Chapter 08: Joints in Human Anatomy and Physiology
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
78 Terms
Joints
Sites where two or more bones meet.
Functions of joints
Give skeleton mobility and hold skeleton together.
Structural classifications of joints
Three types based on what material binds the joints and whether a cavity is present.
Fibrous joints
Bones joined by dense fibrous connective tissue with no joint cavity.
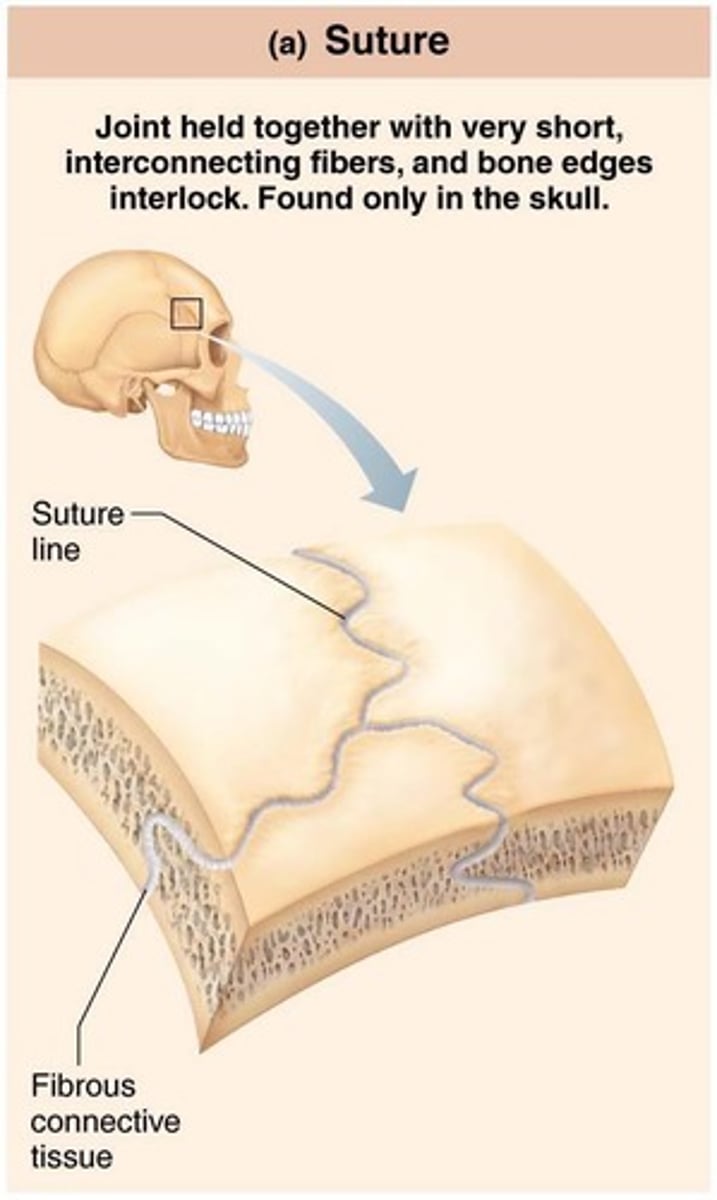
Sutures
Rigid, interlocking joints of skull that allow for growth during youth.
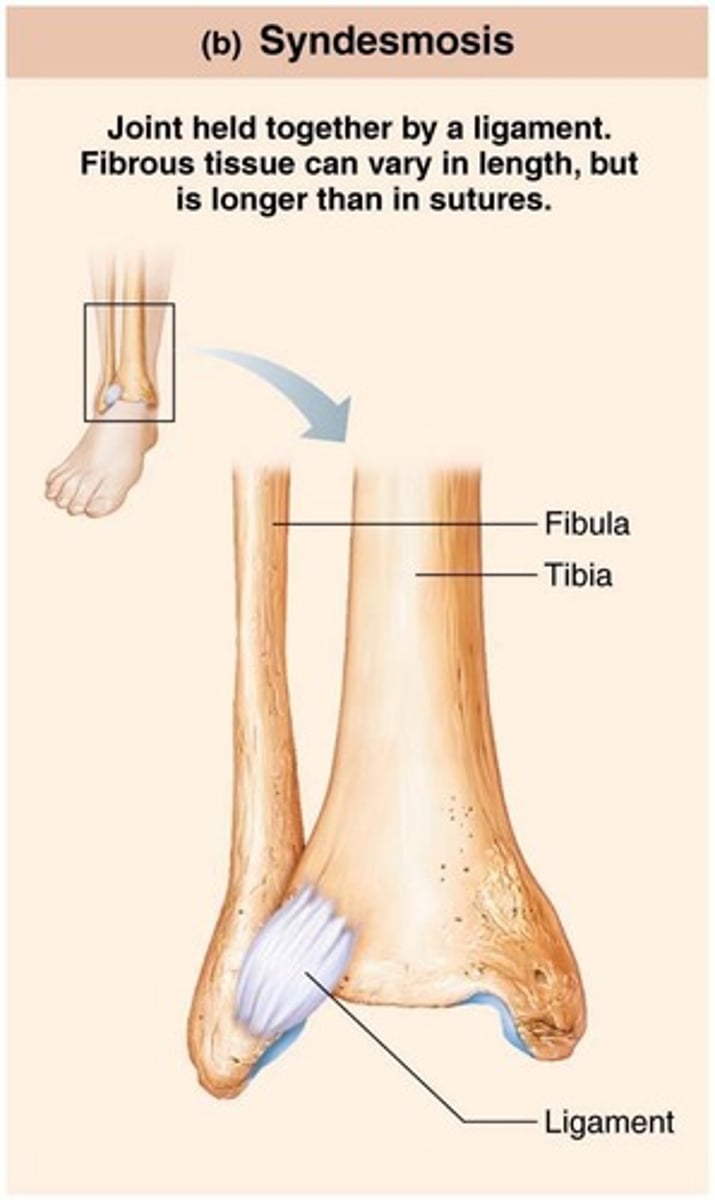
Syndesmoses
Bones connected by ligaments, with movement varying based on fiber length.
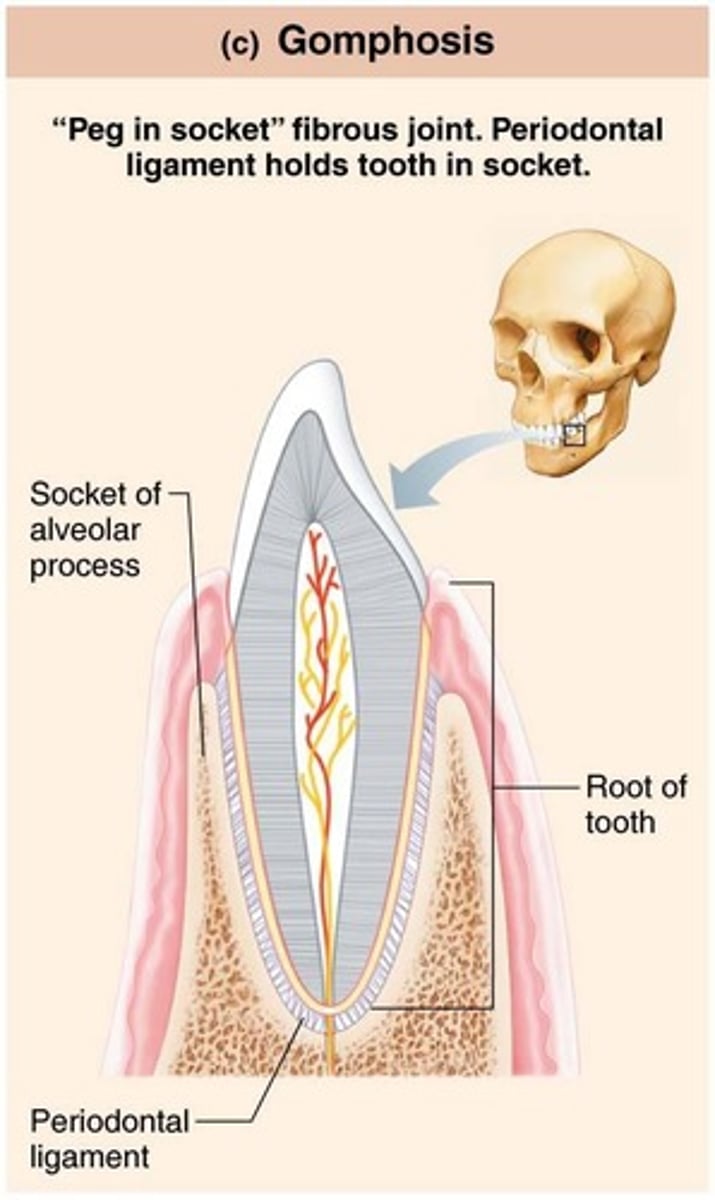
Gomphoses
Peg-in-socket joints, specifically the teeth in alveolar sockets.
Cartilaginous joints
Bones united by cartilage, similar to fibrous joints, with no joint cavity.
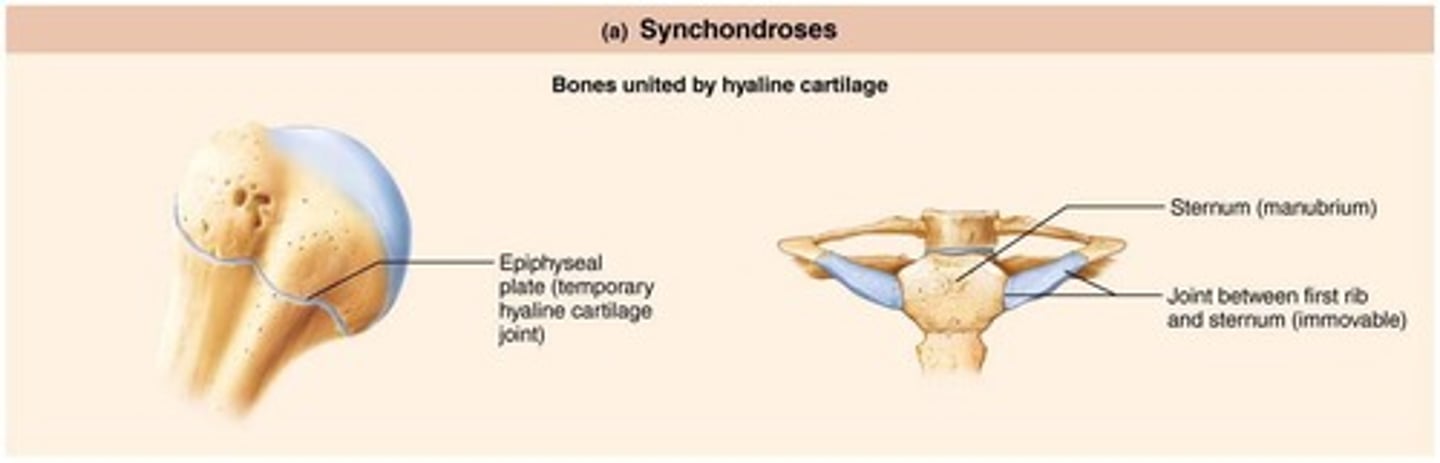
Synchondroses
Bar or plate of hyaline cartilage that unites bones, almost all are synarthrotic.
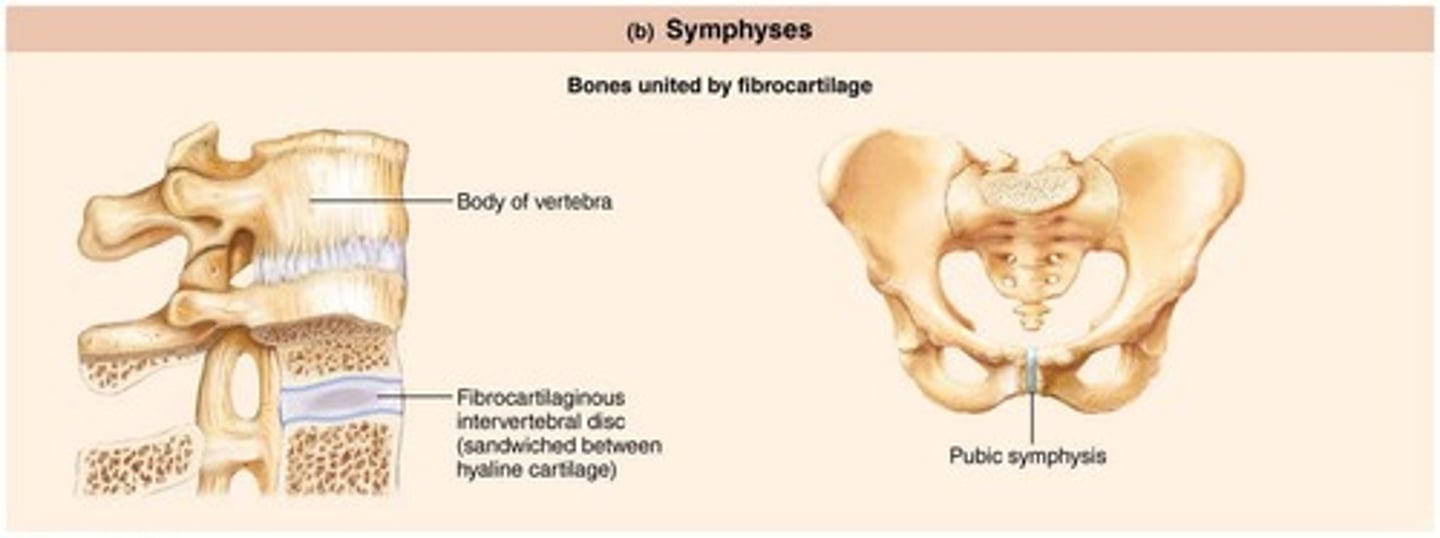
Symphyses
Fibrocartilage unites bone in symphysis joint, strong and slightly movable.
Synovial joints
Bones separated by fluid-filled joint cavity, all are diarthrotic.
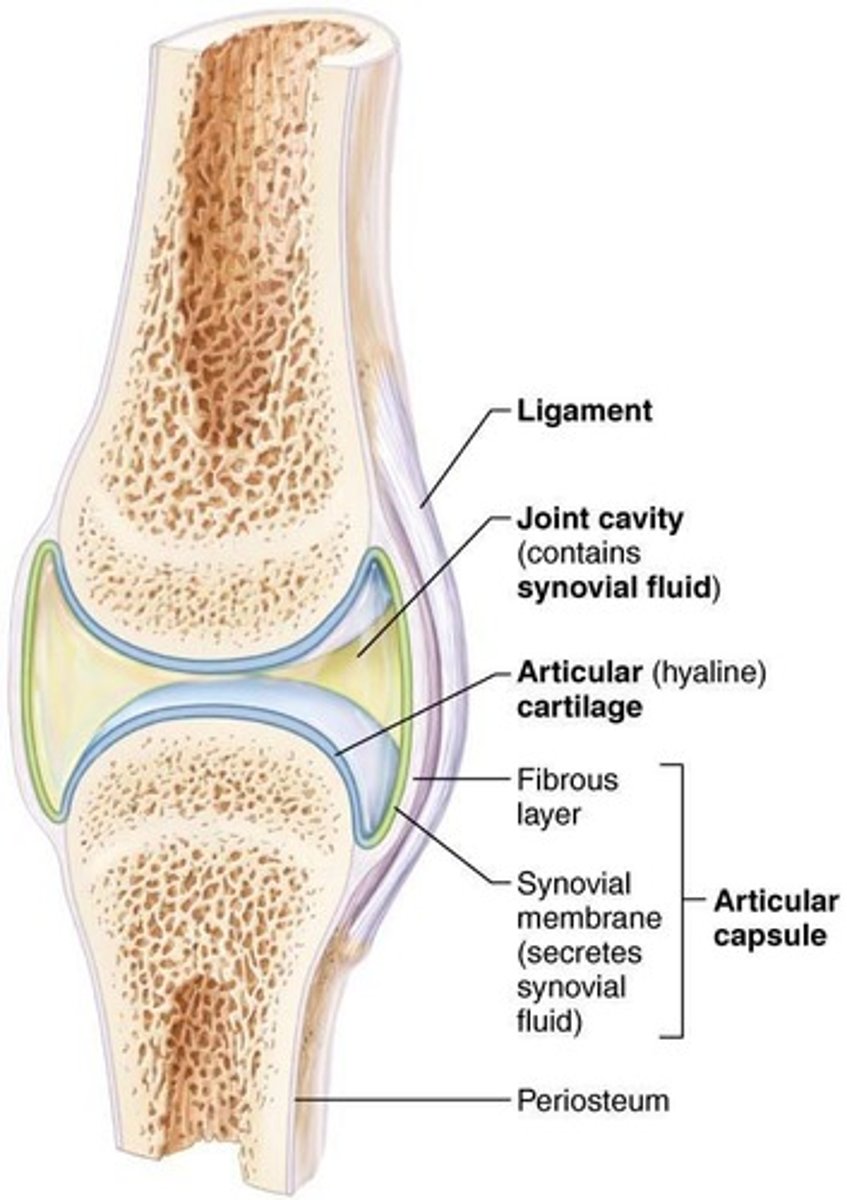
Articular cartilage
Consists of hyaline cartilage covering ends of bones, prevents crushing of bone ends.
Joint (synovial) cavity
Small, fluid-filled potential space that is unique to synovial joints.
Articular (joint) capsule
Two layers thick: external fibrous layer and inner synovial membrane.
Synovial fluid
Viscous, slippery filtrate of plasma and hyaluronic acid that lubricates and nourishes articular cartilage.
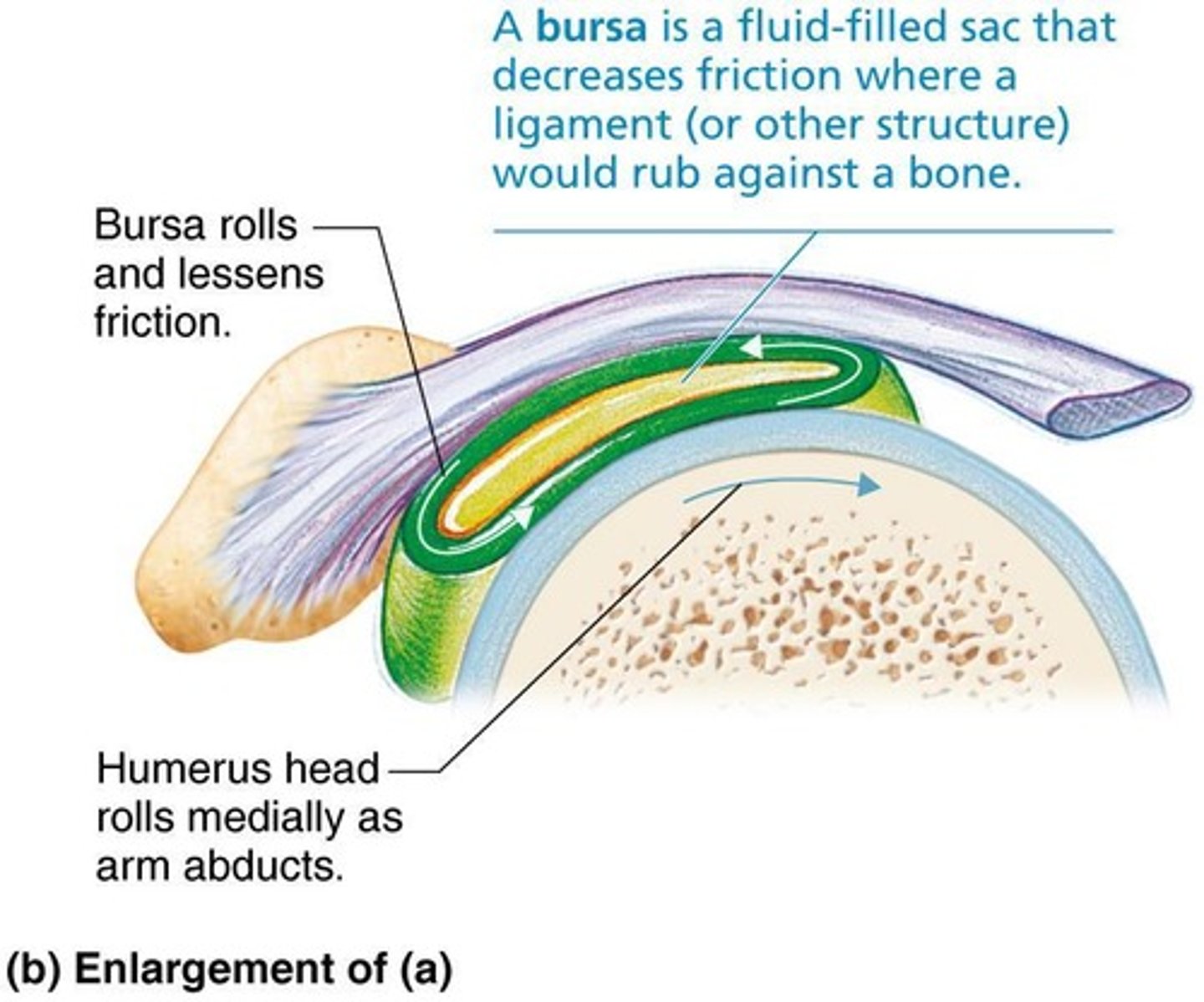
Bursae
Fluid-filled sacs that reduce friction between moving parts in joints.
Tendon sheaths
Elongated bursa that wraps around a tendon to reduce friction.
Diarthroses
Freely movable joints.
Synarthroses
Immovable joints.
Amphiarthroses
Slightly movable joints.
Sutures ossify
In middle age, sutures fuse and become immovable joints referred to as synostoses.
Interosseous membrane
Connects radius and ulna, allowing a larger amount of movement.
Temporary epiphyseal plate joints
Become synostoses after plate closure.
Cartilage of 1st rib
Joins with manubrium of sternum.
Intervertebral joints
Examples of symphyses that are slightly movable.
Pubic symphysis
Example of a symphysis joint that is slightly movable.
Hyaline cartilage
Present as articular cartilage on bony surfaces in symphyses.
Phagocytic cells
Cells contained in synovial fluid that remove microbes and debris.
Capsular
Thickened part of fibrous layer
Extracapsular
Outside the capsule
Intracapsular
Deep to capsule; covered by synovial membrane
Nerves
Detect pain; monitor joint position and stretch
Capillary beds
Supply filtrate for synovial fluid
Fatty pads
For cushioning between fibrous layer of capsule and synovial membrane or bone
Articular discs (menisci)
Fibrocartilage separates articular surfaces to improve 'fit' of bone ends, stabilize joint, and reduce wear and tear
Bursae
Reduce friction where ligaments, muscles, skin, tendons, or bones rub together
Tendon sheaths
Elongated bursae wrapped completely around tendons subjected to friction
Stability of joints
Three factors determine stability to prevent dislocations: shape of articular surface, ligament number and location, and muscle tone
Shape of articular surface
Minor role; shallow surfaces less stable than ball-and-socket
Ligament number and location
Limited role; the more ligaments, the stronger the joint
Muscle tone
Keeps tendons taut as they cross joints; most important in reinforcing shoulder and knee joints and arches of the foot
Origin
Attachment to immovable bone
Insertion
Attachment to movable bone
Nonaxial movement
Slipping movements only
Uniaxial movement
Movement in one plane
Biaxial movement
Movement in two planes
Multiaxial movement
Movement in or around all three planes
Gliding movements
One flat bone surface glides or slips over another similar surface
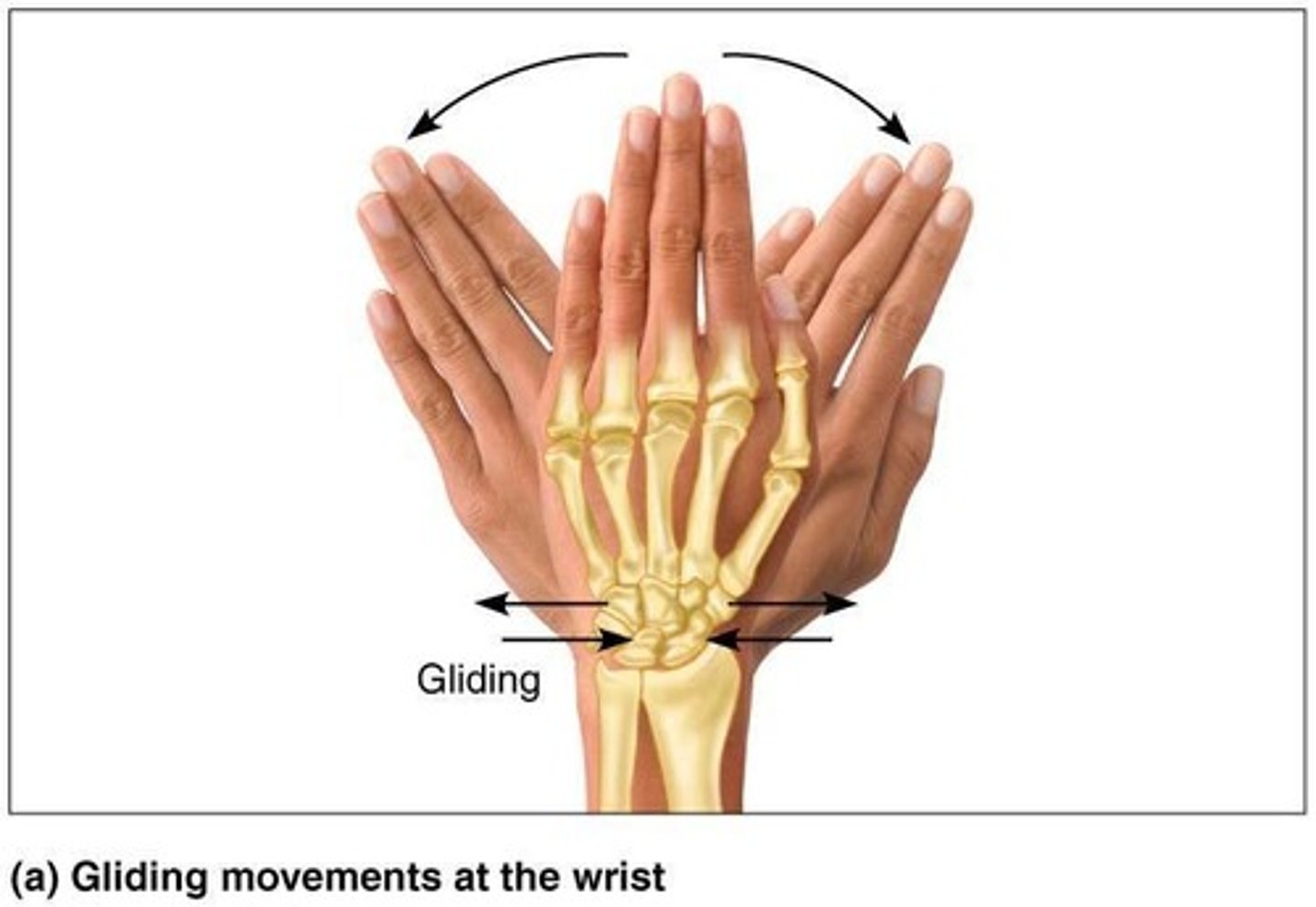
Examples of gliding movements
Intercarpal joints, Intertarsal joints, Between articular processes of vertebrae
Angular movements
Increase or decrease angle between two bones
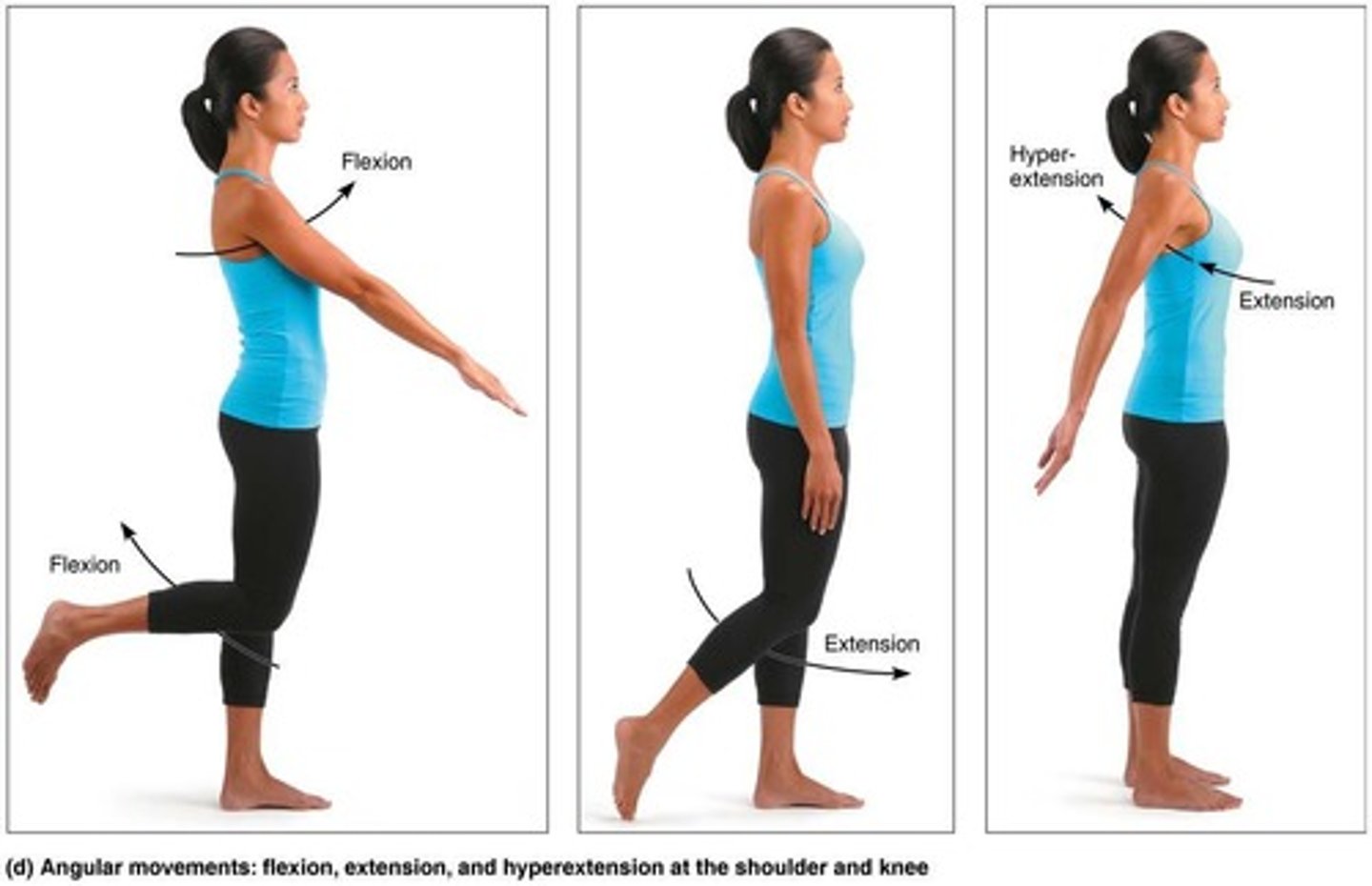
Flexion
Decreases the angle of the joint
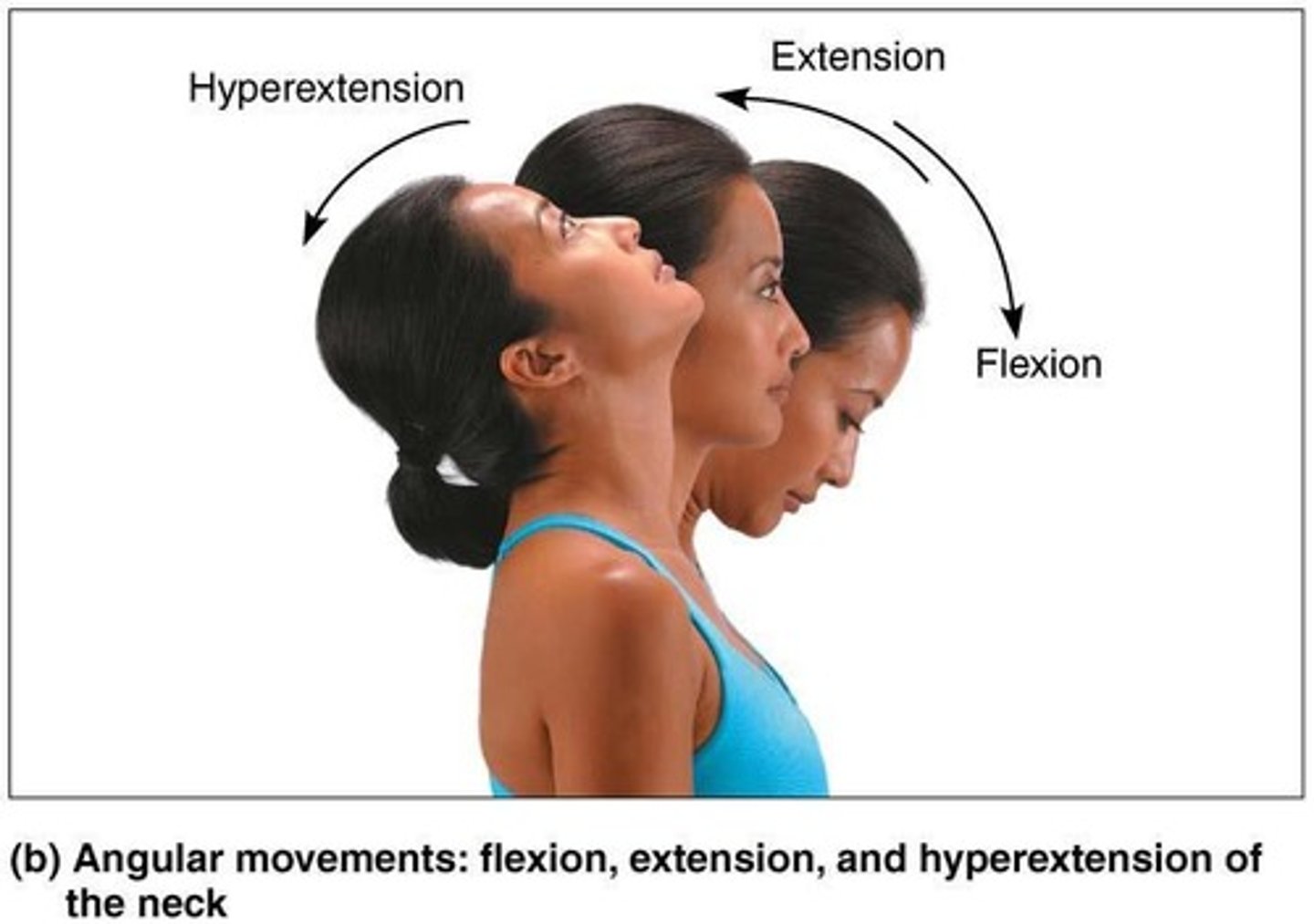
Extension
Increases the angle of the joint
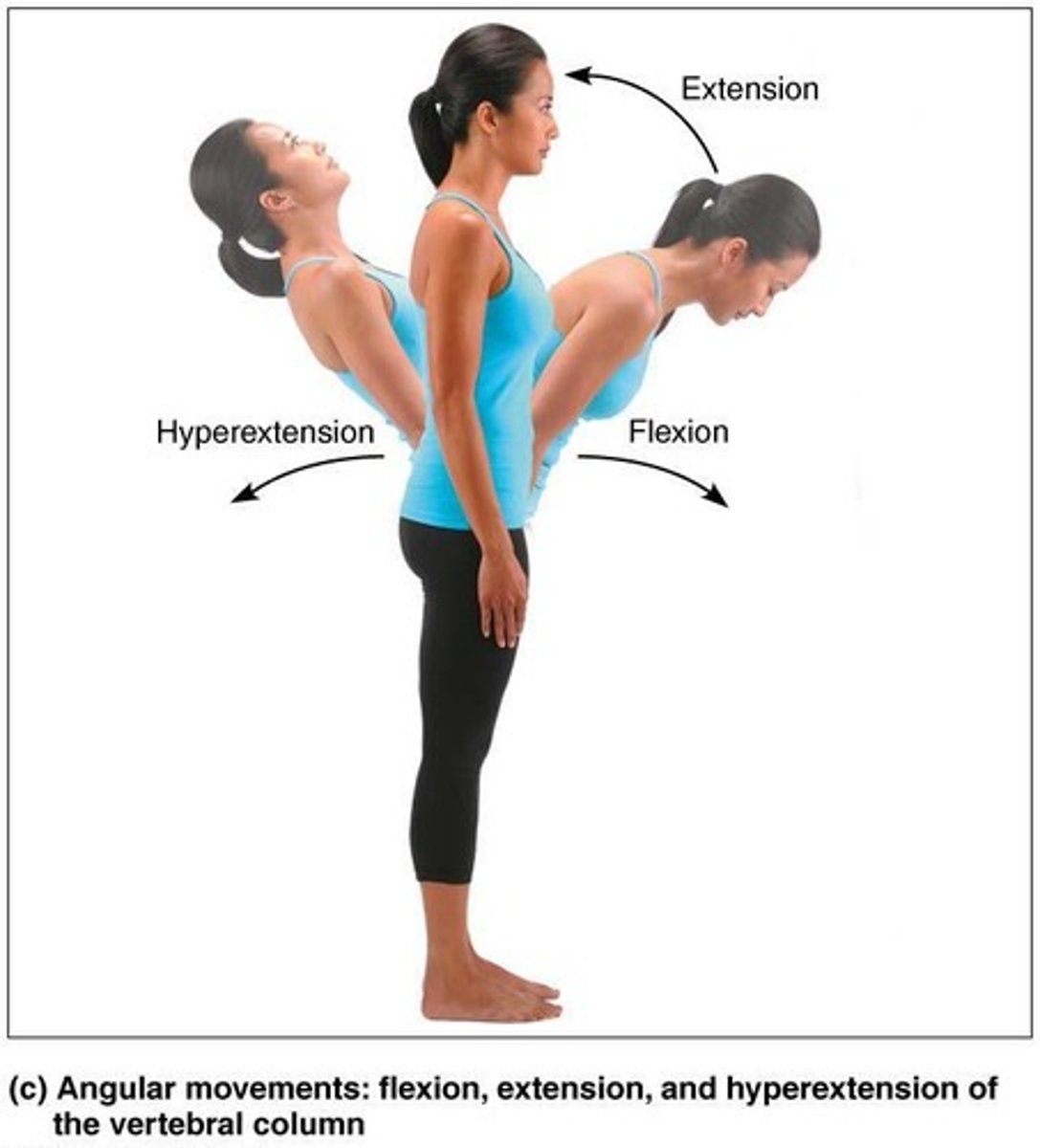
Hyperextension
Movement beyond the anatomical position
Three general types of movements
Gliding, Angular movements, Rotation
Abduction
Movement along frontal plane, away from the midline.
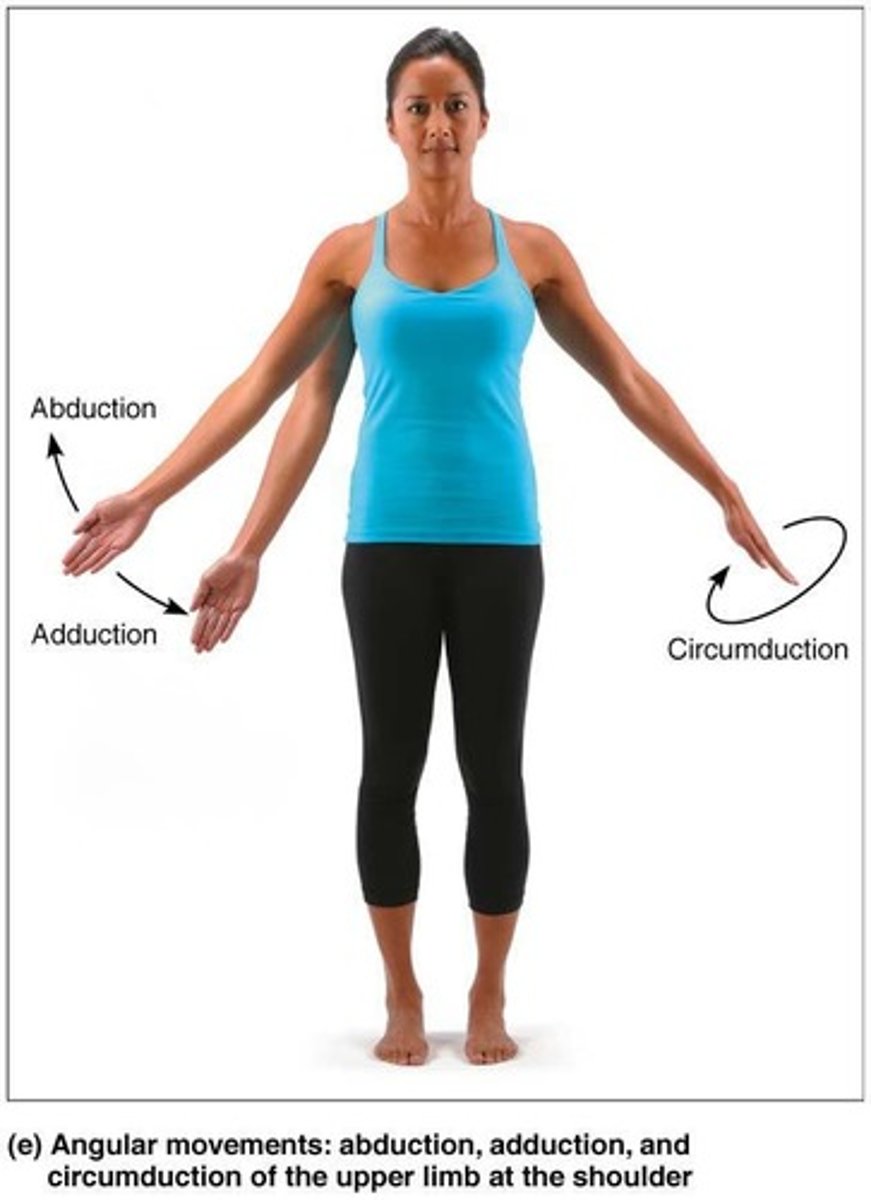
Adduction
Movement along frontal plane, toward the midline.
Circumduction
Involves flexion, abduction, extension, and adduction of limb; limb describes cone in space.
Rotation
Turning of bone around its own long axis, toward midline or away from it.
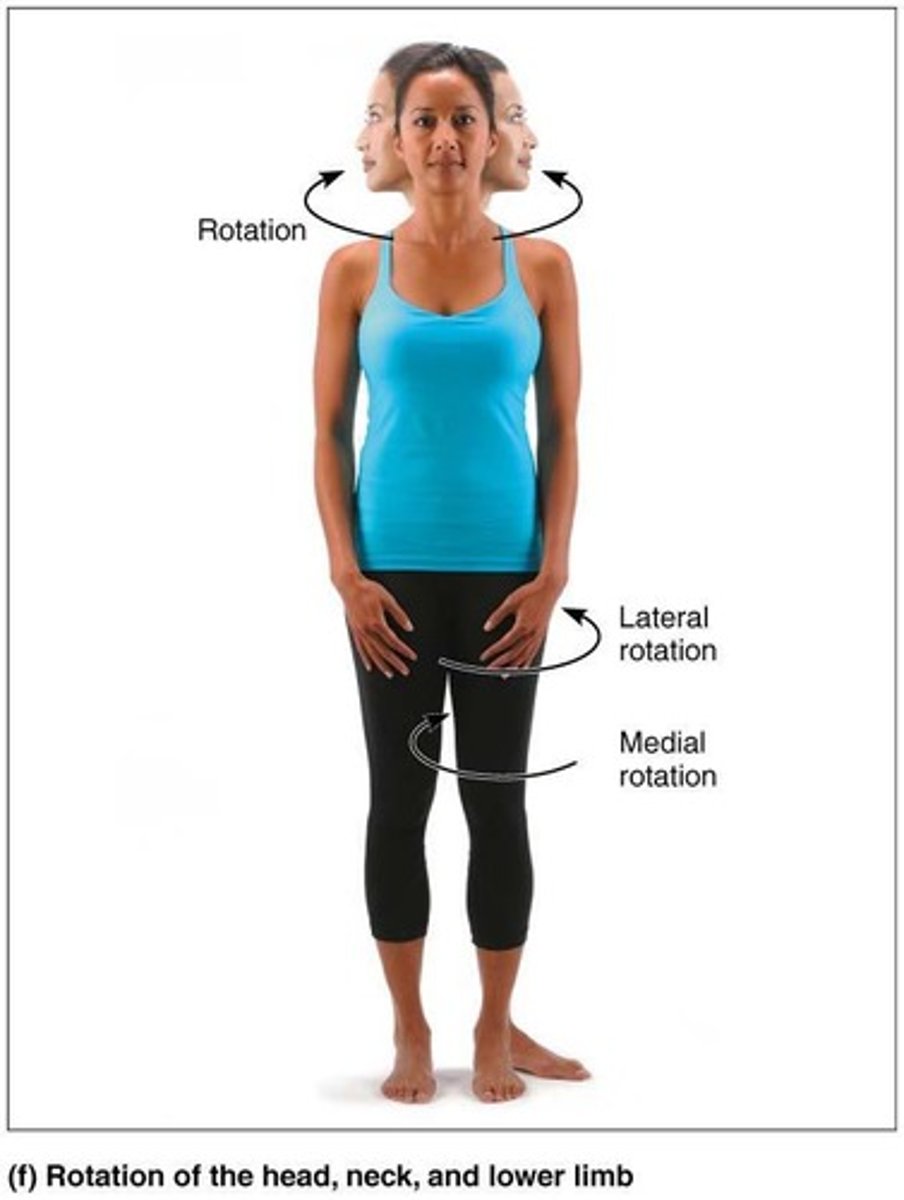
Medial Rotation
Rotation toward midline.
Lateral Rotation
Rotation away from midline.
Supination
Palms face anteriorly; radius and ulna are parallel.
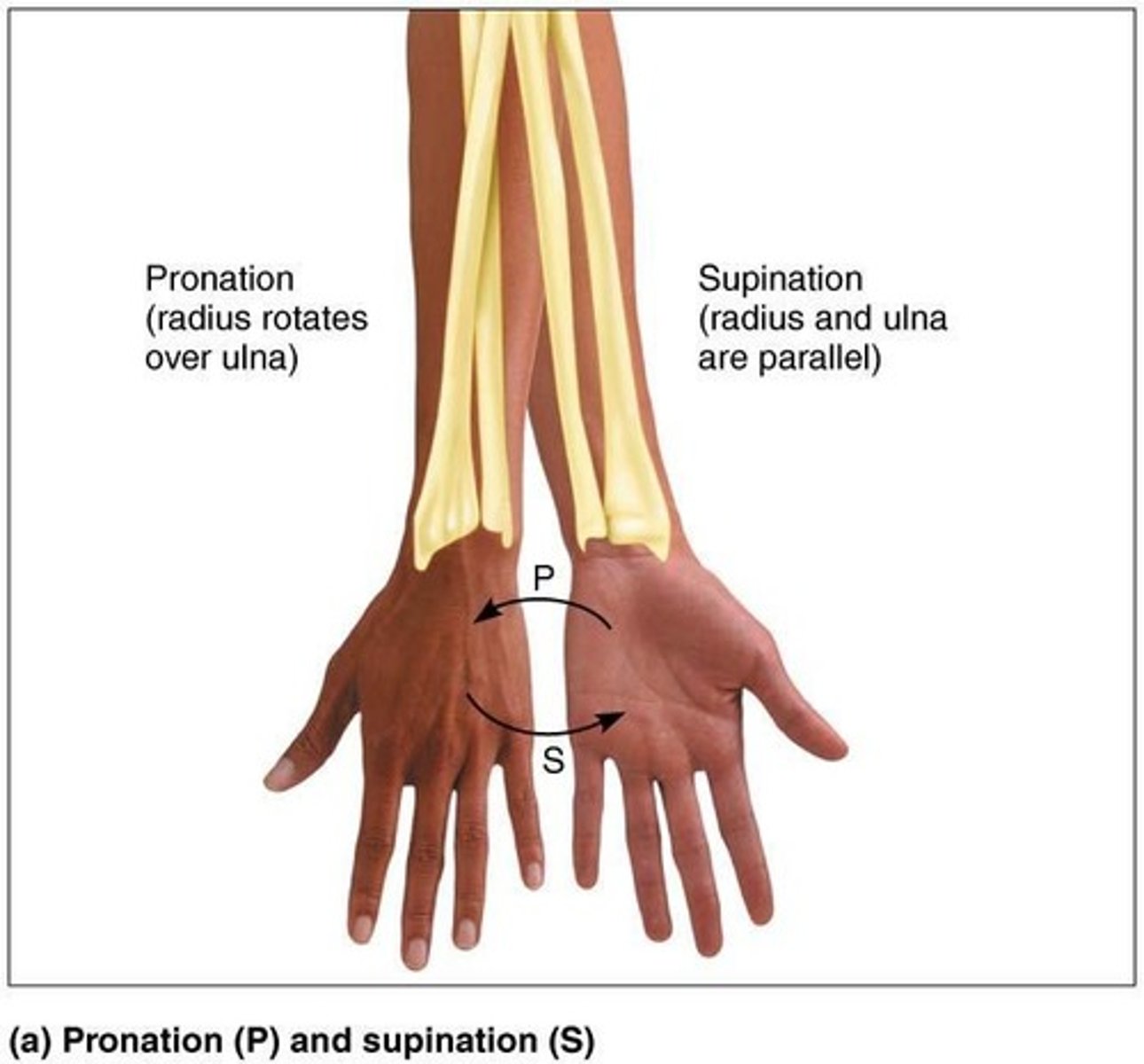
Pronation
Palms face posteriorly; radius rotates over ulna.
Dorsiflexion
Bending foot toward shin.
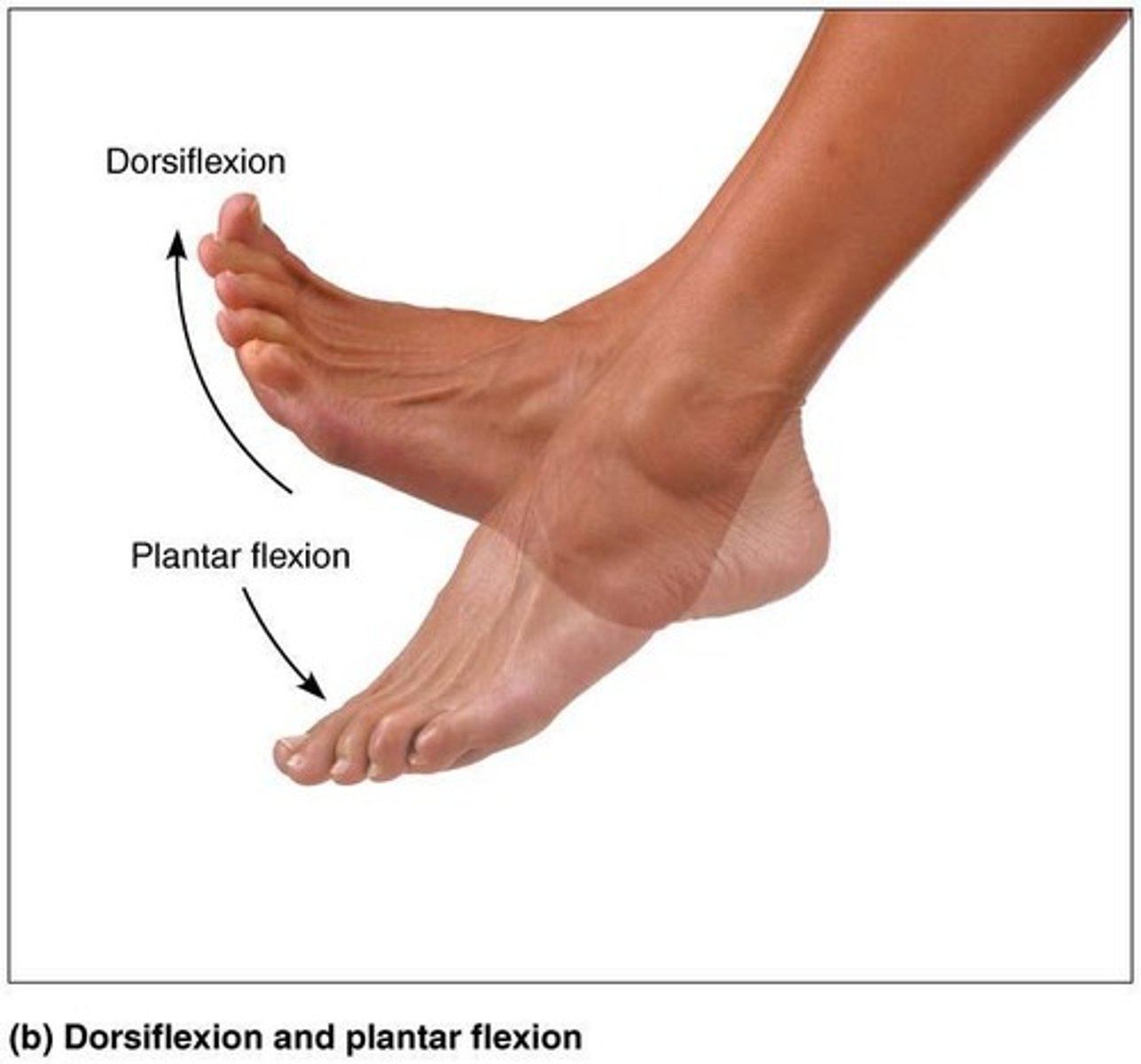
Plantar Flexion
Pointing toes.
Inversion
Sole of foot faces medially.
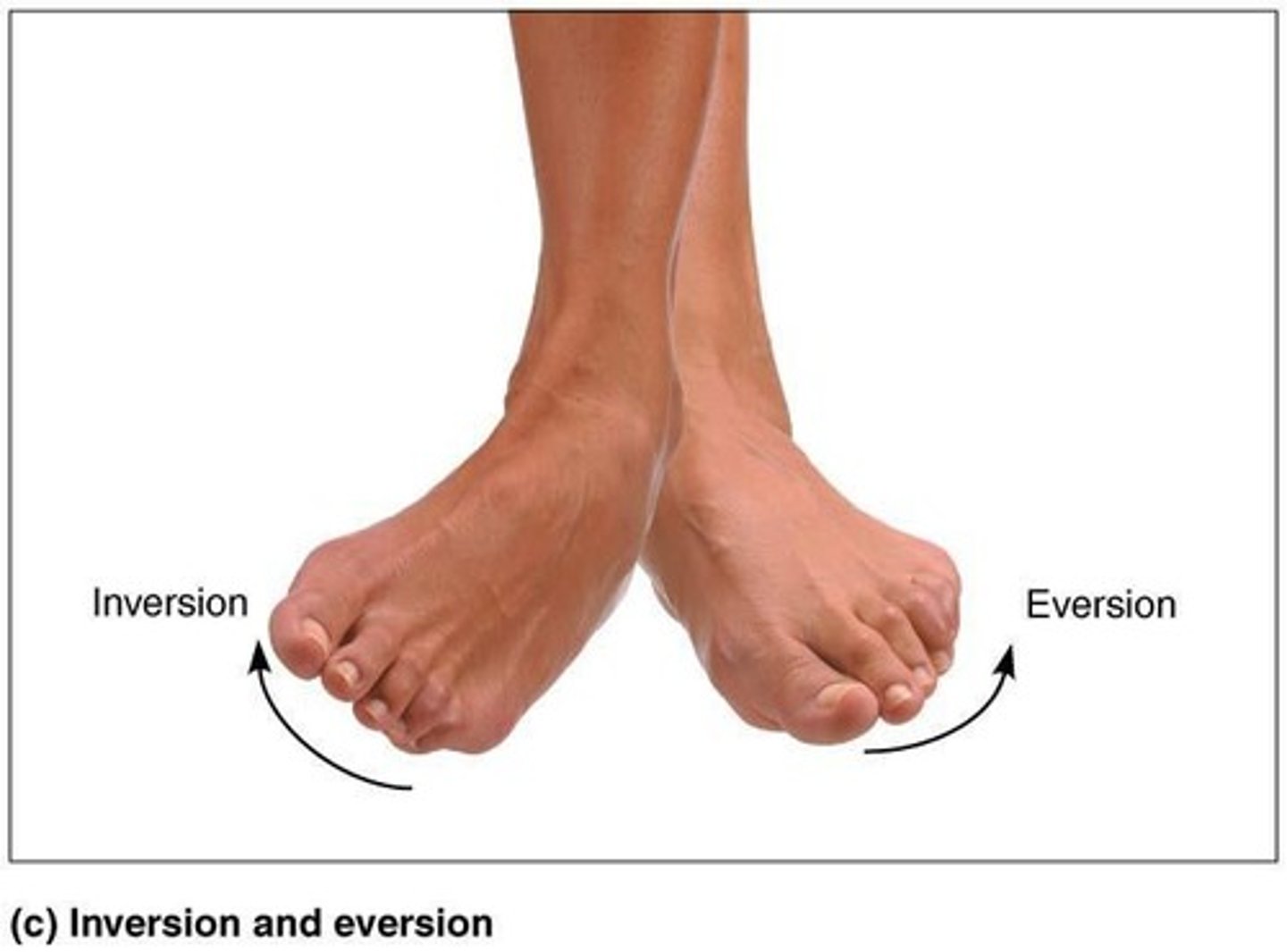
Eversion
Sole of foot faces laterally.
Protraction
Mandible juts out.
Retraction
Mandible is pulled toward neck.
Elevation
Lifting body part superiorly; example: shrugging shoulders.
Depression
Lowering body part; example: opening jaw.
Opposition
Movement of thumb; example: touching thumb to tips of other fingers on same hand or any grasping movement.
Types of Synovial Joints
There are six different types of synovial joints based on shape of articular surface and movement joint is capable of.
Plane Joint
One of the six types of synovial joints.
Hinge Joint
One of the six types of synovial joints.
Pivot Joint
One of the six types of synovial joints.
Condylar Joint
One of the six types of synovial joints.
Saddle Joint
One of the six types of synovial joints.
Ball-and-Socket Joint
One of the six types of synovial joints.