Module 2- Cartilage Growth and Development
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
types of cartilage
-hyaline
-elastic
-fibrocartilage
hyaline cartilage
-glassy looking matrix
-chondrocytes found in lacunae
-mostly type II cartilage and chondroitin sulfate
-found in costal cartilage of ribs, larynx, tracheal rings, bronchi, articular surface of bones, nasal septal cartilage
elastic cartilage
-chondrocytes in lacunae
-matrix contains collagen, but dominated by elastin fibers
-outer ear, pharyngotympanic tube, epiglottis
fibrocartilage
-contains abundance of type I and II collagen
-found in pubic symphysis, annulus fibrosus, menisci, TMJ
cranial cartilage
-consists of elastic artilage in ear and epiglottis, rest is hyaline cartilage
cartilage development
-2 step process: chondroblast differentiation and morphogenesis of tissue
-cartilage begins as mesenchymal condensation
-condensations involve: cell recruitment (migration, mitoses), formation of cell-cell contacts (adherens and gap junctions), and formation of cell-ECM adhesions (integrin-fibronectin, ECM can include hyaluronan, versican, tenascin, and syndecan-3)
-as condensations begin to differentiate into cartilage, there is a DECREASE in proliferation, differentiation as well as fibronectin
mesenchyme
-tissue type characterized by loosely associated cells that lack polarity and are surrounded by large extracellular matrix
cartilage differentiation factors
1) WNTs/B catenin followed by expression of TF Runx1
2) areas of compression and relatively low pO2 (committed, separation of paths for bone formation and cartilage formation)
3) FGFs (activate Notch signaling) IHH (indian hedgehog homologue)
4) transforming growth factors followed by expression of TFs Sox9 and later Sox5 and 6
-all activate cartilage specific protiens
-both cartilage and bone have same first pattern of differentiation- under influence of WNT/B catenin
-both pre-osseus and pre-cartilagenous condensation have expression of TF Runx1
cartilage
-type of skeletal connective tissue characterized by a specific cell type AND the ECM that these cells secrete
ECM- fibrous matrix
-50% of dry weight
-includes collagens II, IX, XI, (VI), fibers of microfibrillar-elastin system, occasionally elastic fibers
-collage IX: found on surface, restricting growth in diameter of collagen fiber
-collagen XI: built in with the overall model
ECM- ground substance
-other 50% of dry weight
-includes large proteoglycan aggrecan, small leucine rich proteoglycans (decorin, biglycan, fibromodulin), adhesive glycoproteins (fibronectin, vitronectin), matricellular proteins (tenascin, osteonectin, osteopontin, thrombospondin, matrilins, cartilage oligomeric protein (COMP))
-large proteoglycan aggregan resists compression because large side chains repel each other
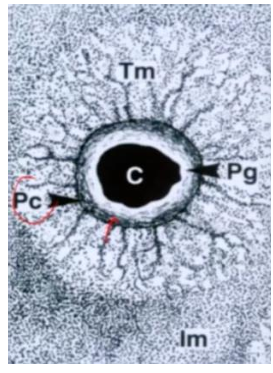
chondrocytic lacunae
-2 chondrocytes lying close together
-communicating with surrounding lacuna wall that has pericellular capsule (basket fibers)
-immediately around cells there’s a glycocalyx (Pg), pericellular capsule (Pc), territorial matrix with collagen fibers (Tm, inner matrix is lighter stain whereas outer matrix is darker stain)