Behavior Reduction
1/36
Earn XP
Description and Tags
rtyui
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
Extinction
The process of witholding reinforcement to reduce a behavior
Occurs when reinforcement of a previously reinforced behavior is discontinued
Extinction by Negative Reinforcement / Escape Extinction
Behaviors maintained by negative reinforcement are placed on extinction when those behaviors do not produce a removal of the aversive stimulus
Physically prompting through an activity
Person can’t escape the aversive situation
Ex: Person doesn’t want to brush teeth, therapist does hand-over-hand and push person through task
Extinction by Positive Reinforcement / Access Extinction
Behaviors maintained by positive reinforcement
Placed on extinction when those behaviors do not produce the reinforcer
Planned ignoring, tangible extinction
Ex: When child engages in behavior for attention, they no longer receive attention for that behavior
Extinction of Behavior Maintained by Automatic Reinforcement / Sensory Extinction
Behaviors maintained by automatic reinforcement are placed on extinction by masking or removing the sensory consequence
Considered unethical in many situations → if its a sensory function, the person is gaining something positive for their body
Ex: Student exhibits hand flapping behavior, therapist places weights on hands, reduces positive sensory feeling
Ex: Helmet for headbanging
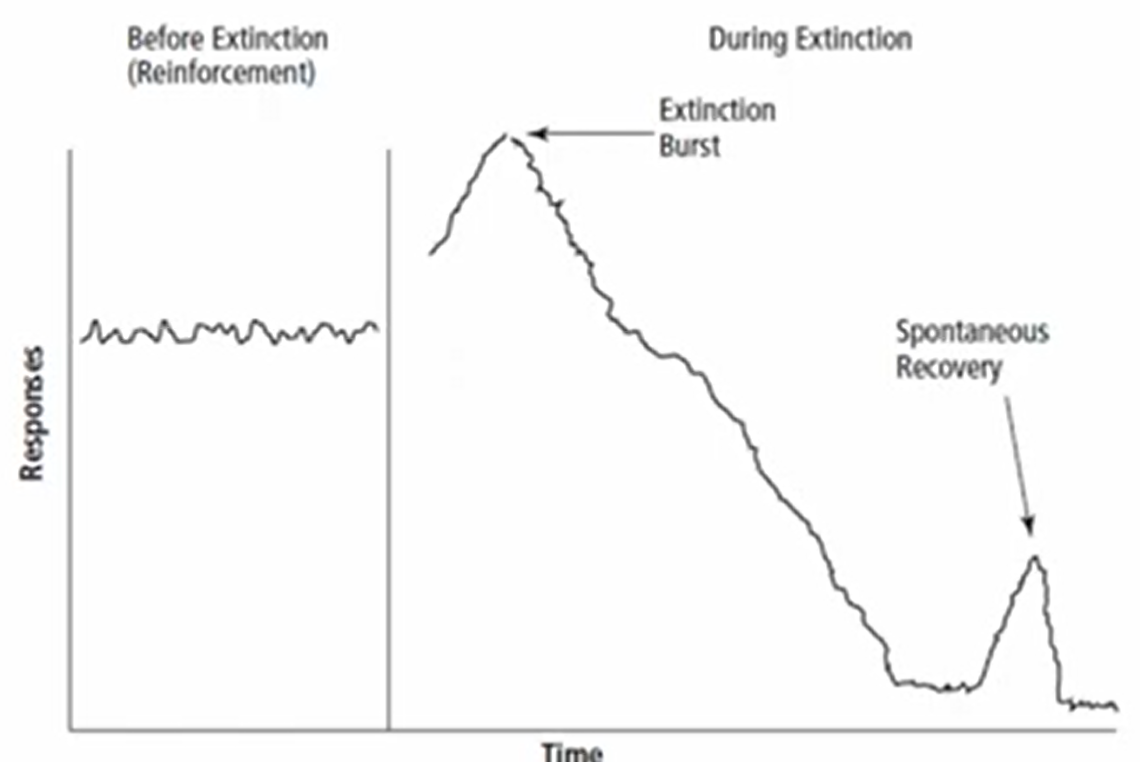
Extinction Burst
The immediate increase in rate of response after removing the positive, negative, or automatic reinforcement
Problem behaviors can worsen during extinction before they show improvement
Ex: Therapist/parents no longer show attention to tantrum behavior from child, child then exhibits bigger/intense tantrums to get attention
Is an indicator that extinction is working
Response Variation
New forms of behavior start
Ex: Tantrums don’t work anymore, child resorts to banging on the wall
Initial Increase in Response Magnitude
An increase in response magnitude may occur during the early stages of enxtinction
Spontaneous Recovery
The reappearance of the behavior after it has diminished to its pre-reinforcement level or stopped entirely
Resurgence
The reoccurrence of a previously reinforced behavior when the reinforcement for an alternative behavior is terminated or decreased
3-phase procedure
Target behavior is reinforced
Target behavior is placed on extinction and reinforcement provided for an alternative behavior
Both responses are placed on extinction
Figure
Continuous and Intermittent Reinforcement
Intermittent reinforcement may produce behavior with greater resistance to extinction than behaviors previously reinforced by continuous reinforcement
When not to use extinction
The behavior is harmful
All sources of reinforcement cannot be withheld
Rapid reduction in response rate is required
Others are likely to imitate the problem behavior
Emotional Responding
Crying, aggression, or frustration when reinforcement is removed
Differential Reinforcement
Reinforcing an alternative behavior while extinguishing the problem behavior
Punishment
Applying a stimulus that decreases the likelihood of a behavior being repeated
Positive
Adding something
Negative
Removing something
Verbal Reprimand
Involves expressing disapproval of a person’s behavior directly to them, often immediately after the undesired behavior occurs
Immediate and direct: delivered right after the undesired behavior to make the connection clear
Specific: Targets the behavior, not the person, to avoid damaging self-esteem
Ex: Student talks out in class, teacher addresses student immediately stating “talking while others are speaking is disrespectful and disrupts learning”
Time-Out from Reinforcement
Removing the opportunity to gain positive reinforcement from the environment
Types:
Non-exclusionary
Exclusionary
Seclusionary
Contingent observation
Non-exclusionary Time Out
Involves decreasing the reinforcement level without isolating the individual from the environment
Examples include withdrawing a specific positive stimulus, or using a visual or auditory signal to indicate inappropriate behavior
Ex: Two boys sit near each other and one of them pinches the other. The pincher is removed from the other boy being pinched
Contingent Observation
The individual is present in the setting but must observe others engaging in appropriate behavior without participating
Helps the individual learn by watching positive examples and understanding the rewards of appropriate behavior
Exclusionary Time-Out
Removes the individual from the environment where the undesired behavior occurred, often to a different room/area
Used when the behavior is disruptive/harmful, ensuring safety and emphasizing the consequence of actions
Seclusionary Time-Out
Involves placing the individual in a completely separate room/enclosed space where they are temporarily isolated from others
Method is highly regulated and generally considered a last resort
Response Cost
Loss of privileges or desired items as a consequence of negative behavior
Ex: Token economy is classrooms, driving penalties, late fees
Overcorrection
Involves requiring an individual to not only correct an inappropriate/undesirable behavior but also to engage in additional behavior to ensure the environment is in a better state than before the inappropriate behavior occurred
Restitutional Overcorrection
Requires the individual to repair/rectify the consequences of their inappropriate behavior.
Ex: Child spills paint on the floor, child is made to clean/organize the painting area, even beyond the mess caused by the spill
Positive Practice Overcorrection
Involves the individual repeatedly practicing the correct form of behavior/an alternative appropriate behavior for a certain period/number of repetitions.
Ex: Student speaks out of turn in class, student practices the appropriate way to request to speak multiple times
Contingent Exercise
Individual is required to perform a physical activity contingent upon displaying an undesirable behavior. The exercise is not related to the behavior but serves as a consequence to decrease future occurrence of said behavior
Ex: Child exhibits aggressive behavior towards peers, child then has to do jumping jacks for a period of time
Guidelines for Effective Punishment
Immediate: Punishment should be applied immediately after the behavior to be most effective
Consistent: Should be consistent to create a clear association between the behavior and consequence
Proportionate: Should be proportionate to the behavior
Explanation: Explain why punishment is being applied to help the individual understand the reason behind it
Secondary Effects of Punishment
Fear and Anxiety: can lead to negative emotions towards punishing agent/environment
Avoidance: Individuals may learn to avoid the punishing agent rather than the behavior itself
Aggression: Can sometimes lead to an increase in aggressive behavior
Modeling: Observing punishment can teach the use of aggression/avoidance as strategies
Alternatives
Positive Reinforcement
Natural Consequences
Choice offering
Modeling
Response Block
Is a physical intervention that occurs immediately when an individual begins to exhibit the problem behavior
Response Interruption and Redirection (RIRD)
Involves interrupting a stereotypical behavior and guiding the learner towards engaging in a more desirable, high-probability response
Emergency Procedures
When a learner engages in behaviors which pose a threat to themselves, or others, emergency procedures will be used
Ex: Restraints, protective gear
Preparation and Planning
Includes the development of individualized emergency plans for each client, which consider their specific needs, behaviors, and potential risks.
Types of Emergencies
Can range from medical emergencies (seizures or allergic reactions), to behavioral crises (severe aggression or elopement (the act of running away or leaving the safety of the caregiver)). May also involve natural disasters, accidents, or any situation that poses an immediate risk to health or safety
Response Protocols
Effective emergency procedures outline clear, actionable steps for immediate response.
This might include removing the individual and others from harm’s way, providing first aid, and securing the environment.
Post-Emergency Debriefing and Support
After an emergency, it’s important to conduct a debriefing session for all involved parties. This provides an opportunity to review the response, address any emotional impact, and adjust emergency plans as needed based on lessons learned.
Ethical Consideration
Ethical considerations are paramount when implementing emergency procedures in ABA.
The dignity and rights of the individual must be respected at all times, with every effort made to ensure their safety and well-being.
Confidentiality must be maintained
Interventions should be the least restrictive necessary to manage the situation effectively.