IMED1002 - DNA Replication
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Summary of DNA replication
- first DNA is unwound so both of the individual strands can act as templates and nucleotides in new strand added via complementary bases pairing.
- each new progeny cell contains one DNA strand from original parent cell and one newly synthesised DNA strand (semiconservative)
How was semiconservative replication shown experimentally
1958 - Meselson and Stahl experiment
How is the double helix unwound?
- Heat can be used but it is high temp (around 90 degrees)
- ATP is needed to break bond
- enzyme can be used: DNA helicase unwinds the double helix by breaking H bonds between complementary strands
RELEARN DNA REPLICATION FROM YEAR 10 QUIZLET
do it
Model for formation of DNA polymers
1. Elongation occurs by addition of 3' end (free 3' -OH)
2. Enzyme = DNA polymerase (more then one)
3. Substrate = deoxyribonucleoside triphosphate (dNTP)
4. Requires a template strand to base pair with
5. Requires short double stranded nucleic acid, supplied by an RNA primer, which anneals to the DNA
6. Requires Mg2+ (co-factor)
- watch a video about it since there seems to be electron pair movement, learn it
How Mg2+ helps
- reaction involves 2Mg2+ ions, incoming dNTP and 3 Asp (acidic) residues in DNA pol
DNA Polymerase
- An enzyme that catalyzes the formation of the DNA molecule.
- Only synthesis DNA in one direction 5' to 3'
- Only add to end of existing double stranded Nucleic acid (needs 3' OH)
- Human DNA Pols (for nuclear DNA replication): alpha (alpha symbol), delta (lowercase delta), epsilon (epsilon symbol)
Alpha DNA Polymerase
Cellular Function: Initiation of nuclear DNA synthesis (adds first 20 bases or so) and DNA repair; has primase activity
Delta DNA Polymerase
Cellular Function: leading and lagging strand synthesis of nuclear DNA, DNA repair, and translesion DNA synthesis
- has high fidelity
Epsilon DNA Polymerase
Cellular Function: Leading-strand synthesis
- have a high fidelity
High Fidelity in DNA Replication
having a high accuracy
Why does Polymerase Delta and Epsilon have high fidelity?
- both have a 3'-5' exonuclease activity = proofreading
- removes mismatched bases by going backwards. If incorrect nt is inserted, can detect this due to misalignment of 3' OH group, will remove and replace with correct nt
Diagram of DNA Synthesis
ON SLIDE 12 ON LECTURE 10 TERM 1
RNA Primer
- to begin DNA replication, require a short double stranded NA (3'OH) supplied by an RNA primer which anneals (binds) to both individual DNA templates
- This is added by DNA polymerase alpha, which has subunits with different activities, including a primase that ads the DNA primer
Replication fork
a Y-shaped point that results when the two strands of a DNA double helix separate so that the DNA molecule can be replicated
- strands of original DNA act as templates for two new strands
- replication fork: handle and tines
- Lagging strand is made discontinuously by DNA polymerase delta
- lagging strand is made continuously by DNA polymerase epsilon as the handle unwinds
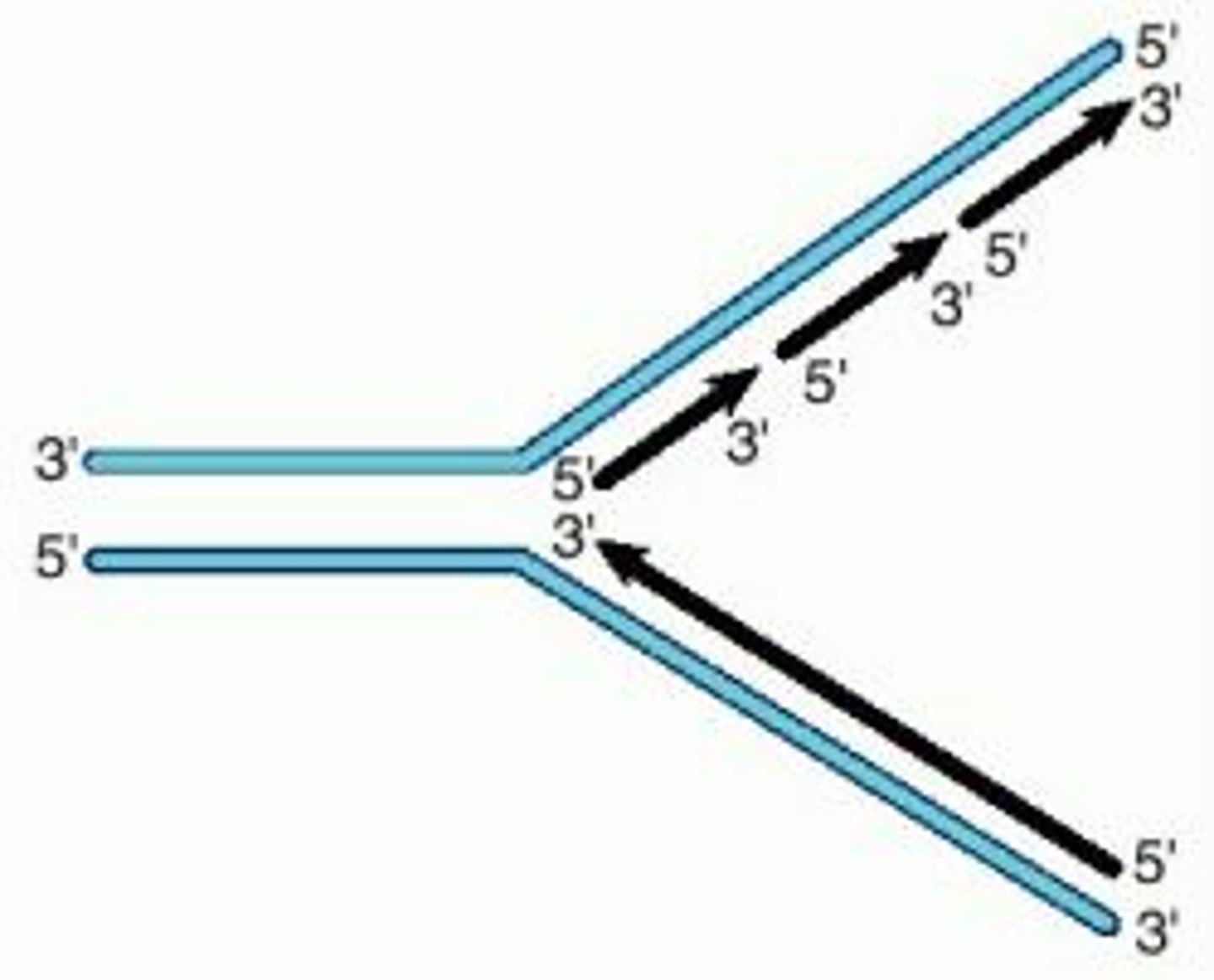
Okazaki Fragments
Small fragments of DNA produced on the lagging strand during DNA replication, joined later by DNA ligase to form a complete strand.
- lagging strand synthesis is discontinuous, need RNA primer to start each Okazaki fragment
RNA primer removal, gap filling and joining
- As DNA extends to the adjacent fragment, it displaces the RNA primer
- DNA ligase connects adjacent fragments by forming a phosphodiester bond
DNA ligase
- joins single DNA strands by forming a phosphodiester bond between adjacent fragments
Great diagram of DNA replication process
SLIDE 20 OF LECTURE 10
Stabilising DNA replication (NOT NEEDED TO KNOW)
- DNA polymerase delta and epsilon are held to template DNA strand by other proteins, making them highly processive enzymes
- Sliding-Clamp Protein: allows stable binding of DNA polymerase and thus efficient strand synthesis
- Clamp-loading proteins: aids in attaching the sliding-clamp proteins
- Single-Stranded DNA Binding Protein: stabilises SSDNA so it does not reanneal
- DNA Gyrase: a type of topoisomerase, relieves torsional stress and helps prevent DNA over-twisting
Replication Factor C (RFC)
clamp loader
Replication Protein A (RPA)
removes RNA primer as intact unit, unwinds RNA and recruits endonucleases (in eukaryotes)
[part of stitching together lagging strand]
Good video to visualise DNA replication
Search: Molecular Visualisation of DNA (2003) Drew berry whi.tv on YouTube
UP TO SLIDE 1 ON LECTURE 11
tes