Nuclear Chemistry
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
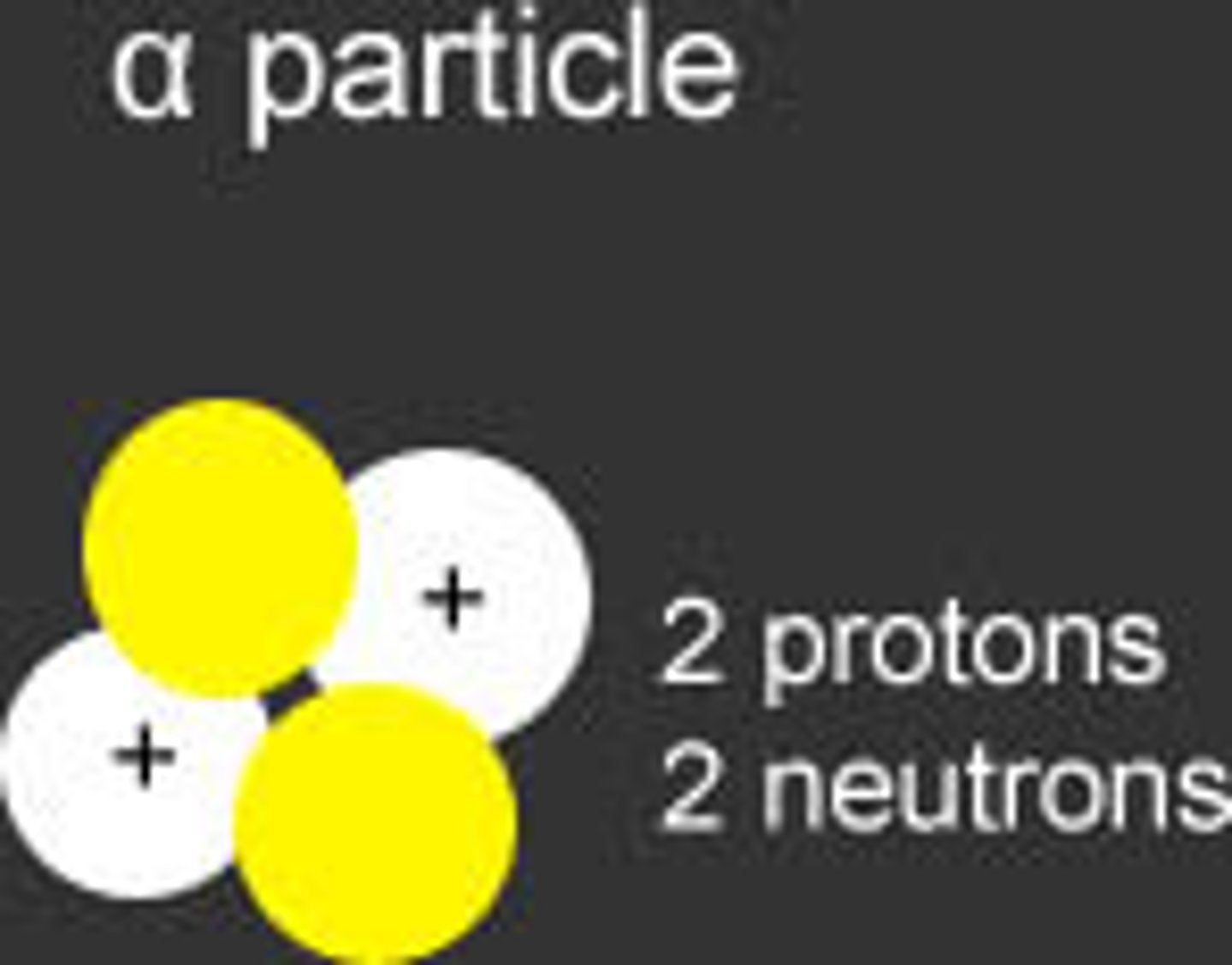
alpha particle
a helium nucleus that is emitted from a radioactive atom. Radiation deflected towards a negative plate.
beta particle
an electron that is emitted from a radioactive atom. Radiation deflected towards a positive plate.
gamma particle
a high-energy photon (particle of light) that is emitted from a radioactive nucleus. Gamma particles have zero mass and zero charge.
symbol for alpha particle
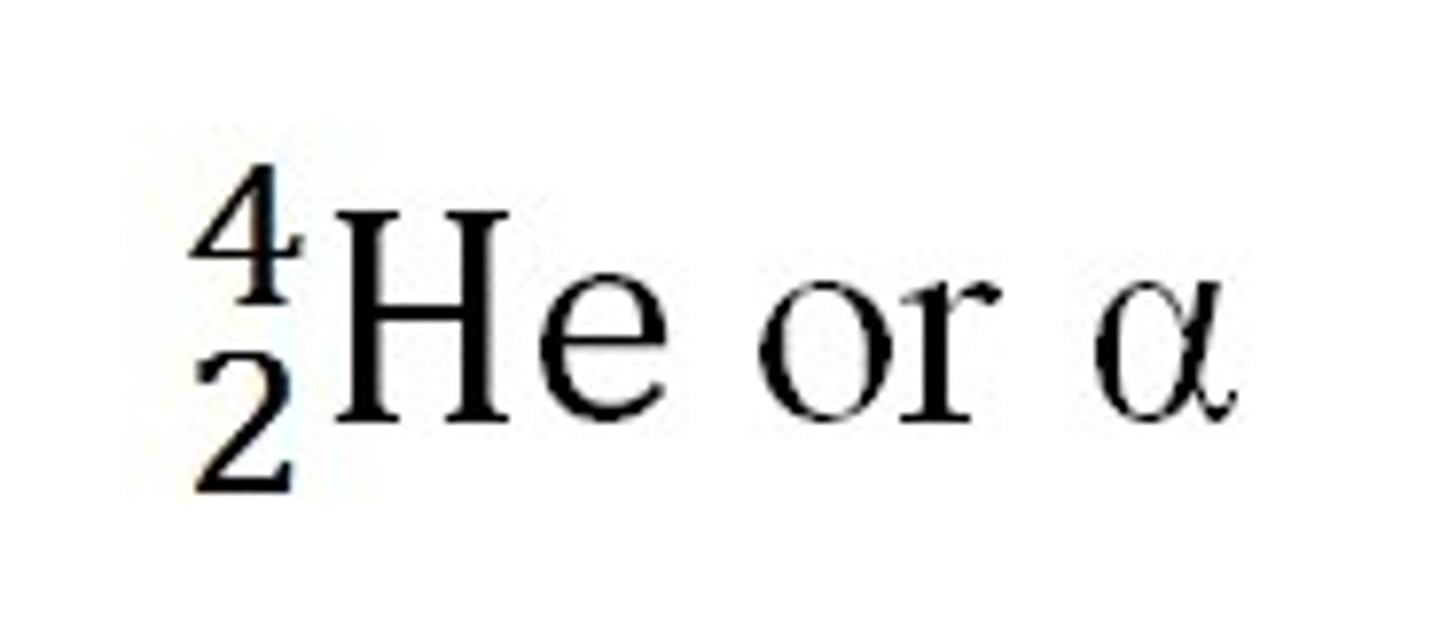
symbol for beta particle
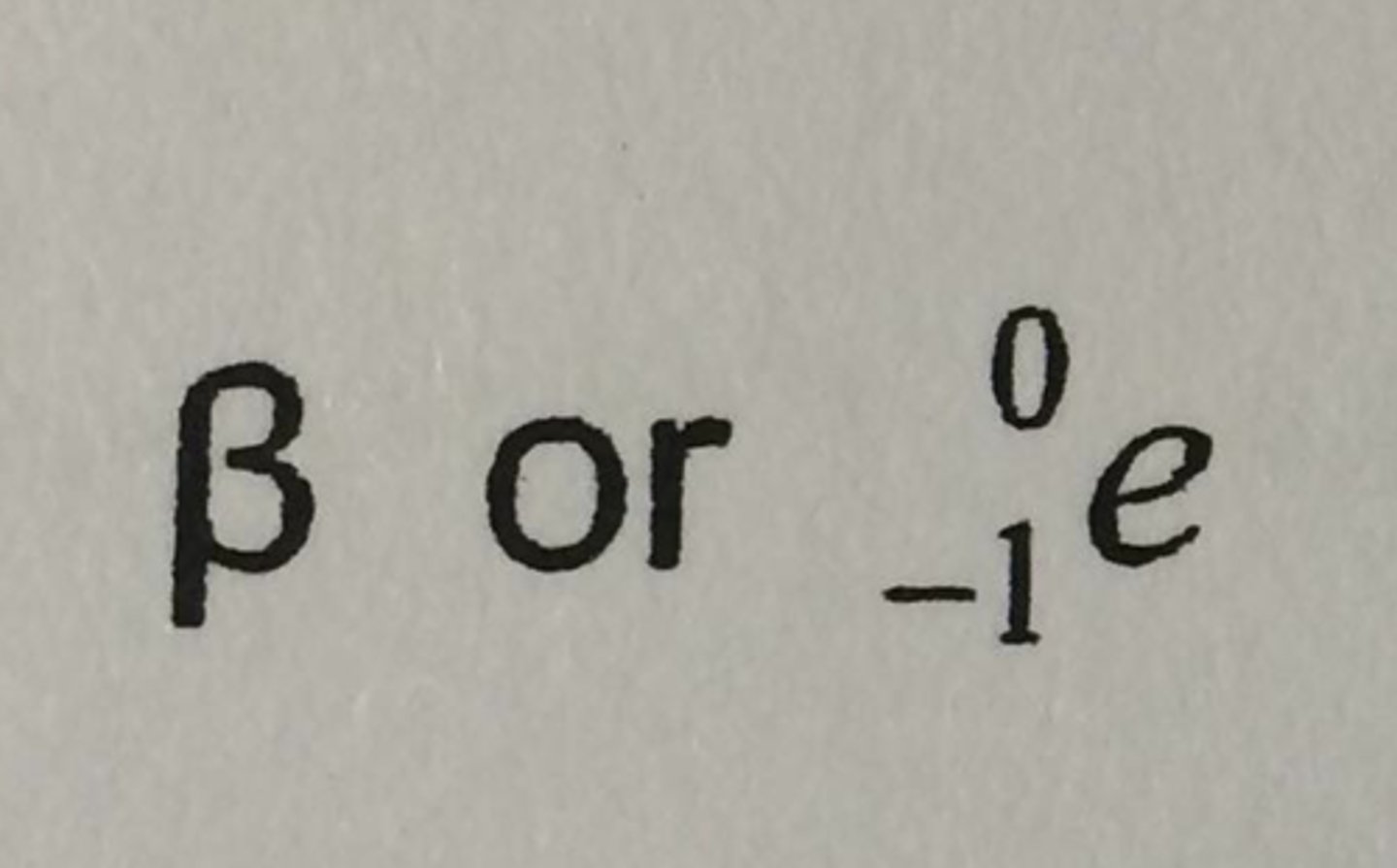
symbol for gamma particle or gamma ray
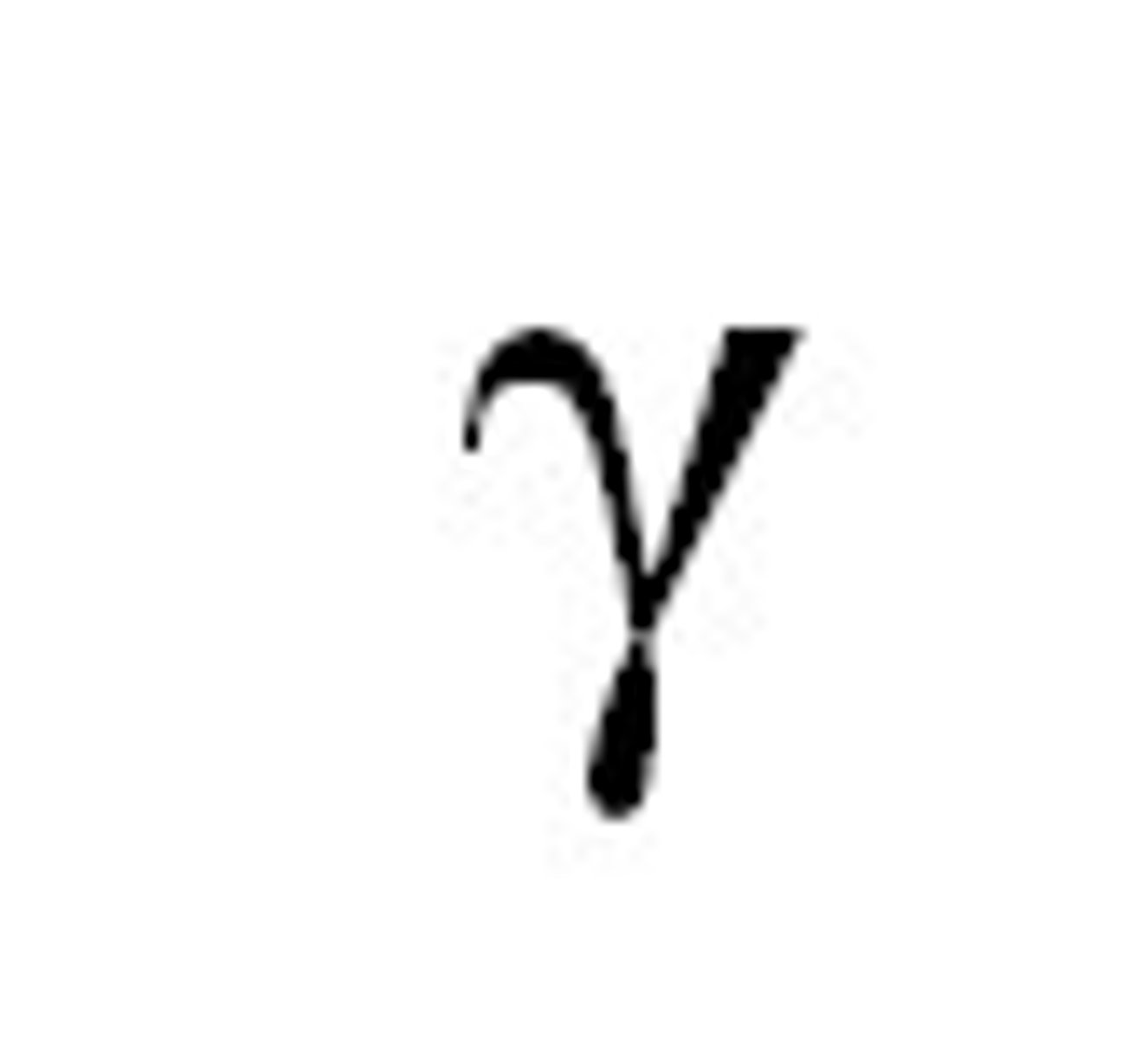
nuclear force (strong force)
holds nucleus together
mass number
the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom
atomic number
the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. The number of protons is unique to each element and defines that element.
Using the periodic table and your knowledge of nuclear chemistry terminology, give the symbol for carbon-14.
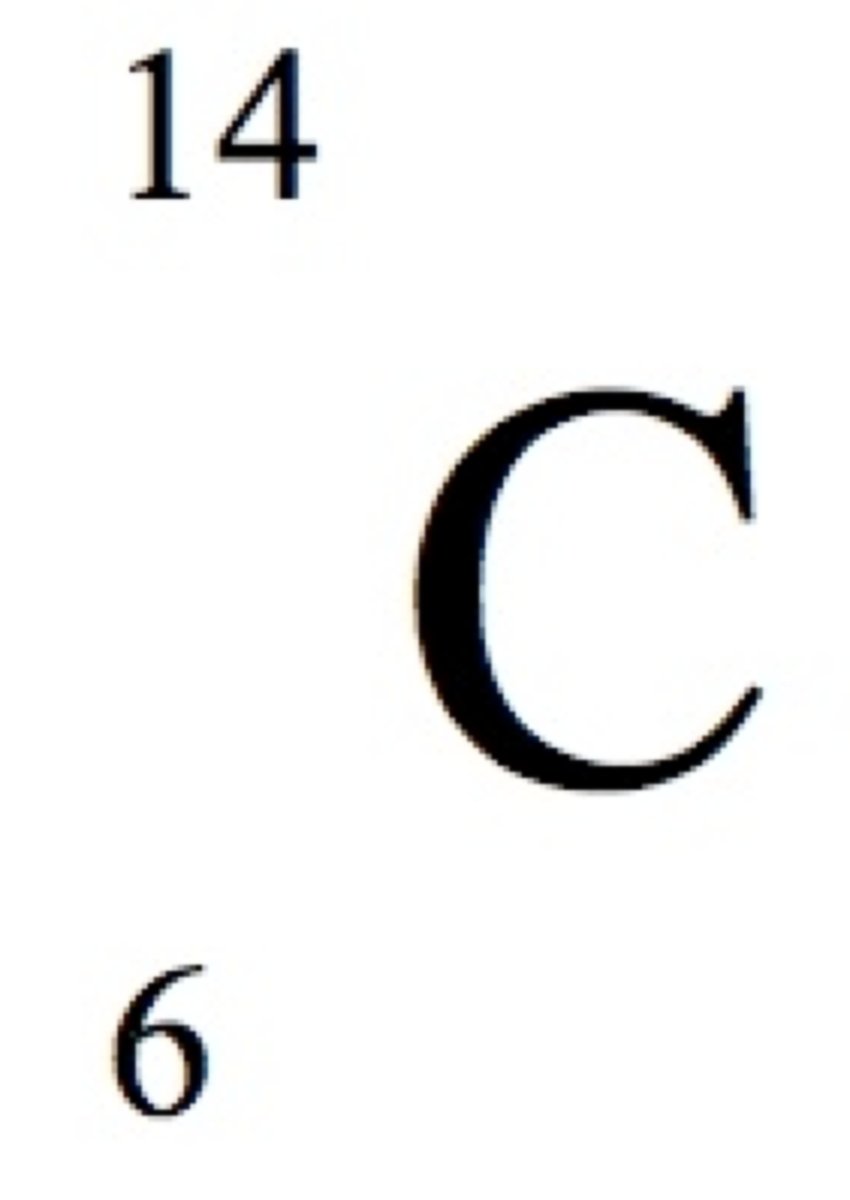
requires energy to start a reaction
both nuclear fission and fusion
nuclear power plant, nuclear bombs
examples of nuclear fission
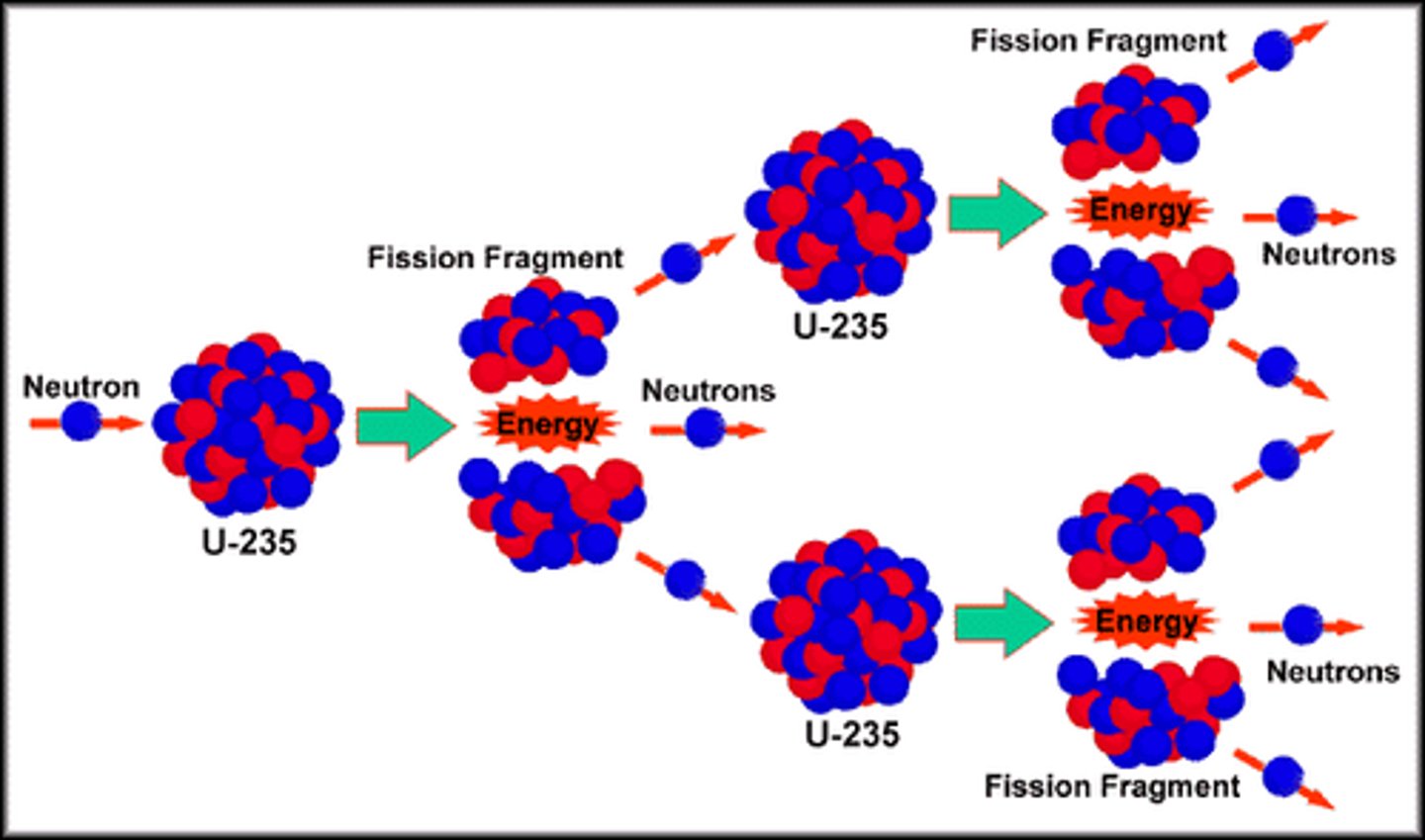
fission
breaking a large nucleus into smaller nuclei.
This is what releases the energy in nuclear reactors and atomic bombs.

What subatomic particle sustains the nuclear chain reaction in nuclear reactors and atomic bombs?
The neutron
fusion
squashing smaller nuclei together to form larger nuclei. This releases even more energy than nuclear fission.
sun and stars
example of nuclear fusion
Radioactive half-life
The radioactive half-life for a given isotope is the time for half the radioactive nuclei in any sample to undergo radioactive decay.