ADAPTIVE IMMUNE SYSTEM- OWN
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
Adaptive immune system ___________
is acquired
doesn’t occur until pathogen is encountered
adaptive immunity is ______________
very specific
immunity to one doesn’t confer immunity to another
adaptive immunity has a _______________
memory component
it will produce a more effective response when a pathogen is encountered for the second time- faster and stronger.
The two components:
humoral immunity
cell mediated immunity
proteins that produce by the immune system that bind and inactivate foreign antigen________
antibodies
any foreign material that has the ability to activate the adaptive immune system is called___________
immunogens
the actual portion of the antigen that binds to the antibody is called ____________
Epitopes
single antigen will have more than one epitope
immunogenicity
this increases the ability of an antigen to activate the immune system
each epitope
has a distinct antibody
hapten
low molecular weight compound that is too small on its own to activate the adaptive immunity
these are not immunogenic
bind to other molecules such as proteins in blood and tissue
wht are antibodies?
glycolysated protein molecules
what are antibodies also called
immunoglobulins
what are the four subunits of a protein molecule
two identical heavy chains
two identical light chains
what are the 3 distinct regions
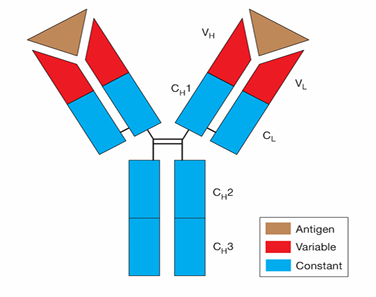
2 identical variable region a.k.a fraction antibody (Fab)
1 constant region a.k.a fraction crystalise region (Fc)
Fab region
provides specificity of the antibody
Fc region
allows for interaction with immune cells
based on differences in Fc region
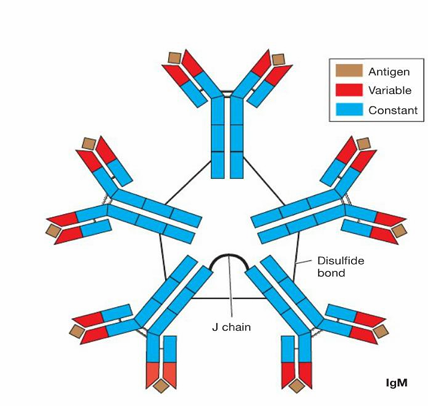
IgM
pentameric
always first Ab to be produced in response to an antigen
on surface of B lymphocytes
low affinity for antigen
very good at agglutination
IgG
monomer
predominate Ab in the blood
also in tissues
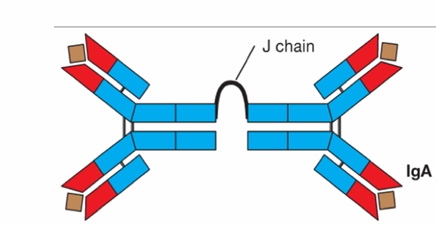
IgA
dimeric
secreted at mucosal sites
defense against respiratory, reproductive, digestive tract information
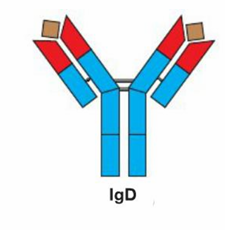
IgD
monomer
surface of B cells
activate B cells to produce Ab against a specific antigen
IgE
monomer
binds to receptor on mast cells and basophils
triggers degranulation and histamine release
allergy
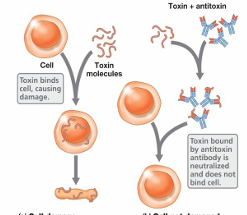
neutralization
Ab binds to antigen blocking attachment sites
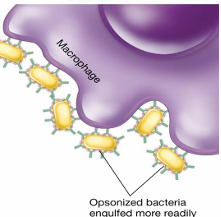
opsonization
Ab coats the surface of the bacterial cell
attracts phagocytes
enhances rate of phagocytosis
phagocyte- ability to interact w/Fc region of the Ab
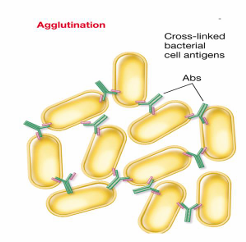
agglutination
clumps many antigens together
phagocytosis occurs more effeciently
antibody mediated cytotoxicity
attachment of antibody to parasites recruits eosinophils
eosinophils attach to Fc componenet of Ab
activated eosinophils release reactive oxygen sp. and hydrolytic enzymes
parasite is dead
complement activation
system consisiting of a series of proteins found in the blood
creates Membrane Attack Complex
MAC (Membrane Attack Complex)
goes into bacteria and creates a pore in the wall
cell contents leak out and bacterium dies
B cells are __________ cells
antigen
All antigen presenting cells can insert ______ into the plasma membrane
MHC II
What is MHC II
Major Histocompatability Complex
Ab is produced against __________
exogenus antigen
what is the first step in Ab production
B cell phagocytoses exogenous antigen
What happens to the digested content in the phagolysosome during antibody production?
It will be complexed together with MHC II and inserted into the extracellular fluid
How is the digested content from the phagolysosome in antibody production different from other phagocytosed material?
It will not be exocytosed to the extracellular fluid
role of T helper cells in Ab production
T helper cells bind to MHC II-Antigen complex, resulting in T helper cell activation.
How do activated T helper cells contribute to antibody production?
The activated T helper cell releases cytokines that bind to receptors on the B cell, resulting in B cell proliferation.
What is the significance of MHC II-Antigen complex in antibody production?
The binding of T helper cells to MHC II-Antigen complex leads to T helper cell activation in the process of antibody production.
What will some of the newly produced B cells become?
plasma cells
What do plasma cells do?
Actively transcribe, translate, and secrete an identical antibody protein to the extracellular fluid.
What are the antibodies produced by plasma cells specific to?
The original exogenous antigen.
What is the primary antibody response?
Occurs the very first time a specific antigen is encountered
What is the secondary antibody response?
Occurs every additional time (after the primary response) a specific antigen is encountered
What is the major goal of the primary antibody response?
Results in the production of memory B cells
what is the difference between 1o Ab response and a 2o Ab response
primary is slow, secondary is fast
what is tolerance
this prevents the immune response against self-antigens
tolerance helps to prevent ______
auto-immune disease
what does cell- mediated immunity do
it recognizes and destroys abnormal cells present in the body
what are endogenous antigen
present inside of the host cell
What type of cells are involved in recognizing and destroying abnormal cells present in the body?
Cytotoxic T cells
What type of antigen is present inside of the host cell and displayed in the plasma membrane complexed with MHC I?
Endogenous antigen
What is released by cytotoxic T cells to cause death of the infected host cell?
Perforins and granzymes - these casue the death of the infected host cell