Chapter 11: Physical Development in Middle Childhood
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
Physical development in middle childhood: increases in height, weight, strength, teeth
Height: 2-3 inches a year
The only period where girls are taller on average (start growth spurt at age 10)
Weight: 5-7 lbs a year, redistributed, loss of “baby fat”
Strength: boys are stronger and bones become harder via ossification
Teeth: start falling out around 4 per year at age 6
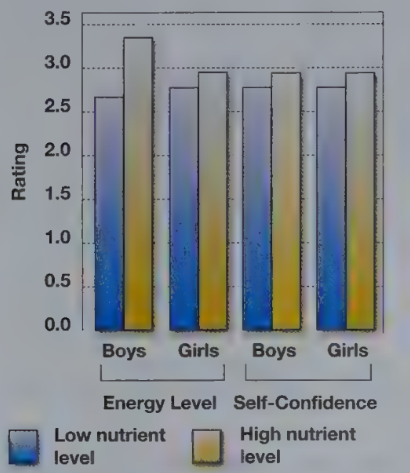
Nutrition is linked to…
Positive emotion, peer involvement, reduced anxiety, verbal abilities, motivation to learn
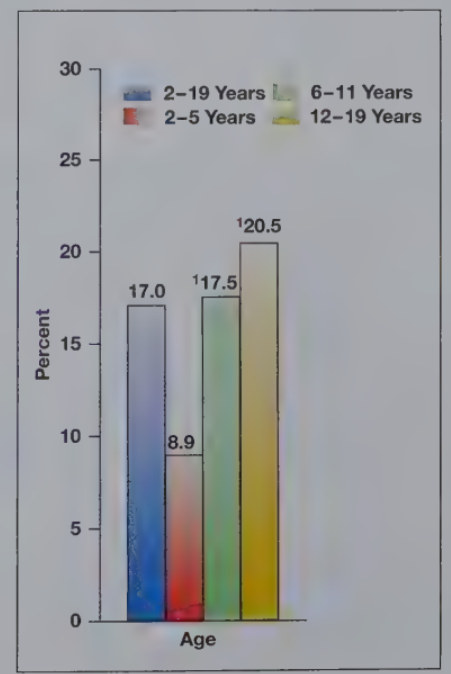
Obesity
A BMI at or above the 95th percentile
17.5% of children in the US are obese
Heightens risk of heart disease, diabetes, and adult obesity
Obesity is caused by…
Genetic factors, poor diet, lack of exercise
Many kids stay inside on technology and snack while they scroll
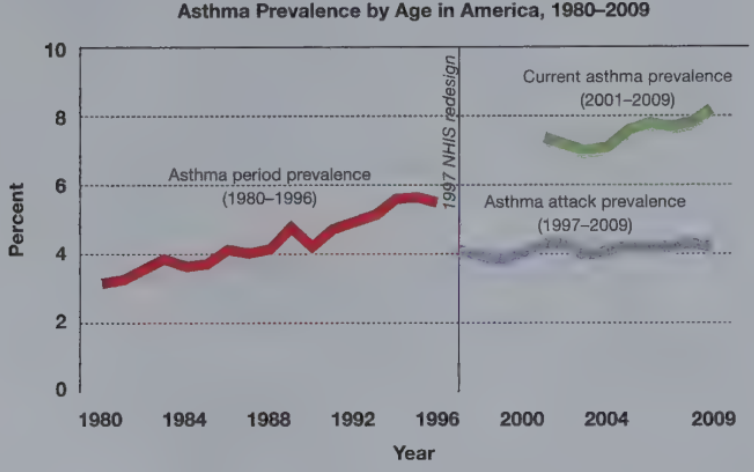
Asthma
A chronic condition characterized by periodic attacks of wheezing, coughing, and shortness of breath when the airways leading to the lungs constrict
Afflicts more than 7million children in the US
Triggered by respiratory infections, airborne irritants, stress, exercise, and sudden changes in air temperature or humidity
More than ____ of children are likely to have at least one serious medical condition during middle childhood and ____ has a chronic condition
90%, 1 in 9
Between __ and __ percent of children in the US experience a mental disorder
13 - 20
Improvement in gross and fine motor skills
Gross: increased muscle coordination
Recent research finds minimal gender variation in motor skills
Fine: able to tie shoes, use hands independently, etc
Significant increase in myelin between ages 6-8
The goals of participation in sports and other physical activities should e to _______, ________, ________, and _______
Maintain physical fitness; learn physical skills; become comfortable with ones body; have fun in the process
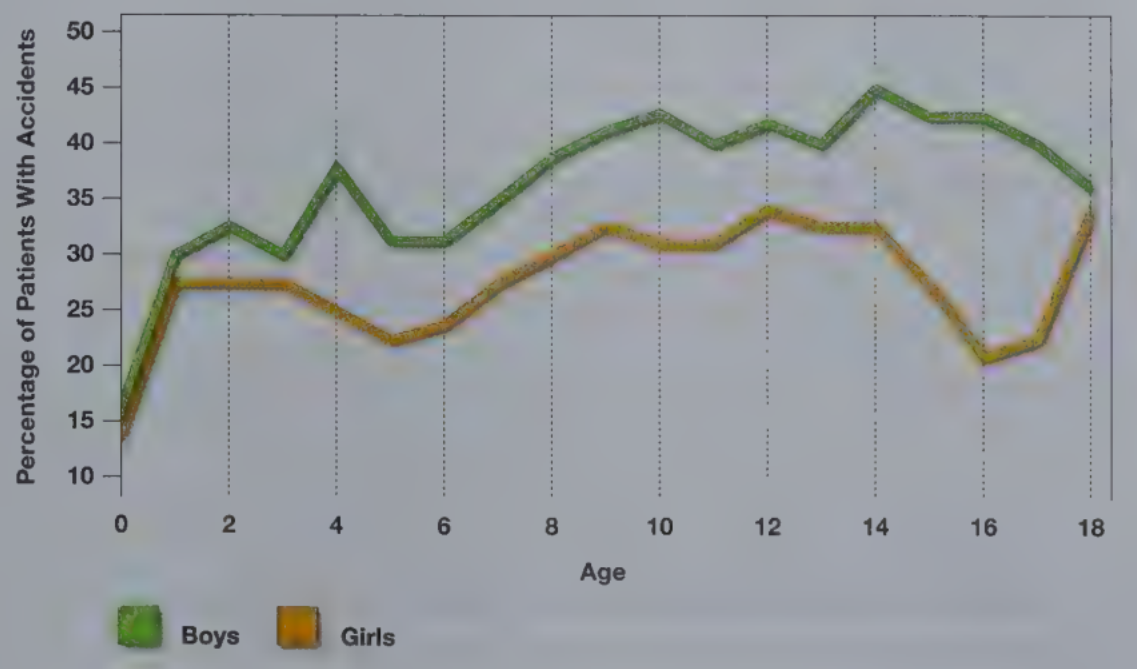
Majors causes of accidents are _____, _____, _____, _____, _____
Increased mobility
Rate of injury increases between ages 5 and 14
Car accidents, fires, drowning, gun-related deaths
Accidents are reduced by helmets and seatbelts
Visual impairment
Difficulties in see that includes blindness (2/200) or partial sightedness (20/70)
Signs: frequent eye irritation, blinking/facial contortions while reading, frequent headaches, dizziness, or burning eyes
Auditory impairments
Hearing loss in infancy will be much more severe than at age 3
Can result in linguistic struggles and difficulties in abstract thinking
Speech impairment
Speech that deviates so much from the speech of others that it calls attention to itself, interferes with communication, or produces maladjustment in the speaker
Childhood-onset fluency disorder (stuttering)
Substantial disruption in the rhythm and fluency of speech
The most common speech impairment
Specific learning disorders
Difficulties in the ability to learn or use specific academic skills such as reading, writing, or arithmetic
Specific learning disorders can be caused by
Brain dysfunction, genetic factors, poor early nutrition, allergies
Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder
A learning disorder marked by inattention, impulsiveness, a low tolerance for frustration, and a great deal of inappropriate activity
Around 9% of children aged 3-17
Common treatments are prescriptions and behavior therapy
Mainstreaming
An educational approach in which exceptional children are integrated as much as possible into the traditional educational system and are provided with a broad range of educational alternatives
Teachers must be given substantial support for it to be effective
Full inclusion
The integration of all students, even those with the most severe disabilities, into regular classes and all other aspects of school and community life