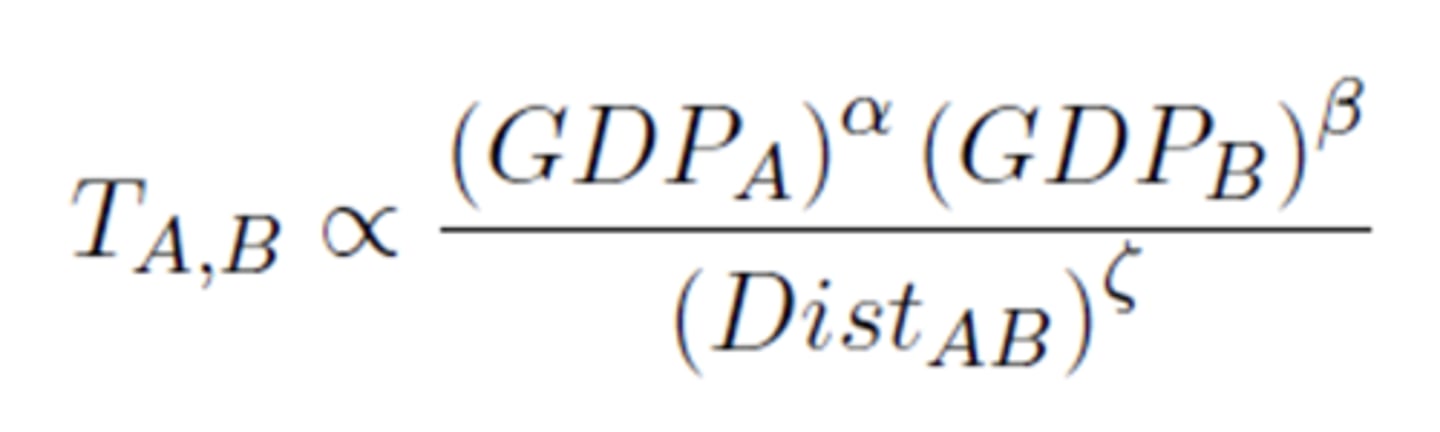
True or False
The subsidiaries of a multinational company are equally integrated and while present different responsiveness level
False
True or False
One of the advantages of Wholly-Owned Subsidiary (WOS) is the total control of the business unit
True
True or False
Foreign Direct investment occurs when a firm exports goods or services to consumers in another country
False
True or False
One of the benefits of the establishment of the EURO is the comparability of prices across Europe
True
True or False
The problem with the Hofstede framework is its generalization
True
True or False
In the "Common Market" mode, there are no barriers to trade between member countries, a common external trade policy, and the free movement of the factors of production (people, equipment, capital, knowledge)
True
True or False
Leaders have zero impact on the establishment of the culture of an organization
False
True or False
One example of the categories of institutional voids is "Capital Market"
True
True or False
Administrative trade policies are bureaucratic rules designed to make it difficult for imports to enter a country. They may hurt consumers by denying access to possibly superior foreign products
True
True or False
In the "Economic Union" mode, countries committed to the free flow of products and factors of production between members, adoption of a common currency, harmonization of tax rates, and pursuit of a common external trade policy. This mode involves sacrificing a significant amount of national sovereignty.
True
True or False
Some examples of common ethical issues in business are (i) employment practices, (ii) human rights, (iii) environmental regulations, and (iv) moral obligations
True
True or False
Human Resource Management (HRM) is more complex in an international business because of the differences between countries in labor markets, culture, legal systems, economic systems, for instance
True
True or False
Due to the competitive business environment in the 21st century, improvements in operational effectiveness are examples of a strategy
False
True or False
A tariff rate quota is a hybrid of a quota and a tariff; a lower tariff is applied to imports within the quota than those over the quota
True
True or False
In Low-income countries, industrialization is limited
True
True or False
Economies of Scale are reductions in unit cost achieved by producing a large volume of a product
True
True or False
Dumping occurs when a company (or country) sells goods in a foreign market above their cost of production or above their "fair" market value
False
True or False
Culture is a static concept. In addition, cross cultural literacy is an understanding of how cultural differences across and within nations can affect the way business is practiced
False
True or False
The Argentine Paradox occurs when a country achieves advanced development and flourishes economically, increasing both GDP and GDP per capita
False
True or False
Tariffs are generally pro-producer and anti-consumer.
True
True or False
Tariffs, subsidies, import quotas, and local content requirements are some of the instruments of international trade policy.
True
True or False
Import tariffs reduce the overall efficiency of the world economy.
True
True or False
The International Monetary Fund (IMF) promotes development using low-interest loans.
False
True or False
Local content requirements are a demand that some specific fraction of a good be produced domestically, and it benefits domestic customers, but domestic producers face higher prices
False
True or False
In a Market Economy, the goods and services a country produces and the quantities in which they are produced are determined by supply and demand
True
True or False
In Emerging Markets the poor will not "waste" money on non-essential goods
False
In a Command Economy, the goods and services a country produces, the quantities in which they are produced, and the price at which they are sold are determined by supply and demand
False
True or False
The three different legal systems we studied in class are:
Common Law: based on tradition, precedent, and custom (found in most of Great Britain's former colonies, including the US)
Civil Law: based on a denial set of laws organized into codes (found in more than 80 countries, including Germany, France, Japan, and Russia)
Theocratic Law: based on religious teachings (Islamic law is most widely practiced)
True
True or False
The CAGE distances are:
-CULTURAL: languages, ethnicity, religions, and values
-ADMINISTRATIVE: presence/lack of colonial ties, trade blocs, political hostility
-GEOGRAPHIC: physical distance, time zones, weather and common frontiers
-ECONOMIC: type of economy (Service vs manufacturing vs agriculture), openness of the economy, existence/lack of natural resources and infrastucture)
True
True or False
A subsidy is a government tax on a domestic producer generally speaking, subsidies make it harder for domestic produces and makes it harder for them to compete against low-costs important and gain export markets.
False
True or False
One of the mistaken assumptions about Emerging Markets is that global companies always win in Emerging Markets
True
True or False
Foreign Direct Investment occurs when a firm exports goods or services to consumers in another country
False
True or False
The history of innovation cycles has shown that more recent innovation cycles are becoming longer than ones in the past.
False
True or False
Consumers typically absorb the costs of subsidies
True
True or False
The Group of Twenty (G20) became a forum for a coordinated policy response to the financial crisis of 2008 and 2009. They represent 10% of the global GDP.
False
True or False
The United States follow the common law
True
True or False
Specific tariffs: levied as a fixed charge for each unit of imported good
Ad valorem tariffs: levied as a proportion of the value of an imported good
True
True or False
Traditions, language, and architecture are visible aspects of Culture, while ideas about justice are invisible aspects of culture
True
True or False
Dumping occurs when a company (or country) sells goods in a foreign market above their cost of production or above their "Fair" market value
False
True or False
The globalization of Production (supply side) the merging of historically distinct and separate national markets into one huge global marketplace
False
True or False
The "Customs Union" eliminates trade barriers between member countries and adopts a common external trade policy
True
True or False
In a mixed economy the government does not interfere with the market
False
True or False
Culture is a system of values and norms shared among a group of people and when taken together, constitute a design for living
True
True or False
Administrative trade policies are bureaucratic rules designed to make it easer for imports to enter a country. They may hurt consumers by denying access to possibly superior foreign products
False
True or False
The three types of Intellectual Property we studied were:
-Patents: give inventor exclusive rights to the manufacture, use, or sale of that invention
-Copyrights: exclusive legal rights of authors, composers, playwrights, artists and publishers to publish and dispose of their work as they see fit.
-Trademarks: designs and names, often officially registered, by which merchants or manufacturers designate and differentiate their products
True
True or False
Characteristics of High-Income countries is that
- households have high ownership levels of basic products
- the service sector is a high proportion (more than 50% of the Gross National Income (GNI).
- Cheap Labor
- Labor intensive industries
False
True or False
Antidumping duties, voluntary export restraints, and import quotas are some of the instruments of international trade policy
True
True or False
In the "Economic Union" mode, countries committed to the free flow of products and factors of production between members, adoption of a common currency, harmonization of tax rates, and pursuit of a common external trade policy. This mode involves increased national sovereignty
False
True or False
We analyzed in class three era of globalization:
- Globalization 1.0: In this era globalization was centered around countries
- Globalization 2.0: In this era, globalization was centered around multinational companies
- Globalization 3.0: In our current era, globalization is centered around the convergence of the personal computer, fiber-optic internet connections, and software, which allows small groups and even individuals to go global
True
True or False
Some of anti-globalization forces are:
-Nationalism (or maybe a distorted version of it)
-Formal and informal trade barriers.
-Barriers to foreign direct investment (FDI).
-Transportation costs.
-Economic and political risk... Geopolitics matter!
-Managerial challenge for coordinating a globally dispersed supply chain.
True
True or False
The Argentine Paradox is when a country has achieved advanced development and flourishes economically, with increasing GDP and GDP per capita
False
True or False
Culture is a static concept. In addition, cross-cultural literacy is an understanding of how cultural differences across and within nations can affect the way business is practiced
False
True or False
The gravity equation in international trade is one of the most robust empirical findings in economics: bilateral trade between two countries is proportional to their respective economic size, measure by their GDP, and inversely proportional to their geographic distance
True
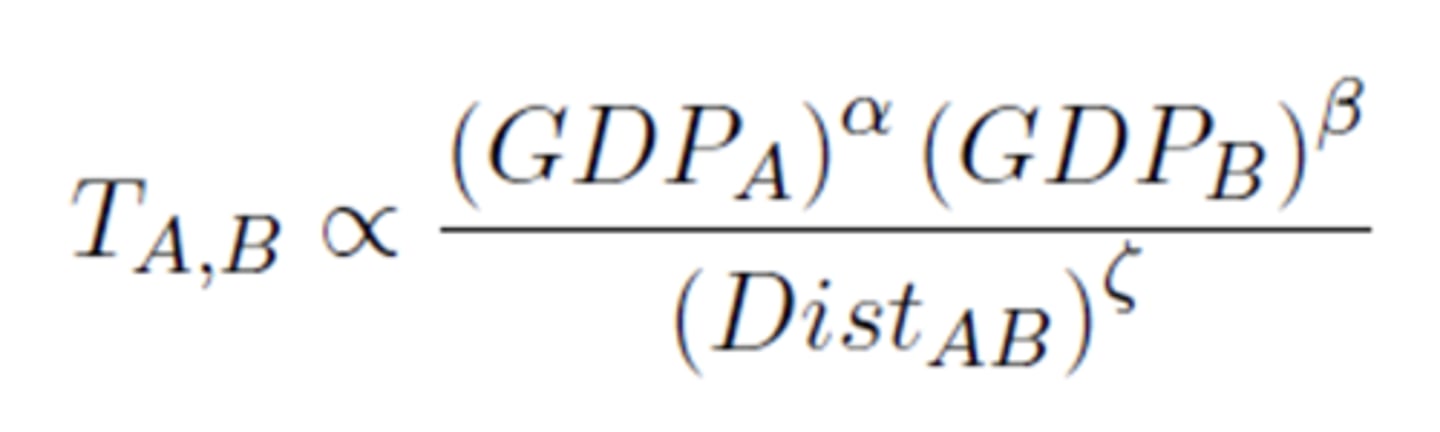
True or False
Leaders have no impact on the establishment of the culture of an organization
False
True or False
Countries with high degree of corruption, foreign direct investment falls, international trade falls, and economic growth increase
False
True or False
Some of the drivers of globalization are:
- Less companies dispersing parts production
- Economies of nation-states becoming less intertwined
- The world is becoming less wealthier
False
True or False
The World Trade Organization (WTO) policies the world trade system and ensures nation0states adhere to the rules established
True
True or False
In Low-Income countries. Industrialization is limited and the service sector is more than 50% of GNI
False
True or False
A Local Content Requirement (LCR) is a demand that some specific fraction of a good be produced domestically. LCR can be in physical terms or in value terms. Additionally, local content requirement benefits foreign producers
False
True or False
Ethics is a set of accepted principles of right or wrong that govern conduct of a person, members of a profession, or actions of an organizations
True
True or False
Economic transactions never take place in a vacuum, but rather are always integrated into a specific social and cultural context
True
True or False
PESTEL:
P: Government Policy, political stability, corruption, foreign trade policy, tax policy, labour law, trade restrictions
E: Economic growth, exchange rates, interest rates, inflation rates, disposable income, unemployment rates
S: Population growth, Age distribution, Career attitudes, safety emphasis, health consciousness, lifestyle attitudes, cultural barriers
T: Technology Incentives, Level of innovation, automation, R&D activity, technological changes, technological awareness
E: Weather, Climate, environmental policies, climate change, pressures from NGOs
L: Discrimination laws, antitrust law, employment laws, consumer protection laws, copyright and patent laws, health and safety laws
True
True or False
The three expansion decisions are:
1. Which market to enter?
2. When to enter?
3. Scale of entry
True
True or False
The international expansion of multinationals can never be reversed
False
True or False
Strategy is a combination of ends (goals) for which the firm is striving and the means (policies by which it is seeking to there)
True
True or False
The causes of the problems of the Chiquita company can be divided into three categories:
a. Industry causes
b. Managerial causes
c. Political causes
True
True or False
Small firms should focus on the area marked in red
True

True or False
On the one hand, external factors lead firms to disperse geographically R&D activities to exploit the attractiveness of locations. Firms may want to locate close to other firms/customers (co-location between firms). On the other hand, internal factors may drive firms to co-locate their value chain activities (e.g, production, sourcing) in the same location (co location within the firm - manufacturing and procurement in most firms).
True
True or False
One example of the categories of institution voids is "Capital Market"
True
True or False
The Eclectic paradigm (or OLI) explains foreign investment activities by ownership of specific advantages (O), location-specific advantages (L), and internalization advantages (I).
True
True or False
Due to the competitive business environment in the 21st century, improvements in operational effectiveness are examples of a strategy
False
True or False
Protectionism remains a key feature of the global trading system. Countries have always used protectionism, and will continue to sue protectionism, to serve their policy objectives
True
True or False
One of the challenges of Merger & Acquisitions is the post merger integration
True
True or False
These are financial reasons for internationaliztion strategies:
-To reduce cost
-To Enter New Markets
-To improve efficiency
True
True or False
Embeddedness is the extent to which the firm is anchored in a particular space to be integrated into local networks of economic and social relations
True
True or False
In modes of services, Mode 1: the service provider does not leave its home territory, and serves are prodivded virtually
True
True or False
One of the advantages of Wholly-Owned Subsidiary (WOS) is the total control of the business unit
True
True or False
Early entry is when a firm enters a foreign market at the same time as everyone else
False
True or False
Companies deal with Institutional voids in two ways: Shape and Adapt
False
True or False
In modes of services mode 2: the service provider opens a subsidiary or a representative office in another member country
False
True or False
One of advantages of "Licensing and Franchising" is the dependence on licensees during the contract
False
True or False
Operational effectiveness means performing similar activities better than rivals perform them and it is a strategy
False
True or False
Multinational companies need to understand the political forces that give rise to protectionist impulse; they will need to survey the landscape in which they operate for signs of impeding protectionism; and they will need to rehearse various scenarios - both commercial and political - for dealing with protectionism when it arises
True
True or False
The Uppsala Model for internationalization advocates that international expansion should occur in countries with large markets
False
True or False
Human Resource Management (HRM) is more expel in an international business because of differences between countries in labor markets, culture, legal systems, economic systems, for instance
True
True or False
Michael Porter's Basic strategies are
- Differentiation
- Low cost
- Niche
True
True or False
Experience curve: systematic increases in productions costs that occur over a products life
False
True or False
Economies of scale are reductions in unit cost achieved by producing a large volume of a product
True