GV-3 Transcriptional Regulation
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
What are steroids?
Endogenous agents w/homeostatic functions, and therapeutic anti-inflammatory agents.
What process means cells can differentiate into dif cell types?
Controlled expression of genes in a temporal and spatial manner.
Eg through transcriptional regulation!
What is transcription?
when DNA is transcribed into mRNA in the nucleus.c
Give an example of temporal gene expression.
Bone marrow continuously produces WBCs, requiring constant activation of proliferator genes.
What other factors influence gene expression beyond transcription?
Epigenetics, microRNA, post-translational modifications.
How does microRNA regulate gene expression?
It controls gene expression at the translation level by preventing protein production.
What are some examples of post-translational modifications?
Acetylation, phosphorylation, and protein folding modifications.
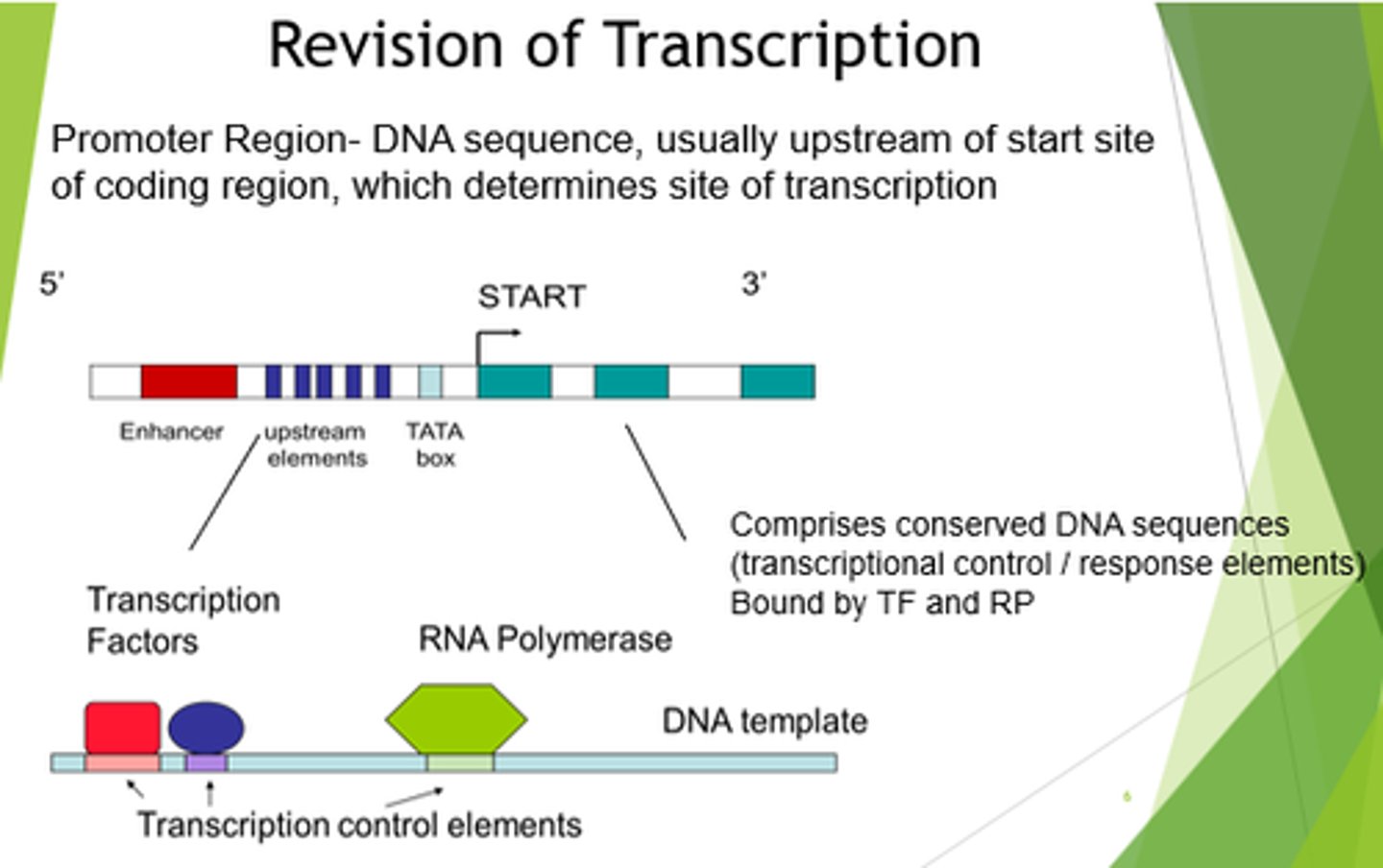
What are promoters?
Short DNA sequences that determine the site of transcription initiation for an RNA polymerase.
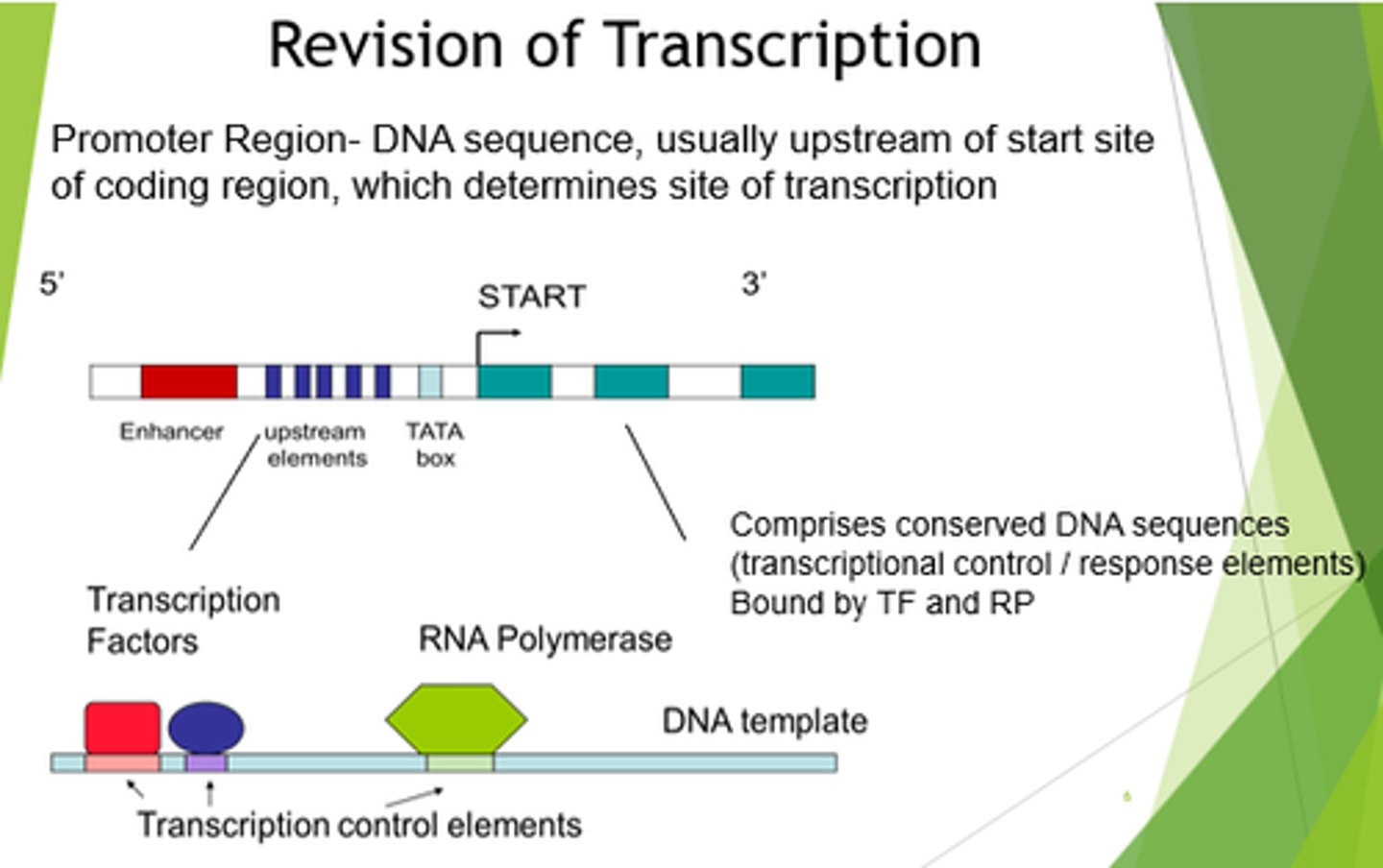
What are promoters composed of?
Sets of conserved DNA sequences.
Where are promoters present?
In DNA upstream of transcriptional start sites.
What are promoter sequences recognised by?
Transcription factors or RNA polymerases.
What is the purpose of the promoter region?
- RNA polymerase is non-selective for genes, so needs to be told which to bind to.
- Determines site of transcription initiation for an RNA polymerase.
- Positions RNA polymerase at the start of the gene we want to copy.
- Enhance ability of RNA polymerase to sit on TATA box.
Where does specificity arise in gene transcription?
- At the enhancer region.
- By binding dif transcription factor proteins, we control which genes are transcribed at which time.
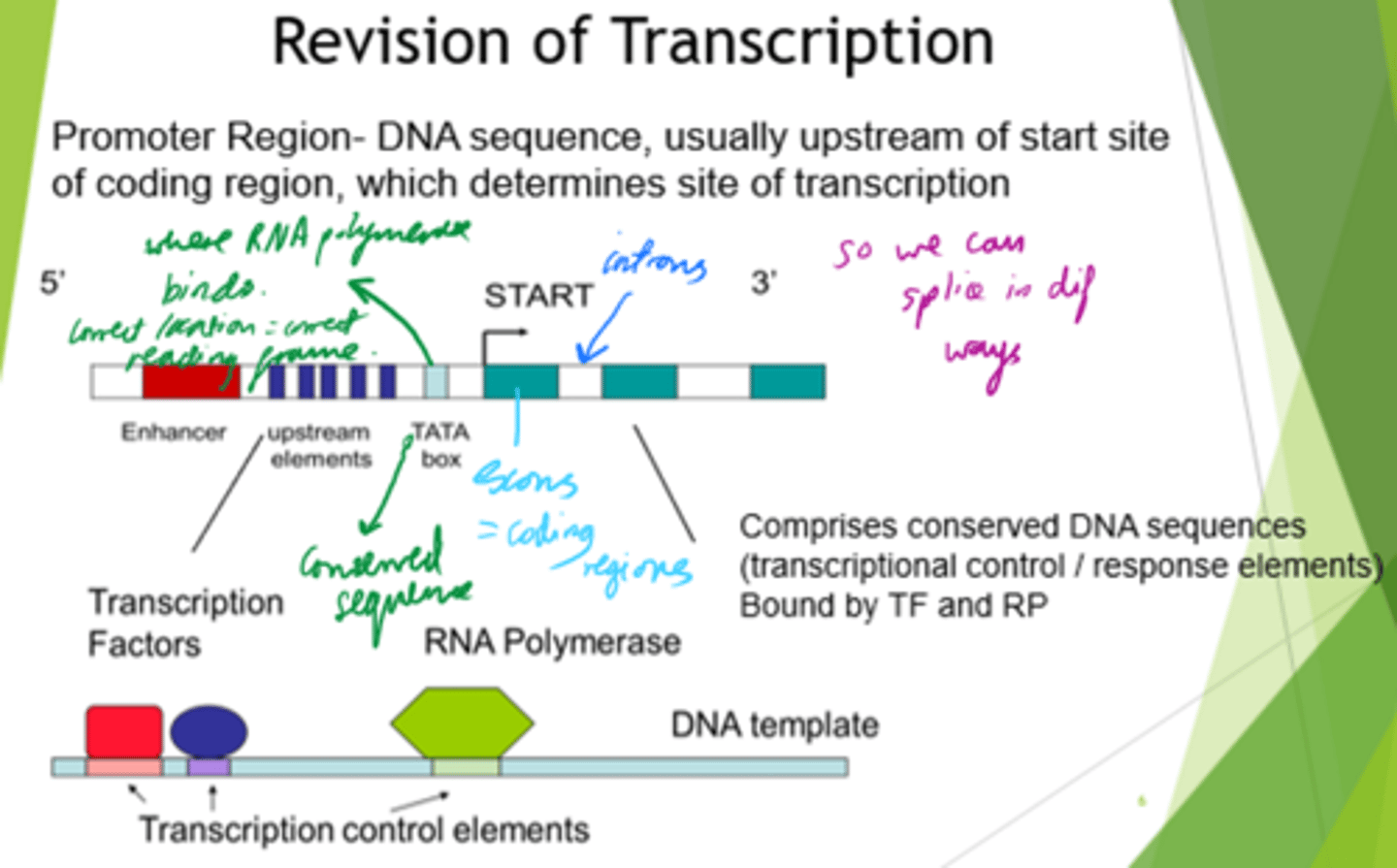
What is the TATA box?
- DNA sequence in the promoter region of eukaryotic genes.
- Role in transcription initiation.
- Found in highly expressed genes.
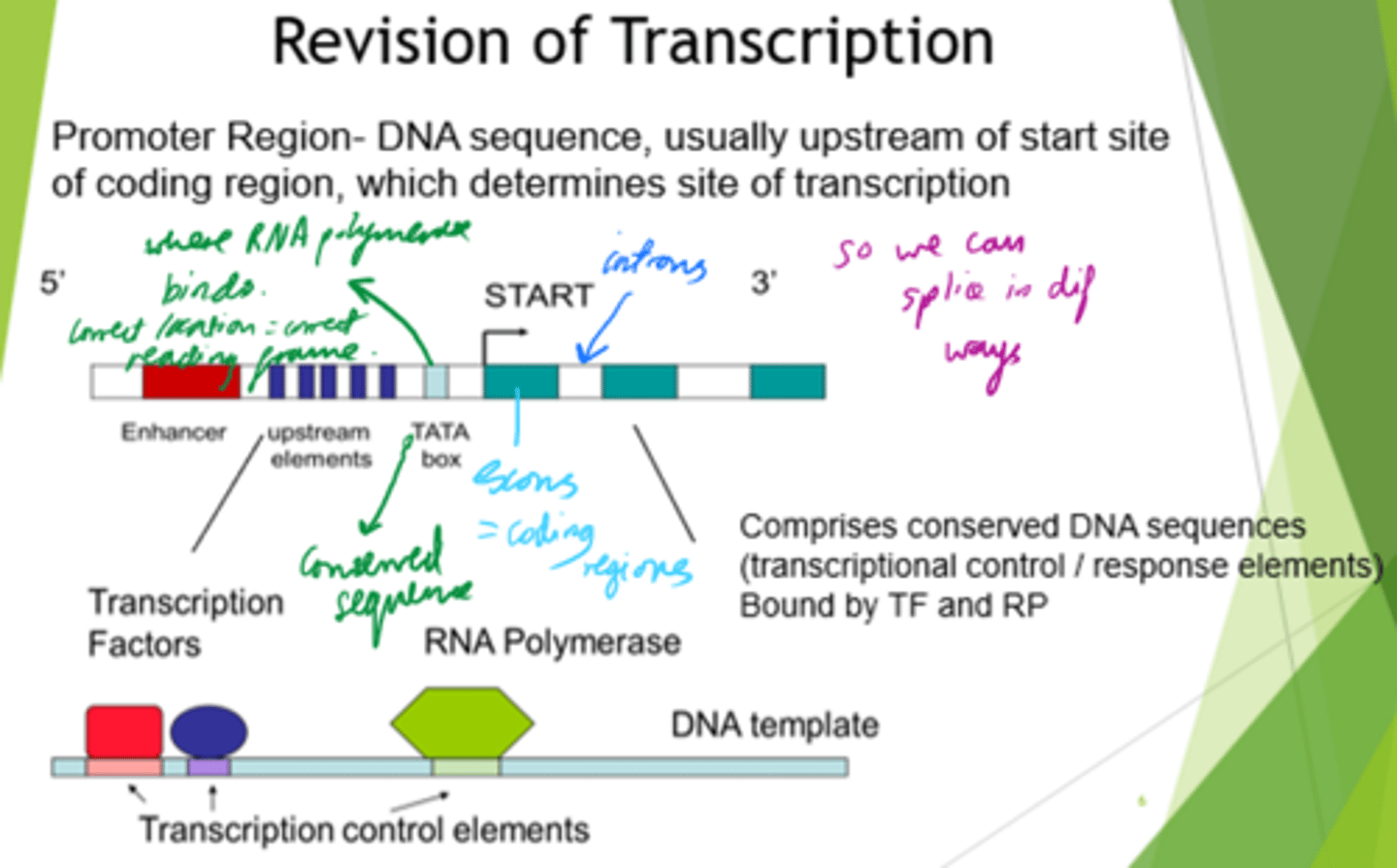
What are gene transcription processes driven by?
- Availability/activation of transcription factors.
- Accessibility of DNA.
- Chromatin structure (DNA + histone proteins)
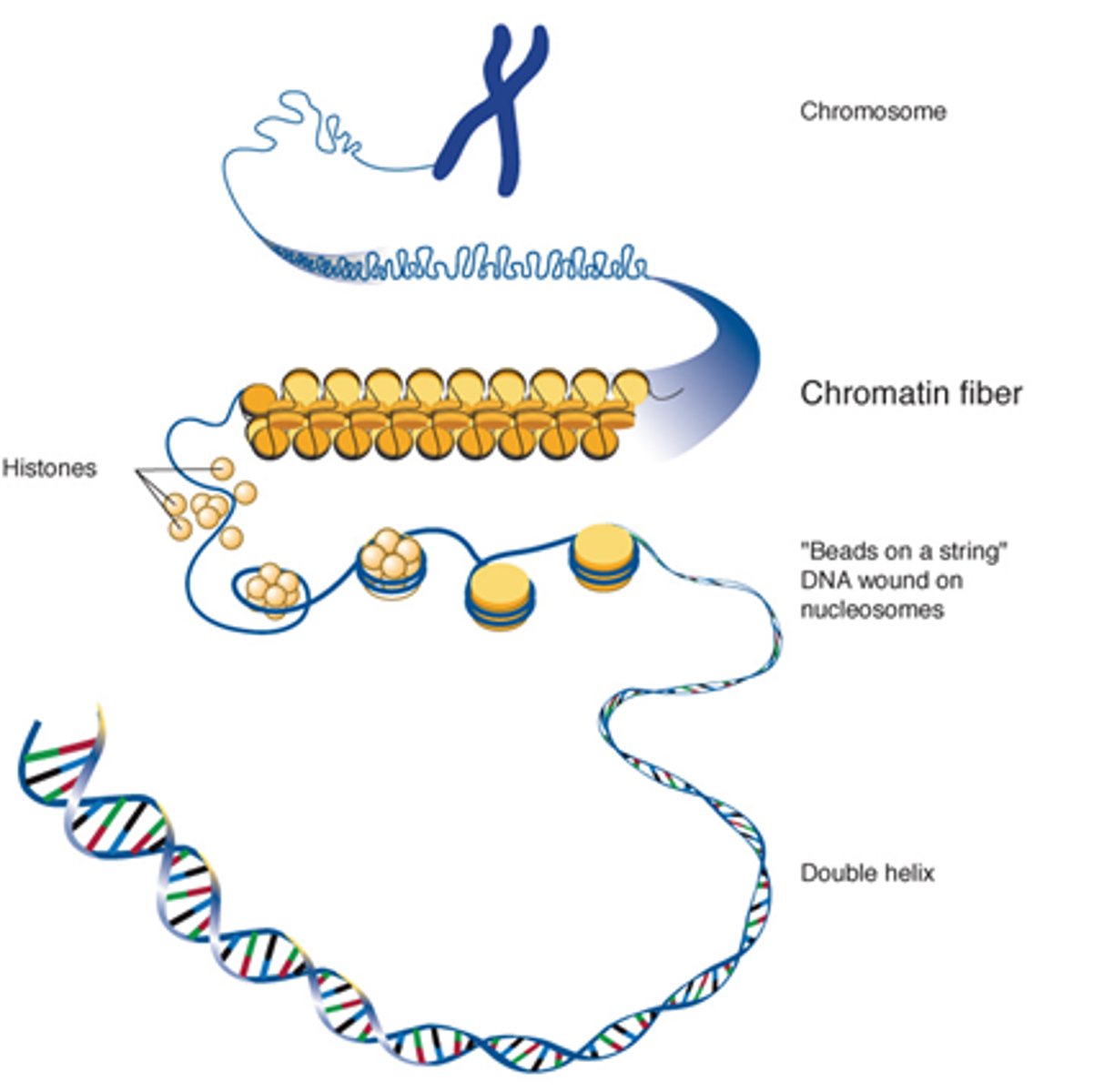
What is required to unwind DNA?
Coactivator proteins
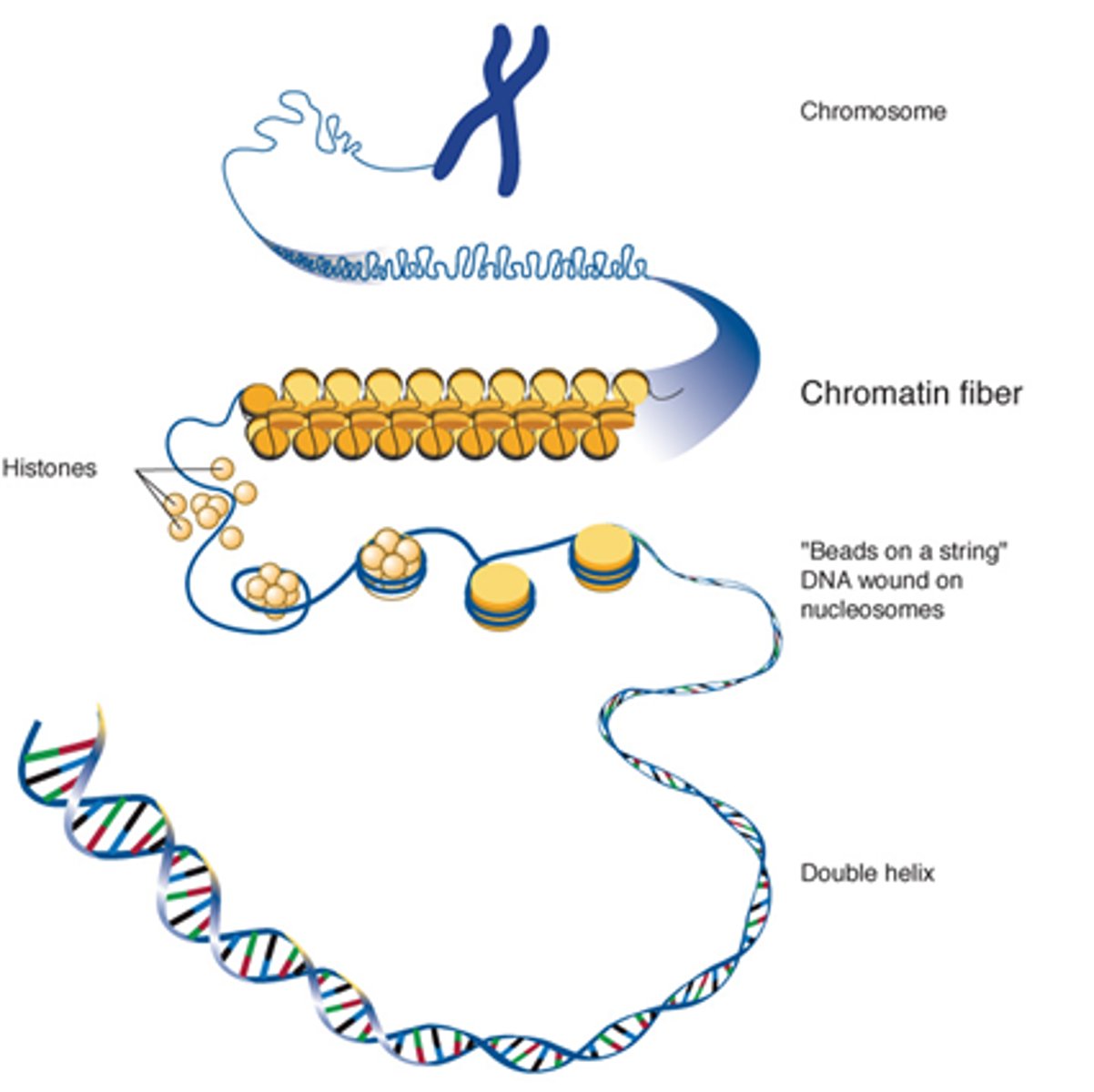
How is DNA compacted?
Supercoiled around histone proteins.
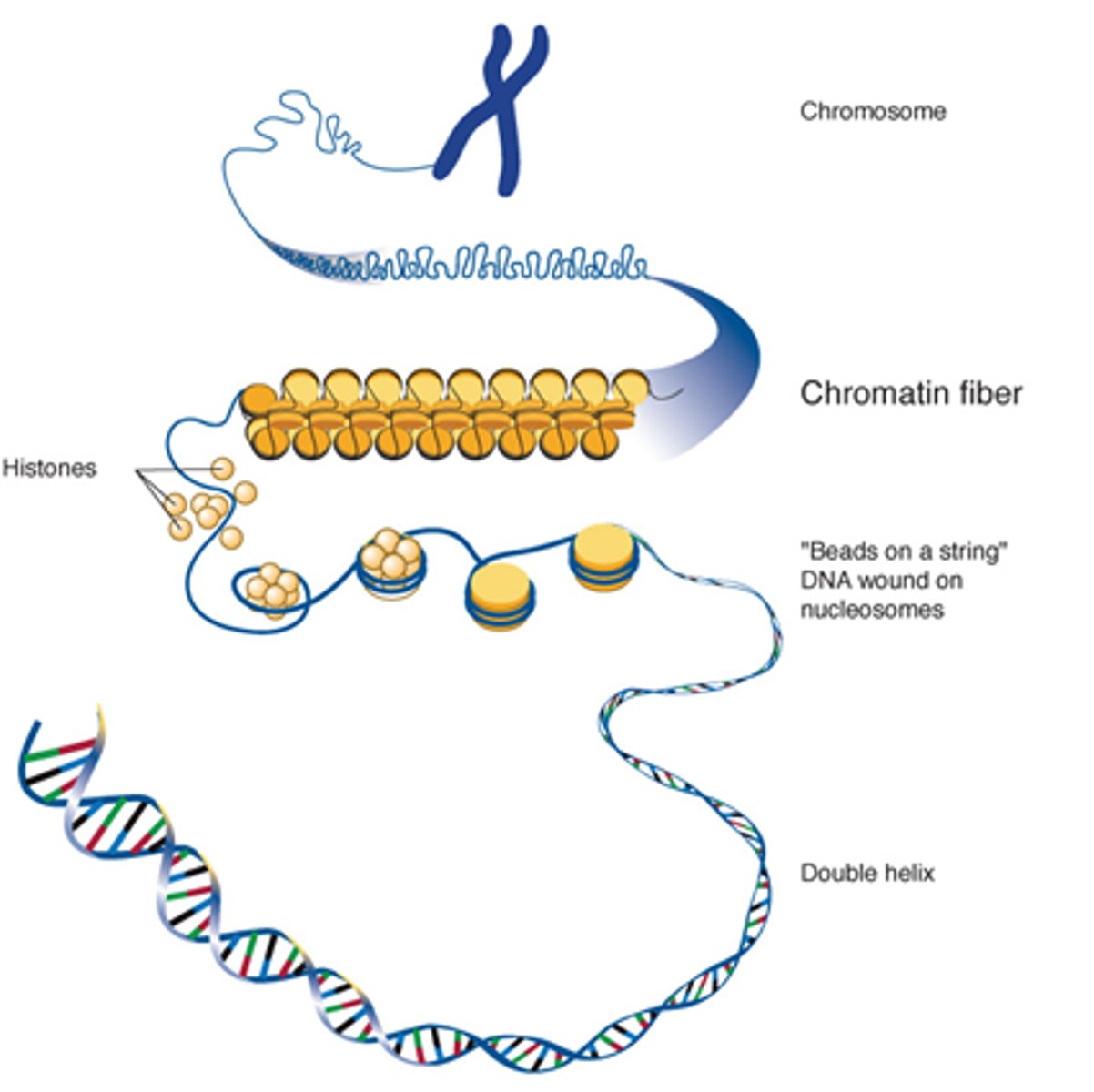
What does assembling 8 histones together form?
Solenoid fibres
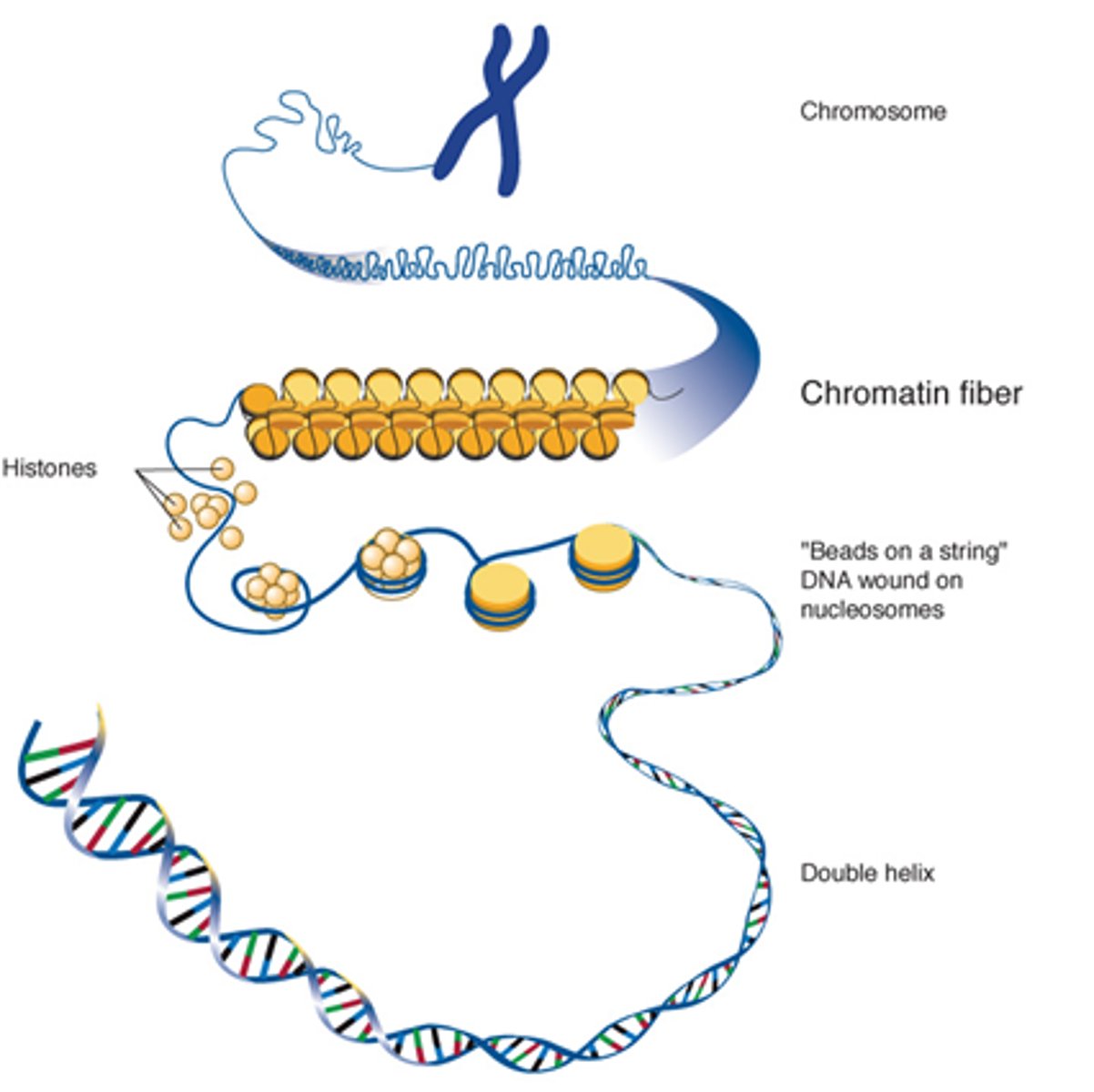
Describe how DNA is stored in the nucleolus.
DNA -> histone proteins supercoiling -> solenoids -> chromatin fibres -> chromosomes.
Need to unwind the chromosome for access in transcription.
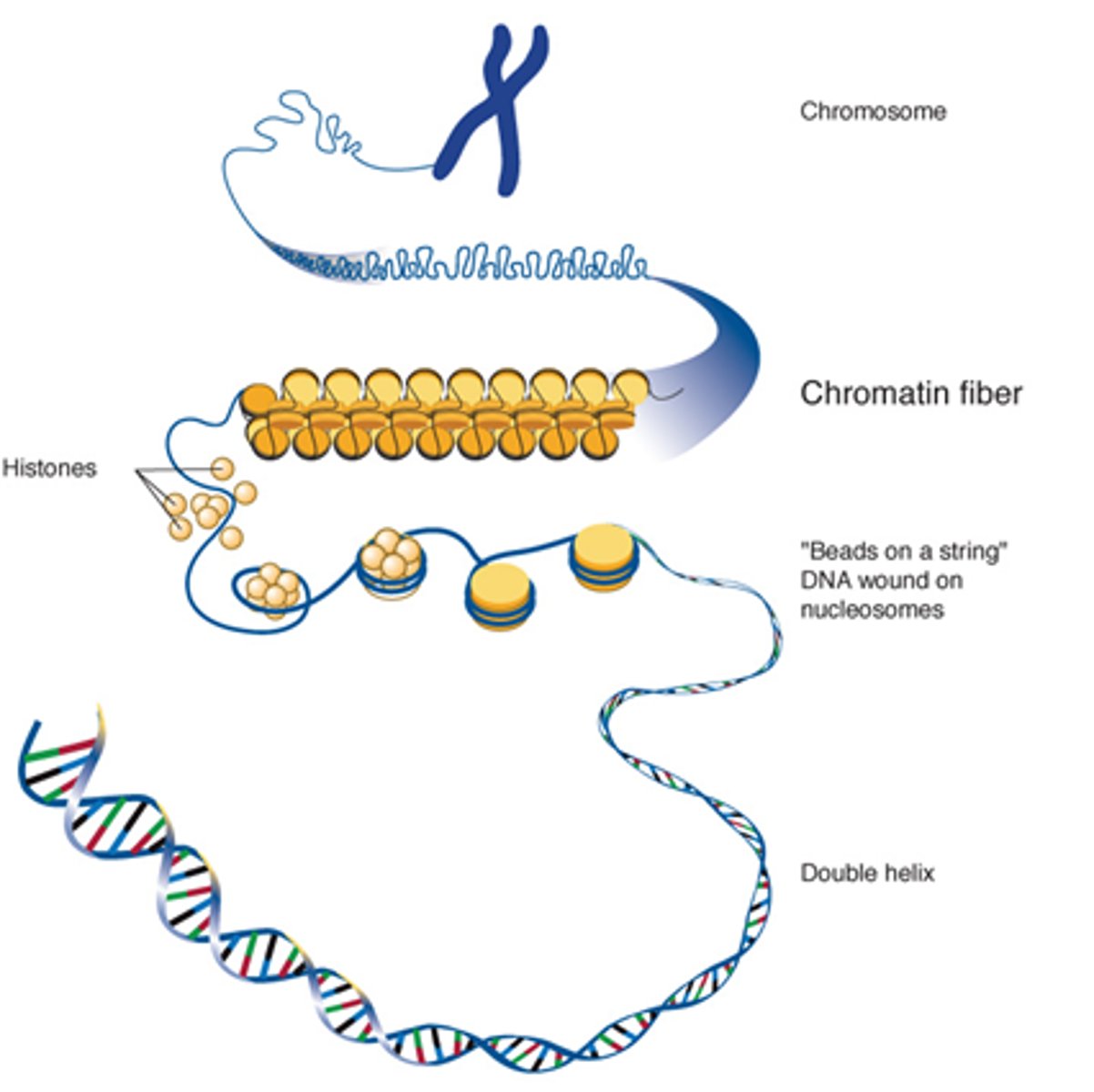
What is the role of histones?
+ve histones attract -ve DNA phosphate backbone.
Enables interaction for supercoiling.
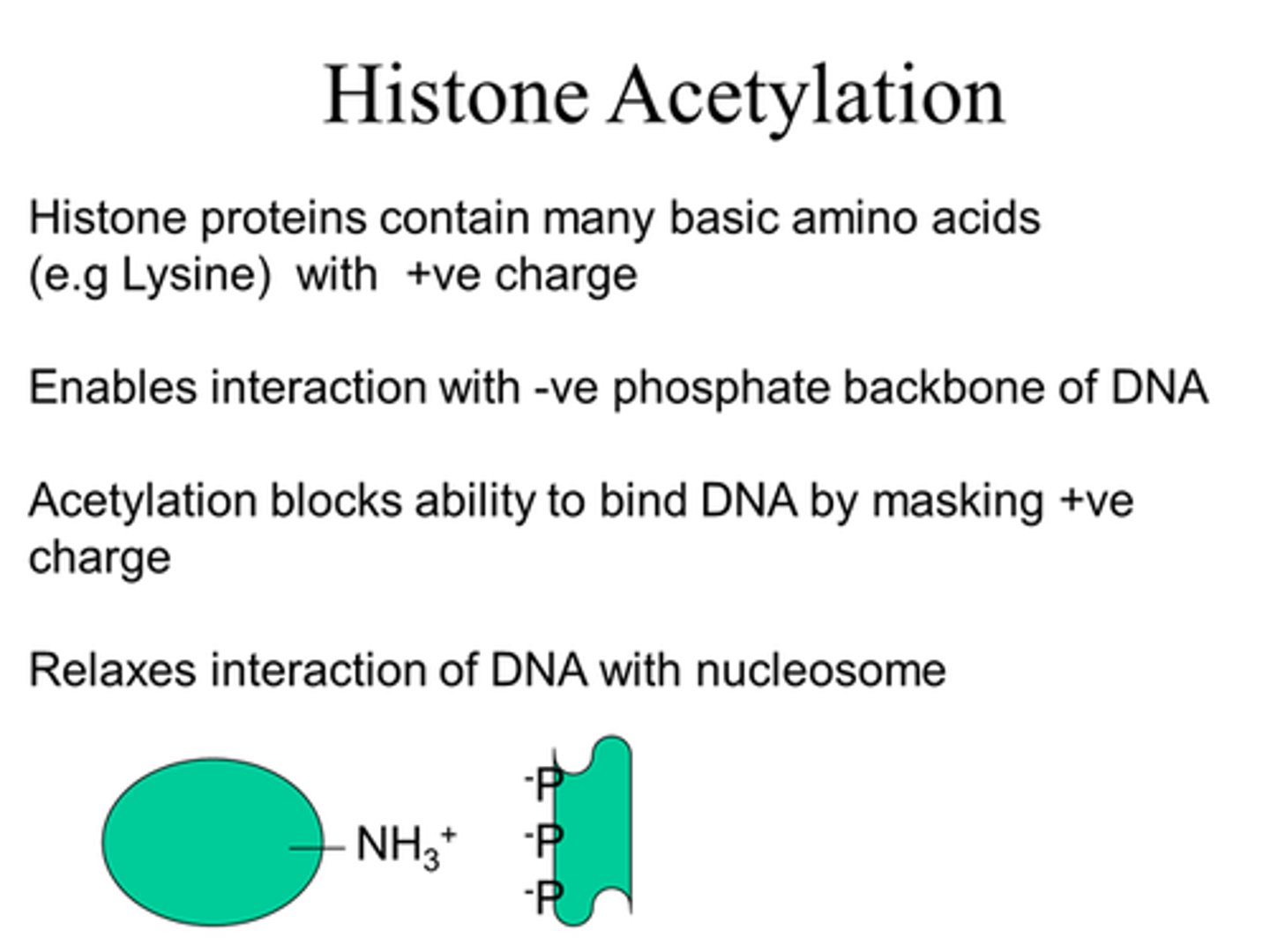
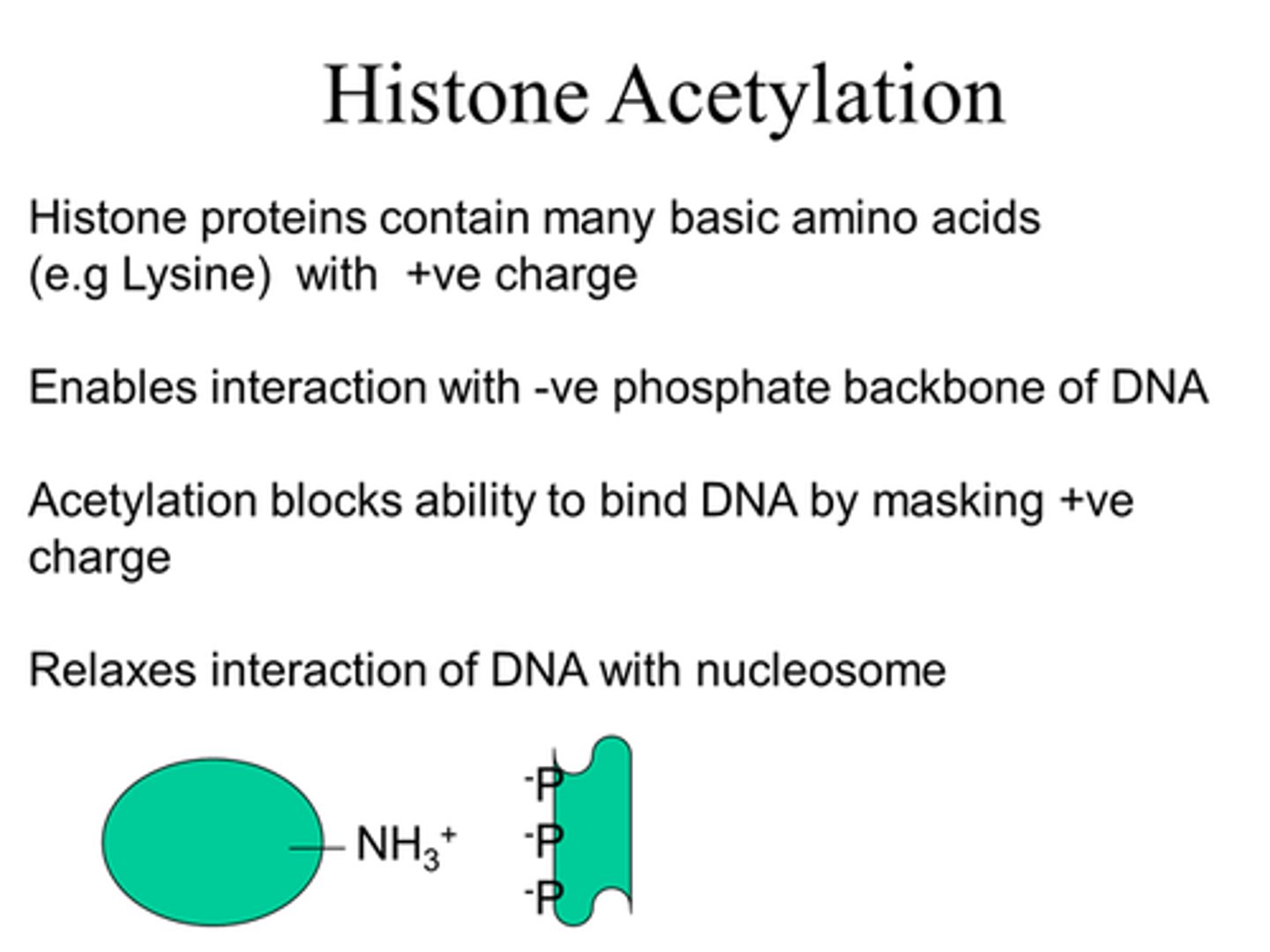
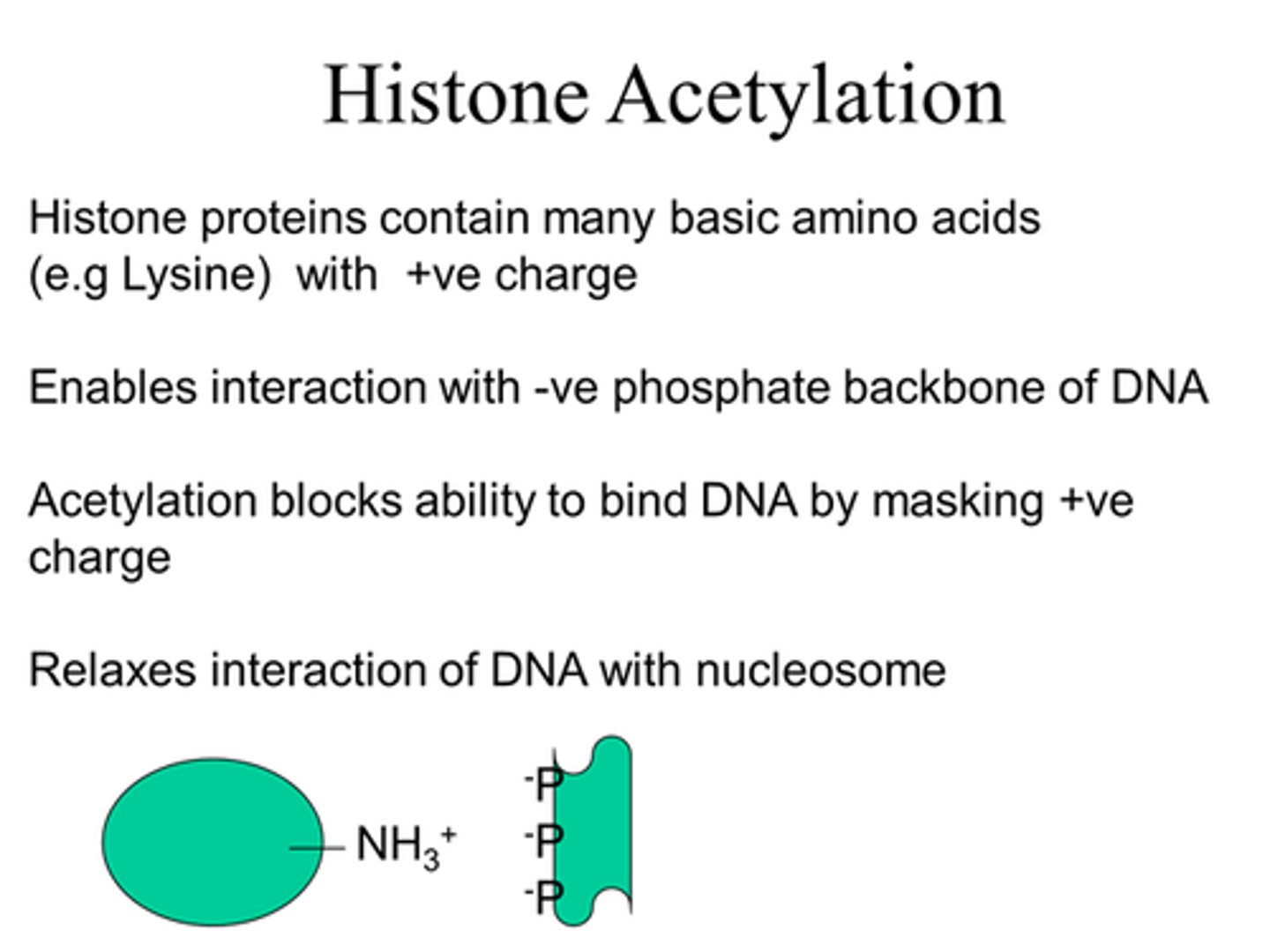
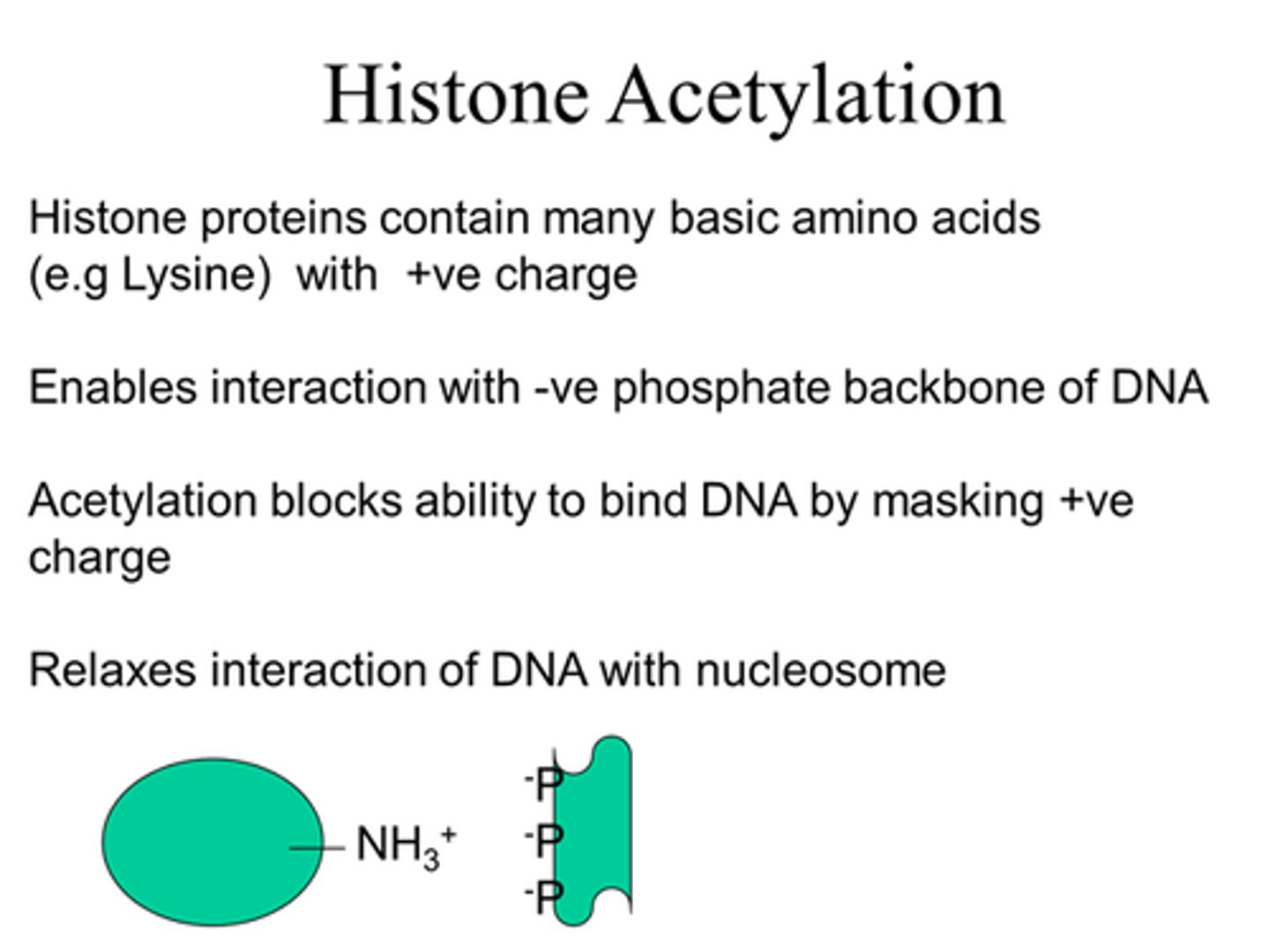
What do histones contain that enable interaction with -ve phosphate backbone of DNA?
Many basic amino acids with +ve charges at cellularl pH.
Eg Lysine
How can we mask positive charge of the histone protein?
By acetylation - add an acetyl group.
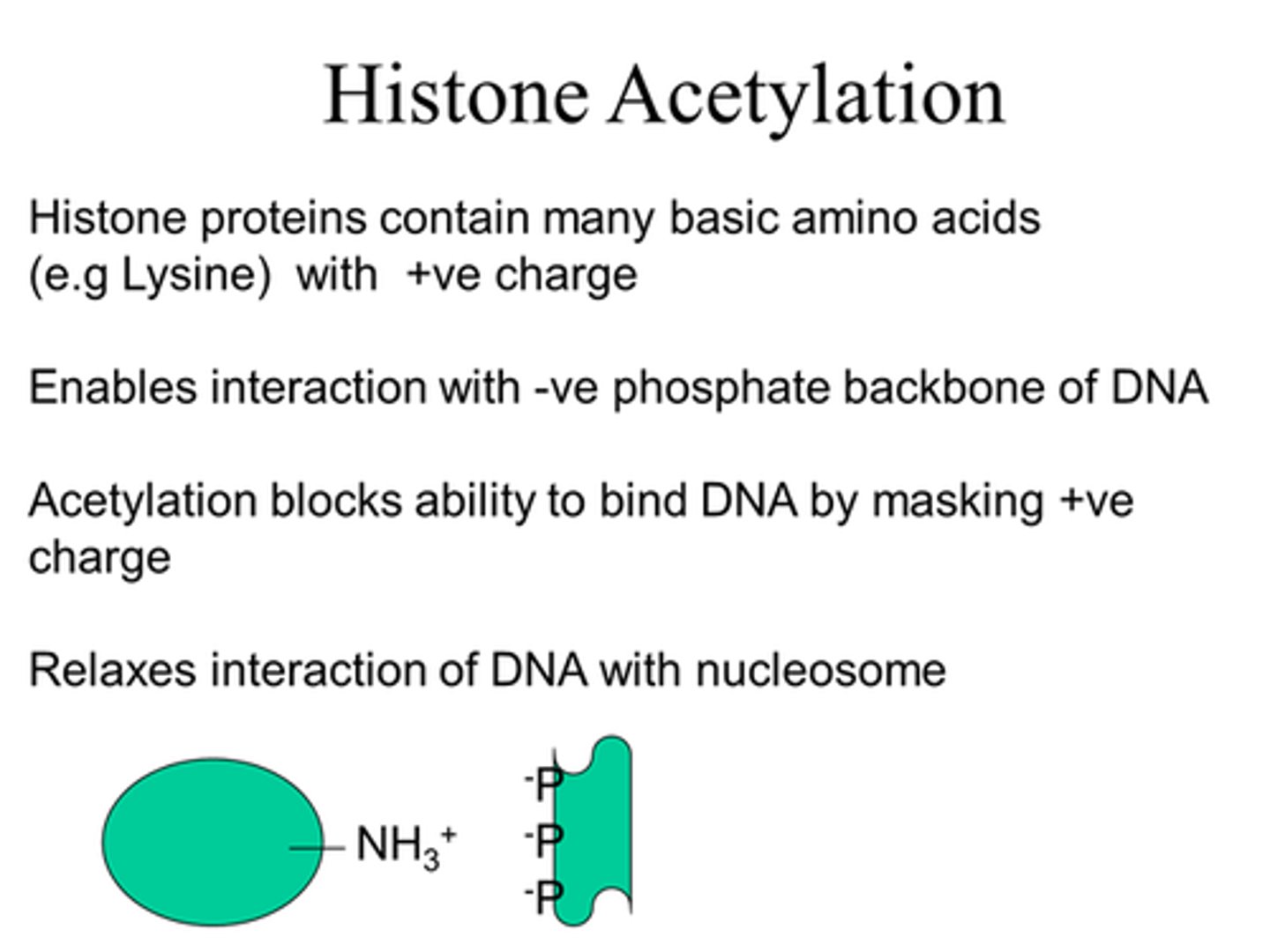
How can we unwind DNA from a histone protein?
Via acetylation - add acetyl group to mask +ve charge, relaxing the DNA-histone complex, allowing unwinding.
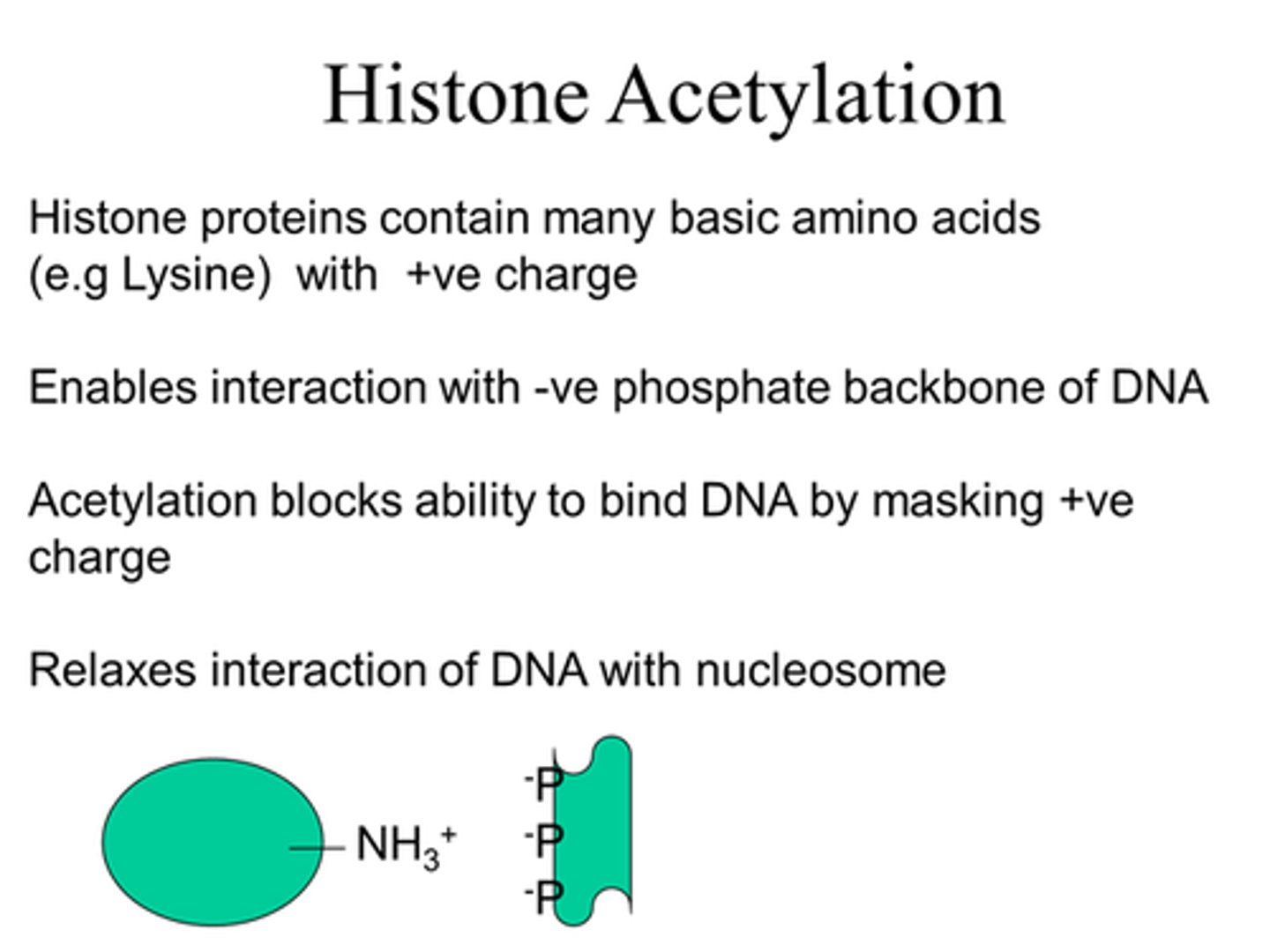
What does acetylation do?
Adds an acetyl group, blocking the ability of histones to bind DNA by masking their +ve charge.
How are histones acetylated?
By HAT - Histone Acetyl Transferase from Coactivators (unwinding proteins).
How is histone deacetylation carried out? When?
- By HCACs after gene transcription.
- Histone DeAcetylases remove acetyl groups.
What 2x forms does chromatin exist in?
Heterochromatin or euchromatin.
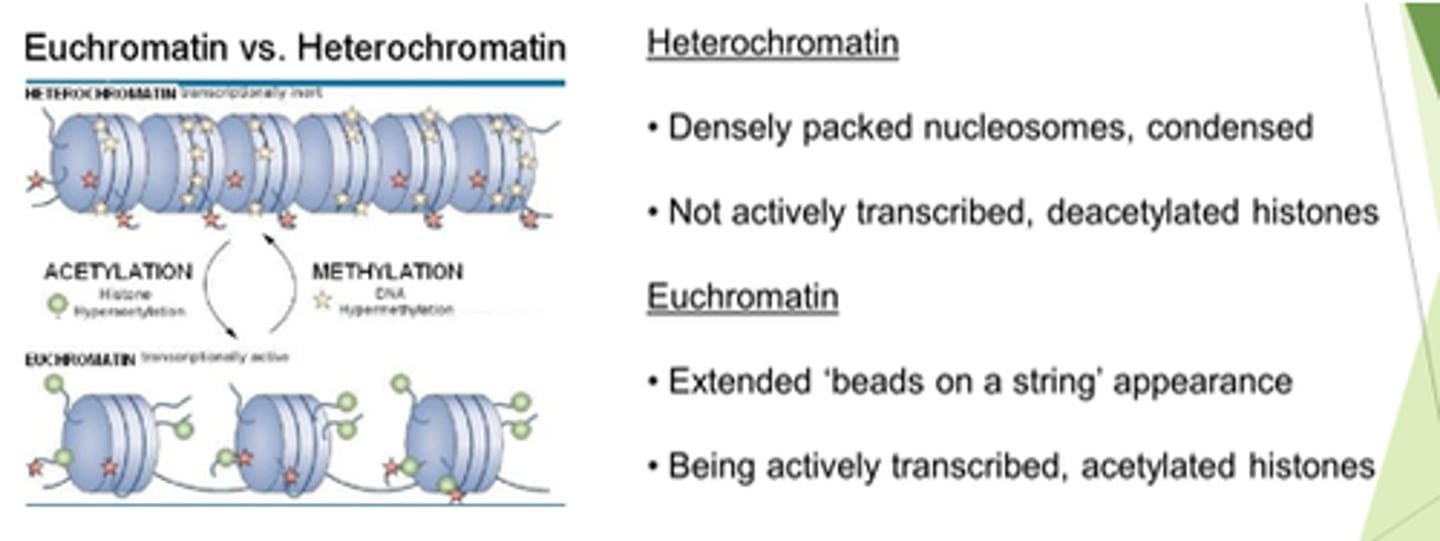
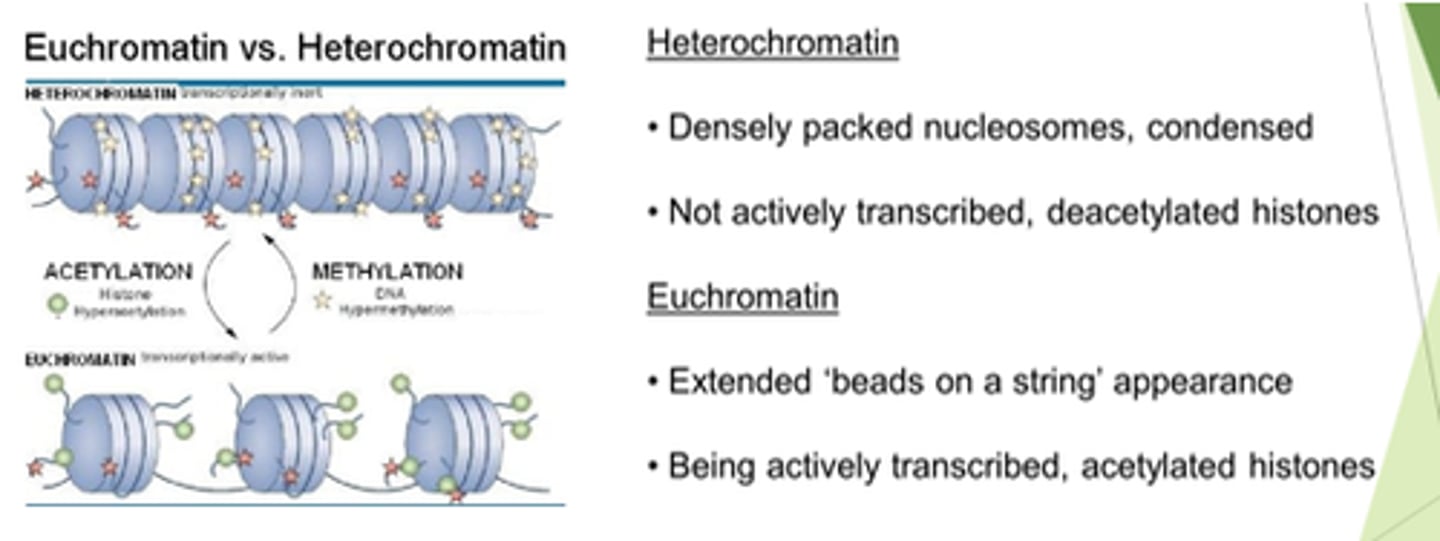
Describe heterochromatin.
Transcribed? State of histones?
- Densely packed nucleosomes.
- Condensed.
- Not actively transcribed.
- Histones are deacetylated.
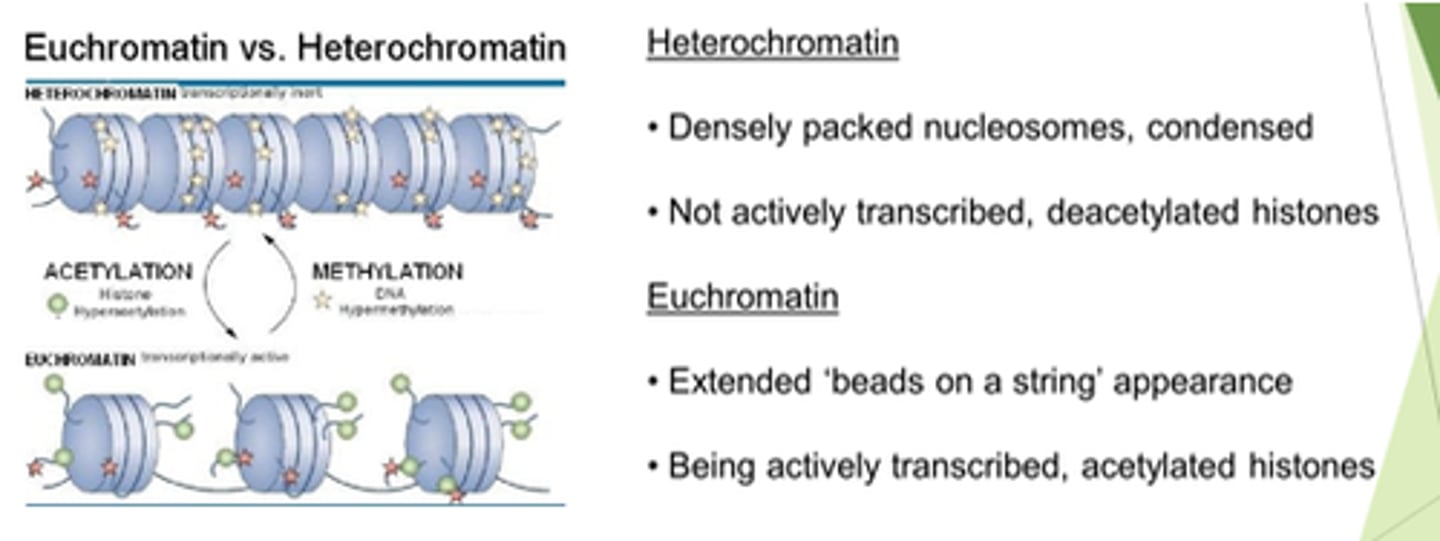
Describe euchromatin.
Transcribed? State of histones?
- Extended beads on a string appearance.
- Actively transcribed.
- Histones are acetylated.
What is the process of acetylation and deacetylation also referred to as?
Epigenetics
Name a process that happens to DNA that reduces transcription.
Methylation
How can oncogenes cause cancer?
- Oncogenes get over-acetylated.
- More DNA transcription, more growth factors.
- Drives excessive cell growth.
How can tumour suppressor genes cause cancer?
- Methylation of DNA.
- Methlated DNA is more compact, so can't be reached by transcription factors.
- So TSGs aren't expressed and can't suppress tumours as well.
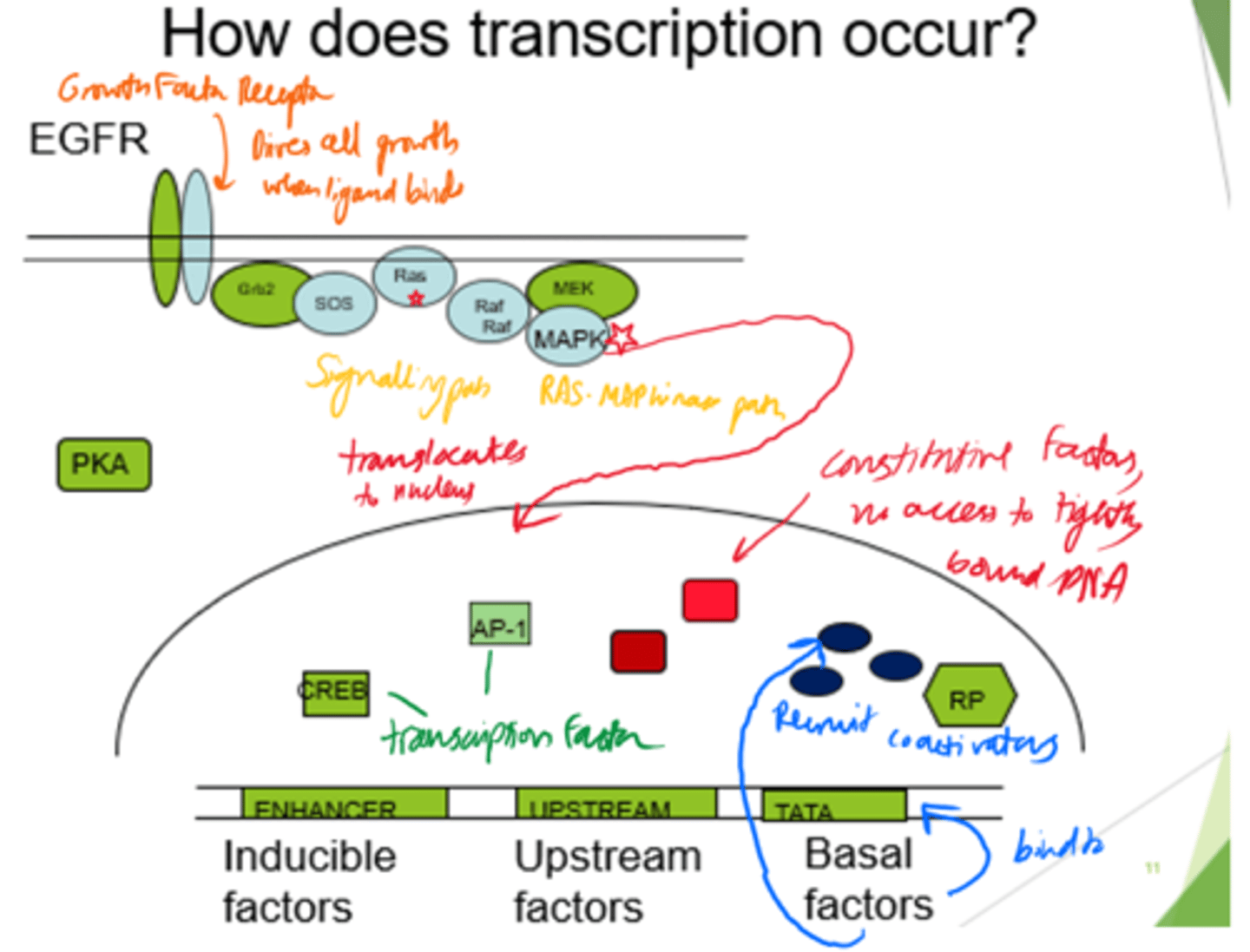
Transcription factors are not good drug targets. What do we need to target instead?
Protein-protein interactions.
How is cellular function controlled and regulated?
Controlled: protein expression
Regulated: gene expression
How is gene expression regulated?
By transcription being switched on and off temporaily and spatially.
What controls the process of transcriptional regulation?
Expression
Activation
Binding of transcription factors to promoter sequences
What regulates the accessibility of transcription factor binding?
Coactivator proteins that release, unwind and loop DNA, making it more accessible for transcription.