(biochemical pathways, cholesterol, insulin)
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
Glycogenesis
Glucose —> Glycogen
Glycogenolysis
Glycogen —> Glucose
Protein synthesis
Amino acids —> Proteins
Proteolysis
Proteins —> Amino acids
Lipogenesis
Fatty acids —> fat (triglyceride)
Lipolysis
Fat (triglyceride) —> fatty acids + glycerol
Glucogenesis
Amino acids —> glucose
Glucose oxidation
Glucose —> ATP, CO2, H2O
Fatty acid oxidation
Fatty acids —> ATP, CO2, H2O
Pancreas
Lies in the loop between the inferior border of the stomach and the proximal portion of the small intestine
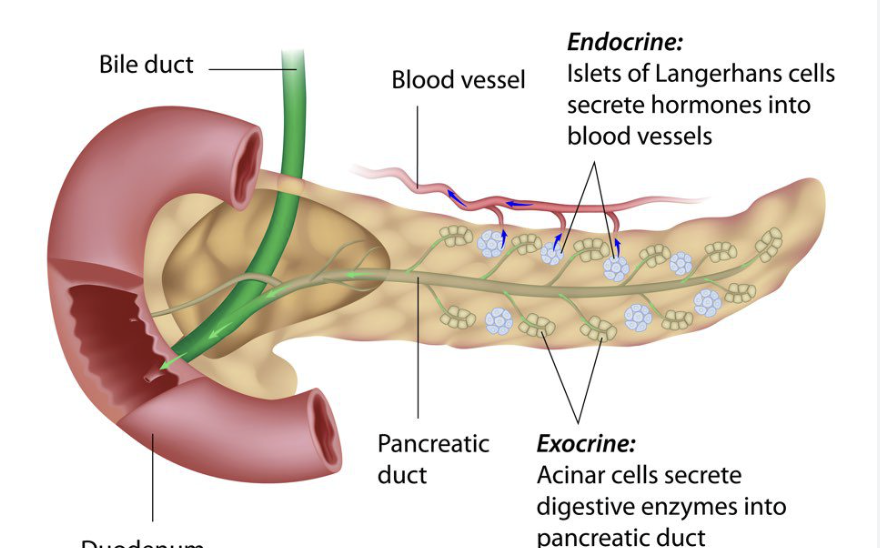
exocrine pancreas
99% of the organs volume which contains clusters of gland cells and their attatched ducts
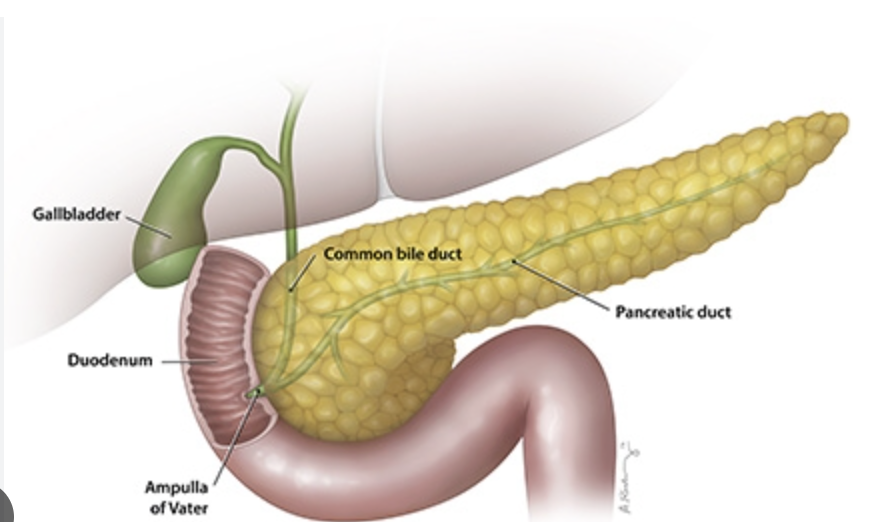
Pancreatic ducts
Where the alkaline, enzyme-rich fluid secretes from
endocrine pancreas
consists of small groups of cells scattered among the exocrine cells
Pancreatic islets
the small groups of cells in the endocrine pancreas
Alpha cells
Produces the hormone glucagon which raises glucose levels
Beta cells
Produces the hormone insulin which lowers the blood glucose levels
How do alpha cells raise glucose levels
Done through the breakdown of glycogen and glucose release in the liver
How do beta cells lower glucose levels
increasing the rate of glucose uptake and use by most body cells as well as increasing glycogen synthesis in the skeletal muscles and the liver
Pancreatic acini
exocrine small clusters
Delta cells
Produces a growth inhibiting hormone which suppresses the release of glucagon and insulin
Pancreatic polypeptide cells (PP cells)
inhibits gallbladder contractions and regulates the production of some pancreatic enzymes
Primary hormones responsible of the blood glucose level
insulin and glucagon
Homeostasis disturbed by increasing blood glucose levels
Beta cells in pancreatic islets secrete insulin, effecting all body cells, which respond with conversion of glucose to glycogen as well as overall increase of glucose, restoring to decreased glucose levels
Homeostasis disturbed by decreasing blood glucose levels
Alpha cells in pancreatic islets secrete glucagon which effects the liver and the skeletal muscle, the response is a breakdown of glycogen to glucose/increased breakdown of fat to fatty acids
Diabetes mellitus
A glucose concentration high enough to overwhelm the reabsorption capabilities of the kidneys
Hyperglecimia
Abnormally high glucose levels
Glycosuria
Glucose is appears in the urine
Polyuria
Urin volume becomes excessive
Type 1 diabetes
Inadequate insulin production by the pancreatic beta cells (5-10% population)
Type 2 diabetes
produce normal levels of insulin, but their tissues do not respond properly (insulin resistance)
diabetic retinopathy
proliferation of capillaries and hemorrhaging at the retina which can cause partial or full blindness
diabetic nephropathy
degnerative changes in the kidney
diabetic neuropathy
peripheral nerve damage caused by abnormal blood flow
Arteriosclerosis
Thickening and toughening of artery walls
Atherosclerosis
formation of lipid deposits in the arterial tunica media (caused by people who have high levels of cholesterol)
plauque
fatty mass tissue that projects into the lumen of the vessel and restricts blood flow
What type of reactions does insulin promote
Anabolic
Which type of reactions does insulin inhibit
Catabolic reactions
What is insulins overall goal to maintain homeostasis in the human body
Regulate blood glucose levels by promoting storage and use of glucose
is gluconeogenesis inhibited or stimulated by insulin
Inhibited
Is Glycogenolysis inhibited or stimulated by insulin
Inhibited
is lipolysis inhibited or stimulated by insulin
inhibited
is Glycogenesis stimulated or inhibited by insulin
Stimulated
Is lipogenesis stimulated or inhibited by insulin
Stimulated
Is protein synthesis stimulated or inhibited by insulin
stimulated
What is insulins second goal
TO promote tissue building
what is LDL
The “bad” cholesterol/ saturated fats
What is HDL
The “good” cholesterol/ unsaturated fats
What does LDL do
Carries cholesterol from the liver to the tissues
What does HDL do?
Carries cholesterol from the